第一次Blog
-
前言
第一次题目集是对类的设计,类与对象的使用和类与数组关联类的考察。第二次题目集是类与对象之间的创建以及运用的考察。第三次题目集是对类的封装性以及Java自带时间包的运用的考察。总而言之,三次题目集的题目量并不算大,题目集的难度也是比较中等。 -
设计与分析
![]()
这是答题判题程序-1中相应类的设计。
Text是题目类,它包含题号(num)、问题(que)、标准答案(standardAnswer),判断题目是否正确的match()方法和每个私有属性的getter()和setter()方法。
Paper是试卷类,它包含组成试卷的每道题目的数组(textList)、试卷的题目数量(sum),添加试卷题目的add()方法、判断某道题目是否正确的match()方法以及sum属性的getter()方法和textList的getter()和setter()方法。
Answer是答卷类,它包含答卷对应的试卷(paper)、答案数组(answerList)、每道题是否正确的判题数组(matchList),获得答案数组和判题数组的list()方法和按要求输出答卷信息的output()方法。
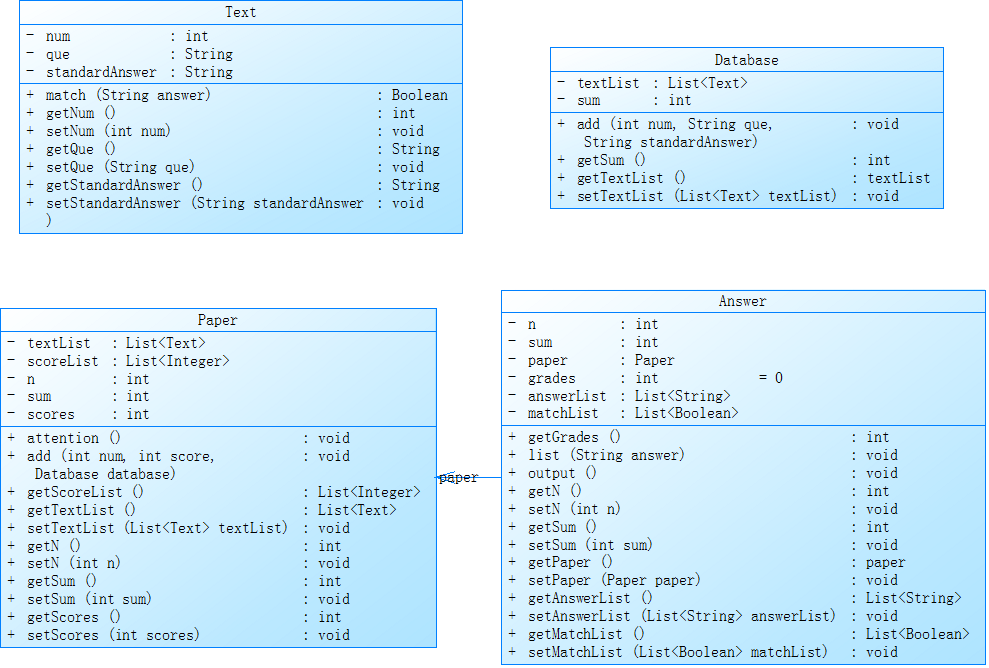
这是答题判题程序-2中相应类的设计。
Text类与第一次Text类的设计是一样的。
新加了一个Database的题库类,用来存储所有的题目。它包含题目数组(textList)、所有的题目数量(sum)。添加题目信息的add()方法、sum属性的getter()方法和textList的getter()和setter()方法。
Paper的试卷类在原有的基础上加入了每道题目的分数所组成的数组(scoreList)、试卷号(n)、总题目数(sum)、试卷的总分值(scoers)。方法中新加入了警示试卷满分不是100分的attention()方法以及新加入属性的getter()和setter()方法,删除了判断某道题目是否正确的match()方法。
Answer的答卷类在原有的基础上加入了答卷对应的试卷号(n)、答案的总数(sum)、整张试卷获得的分数(grades)。方法中加入了获得整张试卷分数的getGrades()方法以及新加入属性的getter()和setter()方法。

这是答题判题程序-3中相应类的设计。
Text类、Database类与Paper类没有变化。
新加入的Student类用来存放学生信息,它包含学生学号(del)、学生姓名(name)。学生学号和姓名的getter()和setter()方法。
Answer的答卷类在原有的基础上加入了答答卷的学生的学号(del)、姓名(mane)、以及最后输出答卷信息的每行结果的数组(resultList)。answerlist()方法是用来获得试卷的答案数组、list()方法则是用来获得判题数组和结果数组、gsetGrades()方法使用来获得整张答卷学生获得的总分。其他方法都是某些基本属性的getter()和setter()方法在答题判题程序-2的基础上删除了一些属性没有必要使用getter()和setter()方法的情况。
- 踩坑心得
基本上将类的设计做好、将类的功能实现,大部分的测试点都能通过,最后调整一下正则表达式就可以了。
在提交的答题判题程序-1中我获取题目的正则表达式是
#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*#Q:(.*?)\\s*#A:(\\S+)
而获取答案的正则表达式是
#A:(\\S+)
很明显我没有考虑到标准答案与回答的答案之间可能存在空格的情况。所以我将获取题目的正则表达式改为了
#N:\\s*(\\d+)\\s*#Q:(.*?) #A:(.+)
用.+的贪婪匹配方法获取标准答案的信息再用trim()方法删除字符串首尾的空格。
而获取答案的正则表达式改为#A:(.+)或#A:(.*?)都是不行的,前者是贪婪匹配当匹配#A:2 #A:4时(.+)会成功匹配2 #A:4;而后者是非贪婪匹配,它会与空字符成功匹配。
这个时候我们考虑可以用?=来进一步限定字符串所以我将获取答案的正则表达式改为了#A:(.*?)(?=#A:|$)用非贪婪匹配的方式当匹配到字符串最后现#A:或$才算匹配成功。
在答题判题程序-2中的测试点相对没有第一次的严格,所有在提交时我用#N:(\\d+) #Q:(.*?) #A:(\\S+)也成功的通过了测试点。
答题判题程序-3相比于答题判题程序-2并没有增加很多类,但是增加了许多报错提醒。因为可能有格式上的输入错误所以在正则表达式的前面要加上^、末尾要加上$,防止中间匹配成功而前后加上了错误格式的模式。其次,学生的信息之间是以-结尾的所以正则表达式中要用^#X:(\\w+ [^\\s-]+)?(-\\w+ [^\\s-]+)*$来读取学生学号和姓名。最后,答卷上可能出现空白卷和答案是空字符的情况,所以正则表达式要用^#S:(\\d+) (\\S*)( #A:\\d+-(.+))*,用*来实现可能存在的空白卷和答案是空字符的情况。
对于答题判题程序-3中增加很多报错信息的提示,同时报错信息的提示之间还有优先级,只要一不注意就会出问题。
所以我在main方法中首先判断答卷对应的试卷号是否存在,
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#S:(\\d+) (\\S*)( #A:\\d+-(.+))*");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Answer answer=new Answer(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)),mat.group(2).trim());
for(Paper j:paperList)
{
if(j.getN()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
answer.setPaper(j);
break;
}
}
if(answer.getPaper()==null)
{
text.add("The test paper number does not exist");
list.remove(i);
continue;
}
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("#A:(\\d+)-(.*?)(?=#A:|$)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
answer.answerlist(Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1)),mat1.group(2).trim());
}
answerList.add(answer);
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
然后我再在Answer类的list()方法中判断是否有该题目以及答案是否存在
public void list()
{
for(int i=0;i<paper.getSum();i++)
{
if(answerList.get(i+1)!=null)
{
if(paper.getTextList().get(i).getQue()!=null)
{
if(paper.getTextList().get(i).getQue().equals("non-existent question"))
{
matchList.add(false);
resultList.add("non-existent question~0");
}
else
{
matchList.add(paper.getTextList().get(i).match(answerList.get(i+1)));
resultList.add(paper.getTextList().get(i).getQue()+"~"+answerList.get(i+1)+"~"+paper.getTextList().get(i).match(answerList.get(i+1)));
}
}
else
{
matchList.add(false);
resultList.add("the question "+paper.getTextList().get(i).getNum()+" invalid~0");
}
}
else
{
resultList.add("answer is null");
matchList.add(false);
}
}
}
最后,再在Answer类的output()方法中判断学号对应的学生是否存在
public void output(ArrayList<Student> studentlist)
{
list();
getName(studentlist);
for(String i:resultList)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
if(this.name!=null)
{
System.out.print(del+" "+name+":");
for(int i=0;i<matchList.size();i++)
{
if(matchList.get(i))
System.out.print(" "+paper.getScoreList().get(i));
else
System.out.print(" 0");
}
System.out.println("~"+gsetGrades());
}
else
System.out.println(del+" not found");
}
虽然最后通过了测试点,但过程思路较为混乱,仍然具有很多可以改进的地方。
- 改进建议
1)对于大部分类的属性我都在eclipse中直接生成了它的getter()和setter()方法,而实际情况中有些属性是不需要的,应该根据实际情况来设计属性的方法。
2)对于答题判题程序-3中对题目的删除我是直接将题目的问题和标准答案赋为了null
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#D:N-(\\d+)$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
for(Text j:database.getTextList())
{
if(j.getNum()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
j.setQue(null);
j.setStandardAnswer(null);
}
}
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
但我觉得可以在Text类中加入一个boolean类型的数来判断这道题目是否有被删除,这样可以方便对以后题目的再次使用以及对题目的修改有较大帮助。
3)随着读取信息的增多,main方法中for循环的使用也越来越频繁
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#N:(\\d+) #Q:(.+) #A:(.+)");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
database.add(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1).trim()),mat.group(2).trim(),mat.group(3).trim());
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#D:N-(\\d+)$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
for(Text j:database.getTextList())
{
if(j.getNum()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
j.setQue(null);
j.setStandardAnswer(null);
}
}
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#T:(\\d+)( \\d+-\\d+)*$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Paper paper=new Paper(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)));
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("(\\d+)-(\\d+)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
paper.add(Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1)),Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(2)),database);
}
paperList.add(paper);
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#X:(\\w+ [^\\s-]+)?(-\\w+ [^\\s-]+)*$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("(\\w+) ([^\\s-]+)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
Student student=new Student();
student.setStu(mat1.group(1).trim(),mat1.group(2));
stulist.add(student);
}
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#S:(\\d+) (\\S*)( #A:\\d+-(.+))*");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Answer answer=new Answer(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)),mat.group(2).trim());
for(Paper j:paperList)
{
if(j.getN()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
answer.setPaper(j);
break;
}
}
if(answer.getPaper()==null)
{
text.add("The test paper number does not exist");
list.remove(i);
continue;
}
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("#A:(\\d+)-(.*?)(?=#A:|$)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
answer.answerlist(Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1)),mat1.group(2).trim());
}
answerList.add(answer);
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
其实,以上for循环的内容都大差不差,可以尝试着用一个方法来完成功能,减少main方法中的圈复杂度,使代码更加简洁。
4)在有些类的方法中,我使用了大量的循环以及if else来实现功能
public void output()
{
for(int i=this.sum;i<paper.getSum();i++)
{
matchList.add(false);
}
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++)
{
System.out.println(paper.getTextList().get(i).getQue()+"~"+answerList.get(i)+"~"+matchList.get(i));
}
for(int i=0;i<(paper.getSum()-this.sum);i++)
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
for(int i=0;i<paper.getSum()-1;i++)
{
if(matchList.get(i))
System.out.print(paper.getScoreList().get(i)+" ");
else
System.out.print("0 ");
}
if(matchList.get(paper.getSum()-1))
System.out.print(paper.getScoreList().get(paper.getSum()-1)+"~");
else
System.out.print("0~");
System.out.println(gsetGrades());
}
其实可以尝试着简化方法的内容和步骤,使得代码更加简洁。
5)对于答题判题程序-3中提示错误输入,我是将所以的正确代码都读取完之后再remove掉,那么剩下的代码就都是格式错误的代码
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#N:(\\d+) #Q:(.+) #A:(.+)");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
database.add(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1).trim()),mat.group(2).trim(),mat.group(3).trim());
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#D:N-(\\d+)$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
for(Text j:database.getTextList())
{
if(j.getNum()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
j.setQue(null);
j.setStandardAnswer(null);
}
}
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#T:(\\d+)( \\d+-\\d+)*$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Paper paper=new Paper(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)));
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("(\\d+)-(\\d+)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
paper.add(Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1)),Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(2)),database);
}
paperList.add(paper);
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#X:(\\w+ [^\\s-]+)?(-\\w+ [^\\s-]+)*$");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("(\\w+) ([^\\s-]+)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
Student student=new Student();
student.setStu(mat1.group(1).trim(),mat1.group(2));
stulist.add(student);
}
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
for(int i=0;i<list.size();)
{
Pattern pat=Pattern.compile("^#S:(\\d+) (\\S*)( #A:\\d+-(.+))*");
Matcher mat=pat.matcher(list.get(i));
if(mat.find())
{
Answer answer=new Answer(Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)),mat.group(2).trim());
for(Paper j:paperList)
{
if(j.getN()==Integer.parseInt(mat.group(1)))
{
answer.setPaper(j);
break;
}
}
if(answer.getPaper()==null)
{
text.add("The test paper number does not exist");
list.remove(i);
continue;
}
Pattern pat1=Pattern.compile("#A:(\\d+)-(.*?)(?=#A:|$)");
Matcher mat1=pat1.matcher(list.get(i));
while(mat1.find())
{
answer.answerlist(Integer.parseInt(mat1.group(1)),mat1.group(2).trim());
}
answerList.add(answer);
list.remove(i);
}
else
i++;
}
其实,以上for循环的内容都大差不差,可以尝试着用一个方法来完成功能,减少main方法中的圈复杂度,使代码更加简洁。
4)在有些类的方法中,我使用了大量的循环以及if else来实现功能
public void output()
{
for(int i=this.sum;i<paper.getSum();i++)
{
matchList.add(false);
}
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++)
{
System.out.println(paper.getTextList().get(i).getQue()+"~"+answerList.get(i)+"~"+matchList.get(i));
}
for(int i=0;i<(paper.getSum()-this.sum);i++)
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
for(int i=0;i<paper.getSum()-1;i++)
{
if(matchList.get(i))
System.out.print(paper.getScoreList().get(i)+" ");
else
System.out.print("0 ");
}
if(matchList.get(paper.getSum()-1))
System.out.print(paper.getScoreList().get(paper.getSum()-1)+"~");
else
System.out.print("0~");
System.out.println(gsetGrades());
}
其实可以尝试在最开始就判断格式输入是否正确,这样就省去了后面代码多次用if else判断格式是否正确,是否需要remove掉。
- 总结
三次题目集的难度其实并不大,只是随着类的增加,类的功能、类与类之间的关系变得越来越复杂,容易让人产生思维紊乱。经过三次题目集的训练,受益最多的就是我对于正则表达式的运用,对于正则表达式的好处也越来越深刻。当然,对于类的属性和方法的设计还需要进一步的学习和改进,使得设计更加合理。其次,对于Java自带的日期包的学习和运用还是不是很深刻,还需要进一步的学习和研究。最后,值得一提的就是和同伴们一起讨论,总有些自己过不去的测试点思考了很久还是没有思路,当时经过与同伴们的谈论有时真的能很快找到问题所在,也希望以后能有更多机会能够和同伴们一起讨论学习。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号