第二次博客
前言
这次的作业难度确实非常大,尤其是对于这种来C语言都还没学明白的学生来说,更是一种巨大的挑战。这几次练习我们需要熟练运用正则表达式(如题目集4,7-1水文数据校验及处理;题目集5,7-4 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数;题目集6的四道正则表达式的训练题),掌握继承(题目集4,7-3 图形继承 ;题目集6,7-5 图形继承与多态 )和多态(题目集6,7-5 图形继承与多态 ),以及Java中与类有关的构造方法等的相关知识点(题目集4,7-2 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一);题目集5,7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二) )并熟练运用。其中的题目7-2和题目7-5作为大作业,更是考察了我们很多综合性的东西,要求我们能对所学知识做到活学活用,更全面的考察了我们综合编程设计能力。
本次Blog主要分析的内容如下: ①题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较②题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结④题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结:
对于编程能力薄弱的我来说,刚刚一接触这两道题的时候,有种头大的感觉。但在网上查阅了相关内容,以及在同学的讲解下有了一个较为模糊的轮廓,接下来是查阅到的一些相关知识:聚合一总体来说是对类的一个串连,一层套一层的,关联性较高,因为每个类都是连接在一起的,若是后期的需要修改以及优化会产生很大的麻烦,改一处的话就要有很多地方的改动,耦合性太大,不利于程序的维护。并且将每个类都串在一起的话,代码的可读性很差,聚合二中的类分开实现,耦合性不大。如果需要改动代码,只需要改动当前类中的内容,整体代码不需要有太大的改动,并且聚合二代码可读性较强。
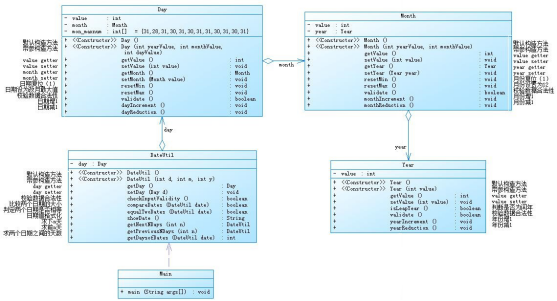
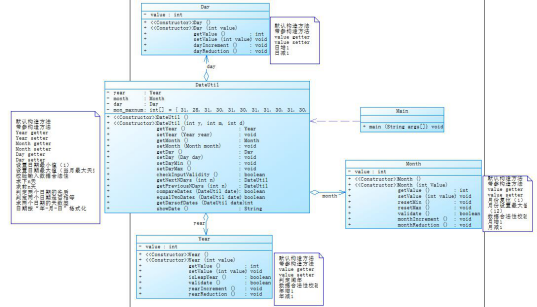
7-2代码
import java.util.Scanner; import java.lang.Math; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { double abscissa, ordinate; double length, width; int count = 0; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); abscissa = input.nextDouble(); ordinate = input.nextDouble(); length = input.nextDouble(); width = input.nextDouble(); count = input.nextInt(); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(new Coordinate(abscissa,ordinate), length,width); MonteCarloSimulation monteCarlo = new MonteCarloSimulation(rectangle); if (monteCarlo.validateRectangle()) { monteCarlo.setCircle(); double c = (double) Math.abs(monteCarlo.simulation(count) - Math.PI); if (c<= 1e-3) { System.out.println("Success"); } else { System.out.println("failed"); } } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } static class Coordinate { private double abscissa; private double ordinate; public Coordinate() { } public Coordinate(double abscissa,double ordinate) { setAbscissa(abscissa); setOrdinate(ordinate); } public double getAbscissa() { return abscissa; } public void setAbscissa(double abscissa) { this.abscissa = abscissa; } public double getOrdinate() { return ordinate; } public void setOrdinate(double ordinate) { this.ordinate = ordinate; } } static class Rectangle { private static Coordinate coordinate; private static double width; private static double length; public Rectangle() { } public Rectangle(Coordinate coordinate,double width,double length) { setCoordinate(coordinate); setWidth(width); setLength(length); } public Coordinate getCoordinate() { return coordinate; } public void setCoordinate(Coordinate coordinate) { this.coordinate = coordinate; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } } static class Circle{ private Coordinate coordinate = new Coordinate(); private double radius; public Circle() { } public Circle(Coordinate coordinate,double radius) { } public Coordinate getCoordinate() { return coordinate; } public void setCoordinate(Coordinate coordinate) { this.coordinate = coordinate; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } } static class MonteCarloSimulation{ private static Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); private static Circle circle = new Circle(); public MonteCarloSimulation() { } public MonteCarloSimulation(Rectangle rectangle,Circle circle) { setRectangle(rectangle); setCircle(circle); } public MonteCarloSimulation(Rectangle rectangle) { } public Rectangle getRectangle() { return rectangle; } public void setRectangle(Rectangle rectangle) { this.rectangle = rectangle; } public Circle getCircle() { return circle; } public void setCircle(Circle circle) { this.circle = circle; } public boolean validateRectangle() { if(rectangle.getLength()>0&&rectangle.getWidth()>0&&rectangle.getLength()==rectangle.getWidth()) { return true; } return false; } public void setCircle() { circle.setRadius(rectangle.getLength()/2); circle.getCoordinate().setAbscissa(rectangle.getCoordinate().getAbscissa()+(rectangle.getLength()/2)); circle.getCoordinate().setOrdinate(rectangle.getCoordinate().getOrdinate()-(rectangle.getWidth()/2)); } public double simulation(int n) { double x=rectangle.getCoordinate().getAbscissa(); double y=rectangle.getCoordinate().getOrdinate(); int m = 0; for(int i =0; i<n; i++) { rectangle.getCoordinate().setAbscissa((double)(Math.random()*(rectangle.getLength())+(x))); rectangle.getCoordinate().setOrdinate((double)(Math.random()*(rectangle.getLength())+(y-rectangle.getLength()))); if(getDistance(rectangle.getCoordinate(),circle.getCoordinate())<=circle.getRadius()) { m++; } } double c = (double) m/n*4; return c; } public double getDistance(Coordinate coord1,Coordinate coord2) { return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(coord1.getAbscissa()-coord2.getAbscissa(),2)+Math.pow(coord1.getOrdinate()-coord2.getOrdinate(), 2)); } } }
题目7-4代码太长,这里就不展示。
题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等),这些都是最近JAVA的核心内容,有一定难度。
7-3代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice;
choice = input.nextInt();
if(choice==1) {
double i=input.nextDouble();
if(i<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setRadius(i);
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",circle.getArea());
}
else if(choice==2){
double i=input.nextDouble();
double j=input.nextDouble();
if(i<=0||j<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setWidth(i);
rectangle.setLength(j);
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",rectangle.getArea());
}
else if(choice==3) {
double i=input.nextDouble();
if(i<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Ball ball = new Ball();
ball.setRadius(i);
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f",ball.getArea());
System.out.println("");
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",ball.getVolume());
}
else if(choice==4) {
double i=input.nextDouble();
double j=input.nextDouble();
double k=input.nextDouble();
if(i<=0||j<=0||k<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
Box box = new Box();
box.setWidth(i);
box.setLength(j);
box.setHeight(k);
if(box.getHeight()<=0||box.getLength()<=0||box.getWidth()<=0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f",box.getArea());
System.out.println("");
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",box.getVolume());
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
Circle() {
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.pow(radius, 2) * Math.PI;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
Rectangle() {
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
private double width, length;
public double getArea() {
return width * length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle {
Ball() {
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
public double getArea() {
return 4 * super.getArea();
}
public double getVolume() {
return 4*Math.PI * Math.pow(super.getRadius(),3)/3;
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle {
Box() {
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
}
private double height;
public double getArea() {
return super.getArea() * 2 + 2 * (super.getWidth() * height) + 2*(super.getLength()*height);
}
public double getVolume() {
return super.getArea()*height;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
}
class Shape {
Shape(){
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
}
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
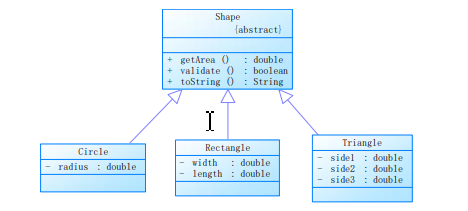
7-3定义了类Shape,子类Circle与Rectangle继承自Shape父类,均重写父类继承来的求面积方法。类Ball与类Box又分别继承自Circle与Rectangle类,也均重写了父类继承来的求面积方法。7-4作业重点研究的是平面图形相关的处理方法,与题7-3类似。对于题目集6(7-6)主要体现了对接口的使用,使用接口有这几个注意事项:接口内部的属性默认用final关键字修饰,方法默认并且只能使用抽象方法。定义一个求面积的接口,内部有抽象的一个求面积的方法。然后按题目要求定义的Circle类和Rectangle类使用这个接口并重写里面的求面积方法。③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结题目集一当中水文数字校验使用到的正则表达式最为复杂,很容易出错;题目集二 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 这题未能做出来,不清楚用没用正则;题目集三第一题是对数字(验证QQ号)的正则表达式的考察,第三题是对数字与字母混合(验证码的校验)的考察,第四题是对学号的考察,只要细心,这正则的题目都不难,代码很简洁。④题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结 该题是 统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 。自己不会写,网上搜了,好复杂,说实话没花心思看。。。充分暴漏了自己之前说的问题,说明自己学的还远远不够,课后肯定要多花时间的。
三、踩坑心得做日期类的聚合这种题目,一定要写完一个方法,立马测试,千万别一下写几个方法,那样错都不知道错在那,对于那些代码量较大的更应如此,改掉自己所有类都放到一起的操作,不然在后面愈加深入的学习中只能寸步难行。四、改进建议个人比较菜,只希望在后面的学习中,认真负责独立完成今后的每一次作业。
总结:
通过这三次题目集的练习,加深了我对对java程序的代码风格和相对c语言的不同之处的感受。进一步了解了java的封装性,继承,多态和接口,同时也暴露了自己对基础语法的不熟悉以及掌握程度不够。希望后续的练习,我能够了解更多的java知识,不断锻炼自我,改善自我。JAVA即使现阶段我还很菜,但我肯定会花时间把它学好的,这点毋庸置疑。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号