【学习笔记】K-D Tree
K-D Tree 是一种可以维护高维空间信息的数据结构,其结构和平衡树比较相似。
维护高维子空间信息
以一道板子题为例:
在 \(k\) 维空间中,有一个由整点构成的可重集 \(S\)(初始为空),\(S\) 中每个点都有一个权值。记整点 \(A\) 的第 \(d\) 维坐标为 \(x_d(A)\)。
你需要维护三种操作:
- 操作一:向 \(S\) 中插入点 \(A\),权值为 \(v\)。
- 操作二:给定整点 \(A\) 与整点 \(B\),将满足 \(C\in S\) 且 \(\forall d\in\{1,2,\cdots,k\},x_d(A)\le x_d(C)\le x_d(B)\) 的所有整点 \(C\) 的权值增加 \(v\)。
- 操作三:给定整点 \(A\) 与整点 \(B\),查询满足 \(C\in S\) 且 \(\forall d\in\{1,2,\cdots,k\},x_d(A)\le x_d(C)\le x_d(B)\) 的所有整点 \(C\) 权值之和。
Data Range: \(1\le m\le 1.5\times 10^5,k\in\lbrace 2,3\rbrace\),时间限制 \(5.00s\)。
本题强制在线。
下面将使用 K-D Tree 来解决这个问题:
build
和平衡树一样,若将 \(n\) 个 \(k\) 维空间上的点建一棵 K-D Tree,则可以递归建树:
- 若当前 \(n=0\),则什么也不做。
- 若当前 \(n=1\),则建立一棵以这个点本身为根,没有儿子结点的树,然后返回上一层。
- 若当前 \(n>1\),则首先选择一个维度 \(d\),把所有点按照 \(d\) 维度上的坐标从小到大排序。然后选择一个点 \(mid\),以 \(mid\) 为根结点建树,然后把 \([l,mid-1]\) 和 \([mid+1,r]\) 两个区间内的点分别放到左子树和右子树上并递归处理。
其中 \(mid\) 选取当前点集排序后的中间元素。
可以证明下面几种选择维度 \(d\) 的方法,都可以保证后续操作时间复杂度正确:
- 随机选取维度 \(d\)
- 轮流选取每个维度,即选取的维度的顺序为:\(1,2,3,\ldots,k,1,2,3,\ldots,k,1,2,\ldots\)
- 选取当前下标方差最大的维度
直接模拟上述过程,建树部分的时间复杂度为 \(O(n\log^2n)\) / \(O(nk\log^2n)\),若使用 nth_element 替代 sort 可以做到 \(O(n\log n)\) / \(O(nk\log n)\)。
其中通常使用第二种方法建树,后面的时间复杂度分析中也只会分析第二种方法。
query
现在考虑在高维空间中对其一个子空间的信息做查询。
一个暴力的做法是直接递归到每一个叶子结点,单次查询时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\),显然不可行。
考虑类比平衡树的操作方法,将当前查询空间 \(Q\) 和当前访问的空间 \(S\) 之间的关系分为三类:
- \(Q\cap S=\varnothing\)
- \(Q\subseteq S\)
- Other
其中第一类情况可以直接不继续递归处理子树,第二类情况可以在建树的时候维护每个结点子树的信息,然后直接查,不继续递归处理子树。剩下的第三类情况继续递归子树处理。
考虑分析其时间复杂度:在轮流划分维度建树时,每过 \(k\) 次就会划分到同一个维度。因此考虑对于一个结点,处理其 \(k-1\) 级的 \(2^{k-1}\) 个儿子结点。然后因为询问的矩形每一条边都是和坐标轴平行的,所以这样最多会切到 \(2\) 个区域,即每过 \(2^{k-1}\) 个结点就只会留下 \(2\) 个结点继续递归子树。
考虑用 Master Theorem 来计算时间复杂度,有:
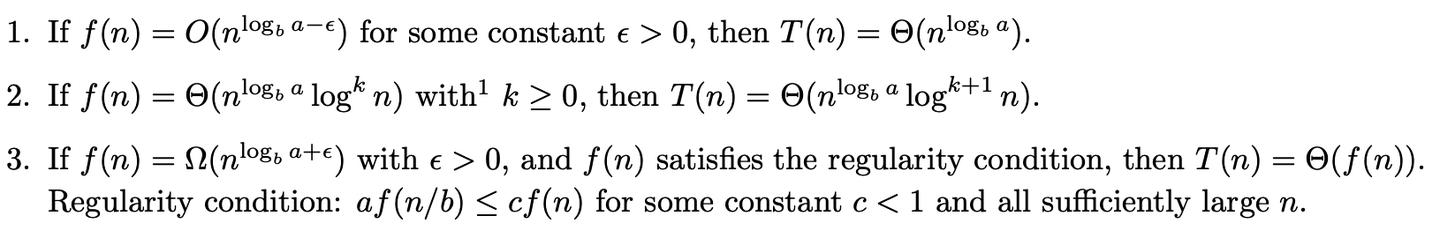
容易计算得到有 \(T(n)=O(n^{1-\frac1k})\),因此查询操作的时间复杂度即为 \(O(n^{1-\frac1k})\)(记住:不是 \(O(n^{\frac1k})\))。
insert
上面 K-D Tree 的操作都是静态的,现在要添加插入一个点的操作。
一个比较简单的想法是直接递归整棵 K-D Tree 到叶子结点插入然后一路 pushup 回来。但是注意到此时 K-D Tree 将不再平衡,同时其无法像平衡树一样左旋右旋或者双旋来调整时间复杂度,因此需要一些特殊的手段处理:
根号重构
一个比较容易想到的做法。设立阈值 \(B\),然后对于插入操作,把插入的点单独存储到集合 \(S\) 中,若 \(|S|=B\),则直接暴力重构整棵 K-D Tree。
而查询的时候,先不考虑 \(S\) 集合内的点,在树中直接查询子空间内信息,然后对 \(S\) 集合内的每个点暴力将其与原有信息合并。
此时插入操作的时间复杂度为:
- 若 \(|S|\neq B\),则时间复杂度为 \(O(1)\)
- 若 \(|S|=B\),则时间复杂度为 \(O(n\log n)\)
均摊一下,单点插入的时候时间复杂度即为 \(O(\frac{n\log n}B)\)。
而查询操作的时间复杂度为 \(O(n^{1-\frac 1k}+B)\),考虑对其根号平衡,即解方程 \(O(\frac{n\log n}B)=O(n^{1-\frac1k}+B)\)。通常取 \(B=O(\sqrt{n\log n})\) 时最优,此时插入时间复杂度为 \(O(\sqrt{n\log n})\),查询时间复杂度为 \(O(n^{1-\frac 1k}+\sqrt{n\log n})\)。
二进制分组
一种时间复杂度更优的做法。
考虑维护 \(O(\log n)\) 个 K-D Tree,其大小均为 \(2\) 的若干次幂,且没有两个树大小相等,且还需保证每个点被恰好划在了一个 K-D Tree 里。
每次插入一个点,就建立一个只有一个点的 K-D Tree,然后此时若存在两个 K-D Tree 的大小相等,就将其直接暴力重构。
查询的时候就直接在每一个 K-D Tree 里分别查询,然后对每个查询得到的信息合并即可。
然后根据进制理论,容易证明每次暴力重构都是从大小最小的树开始按照大小顺序连续的合并,直到一个大小 \(2^p\) 不再合并。因为合并的时间复杂度为 \(O(n\log n)\),而插入会合并的次数均摊是 \(O(\log n)\) 的,所以每次插入的均摊时间复杂度即为 \(O(n\log^2n)\),而不是 \(O(n\log^3n)\)。
然后再分析此时查询的时间复杂度。对大小为 \(2^p\) 的树而言,查询其的时间复杂度为 \(O({(2^p)}^{1-\frac 1k})\),因此总时间复杂度为 \(O((\sum\limits_{p=0}^{\lfloor\log n\rfloor}2^p)^{1-\frac1k})=O(n^{1-\frac1k})\)。
modify
单点修改信息是容易的,直接暴力递归到叶子结点然后倒序 pushup,时间复杂度为 \(O(\log n)\) 且不会影响树的结构。
而若要整体修改一个空间 \(S\) 内的信息,暴力处理每个 \(x\in S\),时间复杂度显然不对。考虑类比平衡树,在每个结点上维护 \(tag\) 标记,表示当前结点有哪些信息没有被下传到其子树内。
具体的,将当前查询空间 \(Q\) 和当前访问的空间 \(S\) 之间的关系分为三类:
- \(Q\cap S=\varnothing\)
- \(Q\subseteq S\)
- Other
对于第一种情况,无需继续递归修改,第二种情况子树内所有元素均需递归修改,所以考虑直接在当前结点上打懒惰标记 \(tag\),然后直接返回其父节点即可。剩下的第三类情况继续递归子树处理。
而在每次 modify 和 query 操作之前,均把当前结点的信息 pushdown 到其儿子结点,就可以保证访问到该结点时,其对应的信息是正确的。
时间复杂度和 query 的时间复杂度相同,均为 \(O(n^{1-\frac 1k})\)。
细节处理
在本题中,需要对 K-D Tree 上的每个结点,维护下面的信息:
- \(x[0:k-1]\):表示当前结点对应的点第 \(0\ldots k-1\) 维的坐标。
- \(val,sum\):分别表示当前结点对应的点的信息,以及其子树内所有结点对应信息的并,在本题中为点权 / 子树点权和。
- \(l,r\):当前结点的左儿子 / 右儿子结点。
- \(L[0:k-1],R[0:k-1]\):表示当前结点子树内第 \(0\ldots k-1\) 维中坐标最小 / 最大值是多少。
- \(siz\):表示当前结点子树内有多少个结点,即子树大小。
- \(tag\):懒标记信息,本题中为需要懒惰下传的区间加的数值。
在 pushup 的过程中,\(u\) 结点更新的信息有:
u.sum信息,更新方法为u.sum = (u.l).sum + (u.r).sum + u.val(注意要加上u.val即当前点的点权)- 对每个维度,均重新更新
u.L,u.R两个数组内维护的信息,同样需要加上当前结点u.x内对应的信息。 - 不要清空懒标记。
具体实现如下:
struct Node
{
int x[3], val, sum, l, r, L[3], R[3], siz, tag;
// inline Node() { x[0] = x[1] = x[2] = L[0] = L[1] = L[2] = R[0] = R[1] = R[2] = val = sum = l = r = siz = tag = 0; }
// x[i] 表示当前结点 i 维度的位置(即当前结点坐标)
// val 是当前点的权值 sum 是维护的信息
// l / r 表示其左儿子 / 右儿子的标号
// L[i] / R[i] 表示当前结点中 i 维度最小 / 最大值
// siz 是 i 结点对应的子树的大小
// tag 是平面 / 空间加时 需要处理的 懒标记
} tree[N];
int dest[N], root[20], cnt, idx;
inline void pushup(int rt)
{
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + tree[tree[rt].r].sum + tree[rt].val;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
pushdown 的过程和平衡树是类似的。
inline void pushdown(int rt)
{
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[tree[rt].l].tag += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].l].val += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].l].sum += tree[tree[rt].l].siz * tree[rt].tag;
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[tree[rt].r].tag += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].r].val += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].r].sum += tree[tree[rt].r].siz * tree[rt].tag;
}
tree[rt].tag = 0;
}
build 的过程中,因为在重构的时候也会调用,所以应注意对其左右儿子的信息的处理(即在 build 之前先清空信息):
inline int build(int l, int r, int dim_op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{
return tree[l].x[dim_op] < tree[r].x[dim_op];
});
tree[dest[mid]].l = tree[dest[mid]].r = 0;
tree[dest[mid]].siz = 1;
if (l < mid)
{
tree[dest[mid]].l = build(l, mid - 1, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
tree[dest[mid]].siz += tree[tree[dest[mid]].l].siz;
}
if (mid < r)
{
tree[dest[mid]].r = build(mid + 1, r, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
tree[dest[mid]].siz += tree[tree[dest[mid]].r].siz;
}
tree[dest[mid]].tag = 0;
pushup(dest[mid]);
return dest[mid];
}
其中 dest 数组内存储了当前需要建树的空间内的所有点的信息。
然后是暴力重构部分,在找到第一个合并位置的时候一定要直接 break,不然可能会出现一些奇奇怪怪的错误。同时还需要记得每次重构之前清空 dest 数组的信息。
重构之前要先清空每个需要重构的结点的懒标记,即直接暴力递归整棵树 pushdown,在下面的代码中对应 push_cache 函数。
一些奇奇怪怪的错误是比如说忘记清空 dest 数组的使用位置指针 cnt 了,或者新建结点的时候直接复用了老结点的信息。
inline void push_cache(int &rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
pushdown(rt);
if (tree[rt].l)
push_cache(tree[rt].l);
dest[++cnt] = rt;
if (tree[rt].r)
push_cache(tree[rt].r);
rt = 0;
}
if (o == 1)
{
int x[3], val;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> x[i], x[i] ^= la;
cin >> val, val ^= la;
++idx;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
tree[idx].x[i] = x[i];
tree[idx].val = val;
dest[cnt = 1] = idx;
for (int i = 0; ; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
最后剩下 modify 和 query 两个函数,这里需要特别注意特判掉当前子树根的结点的信息。一些其他的细节是特判子空间的子集关系时一定需要判掉所有的维度,而不能只判断一个维度为子集关系就直接确认关系。
(其中 loyalty 函数是修改,luminescent 函数是查询,至于为什么用这两个名字你不用管)
inline void loyalty(int rt, int val)
{
if (!rt)
return;
pushdown(rt);
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[rt].L[i] && tree[rt].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
{
tree[rt].sum += tree[rt].siz * val;
tree[rt].tag += val;
tree[rt].val += val;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (tree[rt].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[rt].L[i])
return;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[rt].x[i] && tree[rt].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
tree[rt].sum += val, tree[rt].val += val;
loyalty(tree[rt].l, val);
loyalty(tree[rt].r, val);
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + tree[tree[rt].r].sum + tree[rt].val;
// pushup(rt);
}
inline int luminescent(int rt)
{
if (!rt)
return 0;
pushdown(rt);
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[rt].L[i] && tree[rt].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return tree[rt].sum;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (tree[rt].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[rt].L[i])
return 0;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[rt].x[i] && tree[rt].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return luminescent(tree[rt].l) + luminescent(tree[rt].r) + tree[rt].val;
return luminescent(tree[rt].l) + luminescent(tree[rt].r);
}
而在修改 / 查询的时候,需要对所有 \(O(\log n)\) 个 K-D Tree 均做修改 / 查询,所以主函数内应这样调用:
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
loyalty(root[i], val);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
cnt += luminescent(root[i]);
cout << (la = cnt) << '\n';
例题
P14312 【模板】K-D Tree**
直接把刚才那几个操作合起来即可。
// Author: 美丽好 rua 的大宋宋
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <bits/stl_algo.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010;
const int inf = 1e18;
const int mod = 998244353;
inline int power(int a, int b, int c)
{
int ans = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
ans = ans * a % c;
a = a * a % c, b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
inline int inversion(int x) { return power(x, mod - 2, mod); }
using ull = unsigned long long;
using i128 = __int128;
int dim, m, lx[3], rx[3];
struct Node
{
int x[3], val, sum, l, r, L[3], R[3], siz, tag;
// inline Node() { x[0] = x[1] = x[2] = L[0] = L[1] = L[2] = R[0] = R[1] = R[2] = val = sum = l = r = siz = tag = 0; }
// x[i] 表示当前结点 i 维度的位置(即当前结点坐标)
// val 是当前点的权值 sum 是维护的信息
// l / r 表示其左儿子 / 右儿子的标号
// L[i] / R[i] 表示当前结点中 i 维度最小 / 最大值
// siz 是 i 结点对应的子树的大小
// tag 是平面 / 空间加时 需要处理的 懒标记
} tree[N];
int dest[N], root[20], cnt, idx;
inline void pushup(int rt)
{
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + tree[tree[rt].r].sum + tree[rt].val;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
inline int build(int l, int r, int dim_op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{
return tree[l].x[dim_op] < tree[r].x[dim_op];
});
tree[dest[mid]].l = tree[dest[mid]].r = 0;
tree[dest[mid]].siz = 1;
if (l < mid)
{
tree[dest[mid]].l = build(l, mid - 1, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
tree[dest[mid]].siz += tree[tree[dest[mid]].l].siz;
}
if (mid < r)
{
tree[dest[mid]].r = build(mid + 1, r, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
tree[dest[mid]].siz += tree[tree[dest[mid]].r].siz;
}
tree[dest[mid]].tag = 0;
pushup(dest[mid]);
return dest[mid];
}
inline void pushdown(int rt)
{
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[tree[rt].l].tag += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].l].val += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].l].sum += tree[tree[rt].l].siz * tree[rt].tag;
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[tree[rt].r].tag += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].r].val += tree[rt].tag;
tree[tree[rt].r].sum += tree[tree[rt].r].siz * tree[rt].tag;
}
tree[rt].tag = 0;
}
inline void push_cache(int &rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
pushdown(rt);
if (tree[rt].l)
push_cache(tree[rt].l);
dest[++cnt] = rt;
if (tree[rt].r)
push_cache(tree[rt].r);
rt = 0;
}
inline void loyalty(int rt, int val)
{
if (!rt)
return;
pushdown(rt);
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[rt].L[i] && tree[rt].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
{
tree[rt].sum += tree[rt].siz * val;
tree[rt].tag += val;
tree[rt].val += val;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (tree[rt].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[rt].L[i])
return;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[rt].x[i] && tree[rt].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
tree[rt].sum += val, tree[rt].val += val;
loyalty(tree[rt].l, val);
loyalty(tree[rt].r, val);
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + tree[tree[rt].r].sum + tree[rt].val;
// pushup(rt);
}
inline int luminescent(int rt)
{
if (!rt)
return 0;
pushdown(rt);
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[rt].L[i] && tree[rt].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return tree[rt].sum;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (tree[rt].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[rt].L[i])
return 0;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[rt].x[i] && tree[rt].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return luminescent(tree[rt].l) + luminescent(tree[rt].r) + tree[rt].val;
return luminescent(tree[rt].l) + luminescent(tree[rt].r);
}
signed main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("1.out", "w", stdout);
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> dim >> m;
int la = 0;
while (m--)
{
// cerr << "!!!\n";
int o;
cin >> o;
if (o == 1)
{
int x[3], val;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> x[i], x[i] ^= la;
cin >> val, val ^= la;
++idx;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
tree[idx].x[i] = x[i];
tree[idx].val = val;
dest[cnt = 1] = idx;
for (int i = 0; ; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
else if (o == 2)
{
int val;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> lx[i];
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> rx[i], lx[i] ^= la, rx[i] ^= la;
cin >> val, val ^= la;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
loyalty(root[i], val);
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> lx[i];
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
cin >> rx[i], lx[i] ^= la, rx[i] ^= la;
int cnt = 0;
// cerr << "root: ";
// for (int i = 0; i < 20 ;++i)
// cerr << root[i] << ' ';
// cerr << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
cnt += luminescent(root[i]);
cout << (la = cnt) << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
P4148 简单题**
(甚至比刚才那个还简单,连子空间修改操作都没了)
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int idx, cnt, dest[N], root[N], lx[2], rx[2];
struct Node
{
int x[2], val, sum, l, r, L[2], R[2];
} tree[N];
void pushup(int rt)
{
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + tree[tree[rt].r].sum + tree[rt].val;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{ return tree[l].x[op] < tree[r].x[op]; });
if (l < mid)
tree[dest[mid]].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[dest[mid]].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(dest[mid]);
return dest[mid];
}
void push_cache(int &root)
{
if (!root)
return;
dest[++cnt] = root;
push_cache(tree[root].l), push_cache(tree[root].r);
root = 0;
}
int luminescent(int root)
{
if (!root)
return 0;
int ok = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[root].L[i] && tree[root].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 1;
break;
}
if (!ok)
return tree[root].sum;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (tree[root].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[root].L[i])
return 0;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[root].x[i] && tree[root].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return luminescent(tree[root].l) + luminescent(tree[root].r) + tree[root].val;
return luminescent(tree[root].l) + luminescent(tree[root].r);
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int _, op, la = 0;
cin >> _;
while (cin >> op, op != 3)
{
if (op == 1)
{
int x, y, a;
cin >> x >> y >> a;
x ^= la, y ^= la, a ^= la;
cnt = 0;
++idx;
tree[idx].x[0] = x;
tree[idx].x[1] = y;
tree[idx].val = a;
dest[++cnt] = idx;
for (int i = 0;; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
else
{
cin >> lx[0] >> lx[1] >> rx[0] >> rx[1];
lx[0] ^= la, lx[1] ^= la, rx[0] ^= la, rx[1] ^= la;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
cnt += luminescent(root[i]);
cout << (la = cnt) << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
邻域查询
note:K-D Tree 上邻域查询的时间复杂度是没有保障的,其在随机数据下跑的很快,但是可以构造数据卡到 \(O(n)\)。
以一道板子题为例:
平面上给定 \(n\) 个点 \((x_i,y_i)\),设 \(\text{Dist}(i,j)=|x_i-x_j|+|y_i-y_j|\),求 \(\max\limits_{1\le i\le j\le n}\text{Dist}(i,j)\) 的值。
Data Range: \(1\le n\le 10^5\)
常规解法是曼哈顿转切比雪夫或者拆绝对值,这里提供一种使用 K-D Tree 的做法。
先拆分上面的式子,可以看作是对每个 \(i\),求出 \(res_i\) 表示平面上距离 \(i\) 点最远的点的距离。那么答案就是 \(\max\limits_{i=1}^nres_i\)。
而求 \(res_i\),一个直接的想法是直接遍历整棵 K-D Tree 的所有结点,依次更新答案,但是这样单次查询时间复杂度为 \(O(n)\),显然无法通过。
考虑使用一些剪枝来优化运行效率:
(1)在递归到某个结点时,先处理当前根结点对应坐标的信息,这个处理的时间复杂度为 \(O(1)\)。
(2)一个比较简单的剪枝是考虑在 K-D Tree 上的每个结点都维护信息 \(x_{max},y_{max},x_{min},y_{min}\) 即当前点所在子树中所有坐标点 \(x,y\) 两个维度的最大值 / 最小值。遍历到某个结点时,若该结点到坐标 \((x_{max},y_{max}),(x_{max},y_{min}),(x_{min},y_{max}),(x_{min},y_{min})\) 四个坐标点的距离都不可能比当前已经更新到的最小值要优,那么就不再遍历当前分岔。
(3)类似于 A*,考虑给每个点都设一个估价函数。例如在该问题中,估价函数就可以设为该点到询问空间内所有点的最长距离。此时按照估价函数从大到小遍历每个分岔即可。例如在二维空间中(即本问题中),就可以这样设计估价函数:
inline int expmax(int o, int id)
{
if (!o)
return -1e18;
return max(tree[id].x[0] - tree[o].L[0], tree[o].R[0] - tree[id].x[0]) + max(tree[id].x[1] - tree[o].L[1], tree[o].R[1] - tree[id].x[1]);
}
使用上述剪枝优化该算法后,时间复杂度仍为 \(O(n)\),但是在随机数据下运行效率极高。同时因为该算法本质上就是暴力搜索加剪枝,所以也可以同时轻松的找出一组最远点对。
P2479 [SDOI2010] 捉迷藏**
这个问题在刚才问题的基础上额外需要求最近点对距离,因此同样的,类比最远点对距离,设一个最近点对距离的估价函数。容易想到设该估价函数为当前点到当前所处空间的最近距离,即:
inline int expmin(int o, int id)
{
if (!o)
return 1e18;
return max(0ll, tree[id].x[0] - tree[o].R[0]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[0] - tree[id].x[0]) + max(0ll, tree[id].x[1] - tree[o].R[1]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[1] - tree[id].x[1]);
}
剩下的部分和刚才的分析是一样的。
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int idx, cnt, dest[N], root[N], lx[2], rx[2];
struct Node
{
int l, r, L[2], R[2], x[2];
} tree[N];
void pushup(int rt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(tree + l, tree + mid, tree + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{ return l.x[op] < r.x[op]; });
if (l < mid)
tree[mid].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[mid].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(mid);
return mid;
}
int mx, mi;
inline int expmin(int o, int id)
{
if (!o)
return 1e18;
return max(0ll, tree[id].x[0] - tree[o].R[0]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[0] - tree[id].x[0]) + max(0ll, tree[id].x[1] - tree[o].R[1]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[1] - tree[id].x[1]);
}
inline int expmax(int o, int id)
{
if (!o)
return -1e18;
return max(tree[id].x[0] - tree[o].L[0], tree[o].R[0] - tree[id].x[0]) + max(tree[id].x[1] - tree[o].L[1], tree[o].R[1] - tree[id].x[1]);
}
inline int dist(int x, int y)
{
return abs(tree[x].x[0] - tree[y].x[0]) + abs(tree[x].x[1] - tree[y].x[1]);
}
void dfsmax(int rt, int id)
{
if (!rt)
return;
// cerr << rt << " awa " << id << '\n';
if (rt != id)
mx = max(mx, dist(rt, id));
int d1 = expmax(tree[rt].l, id), d2 = expmax(tree[rt].r, id);
if (d1 < d2)
{
if (d2 > mx)
dfsmax(tree[rt].r, id);
if (d1 > mx)
dfsmax(tree[rt].l, id);
}
else
{
if (d1 > mx)
dfsmax(tree[rt].l, id);
if (d2 > mx)
dfsmax(tree[rt].r, id);
}
}
void dfsmin(int rt, int id)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (rt != id)
mi = min(mi, dist(rt, id));
int d1 = expmin(tree[rt].l, id), d2 = expmin(tree[rt].r, id);
if (d1 < d2)
{
if (d1 < mi)
dfsmin(tree[rt].l, id);
if (d2 < mi)
dfsmin(tree[rt].r, id);
}
else
{
if (d2 < mi)
dfsmin(tree[rt].r, id);
if (d1 < mi)
dfsmin(tree[rt].l, id);
}
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> tree[i].x[0] >> tree[i].x[1];
int res = 1e18, root = build(1, n, 0);
// cout << root << '\n';
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
mx = -1e18;
dfsmax(root, i);
mi = 1e18;
dfsmin(root, i);
// cout << i << ": " << mi << ' ' << mx << '\n';
res = min(res, mx - mi);
}
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
P4357 [CQOI2016] K 远点对**
(弱化版,需保证数据随机)
该问题是求在欧几里得距离下第 \(k\) 远的点对。注意到 \(k\) 很小,因此考虑在 K-D Tree 搜索的过程中直接把前 \(k\) 远的点对全部搜出来。
具体的,用一个小根堆来维护当前所有搜到的距离。若当前搜到的距离比小跟堆堆顶的距离要更远,那么弹出堆顶,将该元素塞到堆里。最后答案即为堆顶元素。
这个题把 K-D Tree 卡了,所以只能用计算几何做法来做。
P2093 [国家集训队] JZPFAR**
刚刚那题的数据弱化版,经过卡常之后可以通过。
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int idx, cnt, dest[N], root[N], lx[2], rx[2];
struct Node
{
int x[2];
int L[2], R[2];
int l, r;
} tree[N];
struct Point
{
int x[2], id;
} a[N];
void pushup(int rt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i] = a[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(a + l, a + mid, a + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{ return l.x[op] < r.x[op]; });
if (l < mid)
tree[mid].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[mid].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(mid);
return mid;
}
int mx, mi;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q;
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline int sq(int x)
{
return x * x;
}
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline int expmax(int o, int x, int y)
{
if (!o)
return -2e18;
int x1 = (tree[o].L[0] - x) * (tree[o].L[0] - x);
int x2 = (tree[o].R[0] - x) * (tree[o].R[0] - x);
int x3 = (tree[o].L[1] - y) * (tree[o].L[1] - y);
int x4 = (tree[o].R[1] - y) * (tree[o].R[1] - y);
return max(x1, x2) + max(x3, x4);
// return max(sq(x - tree[o].R[0]), sq(x - tree[o].L[0])) + max(sq(y - tree[o].R[1]), sq(y - tree[o].L[1]));
}
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline int dist(int x, int y)
{
return sq(tree[x].x[0] - tree[y].x[0]) + sq(tree[x].x[1] - tree[y].x[1]);
}
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline int dist(int x, int yx, int yy)
{
return sq(tree[x].x[0] - yx) + sq(tree[x].x[1] - yy);
}
int px, py, k, x, y, id;
void dfsmax(int rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (q.size() == k && q.top().first > expmax(rt, x, y))
return;
auto oo = q.top();
if (oo < make_pair(dist(rt, x, y), -a[rt].id))
q.pop(), q.emplace(dist(rt, x, y), -a[rt].id);
int d1 = expmax(tree[rt].l, x, y), d2 = expmax(tree[rt].r, x, y);
if (d1 > d2)
{
if (tree[rt].l && d1 >= q.top().first)
dfsmax(tree[rt].l);
if (tree[rt].r && d2 >= q.top().first)
dfsmax(tree[rt].r);
}
else
{
if (tree[rt].r && d2 >= q.top().first)
dfsmax(tree[rt].r);
if (tree[rt].l && d1 >= q.top().first)
dfsmax(tree[rt].l);
}
}
const int inf = 1e18;
// pair{first, second}: dist ;; id
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i].x[0] >> a[i].x[1], a[i].id = i;
int res = 1e18, root = build(1, n, 0);
int m, ca = 1;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
// q.clear();
while (q.size())
q.pop();
cin >> px >> py >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
q.emplace(-inf, inf);
x = px, y = py, id = k;
dfsmax(root);
cout << -q.top().second << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
P4475 巧克力王国**
注意到该题保证数据以某种方式随机生成,因此考虑使用一些比较暴力的方法,如类比上面邻域查询问题时的剪枝。
容易想到先建立 K-D Tree,在树上的每个结点都维护信息 \(x_{max},y_{max},x_{min},y_{min}\) 即当前点所在子树中所有坐标点 \(x,y\) 两个维度的最大值 / 最小值。遍历到某个结点时,容易发现因为固定一个维度之后函数满足单调性,所以该子树内的最大值和最小值一定在下面四个值中的 \(\min,\max\) 值之内:
- \(ax_{max}+by_{max}\)
- \(ax_{min}+by_{max}\)
- \(ax_{max}+by_{min}\)
- \(ax_{min}+by_{max}\)
考虑到这个东西的最大值 / 最小值一定是包含实际的最大值 / 最小值的,因此可以保证正确性的递归。设上面东西求出的最大值为 \(mx\) 最小值为 \(mi\),则考虑分类讨论:
- 若有 \(c\le mi\),则此时显然该子树内所有点都不可能满足条件,直接返回上一层循环即可。
- 若有 \(c>mx\),则此时显然该子树内所有点都可以满足条件,在 K-D Tree 上的每个结点内都额外记录一个信息 \(sum\) 表示子树内所有点的甜度值的和,直接返回当前点的 \(sum\) 值即可。
- 否则,暴力往两个子树内递归。
因为数据是随机生成的,而该启发式算法在随机数据下跑的很快,所以可以轻松通过该题。
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 50010;
int n, m;
struct Node
{
int x[2], L[2], R[2], l, r, sum, val;
} tree[N], a[N];
void pushup(int rt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i] = a[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
tree[rt].sum = tree[rt].val;
if (tree[rt].l)
tree[rt].sum += tree[tree[rt].l].sum;
if (tree[rt].r)
tree[rt].sum += tree[tree[rt].r].sum;
}
int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(a + l, a + mid, a + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{
return l.x[op] < r.x[op];
});
tree[mid] = a[mid];
if (l < mid)
tree[mid].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[mid].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(mid);
return mid;
}
int luminescent(int rt, int a, int b, int c)
{
int x00 = a * tree[rt].L[0] + b * tree[rt].L[1];
int x01 = a * tree[rt].R[0] + b * tree[rt].L[1];
int x10 = a * tree[rt].L[0] + b * tree[rt].R[1];
int x11 = a * tree[rt].R[0] + b * tree[rt].R[1];
// cout << "Abc " << x00 << ' ' << x01 << ' ' << x10 << ' ' << x11 << ' ' << c << '\n';
if (max({x00, x01, x10, x11}) < c)
return tree[rt].sum;
if (min({x00, x01, x10, x11}) >= c)
return 0;
int x2 = a * tree[rt].x[0] + b * tree[rt].x[1], s = 0;
if (x2 < c)
s = tree[rt].val;
if (tree[rt].l)
s += luminescent(tree[rt].l, a, b, c);
if (tree[rt].r)
s += luminescent(tree[rt].r, a, b, c);
return s;
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i].x[0] >> a[i].x[1] >> a[i].val;
int root = build(1, n, 0);
while (m--)
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
cout << luminescent(root, a, b, c) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
一些应用
P3769 [CH弱省胡策R2] TATT
原问题求解的是四维意义下的 LIS,容易想到先按第一维排序,然后转化为三维的偏序关系。
比较常规的解法是 cdq 分治套 cdq 分治优化 dp,但是这里采用 KD-Tree 来优化她。
按照第一维排序后,设 \(f_i\) 表示当前以 \(i\) 点为结尾的 LIS 长度最长是多少。有初始状态 \(f_i=1\),转移方程形如:
考虑用数据结构优化。容易想到写一个树套树。注意到前面部分的查询其实就是在一个三维空间中查询最大值,然后添加 \(i\) 位置就是在 KD-Tree 上单点插入。在每个结点上维护子树最大值信息,可以做到 \(O(n^{5/3})\) 解决该问题。
看上去比较吓人,但是 \(n\) 只有 \(50000\),而且 KDT 的时间复杂度跑不满,所以仍然可以无压力通过。
// Author: 美丽好 rua 的大宋宋
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <bits/stl_algo.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010;
const int inf = 1e18;
const int mod = 998244353;
inline int power(int a, int b, int c)
{
int ans = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
ans = ans * a % c;
a = a * a % c, b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
inline int inversion(int x) { return power(x, mod - 2, mod); }
using ull = unsigned long long;
using i128 = __int128;
const int dim = 3;
int m, lx[3], rx[3];
struct Node
{
int x[3], val, mx, l, r, L[3], R[3];
} tree[N];
int dest[N], root[20], cnt, idx;
inline void pushup(int rt)
{
tree[rt].mx = max({tree[rt].val, tree[tree[rt].l].mx, tree[tree[rt].r].mx});
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
inline int build(int l, int r, int dim_op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{
return tree[l].x[dim_op] < tree[r].x[dim_op];
});
tree[dest[mid]].l = tree[dest[mid]].r = 0;
if (l < mid)
tree[dest[mid]].l = build(l, mid - 1, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
if (mid < r)
tree[dest[mid]].r = build(mid + 1, r, (dim_op + 1) % dim);
pushup(dest[mid]);
return dest[mid];
}
inline void push_cache(int &rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (tree[rt].l)
push_cache(tree[rt].l);
dest[++cnt] = rt;
if (tree[rt].r)
push_cache(tree[rt].r);
rt = 0;
}
inline int luminescent(int rt)
{
if (!rt)
return 0;
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (lx[i] <= tree[rt].L[i] && tree[rt].R[i] <= rx[i])
;
else
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return tree[rt].mx;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (tree[rt].R[i] < lx[i] || rx[i] < tree[rt].L[i])
return 0;
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
if (!(lx[i] <= tree[rt].x[i] && tree[rt].x[i] <= rx[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
if (ok)
return max({luminescent(tree[rt].l), luminescent(tree[rt].r), tree[rt].val});
return max(luminescent(tree[rt].l), luminescent(tree[rt].r));
}
inline void ins(int x[3], int val)
{
++idx;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; ++i)
tree[idx].x[i] = x[i];
tree[idx].val = val;
dest[cnt = 1] = idx;
for (int i = 0; ; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
inline int qry(int _lx[3], int _rx[3])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
lx[i] = _lx[i], rx[i] = _rx[i];
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
mx = max(mx, luminescent(root[i]));
return mx;
}
struct Point
{
int x, y, z, w;
} pnt[N];
int f[N];
signed main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("1.out", "w", stdout);
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
cin >> pnt[i].x >> pnt[i].y >> pnt[i].z >> pnt[i].w;
sort(pnt + 1, pnt + m + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r) { return make_tuple(l.x, l.y, l.z, l.w) < make_tuple(r.x, r.y, r.z, r.w); });
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
f[i] = 1;
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
int x[3] = {pnt[i].y, pnt[i].z, pnt[i].w};
int _[3] = {(int)-1e9, (int)-1e9, (int)-1e9};
int val = qry(_, x) + 1;
mx = max(mx, val);
ins(x, val);
}
cout << mx << '\n';
return 0;
}
在上个题的基础上加了一个点的权值,只需要把上一题的 dp 初始条件修改为 \(f_i=C_i\),转移方程修改为:
按照 \(H\) 从小到大排序转移即可,需要大力卡常才能过。
// Author: 美丽好 rua 的大宋宋
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4.1,sse4.2,avx,avx2,popcnt")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
const int dim = 3;
const int MAXL = 16;
#if defined(__GNUC__)
#define LIKELY(x) (__builtin_expect(!!(x), 1))
#define UNLIKELY(x) (__builtin_expect(!!(x), 0))
#define HOT __attribute__((hot))
#else
#define LIKELY(x) (x)
#define UNLIKELY(x) (x)
#define HOT
#endif
int m, lx[3], rx[3];
struct Node
{
int x[3], l, r, L[3], R[3];
long long val, mx;
} tree[N];
int dest[N], root[MAXL], cnt, idx;
static int OP = 0;
static const int nxt[3] = {1, 2, 0};
static bool cmp_idx(const int &a, const int &b)
{
return tree[a].x[OP] < tree[b].x[OP];
}
inline void pushup(int rt)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
const int l = t.l, r = t.r;
long long mx0 = t.val;
if (l)
{
long long v = tree[l].mx;
if (v > mx0)
mx0 = v;
}
if (r)
{
long long v = tree[r].mx;
if (v > mx0)
mx0 = v;
}
t.mx = mx0;
if (t.mx < 0)
t.mx = 0;
int L0 = t.x[0], R0 = L0;
if (l)
{
if (tree[l].L[0] < L0)
L0 = tree[l].L[0];
if (tree[l].R[0] > R0)
R0 = tree[l].R[0];
}
if (r)
{
if (tree[r].L[0] < L0)
L0 = tree[r].L[0];
if (tree[r].R[0] > R0)
R0 = tree[r].R[0];
}
t.L[0] = L0;
t.R[0] = R0;
int L1 = t.x[1], R1 = L1;
if (l)
{
if (tree[l].L[1] < L1)
L1 = tree[l].L[1];
if (tree[l].R[1] > R1)
R1 = tree[l].R[1];
}
if (r)
{
if (tree[r].L[1] < L1)
L1 = tree[r].L[1];
if (tree[r].R[1] > R1)
R1 = tree[r].R[1];
}
t.L[1] = L1;
t.R[1] = R1;
int L2 = t.x[2], R2 = L2;
if (l)
{
if (tree[l].L[2] < L2)
L2 = tree[l].L[2];
if (tree[l].R[2] > R2)
R2 = tree[l].R[2];
}
if (r)
{
if (tree[r].L[2] < L2)
L2 = tree[r].L[2];
if (tree[r].R[2] > R2)
R2 = tree[r].R[2];
}
t.L[2] = L2;
t.R[2] = R2;
}
inline int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
OP = op;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, cmp_idx);
int rt = dest[mid];
tree[rt].l = tree[rt].r = 0;
if (l < mid)
tree[rt].l = build(l, mid - 1, nxt[op]);
if (mid < r)
tree[rt].r = build(mid + 1, r, nxt[op]);
pushup(rt);
return rt;
}
inline void push_cache(int &rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (tree[rt].l)
push_cache(tree[rt].l);
dest[++cnt] = rt;
if (tree[rt].r)
push_cache(tree[rt].r);
rt = 0;
}
HOT inline void luminescent(int rt, long long &best)
{
if (UNLIKELY(!rt))
return;
if (tree[rt].mx <= best)
return;
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] ||
t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] ||
t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2])
return;
if (lx[0] <= t.L[0] && t.R[0] <= rx[0] &&
lx[1] <= t.L[1] && t.R[1] <= rx[1] &&
lx[2] <= t.L[2] && t.R[2] <= rx[2])
{
if (t.mx > best)
best = t.mx;
return;
}
if (lx[0] <= t.x[0] && t.x[0] <= rx[0] &&
lx[1] <= t.x[1] && t.x[1] <= rx[1] &&
lx[2] <= t.x[2] && t.x[2] <= rx[2])
{
if (t.val > best)
best = t.val;
}
const int lc = t.l, rc = t.r;
#if defined(__GNUC__)
if (lc)
__builtin_prefetch(&tree[lc], 0, 1);
if (rc)
__builtin_prefetch(&tree[rc], 0, 1);
#endif
int first = lc, second = rc;
if (rc && (!lc || tree[rc].mx > tree[lc].mx))
{
first = rc;
second = lc;
}
if (first && tree[first].mx > best)
luminescent(first, best);
if (second && tree[second].mx > best)
luminescent(second, best);
}
inline void ins(int x[3], long long val)
{
++idx;
tree[idx].x[0] = x[0];
tree[idx].x[1] = x[1];
tree[idx].x[2] = x[2];
tree[idx].val = val;
dest[cnt = 1] = idx;
// MAXL 循环展开(0..15)
if (!root[0])
{
root[0] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[0]);
if (!root[1])
{
root[1] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[1]);
if (!root[2])
{
root[2] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[2]);
if (!root[3])
{
root[3] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[3]);
if (!root[4])
{
root[4] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[4]);
if (!root[5])
{
root[5] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[5]);
if (!root[6])
{
root[6] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[6]);
if (!root[7])
{
root[7] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[7]);
if (!root[8])
{
root[8] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[8]);
if (!root[9])
{
root[9] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[9]);
if (!root[10])
{
root[10] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[10]);
if (!root[11])
{
root[11] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[11]);
if (!root[12])
{
root[12] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[12]);
if (!root[13])
{
root[13] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[13]);
if (!root[14])
{
root[14] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[14]);
if (!root[15])
{
root[15] = build(1, cnt, 0);
return;
}
push_cache(root[15]);
root[MAXL - 1] = build(1, cnt, 0);
}
inline long long qry(int _lx[3], int _rx[3])
{
lx[0] = _lx[0];
lx[1] = _lx[1];
lx[2] = _lx[2];
rx[0] = _rx[0];
rx[1] = _rx[1];
rx[2] = _rx[2];
long long best = 0;
// MAXL 循环展开(0..15)
{
int rt = root[0];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[1];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[2];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[3];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[4];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[5];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[6];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[7];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[8];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[9];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[10];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[11];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[12];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[13];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[14];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
{
int rt = root[15];
if (rt)
{
if (tree[rt].mx > best)
{
Node &t = tree[rt];
if (!(t.R[0] < lx[0] || rx[0] < t.L[0] || t.R[1] < lx[1] || rx[1] < t.L[1] || t.R[2] < lx[2] || rx[2] < t.L[2]))
luminescent(rt, best);
}
}
}
return best;
}
struct Point
{
int x, y, z, w, cost;
} pnt[N];
static bool cmp(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
if (a.x != b.x)
return a.x < b.x;
if (a.y != b.y)
return a.y < b.y;
if (a.z != b.z)
return a.z < b.z;
return a.w < b.w;
}
static char buf[1000010];
static char *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
#define gc() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1000000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
static int read()
{
int x = 0, op = 1, c = gc();
while (c < 48)
{
if (c == '-')
op = -1;
c = gc();
}
while (c > 47)
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
c = gc();
}
return x * op;
}
int main()
{
m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
pnt[i].x = read(), pnt[i].y = read(), pnt[i].z = read(),
pnt[i].w = read(), pnt[i].cost = read();
sort(pnt + 1, pnt + m + 1, cmp);
long long ans = LLONG_MIN;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
int x3[3] = {pnt[i].y, pnt[i].z, pnt[i].w};
int lo[3] = {INT_MIN, INT_MIN, INT_MIN};
long long best = qry(lo, x3) + pnt[i].cost;
if (best > ans)
ans = best;
ins(x3, best);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
P4848 崂山白花蛇草水
问题可以转化为矩形查询第 \(k\) 大值,矩形加。
看到查询第 \(k\) 大值容易想到用动态开点值域线段树维护,但是问题是在一个平面上的,也就是说普通的动态开点值域线段树已经无法维护。
因此容易想到树套树,即在动态开点值域线段树的每个结点上,都维护一个 K-D Tree。具体而言:
- 矩形加是简单的。
- 矩形查第 \(k\) 大可以在动态开点值域线段树上二分,对于当前值域线段树上的点 \(u\),若其右儿子 \(r\) 对应的 K-D Tree 上当前矩形有 \(k\) 个点,那么就递归右子树,否则就递归左子树。
外层的动态开点值域线段树时间复杂度为 \(O(\log V)\),内侧的 K-D Tree 时间复杂度为 \(O(n^{\frac12})\),因此总时间复杂度为 \(O(n^{\frac32}\log V)\)。
下面这份代码曾经可以通过,找个时间再来卡常()
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, q;
const int N = 500010;
// const int N = 5010;
namespace KDT
{
struct Node
{
int L[2], R[2], x[2], l, r;
int val, sum;
// Node()
// {
// memset(L, 0, sizeof L);
// memset(R, 0, sizeof R);
// memset(x, 0, sizeof x);
// l = r = val = sum = 0;
// }
} tree[N * 4 * 20];
void pushup(int rt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
tree[rt].sum = tree[tree[rt].l].sum + 1 + tree[tree[rt].r].sum;
}
int idx = 0, top = 0, dest[N * 4 * 20];
void push_cache(int &root)
{
if (!root)
return;
dest[++top] = root;
push_cache(tree[root].l);
push_cache(tree[root].r);
root = 0;
}
int build(int l, int r, int op = 0)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{
return tree[l].x[op] < tree[r].x[op];
});
int x = dest[mid];
if (l < mid)
tree[x].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[x].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(x);
return x;
}
void loyalty(int *root, int x, int y)
{
++idx;
// cout << "idx = " << idx << '\n';
tree[idx].x[0] = x;
tree[idx].x[1] = y;
assert(x > 0 && y > 0);
dest[top = 1] = idx;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, top, 0);
// cout << "BUILD! " << i << ' ' << root[i] << '\n';
return;
}
push_cache(root[i]);
assert(i != 19);
}
}
int luminescent(int root, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
const int x[] = {x1, y1}, y[] = {x2, y2};
int ok = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (x[i] <= tree[root].L[i] && tree[root].R[i] <= y[i])
;
else
{
ok = 1;
break;
}
if (!ok)
return tree[root].sum;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (tree[root].R[i] < x[i] || y[i] < tree[root].L[i])
{
// cout << i << ")) " << x[i] << ' ' << y[i] << ' ' << tree[root].x[i] << ' ' << tree[root].x[i] << '\n';
return 0;
}
ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
if (!(x[i] <= tree[root].x[i] && tree[root].x[i] <= y[i]))
{
ok = 0;
break;
}
return luminescent(tree[root].l, x1, y1, x2, y2) + luminescent(tree[root].r, x1, y1, x2, y2) + ok;
}
}
namespace SegmentTree
{
int idx = 1;
struct Node
{
int l, r, root[20];
// Node()
// {
// l = r = 0;
// memset(root, 0, sizeof root);
// }
// void init(int p)
// {
// l = r = p;
// memset(root, 0, sizeof root);
// }
} tree[N << 5];
void loyalty(int l, int r, int rt, int x, int y, int val)
{
// if (l > 5e7) throw;
KDT::loyalty(tree[rt].root, x, y);
if (l == r)
return;
// cout << "Mod " << tree[rt].root[0] << ' ' << x << ' ' << y << ' ' << val << '\n';
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (val <= mid)
{
if (!tree[rt].l)
tree[rt].l = ++idx;
loyalty(l, mid, tree[rt].l, x, y, val);
}
else
{
if (!tree[rt].r)
tree[rt].r = ++idx;
loyalty(mid + 1, r, tree[rt].r, x, y, val);
}
}
int luminescent(int l, int r, int rt, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int k)
{
// cout << "luminescent: " << l << ' ' << r << ' ' << rt << ' ' << tree[rt].root[0] << '\n';
if (!rt)
return 0;
if (l == r)
{
int s = 0;
// cout << "aucadsf\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
// cout << "mpadfad " << i << ": " << tree[rt].root[i] << '\n';
// if (tree[rt].root[i])
// cout << "wa " << tree[rt].root[i] << ' ' << KDT::tree[1].sum << ' ' << KDT::tree[1].x[0] << ' ' << KDT::tree[1].x[1] << ' ' << KDT::tree[2].x[0] << ' ' << KDT::tree[2].x[1] << ' ' << KDT::tree[3].x[0] << ' ' << KDT::tree[3].x[1] << ' ' << KDT::tree[4].x[0] << ' ' << KDT::tree[4].x[1] << '\n';
s += KDT::luminescent(tree[rt].root[i], x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
if (s >= k)
return l;
return 0;
// return l;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1, s = 0;
if (tree[rt].r)
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
// cout << "njb: " << i << ' ' << tree[rt].r << ' ' << tree[tree[rt].r].root[i] << '\n';
s += KDT::luminescent(tree[tree[rt].r].root[i], x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
// assert(!s);
// cout << "yueqr " << l << ' ' << r << ' ' << rt << ' ' << s << ' ' << k << '\n';
if (s >= k)
return luminescent(mid + 1, r, tree[rt].r, x1, y1, x2, y2, k);
return luminescent(l, mid, tree[rt].l, x1, y1, x2, y2, k - s);
}
}
signed main()
{
// freopen("niji", "w", stdout);
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> q;
int la = 0;
while (q--)
{
int o;
cin >> o;
if (o == 1)
{
int x, y, v;
cin >> x >> y >> v;
x ^= la, y ^= la, v ^= la;
SegmentTree::loyalty(1, 1e9, 1, x, y, v);
}
else
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2, k;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> k;
x1 ^= la, y1 ^= la, x2 ^= la, y2 ^= la, k ^= la;
int res = SegmentTree::luminescent(1, 1e9, 1, x1, y1, x2, y2, k);
cout << ((la = res) ? to_string(res) : "NAIVE!ORZzyz.") << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
P5471 [NOI2019] 弹跳
题意比较复杂,这里 copy 出一个简要题意:
给出二维平面上的 \(n\) 个整点 \((x_i,y_i)\),满足 \(1\le x_i\le w,1\le y_i\le h\)。按给出顺序编号为 \(1,2,\ldots,n\)。有 \(m\) 次连边操作,每次操作给定 \(p,t,L,R,D,U\),从结点 \(p\) 到满足条件 \(L\le x_i\le R,D\le y_i\le U\) 的所有这样的结点 \(i\) 连接一条边权为 \(t\) 的有向边。求在所有连边操作结束后,从编号为 \(1\) 的点到其他点的最短路长度。
Data Range: \(1\le w,h\le n\le 70000,1\le m\le 150000,1\le t_i\le 10000\)
题解:
先考虑一维的情况,此时连边操作形如让一个点 \(p\) 向一段区间 \([l,r]\) 连边,容易发现这就是【模板】线段树优化建图。
扩展到二维,容易想到用 K-D Tree 来优化建图。具体的:
- 建立由这 \(n\) 个点组成的 K-D Tree,该树上有 \(n\) 个结点,令这些点对应过来的编号为 \(n+1,n+2,\ldots,2n\) 号。
- 对于一个点 \(p\) 向一个平面内所有点连边的情况,考虑直接遍历整棵 K-D Tree,对于当前所遍历到的结点 \(u\) 而言:
- 若 \(u\) 点子树对应的平面和查询的平面无交,那么不再递归,直接返回。
- 若 \(u\) 点子树对应的平面是查询平面的子集,那么直接从 \(p\) 点向 \(u+n\) 点连一条边权为 \(t\) 的有向边即可。
- 对于其余情况,特判掉 \(u\) 点自身所对应的坐标在查询平面内的情况,然后直接向左右子树暴力递归即可。
- 最后对于每个 \(i=1\ldots n\),由 \(i+n\) 点向 \(i\) 点连一条边权为 \(0\) 的有向边即可。
由 K-D Tree 的时间复杂度证明可知,这种方式建图会连 \(O(m\sqrt n)\) 条边。因为 \(n\le 70000\),所以该建边方法是可行的。此时如果直接显式建图,大约需要建 \(4\times 10^7\) 条边,会爆内存。将上述做法改为隐式建图即可通过。
注:spfa 被卡了。
P12065 [THOI 2012] 森林旅店
邻域查询板子题,把前面的 P2093 和 P4148 合起来就可以过。
// #pragma GCC optimize(3, "Ofast", "inline", "unroll-loops")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
using ld = long double;
const int N = 1000010;
int n, m, K;
int idx, cnt, dest[N], root[N], lx[2], rx[2];
struct Node
{
int x[2];
int L[2], R[2];
int l, r;
} tree[N];
struct Point
{
int x[2], id;
} a[N];
void pushup(int rt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = tree[rt].R[i] = tree[rt].x[i];
if (tree[rt].l)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].l].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].l].R[i]);
}
if (tree[rt].r)
{
tree[rt].L[i] = min(tree[rt].L[i], tree[tree[rt].r].L[i]);
tree[rt].R[i] = max(tree[rt].R[i], tree[tree[rt].r].R[i]);
}
}
}
int build(int l, int r, int op)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(dest + l, dest + mid, dest + r + 1, [&](auto &l, auto &r)
{ return tree[l].x[op] < tree[r].x[op]; });
if (l < mid)
tree[dest[mid]].l = build(l, mid - 1, op ^ 1);
if (mid < r)
tree[dest[mid]].r = build(mid + 1, r, op ^ 1);
pushup(dest[mid]);
return dest[mid];
}
int mx, mi;
priority_queue<pair<ld, int>> q;
inline ld sq(int x)
{
return x * x;
}
inline ld cb(int x)
{
return 1. * x * x * x;
}
// inline int expmin(int o, int id)
// {
// if (!o)
// return 1e18;
// return max(0ll, tree[id].x[0] - tree[o].R[0]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[0] - tree[id].x[0]) + max(0ll, tree[id].x[1] - tree[o].R[1]) + max(0ll, tree[o].L[1] - tree[id].x[1]);
// }
inline ld dist(int x, int y)
{
if (K == 2)
return sqrt(sq(tree[x].x[0] - tree[y].x[0]) + sq(tree[x].x[1] - tree[y].x[1]));
else if (K == 3)
return cbrt(cb(tree[x].x[0] - tree[y].x[0]) + cb(tree[x].x[1] - tree[y].x[1]));
return abs(tree[x].x[0] - tree[y].x[0]) + abs(tree[x].x[1] - tree[y].x[1]);
}
inline ld dist(int x, int yx, int yy)
{
if (K == 2)
return sqrt(sq(tree[x].x[0] - yx) + sq(tree[x].x[1] - yy));
else if (K == 3)
return cbrt(cb(tree[x].x[0] - yx) + cb(tree[x].x[1] - yy));
return abs(tree[x].x[0] - yx) + abs(tree[x].x[1] - yy);
}
inline ld expmin(int u, int yx, int yy)
{
ld dx = 0, dy = 0;
if (yx < tree[u].L[0])
dx = (ld)(tree[u].L[0] - yx);
else if (yx > tree[u].R[0])
dx = (ld)(yx - tree[u].R[0]);
if (yy < tree[u].L[1])
dy = (ld)(tree[u].L[1] - yy);
else if (yy > tree[u].R[1])
dy = (ld)(yy - tree[u].R[1]);
if (K == 1)
return dx + dy;
if (K == 2)
return sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
return cbrt(dx * dx * dx + dy * dy * dy);
}
int px, py, k, x, y, id;
void dfsmin(int rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (q.size() == k && q.top().first <= expmin(rt, x, y))
return;
// cerr << "nmsl\n";
auto oo = q.top();
if (oo > make_pair(dist(rt, x, y), -a[rt].id))
q.pop(), q.emplace(dist(rt, x, y), -a[rt].id);
int d1 = expmin(tree[rt].l, x, y), d2 = expmin(tree[rt].r, x, y);
if (d1 > d2)
{
if (tree[rt].l && d1 <= q.top().first)
dfsmin(tree[rt].l);
if (tree[rt].r && d2 <= q.top().first)
dfsmin(tree[rt].r);
}
else
{
if (tree[rt].r && d2 <= q.top().first)
dfsmin(tree[rt].r);
if (tree[rt].l && d1 <= q.top().first)
dfsmin(tree[rt].l);
}
}
inline void push_cache(int &rt)
{
if (!rt)
return;
if (tree[rt].l)
push_cache(tree[rt].l);
dest[++cnt] = rt;
if (tree[rt].r)
push_cache(tree[rt].r);
rt = 0;
}
const int inf = 1e18;
// pair{first, second}: dist ;; id
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
cout << fixed << setprecision(4);
cin >> n >> m >> K >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cnt = 0;
++idx;
tree[idx].x[0] = x;
tree[idx].x[1] = y;
dest[++cnt] = idx;
for (int i = 0;; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
int res = 1e18;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
while (q.size())
q.pop();
char o;
cin >> o;
if (o == 'Q')
{
cin >> px >> py;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
q.emplace(inf, inf);
x = px, y = py, id = k;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
if (root[i])
dfsmin(root[i]);
vector<ld> v;
while (q.size())
v.emplace_back(q.top().first), q.pop();
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (ld &x : v)
cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
else
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cnt = 0;
++idx;
tree[idx].x[0] = x;
tree[idx].x[1] = y;
dest[++cnt] = idx;
for (int i = 0;; ++i)
if (!root[i])
{
root[i] = build(1, cnt, 0);
break;
}
else
push_cache(root[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号