第一次个人编程作业
| GitHub地址 | https://github.com/wyy517/WYY517/tree/main/3223003305 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/Class34Grade23ComputerScience/homework/13477 |
| 这个作业的目标 | <完成论文查重项目> |
一、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 45 |
| ·Estimate | ·估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 15 | 20 |
| Development | 开发 | 240 | 270 |
| ·Analysis | ·需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 75 |
| ·Design Spec | ·生成设计文档 | 30 | 40 |
| ·Design Review | ·设计复审 | 15 | 20 |
| ·Coding Standard | ·代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 15 | 20 |
| ·Design | ·具体设计 | 30 | 40 |
| ·Coding | ·具体编码 | 60 | 75 |
| ·Code Review | ·代码复审 | 15 | 20 |
| ·Test | ·测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 40 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 75 |
| ·Test Repor | ·测试报告 | 30 | 40 |
| ·Size Measurement | ·计算工作量 | 15 | 20 |
| ·Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | ·事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 15 | 15 |
| ·合计 | 420 | 505 |
二、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
1.关键函数流程图
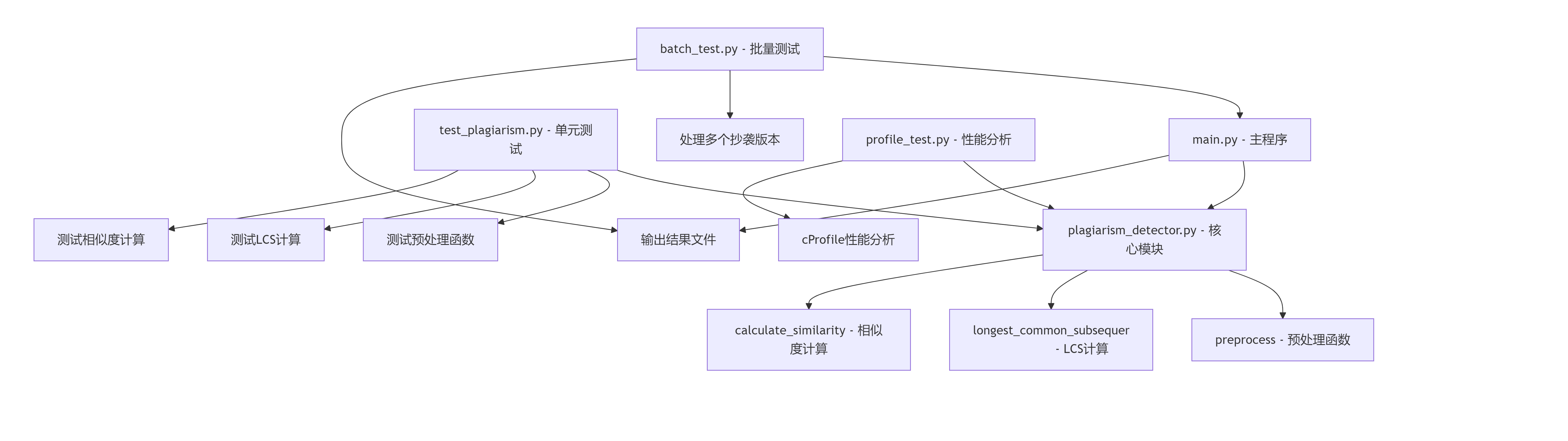
2.算法关键与独到之处
-核心算法:最长公共子序列(LCS)
能有效识别文本中连续的、顺序一致的抄袭片段
对插入、删除、乱序不敏感,适合“增删改”型抄袭检测
比简单词频统计更准确,避免“同义词替换”绕过检测
-独到设计:
(1)灵活的预处理机制:支持按字符、词、句子等粒度分词;可配置是否忽略大小写、标点符号
(2)异常处理前置:在计算前检查文件是否存在、是否为空、编码是否正确;提前抛出清晰错误信息,便于调试
三、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
1. 性能改进思路
原始LCS使用二维数组,空间复杂度高。针对大文件优化:
✅ 优化1:空间压缩:利用 LCS 的状态只依赖上一行的特性;只保留两行数组,滚动更新;节省内存
✅ 优化2:短文本提前退出:若原文长度<100 字,直接使用原始LCS;避免为小文件引入额外逻辑开销
2.性能分析图
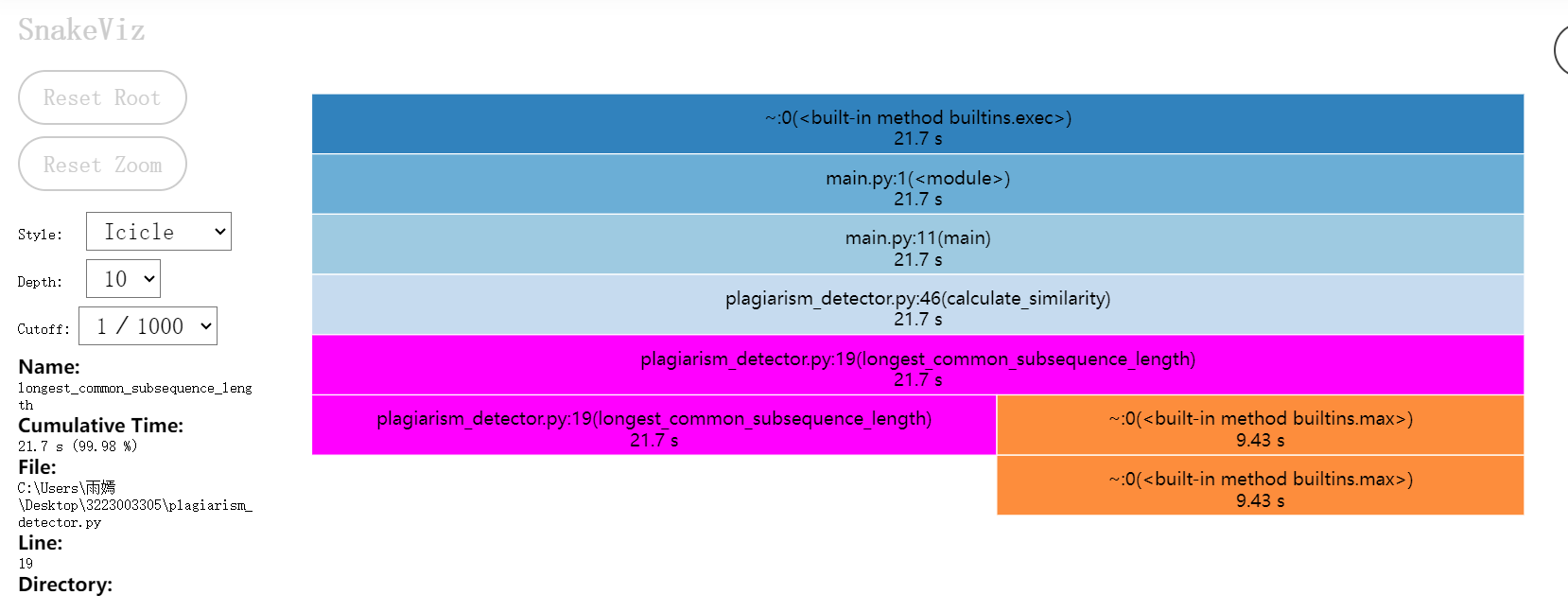
四、计算模块部分单元测试展示
1.单元测试代码示例
# test_plagiarism.py
import pytest
from plagiarism_detector import preprocess, longest_common_subsequence_length
def test_preprocess():
text = "Hello, world! How are you?"
assert preprocess(text) == ["hello", "world", "how", "are", "you"]
def test_lcs_empty():
assert longest_common_subsequence_length([], ["a", "b"]) == 0
def test_lcs_identical():
seq = ["a", "b", "c"]
assert longest_common_subsequence_length(seq, seq) == 3
def test_lcs_partial():
seq1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
seq2 = ["b", "c", "e"]
assert longest_common_subsequence_length(seq1, seq2) == 2 # "b", "c"
2.构造测试数据思路
| 测试类型 | 数据构造思路 |
|---|---|
| 正常情况 | 提供典型文本,验证基本功能 |
| 边界情况 | 空文本、单字符、完全相同文本 |
| 异常情况 | 文件不存在、编码错误、权限不足 |
| 性能测试 | 生成 10KB、100KB 文本测试耗时 |
3.测试覆盖率截图说明
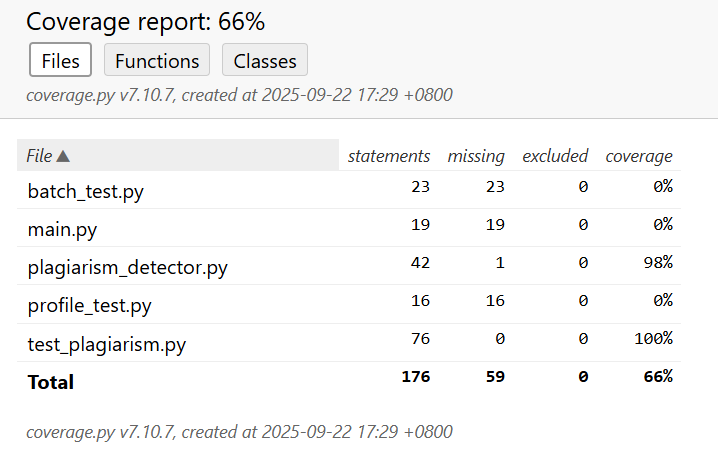
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
1.异常设计目标
| 异常类型 | 设计目标 |
|---|---|
| FileNotFoundError | 明确提示用户文件路径错误,避免程序崩溃 |
| ValueError | 检测空文件或无效输入,防止除零错误 |
| IOError | 处理读取失败(如编码错误、权限问题) |
| TypeError | 防止传入非字符串类型参数 |
2.单元测试样例与场景
-样例1:文件不存在
def test_file_not_found():
with pytest.raises(FileNotFoundError):
calculate_similarity("nonexistent.txt", "orig.txt")
场景:用户输入了错误的文件名
目标:提示“原文文件不存在”,而非程序崩溃
-样例2:原文为空
def test_empty_original():
# 模拟空文件
with open("empty.txt", "w") as f:
pass
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
calculate_similarity("empty.txt", "orig.txt")
场景:上传了空文件
目标:防止 len(orig_tokens) == 0 导致除零错误
-样例3:编码错误
def test_encoding_error():
# 创建一个非UTF-8文件(模拟)
with open("gbk.txt", "w", encoding="gbk") as f:
f.write("中文测试")
with pytest.raises(IOError):
calculate_similarity("gbk.txt", "orig.txt")
场景:文件编码非 UTF-8
目标:捕获异常并提示“请使用 UTF-8 编码”




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号