ELK(elasticsearch-7.17.4-windows-x86_64+logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64+kibana-7.17.4-windows-x86_64)具体使用案例
1、下载ELK(elasticsearch-7.17.4-windows-x86_64+logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64+kibana-7.17.4-windows-x86_64)
2、解压elasticsearch-7.17.4-windows-x86_64,config目录下修改elasticsearch.yml文件,修改elasticsearch.yml内容如下:
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: #集群名称(按实际需要配置名称) cluster.name: lj-application # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: #节点名称 node.name: node-1 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): #数据路径(按实际需要配置日志地址) #path.data: /path/to/data path.data: D:\Temp\ELK\elasticsearch-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\elasticsearch-7.17.4\data # # Path to log files: # #path.logs: /path/to/logs path.logs: D:\Temp\ELK\elasticsearch-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\elasticsearch-7.17.4\logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different # address here to expose this node on the network: # #network.host: 192.168.0.1 #地址(通常使用内网进行配置) network.host: 0.0.0.0 # # By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it # finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here: # #http.port: 9200 #端口号 http.port: 9200 #默认对外端口,ES 进行集群间通信与数据传输的端口,请确保这两个端口没有被占用 transport.port: 9300 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # #discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"] #节点地址 discovery.seed_hosts: ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # # Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes: # #cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"] #集群master cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"] # # For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true # # ---------------------------------- Security ---------------------------------- # # *** WARNING *** # # Elasticsearch security features are not enabled by default. # These features are free, but require configuration changes to enable them. # This means that users don’t have to provide credentials and can get full access # to the cluster. Network connections are also not encrypted. # # To protect your data, we strongly encourage you to enable the Elasticsearch security features. # Refer to the following documentation for instructions. # # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.16/configuring-stack-security.html #跨域(这两项配置手动添加一下) http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
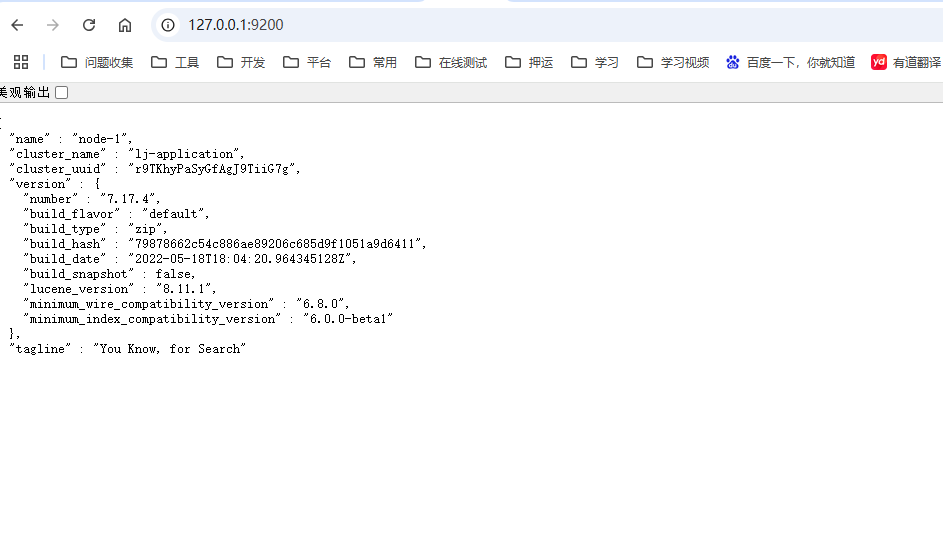
启动 bin目录下,elasticsearch.bat即可,运行成功如下:
3、解压logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64,config目录下修改logstash.yml文件,修改logstash.yml内容如下,加载其他配置文件,可以配置来自filebeat文件,mysql数据库,packetbeat网络,windowlogbeat事件日志,auditbeat审计数据,指标数据metricbeat等beats
# Settings file in YAML # # Settings can be specified either in hierarchical form, e.g.: # # pipeline: # batch: # size: 125 # delay: 5 # # Or as flat keys: # # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # pipeline.batch.delay: 5 # # ------------ Node identity ------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # # node.name: test # # If omitted the node name will default to the machine's host name # # ------------ Data path ------------------ # # Which directory should be used by logstash and its plugins # for any persistent needs. Defaults to LOGSTASH_HOME/data # # path.data: # # ------------ Pipeline Settings -------------- # # The ID of the pipeline. # # pipeline.id: main # # Set the number of workers that will, in parallel, execute the filters+outputs # stage of the pipeline. # # This defaults to the number of the host's CPU cores. # # pipeline.workers: 2 # # How many events to retrieve from inputs before sending to filters+workers # # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # # How long to wait in milliseconds while polling for the next event # before dispatching an undersized batch to filters+outputs # # pipeline.batch.delay: 50 # # Force Logstash to exit during shutdown even if there are still inflight # events in memory. By default, logstash will refuse to quit until all # received events have been pushed to the outputs. # # WARNING: enabling this can lead to data loss during shutdown # # pipeline.unsafe_shutdown: false # # Set the pipeline event ordering. Options are "auto" (the default), "true" or "false". # "auto" will automatically enable ordering if the 'pipeline.workers' setting # is also set to '1'. # "true" will enforce ordering on the pipeline and prevent logstash from starting # if there are multiple workers. # "false" will disable any extra processing necessary for preserving ordering. # # pipeline.ordered: auto # # Sets the pipeline's default value for `ecs_compatibility`, a setting that is # available to plugins that implement an ECS Compatibility mode for use with # the Elastic Common Schema. # Possible values are: # - disabled (default) # - v1 # - v8 # The default value will be `v8` in Logstash 8, making ECS on-by-default. To ensure a # migrated pipeline continues to operate as it did before your upgrade, opt-OUT # of ECS for the individual pipeline in its `pipelines.yml` definition. Setting # it here will set the default for _all_ pipelines, including new ones. # # pipeline.ecs_compatibility: disabled # # ------------ Pipeline Configuration Settings -------------- # # Where to fetch the pipeline configuration for the main pipeline # # path.config: # # Pipeline configuration string for the main pipeline # # config.string: # # At startup, test if the configuration is valid and exit (dry run) # # config.test_and_exit: false # # Periodically check if the configuration has changed and reload the pipeline # This can also be triggered manually through the SIGHUP signal # # config.reload.automatic: false # # How often to check if the pipeline configuration has changed (in seconds) # Note that the unit value (s) is required. Values without a qualifier (e.g. 60) # are treated as nanoseconds. # Setting the interval this way is not recommended and might change in later versions. # # config.reload.interval: 3s # # Show fully compiled configuration as debug log message # NOTE: --log.level must be 'debug' # # config.debug: false # # When enabled, process escaped characters such as \n and \" in strings in the # pipeline configuration files. # # config.support_escapes: false # # ------------ API Settings ------------- # Define settings related to the HTTP API here. # # The HTTP API is enabled by default. It can be disabled, but features that rely # on it will not work as intended. # # api.enabled: true # # By default, the HTTP API is not secured and is therefore bound to only the # host's loopback interface, ensuring that it is not accessible to the rest of # the network. # When secured with SSL and Basic Auth, the API is bound to _all_ interfaces # unless configured otherwise. # # api.http.host: 127.0.0.1 # # The HTTP API web server will listen on an available port from the given range. # Values can be specified as a single port (e.g., `9600`), or an inclusive range # of ports (e.g., `9600-9700`). # # api.http.port: 9600-9700 # # The HTTP API includes a customizable "environment" value in its response, # which can be configured here. # # api.environment: "production" # # The HTTP API can be secured with SSL (TLS). To do so, you will need to provide # the path to a password-protected keystore in p12 or jks format, along with credentials. # # api.ssl.enabled: false # api.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/keystore.jks # api.ssl.keystore.password: "y0uRp4$$w0rD" # # The HTTP API can be configured to require authentication. Acceptable values are # - `none`: no auth is required (default) # - `basic`: clients must authenticate with HTTP Basic auth, as configured # with `api.auth.basic.*` options below # api.auth.type: none # # When configured with `api.auth.type` `basic`, you must provide the credentials # that requests will be validated against. Usage of Environment or Keystore # variable replacements is encouraged (such as the value `"${HTTP_PASS}"`, which # resolves to the value stored in the keystore's `HTTP_PASS` variable if present # or the same variable from the environment) # # api.auth.basic.username: "logstash-user" # api.auth.basic.password: "s3cUreP4$$w0rD" # # ------------ Module Settings --------------- # Define modules here. Modules definitions must be defined as an array. # The simple way to see this is to prepend each `name` with a `-`, and keep # all associated variables under the `name` they are associated with, and # above the next, like this: # # modules: # - name: MODULE_NAME # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE1.PLUGINNAME1.KEY2: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE2.PLUGINNAME1.KEY1: VALUE # var.PLUGINTYPE3.PLUGINNAME3.KEY1: VALUE # # Module variable names must be in the format of # # var.PLUGIN_TYPE.PLUGIN_NAME.KEY # # modules: # # ------------ Cloud Settings --------------- # Define Elastic Cloud settings here. # Format of cloud.id is a base64 value e.g. dXMtZWFzdC0xLmF3cy5mb3VuZC5pbyRub3RhcmVhbCRpZGVudGlmaWVy # and it may have an label prefix e.g. staging:dXMtZ... # This will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.hosts' and 'var.kibana.host' # cloud.id: <identifier> # # Format of cloud.auth is: <user>:<pass> # This is optional # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.elasticsearch.username' and 'var.elasticsearch.password' # If supplied this will overwrite 'var.kibana.username' and 'var.kibana.password' # cloud.auth: elastic:<password> # # ------------ Queuing Settings -------------- # # Internal queuing model, "memory" for legacy in-memory based queuing and # "persisted" for disk-based acked queueing. Defaults is memory # # queue.type: memory # # If using queue.type: persisted, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/queue # # path.queue: # # If using queue.type: persisted, the page data files size. The queue data consists of # append-only data files separated into pages. Default is 64mb # # queue.page_capacity: 64mb # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of unread events in the queue. # Default is 0 (unlimited) # # queue.max_events: 0 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the total capacity of the queue in number of bytes. # If you would like more unacked events to be buffered in Logstash, you can increase the # capacity using this setting. Please make sure your disk drive has capacity greater than # the size specified here. If both max_bytes and max_events are specified, Logstash will pick # whichever criteria is reached first # Default is 1024mb or 1gb # # queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of acked events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # # queue.checkpoint.acks: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of written events before forcing a checkpoint # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # # queue.checkpoint.writes: 1024 # # If using queue.type: persisted, the interval in milliseconds when a checkpoint is forced on the head page # Default is 1000, 0 for no periodic checkpoint. # # queue.checkpoint.interval: 1000 # # ------------ Dead-Letter Queue Settings -------------- # Flag to turn on dead-letter queue. # # dead_letter_queue.enable: false # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the maximum size of each dead letter queue. Entries # will be dropped if they would increase the size of the dead letter queue beyond this setting. # Default is 1024mb # dead_letter_queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the interval in milliseconds where if no further events eligible for the DLQ # have been created, a dead letter queue file will be written. A low value here will mean that more, smaller, queue files # may be written, while a larger value will introduce more latency between items being "written" to the dead letter queue, and # being available to be read by the dead_letter_queue input when items are are written infrequently. # Default is 5000. # # dead_letter_queue.flush_interval: 5000 # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/dead_letter_queue # # path.dead_letter_queue: # # ------------ Debugging Settings -------------- # # Options for log.level: # * fatal # * error # * warn # * info (default) # * debug # * trace # # log.level: info # path.logs: # # ------------ Other Settings -------------- # # Where to find custom plugins # path.plugins: [] # # Flag to output log lines of each pipeline in its separate log file. Each log filename contains the pipeline.name # Default is false # pipeline.separate_logs: false # # ------------ X-Pack Settings (not applicable for OSS build)-------------- # # X-Pack Monitoring # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/monitoring-logstash.html #xpack.monitoring.enabled: false #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_system #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_id: monitoring_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_system:password # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.monitoring.collection.interval: 10s #xpack.monitoring.collection.pipeline.details.enabled: true # # X-Pack Management # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/logstash-centralized-pipeline-management.html #xpack.management.enabled: false #xpack.management.pipeline.id: ["main", "apache_logs"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.username: logstash_admin_user #xpack.management.elasticsearch.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.proxy: ["http://proxy:port"] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://es1:9200", "https://es2:9200"] # an alternative to hosts + username/password settings is to use cloud_id/cloud_auth #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_id: management_cluster_id:xxxxxxxxxx #xpack.management.elasticsearch.cloud_auth: logstash_admin_user:password # another authentication alternative is to use an Elasticsearch API key #xpack.management.elasticsearch.api_key: "id:api_key" #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.certificate_authority: [ "/path/to/ca.crt" ] #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.truststore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.path: /path/to/file #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.keystore.password: password #xpack.management.elasticsearch.ssl.verification_mode: certificate #xpack.management.elasticsearch.sniffing: false #xpack.management.logstash.poll_interval: 5s # X-Pack GeoIP plugin # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/plugins-filters-geoip.html#plugins-filters-geoip-manage_update #xpack.geoip.download.endpoint: "https://geoip.elastic.co/v1/database" #http.host: "0.0.0.0" xpack.monitoring.enabled: true #ES地址 xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: [ "http://127.0.0.1:9200" ] #path.config: /usr/share/logstash/conf.d/*.conf #path.logs: /var/log/logstash/logs config: reload: automatic: true interval: 3s xpack: management.enabled: false monitoring.enabled: false
新建或者修改pipelines.yml内容如下:
# List of pipelines to be loaded by Logstash # # This document must be a list of dictionaries/hashes, where the keys/values are pipeline settings. # Default values for omitted settings are read from the `logstash.yml` file. # When declaring multiple pipelines, each MUST have its own `pipeline.id`. # # Example of two pipelines: # # - pipeline.id: test # pipeline.workers: 1 # pipeline.batch.size: 1 # config.string: "input { generator {} } filter { sleep { time => 1 } } output { stdout { codec => dots } }" # - pipeline.id: another_test # queue.type: persisted # path.config: "/tmp/logstash/*.config" # # Available options: # # # name of the pipeline # pipeline.id: mylogs # # # The configuration string to be used by this pipeline # config.string: "input { generator {} } filter { sleep { time => 1 } } output { stdout { codec => dots } }" # # # The path from where to read the configuration text # path.config: "/etc/conf.d/logstash/myconfig.cfg" # # # How many worker threads execute the Filters+Outputs stage of the pipeline # pipeline.workers: 1 (actually defaults to number of CPUs) # # # How many events to retrieve from inputs before sending to filters+workers # pipeline.batch.size: 125 # # # How long to wait in milliseconds while polling for the next event # # before dispatching an undersized batch to filters+outputs # pipeline.batch.delay: 50 # # # Internal queuing model, "memory" for legacy in-memory based queuing and # # "persisted" for disk-based acked queueing. Defaults is memory # queue.type: memory # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the page data files size. The queue data consists of # # append-only data files separated into pages. Default is 64mb # queue.page_capacity: 64mb # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of unread events in the queue. # # Default is 0 (unlimited) # queue.max_events: 0 # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the total capacity of the queue in number of bytes. # # Default is 1024mb or 1gb # queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of acked events before forcing a checkpoint # # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # queue.checkpoint.acks: 1024 # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the maximum number of written events before forcing a checkpoint # # Default is 1024, 0 for unlimited # queue.checkpoint.writes: 1024 # # # If using queue.type: persisted, the interval in milliseconds when a checkpoint is forced on the head page # # Default is 1000, 0 for no periodic checkpoint. # queue.checkpoint.interval: 1000 # # # Enable Dead Letter Queueing for this pipeline. # dead_letter_queue.enable: false # # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the maximum size of dead letter queue for this pipeline. Entries # will be dropped if they would increase the size of the dead letter queue beyond this setting. # Default is 1024mb # dead_letter_queue.max_bytes: 1024mb # # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the interval in milliseconds where if no further events eligible for the DLQ # have been created, a dead letter queue file will be written. A low value here will mean that more, smaller, queue files # may be written, while a larger value will introduce more latency between items being "written" to the dead letter queue, and # being available to be read by the dead_letter_queue input when items are are written infrequently. # Default is 5000. # # dead_letter_queue.flush_interval: 5000 # # If using dead_letter_queue.enable: true, the directory path where the data files will be stored. # Default is path.data/dead_letter_queue # # path.dead_letter_queue: # 加载其他配置文件,可以配置来自filebeat文件,mysql数据库,packetbeat网络,windowlogbeat事件日志,auditbeat审计数据,指标数据metricbeat等beats - pipeline.id: log_from_file.conf path.config: "D:\Temp\ELK\logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\logstash-7.17.4\config\log_from_file.conf" #- pipeline.id: mysql #path.config: "D:\Temp\ELK\logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\logstash-7.17.4\config\mysql.conf"
新建或者修改log_from_file.conf内容如下:
input { file { path => "D:\Temp\ELK\logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\logstash-7.17.4\config\log.20240406.txt" start_position => "beginning" #或者"end"取决于你想从哪里开始读取 #sincedb_path => "/dev/null" sincedb_path => "" #使用 /dev/null 来避免记录文件读取位置 #codec => "plain" #如果文件不是文本格式,可以指定 codec,例如 "json" 或 "multiline" } #beats { # 监听5044端口 #port => "5044" # 关闭ssl验证 #ssl => false # 指定输入格式为json #codec => json #} } filter { #在这里添加任何过滤器逻辑,例如 grok, mutate 等 #grok{ #match => { "message" => "%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp} %{LOGLEVEL:loglevel} %{NUMBER:pid} --- \[%{DATA:thread}\] %{JAVACLASS:package} : %{GREEDYDATA:message}"} #} #使用mutate过滤器的gsub功能去除message字段中的\r #mutate { #gsub => [ #第一个数组元素是字段名,第二个元素是正则表达式,第三个元素是替换后的文本 #这里我们将message字段里的\r替换为空字符串 #"message", "\r", "", # 如果你也想去除\n,可以添加另一个替换规则 #"message", "\n", "" #] #} } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"] #index => "your_index_name" index => "elk" } #stdout { codec => rubydebug } # 用于调试,查看发送到 Elasticsearch 的数据结构 }
新建或者修改mysql.conf内容如下,并且下载并放入mysql-connector-j-8.0.31.jar,这个主要是用于数据库数据源---暂时未用 。
input { stdin {} jdbc { type => "jdbc" # 数据库连接地址 jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:mysql://ip:port/db_log?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&allowMultiQueries=true" # 数据库连接账号密码; jdbc_user => "XXX" jdbc_password => "XXX" # MySQL依赖包路径; jdbc_driver_library => "/usr/share/logstash/pipeline/mysql-connector-j-8.0.31.jar" # mysql 驱动 jdbc_driver_class => "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" # 数据库重连尝试次数 connection_retry_attempts => "3" # 判断数据库连接是否可用,默认false不开启 jdbc_validate_connection => "true" # 数据库连接可用校验超时时间,默认3600S jdbc_validation_timeout => "3600" # 开启分页查询(默认false不开启); jdbc_paging_enabled => "true" # 单次分页查询条数(默认100000,若字段较多且更新频率较高,建议调低此值); jdbc_page_size => "500" # statement为查询数据sql,如果sql较复杂,建议配通过statement_filepath配置sql文件的存放路径; # sql_last_value为内置的变量,存放上次查询结果中最后一条数据tracking_column的值,此处即为create_time; # statement_filepath => "mysql/jdbc.sql" statement => "select * from db_log.log_info WHERE create_time>= :sql_last_value order by create_time asc" # 是否将字段名转换为小写,默认true(如果有数据序列化、反序列化需求,建议改为false); lowercase_column_names => true # 日志等级: fatal,error,warn,info,debug,默认info; sql_log_level => warn # 是否记录上次执行结果,true表示会将上次执行结果的tracking_column字段的值保存到last_run_metadata_path指定的文件中; record_last_run => true # 需要记录查询结果某字段的值时,此字段为true,否则默认tracking_column为timestamp的值; use_column_value => true # 需要记录的字段,用于增量同步,需是数据库字段 tracking_column => "create_time" # 需要记录的字段的类型 Value can be any of: numeric,timestamp,Default value is "numeric" tracking_column_type => timestamp # record_last_run上次数据存放位置; last_run_metadata_path => "mysql/last_id.txt" # 是否清除last_run_metadata_path的记录,需要增量同步时此字段必须为false; clean_run => false # # 同步频率(分 时 天 月 年),默认每分钟同步一次; schedule => "* * * * *" } } output { #ES地址 elasticsearch { hosts => "http://ip:port" #索引名称 index => "mysql_log" document_id => "%{id}" } stdout { #日志输出 codec => json_lines } }
启动运行,在D:\Temp\ELK\logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\logstash-7.17.4\bin目录下输入cmd
输入:logstash.bat -f D:\Temp\ELK\logstash-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\logstash-7.17.4\config\log_from_file.conf
成功结果如下:

4、解压kibana-7.17.4-windows-x86_64,config目录下修改kibana.yml文件,修改kibana.yml内容如下:
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #服务端口(按实际需求) server.port: 5601 #服务主机(这里是服务器内网地址) server.host: "127.0.0.1" #服务名(按实际需求) server.name: "lj-Kibana" #elasticsearch地址 elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://127.0.0.1:9200"] #设置简体中文 i18n.locale: "zh-CN" #server.port: 5601 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. #server.host: "localhost" # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If # `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath. #server.publicBaseUrl: "" # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayload: 1048576 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. #server.name: "your-hostname" # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. #elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"] # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # The default application to load. #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which # is proxied through the Kibana server. #elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system" #elasticsearch.password: "pass" # Kibana can also authenticate to Elasticsearch via "service account tokens". # If may use this token instead of a username/password. # elasticsearch.serviceAccountToken: "my_token" # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. #server.ssl.enabled: false #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. # These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when # xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value # must be a positive integer. #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. #elasticsearch.logQueries: false # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. #pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid # Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output. #logging.dest: stdout # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. #logging.silent: false # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. #logging.quiet: false # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information # and all requests. #logging.verbose: false # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. #ops.interval: 5000 # Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats. # Supported languages are the following: English - en , by default , Chinese - zh-CN . #i18n.locale: "en"
运行:
D:\Temp\ELK\kibana-7.17.4-windows-x86_64\bin目录下点击kibana.bat即可,
成功如下:

在浏览器输入:http://127.0.0.1:5601/app/home#/,弹出界面如下,即成功

以上即使elk的全部配置以及启动运行,后面再具体说明如何使用elk。
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43526338/article/details/131201798
https://blog.csdn.net/wuliyouMaozhi/article/details/131719603
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41823946/article/details/141105227



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号