实验五
一.二分查找
1.
// 练习:使用二分查找,在一组有序元素中查找数据项 // 形参是数组,实参是数组名 #include <stdio.h> const int N=5; int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item); int main() { int a[N]={1,3,9,16,21}; int i,index, key; printf("数组a中的数据:\n"); for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); printf("输入待查找的数据项: "); scanf("%d", &key); // 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果给index // 补足代码① // ××× index=binarySearch(a,N,key); if(index>=0) printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index); else printf("%d不在数组中\n", key); return 0; } //函数功能描述: //使用二分查找算法在数组x中查找特定值item,数组x大小为n // 如果找到,返回其下标 // 如果没找到,返回-1 int binarySearch(int x[], int n, int item) { int low, high, mid; low = 0; high = n-1; while(low <= high) { mid = (low+high)/2; if (item == x[mid]) return mid; else if(item < x[mid]) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } return -1; }
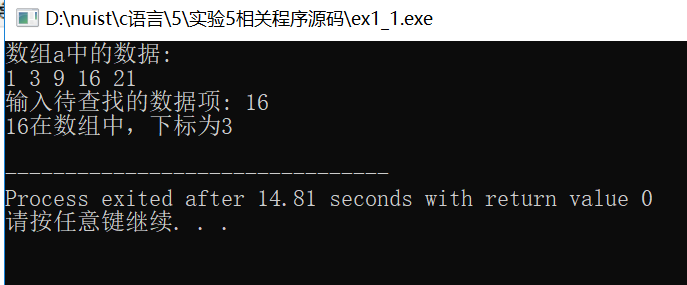
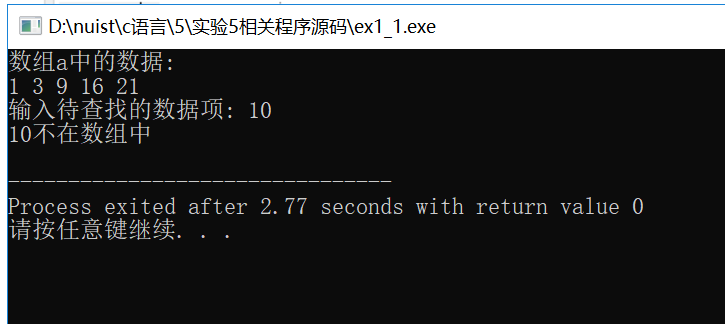
2.
// 练习:使用二分查找,在一组有序元素中查找数据项 // 形参是指针变量,实参是数组名 #include <stdio.h> const int N=5; int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item); int main() { int a[N]={1,3,9,16,21}; int i,index, key; printf("数组a中的数据:\n"); for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); printf("输入待查找的数据项: "); scanf("%d", &key); // 调用函数binarySearch()在数组a中查找指定数据项item,并返回查找结果 // 补足代码① // ××× index-binarySearch(a, N, key); if(index>=0) printf("%d在数组中,下标为%d\n", key, index); else printf("%d不在数组中\n", key); return 0; } //函数功能描述: //使用二分查找算法在x指向的数据项开始的n个数据中,查找item // 如果找到,返回其位置 // 如果没找到,返回-1 int binarySearch(int *x, int n, int item) { int low, high, mid; low = 0; high = n-1; while(low <= high) { mid = (low+high)/2; if (item == *(x+mid)) return mid; else if(item < *(x+mid)) high = mid - 1; else low = mid + 1; } return -1; }
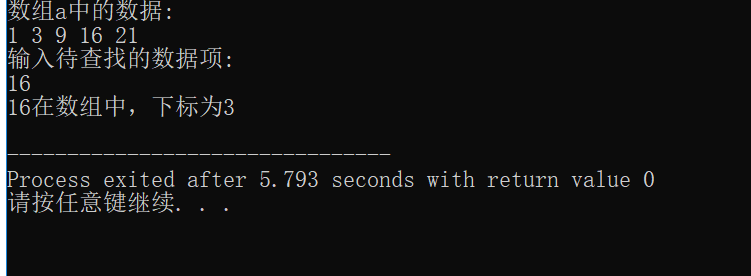
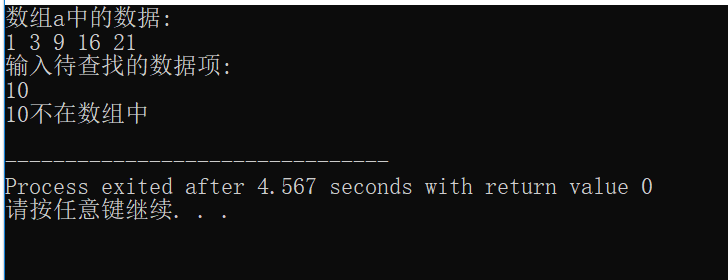
二.选择法排序
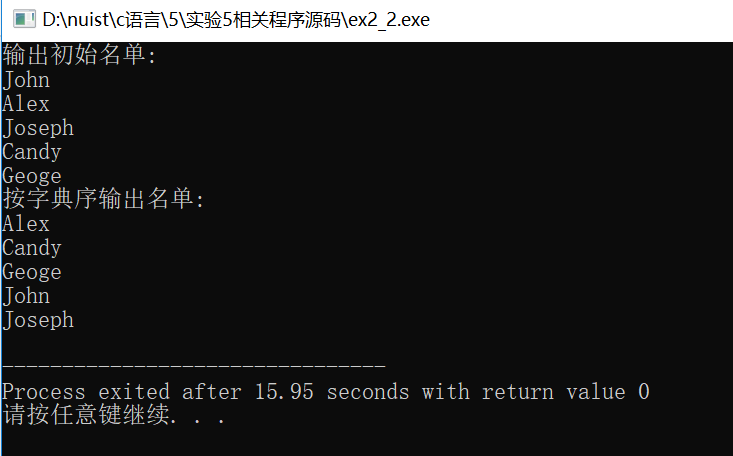
// 练习:使用选择法对字符串按字典序排序 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void selectSort(char str[][20], int n ); // 函数声明,形参str是二维数组名 int main() { char name[][20] = {"John", "Alex", "Joseph", "Candy", "Geoge"}; int i; printf("输出初始名单:\n"); for(i=0; i<5; i++) printf("%s\n", name[i]); selectSort(name, 5); // 调用选择法对name数组中的字符串排序 printf("按字典序输出名单:\n"); for(i=0; i<5; i++) printf("%s\n", name[i]); return 0; } // 函数定义 // 函数功能描述:使用选择法对二维数组str中的n个字符串按字典序排序 void selectSort(char str[][20], int n) { int i, j, k; char temp[20]; for(i=0; i<n-1; i++) { k = i; for(j=i+1; j<n; j++) if (strcmp(str[j],str[k])<0) k = j; if(k != i) { strcpy(temp,str[i]); strcpy(str[i],str[k]); strcpy(str[k],temp); } } }
1.数组名作为参数 vs. 指针变量作为参数,在形参、实参写法,以及函数实现中数组元素表示的差异
形参 实参 函数实现
数组名 int 【】 函数名(a) a[i]
指针变量 int *p 函数名 (pa) p[i]
2.择法排序 使用选择法对字符串排序时注意事项
使用字符串比较时要使用字符串处理函数
3.使用指针变量对字符串进行处理 注意事项总结
字符串和字符数组不一样,字符串只是存储首地址,而不是整个字符串都存储到指针变量里。
字符串要初始化才能使用。
字符串的值可以改变


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号