黑马云盘综合案例
黑马云盘综合案例
学习目标
一 需求说明

实现一个乞丐版云盘。
云盘项目包含客户端和服务端,通过客户端可以查看网盘内容,可以下载网盘中的文件,上传文件到网盘中
二 概要设计
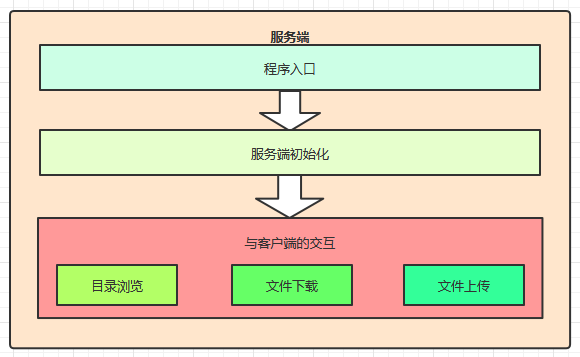
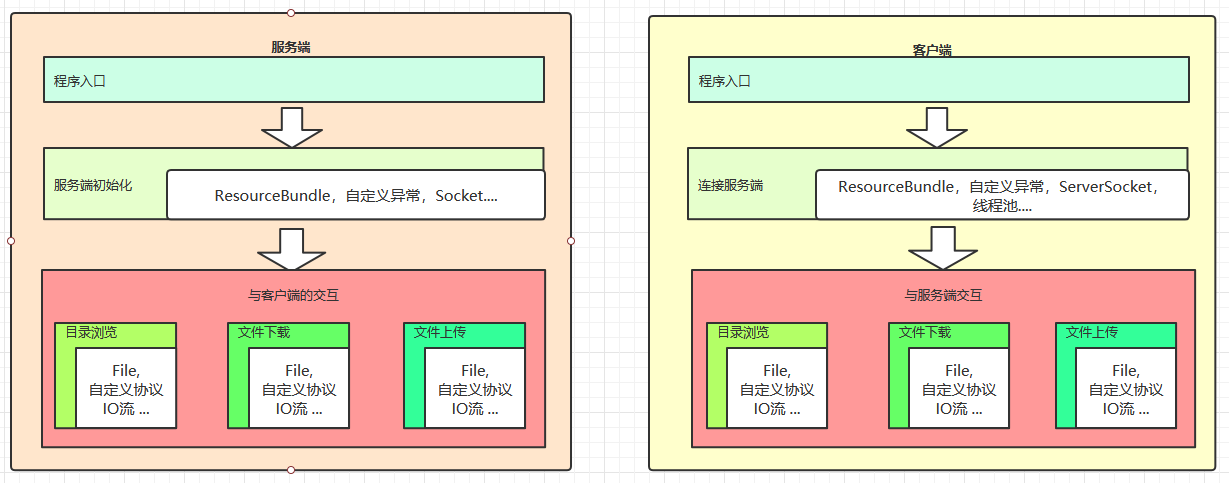
2.1 服务端实现
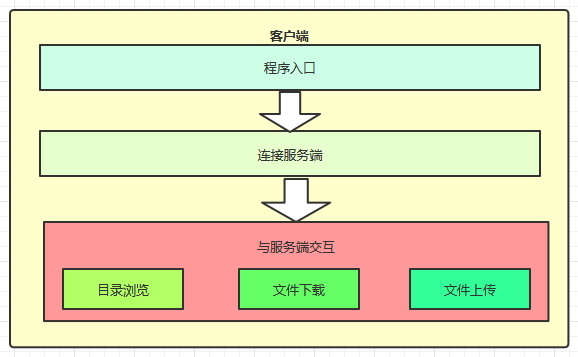
2.2 客户端实现
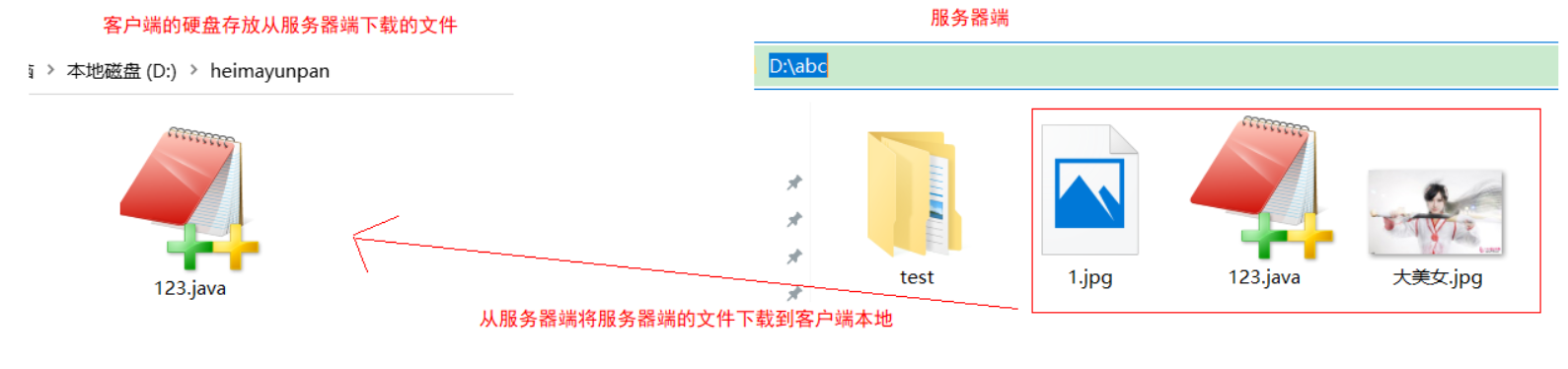
下载:
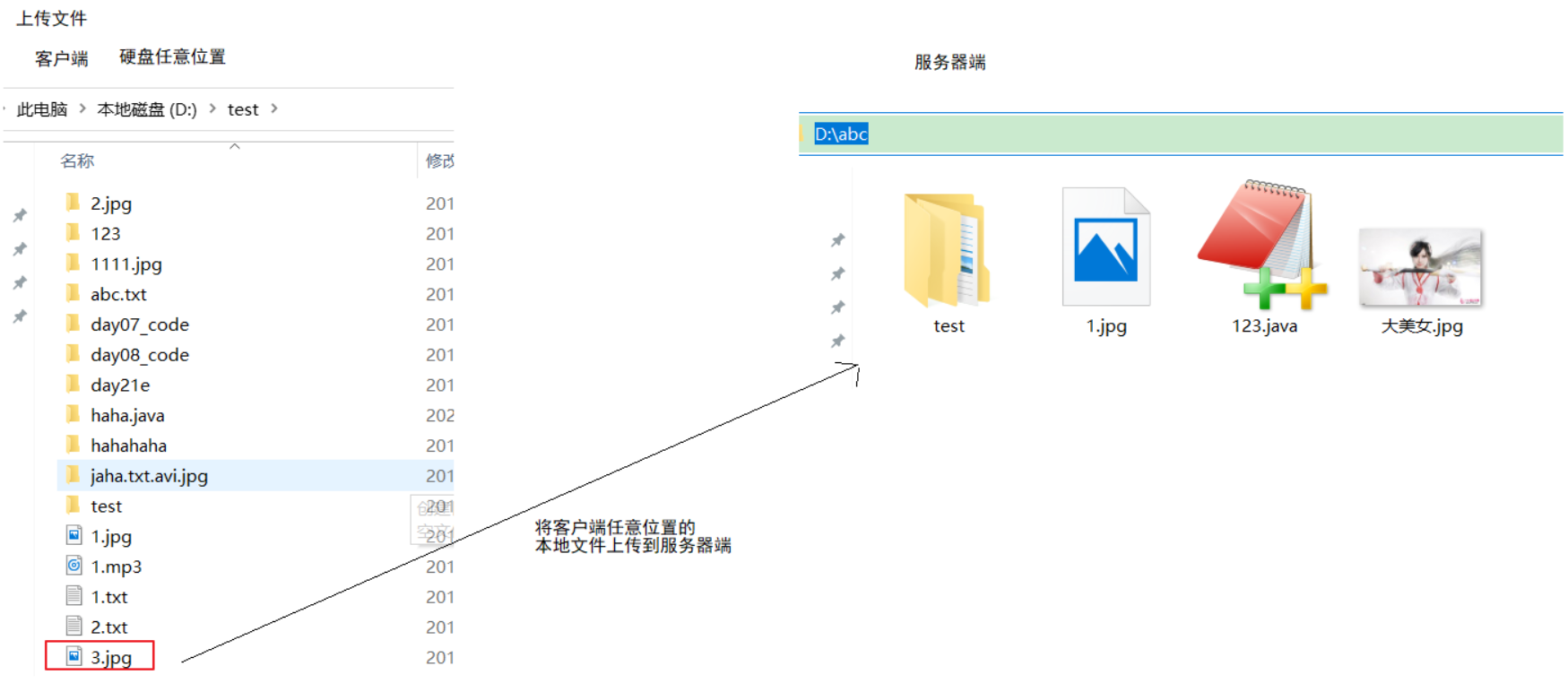
上传:
三 详细设计
3.1 技术选型
- 使用TCP编程技术实现客户端(Socket)和服务端(ServerSocket)的开发,完成文件上传的功能
- 自定义客户端和服务端之间的通讯协议
- 服务端多线程技术,实现高并发访问
- 自定义异常维护业务安全
- 使用JDK现有的API完成相关业务
- Socket,ServerSocket网络编程
- File文件类
- IO流相关类
- ResourceBundle配置文件读取
3.2 协议定义
协议介绍
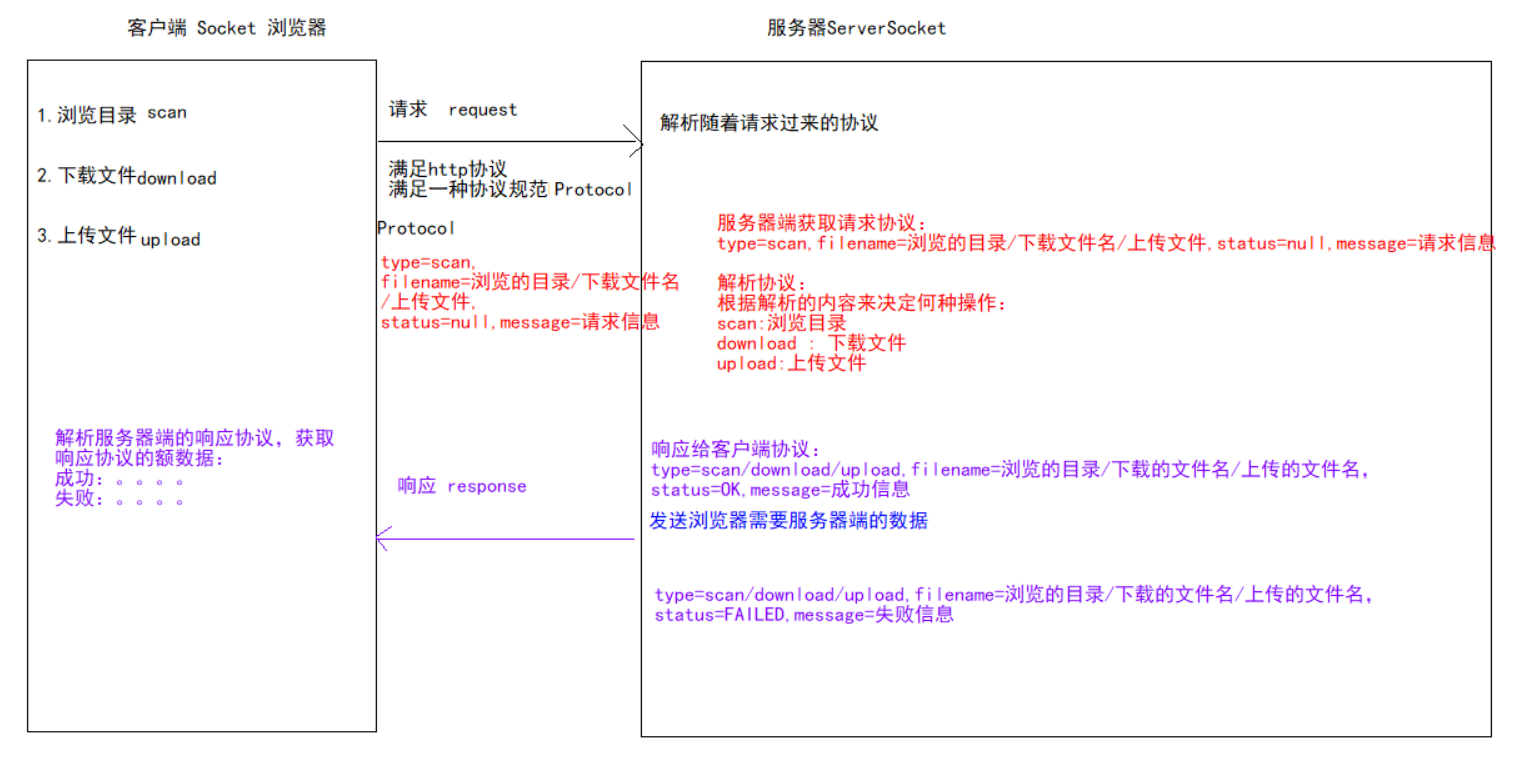
协议就是通讯双方共同遵守的规定。
TCP协议是区分客户端服务端的一个比较底层的协议,传输的数据是字节码数据,如下
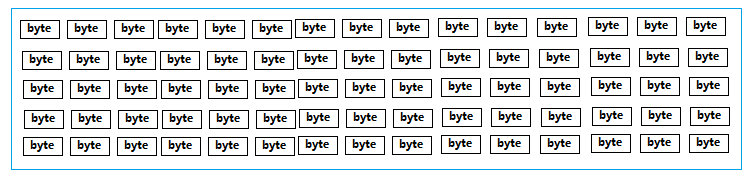
当客户端连接服务端后,若要上传一个文件到服务端。直接将文件数据传给服务端,那么服务端该如何识别这个数据呢。对于服务端来讲收到的都是字节数据,服务端该如何识别客户端的操作意图,如果是上传文件,那么文件的类型是什么,文件的名字是什么等等信息。
怎样让双方在沟通时理解对方的信息呢?
我们可以把要发送给对方的数据前加一行描述信息,我们可以称为头信息。这个头信息包含了我要干什么,我的数据有哪些属性等信息,发头信息后再把具体的数据发送给对方。这样对方先把头信息获取,知道了我要做什么操作,发送过来的数据是是什么有什么数据,再接收具体的数据,就搞定了。
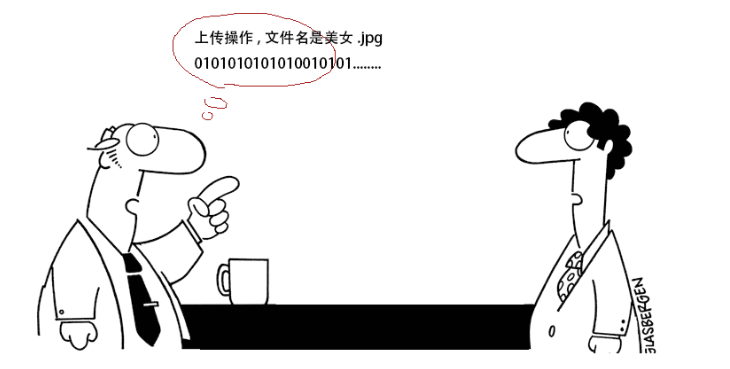
加了头信息的数据如下:
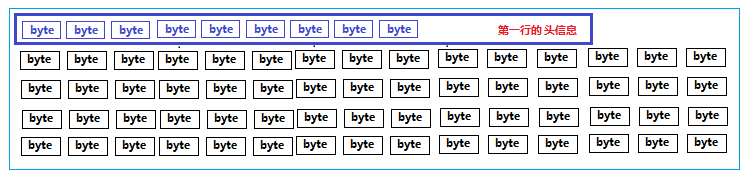
自定义协议
我们约定双方发送数据前要先发送一个头信息,如下
type=操作类型,fileName=文件名,status=操作状态,message=说明信息\r\n
说明:第一行头信息要和数据分开,用行分隔符分开即可,每个信息使用 key=value键值对表示,每个信息使用逗号分隔
-
type:操作类型,对应的值可以是如下:
scan:表示浏览目录操作 upload:表示上传操作 download:表示下载操作 下载操作示例: type=download -
fileName:要浏览操作文件的文件名
下载文件“美女.jpg”示例: type=download,fileName=美女.jpg -
status:操作状态
表示服务端收到客户端请求后回复操作状态,ok表示成功,failed表示失败 -
message:说明信息
其他附加说明信息
一次下载文件的示例:
客户端发送请求:
type=download,fileName=root/美女.jpg,status=null,message=null,\r\n
服务端响应:
-
成功
type=download,fileName=root/美女.jpg,status=ok,message=null,\r\n 01010101010010美女数据010100101001010 -
失败
type=download,fileName=root/美女.jpg,status=failed,message=null,\r\n
协议的封装
直接复制即可
为了方便协议的定义和解析,我们可以使用面向对象的思想进行封装成一个类,Protocol
package com.itheima.sh.bean;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 协议定义:
*/
public class Protocol {
//协议数据
private String type;//操作类型
private String fileName;//操作文件
private String status;//操作状态
private String message;//说明信息
/**
* 操作类型
*/
public static class Type {
public static final String SCAN = "scan";//浏览
public static final String UPLOAD = "upload";//上传
public static final String DOWNLOAD = "download";//下载
}
/**
* 操作状态
*/
public static class Status {
public static final String OK = "ok";//成功
public static final String FAILED = "failed";//失败
}
public Protocol() {
}
/**
* 获取浏览目录协议
*
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static Protocol getScanDirProtocol(String path) {
Protocol protocol = new Protocol();
protocol.setType(Type.SCAN);
protocol.setFileName(path);
return protocol;
}
/**
* 获取文件下载协议
*
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static Protocol getDownloadProtocol(String path) {
Protocol protocol = new Protocol();
protocol.setType(Type.DOWNLOAD);
protocol.setFileName(path);
return protocol;
}
/**
* 获取文件上传协议
*
* @param file
* @return
*/
public static Protocol getUploadProtocol(File file) {
Protocol protocol = new Protocol();
protocol.setType(Type.UPLOAD);
protocol.setFileName(file.getPath());
return protocol;
}
//type=下载 fileName=aa.txt status=OK
/**
* 解析协议
*
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static Protocol parseProtocol(String str) {
Map<String, String> proData = new HashMap<>();
String[] data = str.split(",");
for (String datum : data) {
String[] strs = datum.split("[=:]", 2);
proData.put(strs[0], strs[1]);
}
//通过反射进行数据填充
Protocol protocol = new Protocol();
Field[] declaredFields = protocol.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(protocol, proData.get(field.getName()));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return protocol;
}
public static Protocol parseProtocol(InputStream netIn) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(netIn);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String protocolStr = br.readLine();
Protocol protocol = parseProtocol(protocolStr);
return protocol;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
public void setFileName(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
Field[] fields = getClass().getDeclaredFields();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
sb.append(field.getName()).append("=").append(field.get(this)).append(",");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString() + "\r\n";
}
}
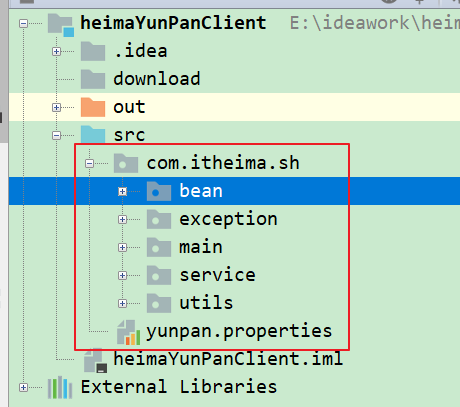
3.3 基础架构
服务端架构
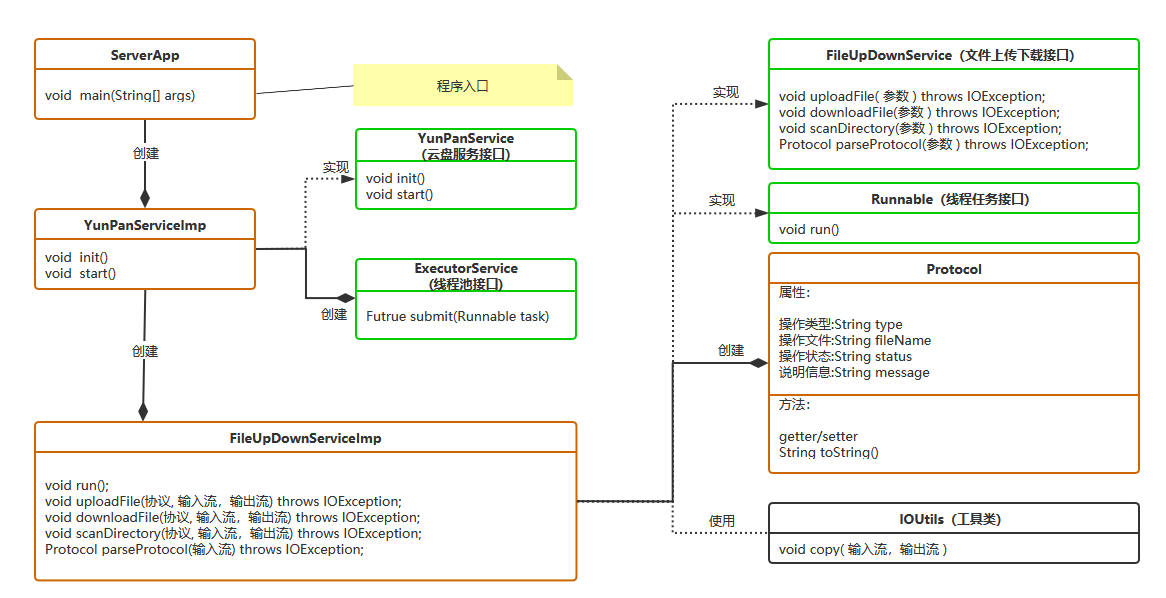
项目结构:
客户端架构
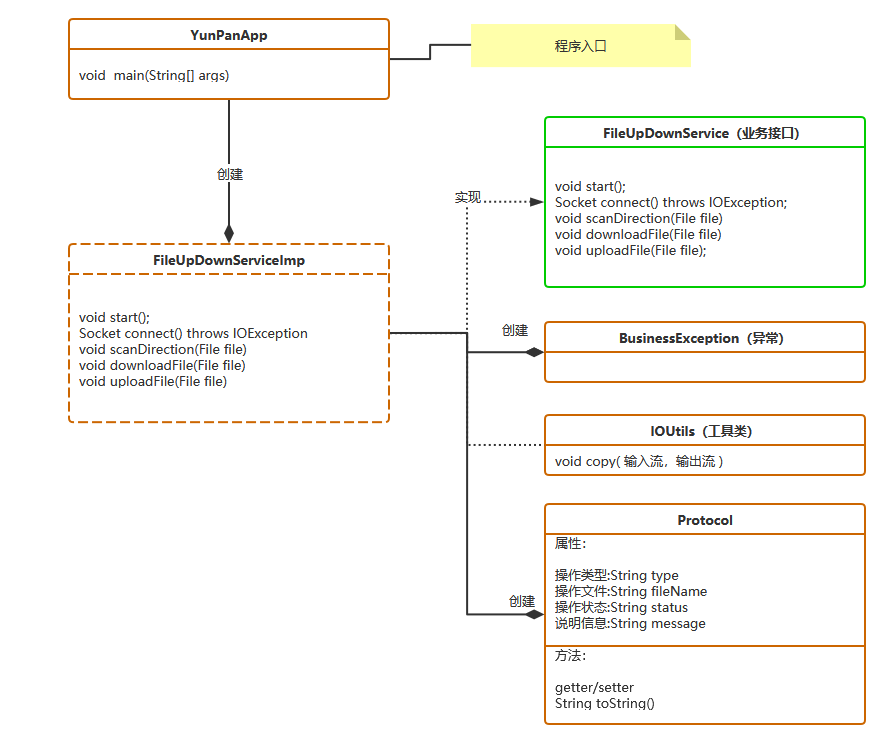
项目结构:
3.4 功能接口的定义
这里的接口,指定的是服务端暴露出来的功能。比如文件浏览功能,只要按照该接口指定的方式传输数据,就能完成功能了。
文件浏览(不用自己编写)
-
客户端与服务端的交互流程
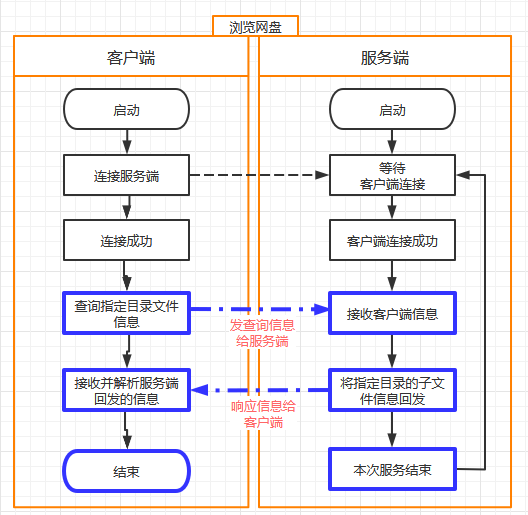
-
数据交互
请求:客户端 ---> 服务端
type=scan,fileName=需要浏览的目录,status=null,message=null\r\n响应: 服务端 --->客户端
-
成功:
type=scan,fileName=需要浏览的目录,status=ok,message=null, xxx目录或者文件名称xxxxxx xxx目录或者文件名称xxxxxx xxx目录或者文件名称xxxxxx -
失败:
type=scan,fileName=null,status=failed,message=目录不存在,只能浏览当前子目录, 没有后续数据失败的原因,就是服务端没有对应的目录,无法遍历。
【1】实现:客户端刚连接服务器端在客户端显示服务器端云盘信息
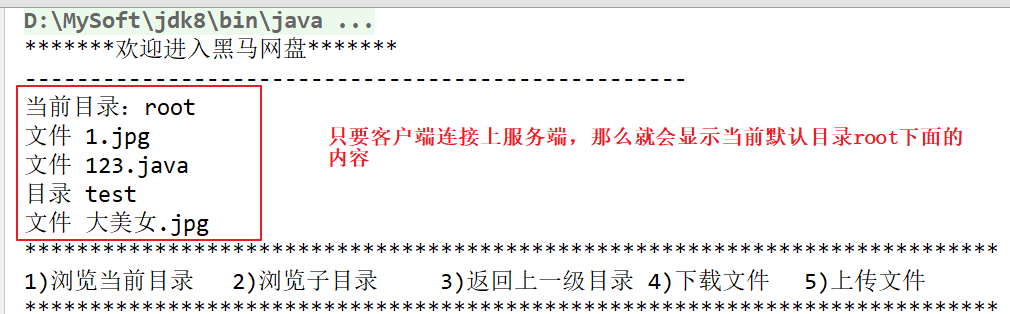
1.客户端
1)主方法入口
public class YunPanApp { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建业务对象 FileUpDownService service = new FileUpDownServiceImp(); //启动客户端的服务 service.start(); } }2)FileUpDownService业务接口:直接拷贝
public interface FileUpDownService { //启动方法 void start(); //连接方法 Socket connect() throws IOException; //浏览目录方法 void scanDirection(File file); //下载方法 void downloadFile(File file); //上传方法 void uploadFile(File file); }3)实现类FileUpDownServiceImp
public class FileUpDownServiceImp implements FileUpDownService { //创建File对象,默认当前路径是root public File current = new File("root"); //启动方法 @Override public void start() { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("*******欢迎进入黑马网盘*******"); //将默认的当前路径 public File current = new File("root"); 传递到scanDirection //浏览文件和文件夹 scanDirection(current); } /** * 文件浏览 * * @param path * @throws IOException */ @Override public void scanDirection(File path) {//public File current = new File("root"); //connect() 表示连接服务器的方法 try (Socket socket = connect(); //获取从通道读取数据的字节输入流 InputStream netIn = socket.getInputStream(); //获取向通道写数据的字节输出流 OutputStream netOut = socket.getOutputStream();) { //获取path对象表示的路径变为String String path1 = path.getPath(); //获取浏览目录协议 :type="scan",fileName="root",status=null,message=null Protocol scanDirProtocol = Protocol.getScanDirProtocol(path1); // send(netOut, scanDirProtocol); //调用toString方法将协议对象scanDirProtocol转换为字符串形式: // "type="scan",fileName="root",status=null,message=null\r\n" String protocolStr = scanDirProtocol.toString(); //System.out.println("客户端发送:" + protocolStr); //发送给服务端 netOut.write(protocolStr.getBytes()); //接收服务器响应的消息 //将关联通道的字节输入流转换为字符输入流 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(netIn); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); //System.out.println("开始接收数据:"); //读取响应协议 String firstLine = br.readLine();//协议 //使用协议工具类:解析协议,将接收的响应数据存储到Protocol类的成员变量中 Protocol protocol = Protocol.parseProtocol(firstLine); //System.err.print("pro:" + protocol); //判断响应是否成功 public static final String OK = "ok";//成功 if (protocol.getStatus().equals(Protocol.Status.OK)) { //成功 //获取当前路径 current = new File(protocol.getFileName()); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println("当前目录:" + current); String content; while ((content = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(content); } } else { System.out.println("浏览失败:" + protocol.getMessage()); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 连接服务端 * * @return * @throws IOException */ @Override public Socket connect() throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888); return socket; } }4)客户端配置文件
DownloadPath=D:/heimayunpan2.服务器端
1)主方法入口
步骤:
a:读取配置文件获取服务器的端口号
b:根据服务器端口号创建服务器端的套接字对象
c:获取线程池,存放50个线程
d:接收客户端连接,使用线程池统一处理,使用死循环控制让服务器一直运行
e:侦听并获取客户端
f:使用线程池执行任务
public class ServerApp { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //读取配置文件中端口信息,初始化服务端 ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("yunpan"); //获取配置文件中的端口号 int port = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("serverPort")); //创建服务器套接字对象 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port); // 线程池初始化 ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50); //接收客户端连接,使用线程池统一处理 //让服务器一直运行,这里使用死循环 while (true) { //侦听并获取客户端 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //使用线程池执行任务 threadPool.submit(new FileUpDownServiceImp(socket)); } } }2)FileUpDownService接口 复制即可,不用写
/**文件上传下载功能定义 */ public interface FileUpDownService { //文件上传 void uploadFile(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException; //文件下载 void downloadFile(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException; //查看目录 void scanDirectory(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException; //解析读取客户端的协议 Protocol parseProtocol(InputStream netIn) throws IOException; }3)实现类FileUpDownServiceImp
a:构造方法给客户端套接字初始化,并且获取服务器端的指定目录
步骤:
- 在构造方法中将接收的客户端套接字对象赋值给成员变量的套接字对象
- 获取配置文件中存放服务器文件的目录
- 判断目录是否是文件,是文件抛异常
- 判断目录是否存在,如果不存在则创建,创建失败抛异常
/* 协议定义: 协议+数据 第一行是协议,第二行开始就是数据 */ public FileUpDownServiceImp(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; //1 读取配置文件中的端口,根目录等配置信息 bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("yunpan"); //目录 D:/abc rootDir = new File(bundle.getString("rootDir")); if (rootDir.isFile()) { //文件 throw new RuntimeException("根目录路径与已存在文件冲突"); } else if (!rootDir.exists() && !rootDir.mkdirs()) { //不存在并且创建文件夹失败 throw new RuntimeException("根目录创建失败,请检查配置路径是否正确"); } }b:任务方法run
//多线程执行任务 @Override public void run() { try ( //客户端套接字 Socket socket = this.socket; //字节输入流 从客户端通道读取数据的字节输入流 InputStream netIn = socket.getInputStream(); //字节输出流 向客户端通道中写数据的字节输出流 OutputStream netOut = socket.getOutputStream(); ) { //读协议 Protocol protocol = parseProtocol(netIn); //type=scan,fileName=root,status=null,message=null, System.out.println(protocol); //识别客户端操作类型 String type = protocol.getType(); switch (type) { //浏览目录 case Protocol.Type.SCAN: //调用浏览目录的方法 scanDirectory(protocol, netIn, netOut); break; case Protocol.Type.DOWNLOAD: //下载 //downloadFile(protocol, netIn, netOut); break; case Protocol.Type.UPLOAD: //上传 //uploadFile(protocol, netIn, netOut); break; } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }c:解析读取客户端协议的方法:
/** * 解析读取客户端的协议 * * @param netIn * @return * @throws IOException */ @Override public Protocol parseProtocol(InputStream netIn) throws IOException { //转换流 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(netIn); //字符输入缓冲流 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); //读取第一行数据获取协议头部信息 //"type="scan",fileName="root",status=null,message=null\r\n" String protocolContent = br.readLine(); //解析协议 //将客户端传递的头的协议封装到Protocol类的成员变量中 Protocol protocol = Protocol.parseProtocol(protocolContent); //返回协议 return protocol; }d:浏览目录方法
/** * 浏览目录 * * @param protocol * @param netIn * @param netOut * @throws IOException */ @Override public void scanDirectory(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException { //创建响应协议的对象 Protocol response = new Protocol(); //获取客户端的fileName即操作文件名,默认是root String fileName = protocol.getFileName(); /* 1.fileName.replace("root", rootDir.toString()) rootDir.toString()的值是D:/abc, 该行代码表示将root替换为D:/abc 此时dir的内容是:D:/abc */ File dir = new File(fileName.replace("root", rootDir.toString())); if (!dir.isDirectory()) { //目录不存在,构建协议返回 //操作类型 浏览 response.setType(Protocol.Type.SCAN); //失败 response.setStatus(Protocol.Status.FAILED); //响应信息 response.setMessage("目录不存在,只能浏览当前子目录"); //向客户端响应信息 send(netOut, response); } else { //目录存在 response.setType(Protocol.Type.SCAN); //成功 response.setStatus(Protocol.Status.OK); //客户端发送的操作文件 response.setFileName(protocol.getFileName()); //向客户端响应信息 send(netOut, response); //把具体数据随后发送 //把文件数据按照:"文件类型 名称" 发送,每一个子文件一行 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(netOut); //列出父目录 D:/abc 下面所有的子目录和子文件 File[] children = dir.listFiles(); //遍历数组 for (File child : children) { //判断是否是文件还是目录 String fileType = child.isFile() ? "文件" : "目录"; //将类型和文件名或者文件夹名响应给客户端 osw.write(fileType + " " + child.getName() + "\r\n");//每个文件一行 } osw.flush(); } }e:向客户端返回信息
//向客户端返回信息 private void send(OutputStream netOut, Protocol response) throws IOException { String pro = response.toString(); //服务端响应:type=scan,fileName=root\test,status=ok,message=null, System.out.println("服务端响应:" + pro); netOut.write(pro.getBytes()); } -
4)服务器端配置文件
#rootDir=D:/heimayunpan
rootDir=D:/abc
serverPort=8888
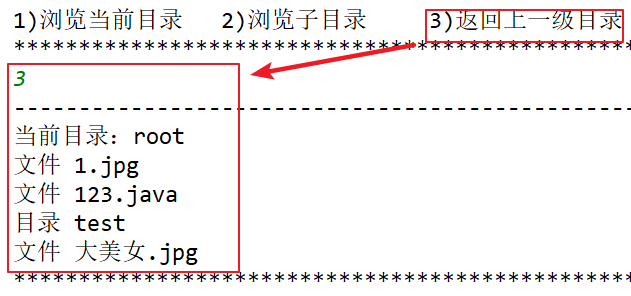
【2】在控制台输入序号完成:1)浏览当前目录 2)浏览子目录 3)返回上一级目录


1.客户端
1)通过键盘录入序号完成浏览当前目录、浏览子目录和返回上一级目录等功能
//为了让程序一直运行
while (true) { System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
System.out.println("1)浏览当前目录 \t2)浏览子目录 \t3)返回上一级目录 \t4)下载文件 \t5)上传文件"); System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
//获取键盘录入的选项
String choice = sc.nextLine();
switch (choice) {
case "1":
//1)浏览当前目录,效果和上述客户端刚连接服务端的效果一样,代码也一致
scanDirection(current);
break;
case "2":
//2)浏览子目录
/*
因为父目录是root目录,在父目录中存在多个子文件或者子目录,所以这里要提示下输入要浏览的子目录
*/
System.out.println("请输入要浏览的子目录:");
//获取输入的子目录
String dir = sc.nextLine();
try {
//扫描
/*
假设父目录root下面具有如下子文件和子目录:
test子目录
123.java子文件
假设输入的dir是test子目录。而父目录current是root
那么这里new File(current, dir) 就是root/test
*/
scanDirection(new File(current, dir));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case "3":
//3)返回上一级目录
/*
current表示: public File current = new File("root");
由于在scanDirection接收服务器端响应的时候修改了current值,代码如下:
current = new File(protocol.getFileName());
所以current值会改变,如果输入的路径是root/test,那么current就是root/test
如果浏览的是root目录,那么current就是root
*/
//判断是否是父目录root
if (current.getName().equals("root")) {
//说明是root目录
System.out.println("没有上一级了");
} else {
//说明不是root目录,例如是root/test。即current就是root/test
// File getParentFile() 方法表示获取父目录,例如当前路径是root/test,那么父目录是root
scanDirection(current.getParentFile());
}
break;
case "4":
//下载
/*System.out.println("请输入要下载的文件名(含后缀):");
String fileName = sc.nextLine();
downloadFile(new File(current, fileName));*/
break;
case "5":
//上传
/*while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入在计算机中要上传的文件路径");
String uploadFilePath = sc.nextLine();
File upFile = new File(uploadFilePath);
if (!upFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在,请重新输入!");
} else if (upFile.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("抱歉,不支持目录上传!");
} else if (upFile.isFile()) {
uploadFile(upFile);
break;
}
}8*/
break;
default:
System.out.println("功能尚在开发中....");
}
}
2.服务器端
说明:服务器端在上述已经完成
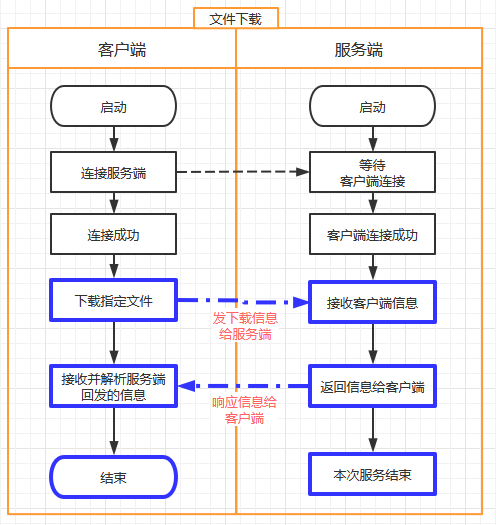
文件下载
-
文件下载流程
-
数据交互
请求:客户端 ---> 服务端
type=download,fileName=下载的文件名,status=null,message=null,响应: 服务端 --->客户端
-
成功
type=download,fileName=下载的文件名,status=ok,message=下载文件大小, 010101010010下载的文件字节数据010101010010100101001010010010010101....需要将下载的文件字节数据保存到文件中
-
失败
type=download,fileName=下载的文件名,status=failed,message=文件不存在,请选择当前存在的子文件,只有协议数据,没有实际下载的文件数据
-
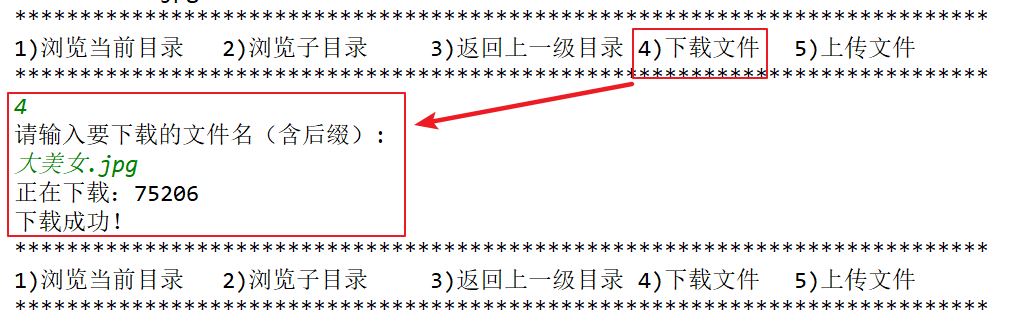
【1】根据客户端输入的操作序号4即下载文件从服务器上将文件下载到客户端
1.客户端
1)在start方法中读取配置文件中的存放下载文件的路径,并判断是否是文件以及是否存在,不存在直接创建目录
//1.初始化下载路径
bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("yunpan");
//DownloadPath=D:/heimayunpan
//downloadPath的值是"D:/heimayunpan"
downloadPath = bundle.getString("DownloadPath");
//1.1根据获取的路径创建File类的对象
File downloadDir = new File(downloadPath);
//1.2判断存放下载文件的路径是否是文件
if (downloadDir.isFile()) {
//是文件,抛出异常
throw new Exception("文件不能当做下载目录,请更改下载路径配置!");
//判断判断存放下载文件的路径是否存在,downloadDir.exists() 不存在返回false
//downloadDir.mkdirs() 执行这个代码说明文件夹不存在,则创建,如果创建失败返回false
} else if (!downloadDir.exists() && !downloadDir.mkdirs()) {
//说明指定的文件夹不存在并且创建失败
throw new Exception("下载目录初始化失败,请检查下载路径配置是否正确!");
}
2)根据输入的序号和路径调用下载方法downloadFile
//为了让程序一直运行
while (true) { System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
System.out.println("1)浏览当前目录 \t2)浏览子目录 \t3)返回上一级目录 \t4)下载文件 \t5)上传文件"); System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
//获取键盘录入的选项
String choice = sc.nextLine();
switch (choice) {
case "1":
//1)浏览当前目录,效果和上述客户端刚连接服务端的效果一样,代码也一致
scanDirection(current);
break;
case "2":
//2)浏览子目录
/*
因为父目录是root目录,在父目录中存在多个子文件或者子目录,所以这里要提示下输入要浏览的子目录
*/
System.out.println("请输入要浏览的子目录:");
//获取输入的子目录
String dir = sc.nextLine();
try {
//扫描
/*
假设父目录root下面具有如下子文件和子目录:
test子目录
123.java子文件
假设输入的dir是test子目录。而父目录current是root
那么这里new File(current, dir) 就是root/test
*/
scanDirection(new File(current, dir));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case "3":
//3)返回上一级目录
/*
current表示: public File current = new File("root");
由于在scanDirection接收服务器端响应的时候修改了current值,代码如下:
current = new File(protocol.getFileName());
所以current值会改变,如果输入的路径是root/test,那么current就是root/test
如果浏览的是root目录,那么current就是root
*/
//判断是否是父目录root
if (current.getName().equals("root")) {
//说明是root目录
System.out.println("没有上一级了");
} else {
//说明不是root目录,例如是root/test。即current就是root/test
// File getParentFile() 方法表示获取父目录,例如当前路径是root/test,那么父目录是root
scanDirection(current.getParentFile());
}
break;
case "4":
//下载
System.out.println("请输入要下载的文件名(含后缀):");
//获取键盘输入要下载的文件名
String fileName = sc.nextLine();
/*
1.current表示当前路径,假设是 root 即服务器上面的D:\abc路径
2.fileName表示当前要下载的文件名:例如123.java
3.new File(current, fileName) 表示根据父目录和子文件创建File类对象:
root\123.java 在服务器上就是D:\abc\123.java
*/
//根据传递的路径执行下载文件方法
downloadFile(new File(current, fileName));
break;
case "5":
//上传文件
/*while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入在计算机中要上传的文件路径");
String uploadFilePath = sc.nextLine();
File upFile = new File(uploadFilePath);
if (!upFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在,请重新输入!");
} else if (upFile.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("抱歉,不支持目录上传!");
} else if (upFile.isFile()) {
uploadFile(upFile);
break;
}
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("功能尚在开发中....");*/
}
}
3)根据上述传递的路径完成文件下载的方法
a:调用connect()方法和服务器建立连接获取客户端套接字对象
b:根据当前接收的路径生成下载的协议
c:调用send方法将下载的协议发送给服务器
d:将服务器发送的协议数据封装到Protocol类的成员变量中
e:如果服务器响应的是成功,则根据路径创建下载的字节输出流对象
f:使用字节输入流从通道读取数据
g:使用创建的字节输出流将读取的数据写到目的地
/**
* 文件下载
*
* @param file
*/
@Override
public void downloadFile(File file) {//File file = new File(current, fileName) :root\123.java
try (Socket socket = connect();
InputStream netIn = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream netOut = socket.getOutputStream();) {
//下载文件
/*
1.file.getPath() 就是 root\123.java
2.dp="type=download,fileName=root\123.java,status=null,message=null"
*/
Protocol dp = Protocol.getDownloadProtocol(file.getPath());
//发送下载的协议
send(netOut, dp);
//接收文件
//先读取第一行协议
//将服务器发送的协议数据封装到Protocol类的成员变量中
Protocol protocol = Protocol.parseProtocol(netIn);
if (protocol.getStatus().equals(Protocol.Status.OK)) {
//可以下载
System.out.println("正在下载:" + protocol.getMessage());
/*
1.downloadPath的值是"D:/heimayunpan"
2.protocol.getFileName() : 假设下载的是123.java 那么这里代码获取的就是123.java
3.downloadPath + "\\" + protocol.getFileName() : 整体表示D:\heimayunpan\123.java 表示将从服务器下载的文件存放的位置
*/
File local = new File(downloadPath + "\\" + protocol.getFileName());
try (
//创建字节输出流对象,地址是:D:\heimayunpan\123.java
FileOutputStream localOut = new FileOutputStream(local)
) {
//从服务器端读取数据
int len;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len = netIn.read(buf)) != -1) {
//向本地写数据
localOut.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
System.out.println("下载成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("下载失败:" + protocol.getMessage());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.服务器端
1)在任务方法run的switch语句位置调用下载文件的方法downloadFile(protocol, netIn, netOut);
//多线程执行任务
@Override
public void run() {
try (
//客户端套接字
Socket socket = this.socket;
//字节输入流 从客户端通道读取数据的字节输入流
InputStream netIn = socket.getInputStream();
//字节输出流 向客户端通道中写数据的字节输出流
OutputStream netOut = socket.getOutputStream();
) {
//读协议
Protocol protocol = parseProtocol(netIn);
//type=scan,fileName=root,status=null,message=null,
System.out.println(protocol);
//识别客户端操作类型
String type = protocol.getType();
switch (type) {
//浏览目录
case Protocol.Type.SCAN:
//调用浏览目录的方法
scanDirectory(protocol, netIn, netOut);
break;
case Protocol.Type.DOWNLOAD:
//调用下载文件的方法
downloadFile(protocol, netIn, netOut);
break;
case Protocol.Type.UPLOAD:
//uploadFile(protocol, netIn, netOut);
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2)文件下载功能
a:从客户端的协议中获取下载的文件路径
b:将默认的文件路径替换为服务器中的真实路径
c:根据真实路径创建File对象
d:创建响应协议对象
e:向响应协议对象中封装操作类型、操作文件
f:判断要下载的是否是文件,如果是将操作成功的状态封装到Protocol协议中,同时将说明信息也封装到Protocol协议中
g:向客户端响应下载的协议信息
h:调用读写工具类的方法进行数据的读写
i:如果下载的内容不是文件,设置响应协议的头为失败
j:封装说明信息
k:发送响应协议
/**
* 文件下载功能
* protocol ="type=download,fileName=root\123.java,status=null,message=null,"
* @param protocol
* @param netIn
* @param netOut
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void downloadFile(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException {
/*
1.protocol.getFileName()获取的值是 "root\123.java"
2.rootDir.toString() 表示的内容是 "D:\\abc"
整体代码表示将"root\123.java" 变为 "D:\\abc\\123.java" 该路径是真正存放文件和文件夹的路径
*/
String fileName = protocol.getFileName().replace("root", rootDir.toString());
//创建File对象----》"D:\\abc\\123.java"
File file = new File(fileName);
//创建响应协议的对象
Protocol response = new Protocol();
//操作类型 public static final String DOWNLOAD = "download";下载
response.setType(Protocol.Type.DOWNLOAD);
//操作文件 123.java
response.setFileName(file.getName());
if (file.isFile()) {
//说明是文件
//操作状态 : public static final String OK = "ok";//成功
response.setStatus(Protocol.Status.OK);
//说明信息 :file.length() 文件的长度
response.setMessage(file.length() + "");
//向客户端响应下载的协议信息
send(netOut, response);
try (FileInputStream localIn = new FileInputStream(file)) {
//调用读写工具类的方法进行数据的读写
IOUtil.copy(localIn, netOut);
}
} else {
//下载的内容不是文件
//设置响应协议的头为失败
response.setStatus(Protocol.Status.FAILED);
//说明信息
response.setMessage(file.getName() + "文件不存在,请选择当前存在的子文件");
//发送响应协议
send(netOut, response);
}
}
3)读写工具类 直接复制,不用写
package com.itheima.sh.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/*
读写工具类
*/
public class IOUtil {
public static void copy(InputStream in, OutputStream out) throws IOException {
int len;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.println("read len=" + len);
out.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
}
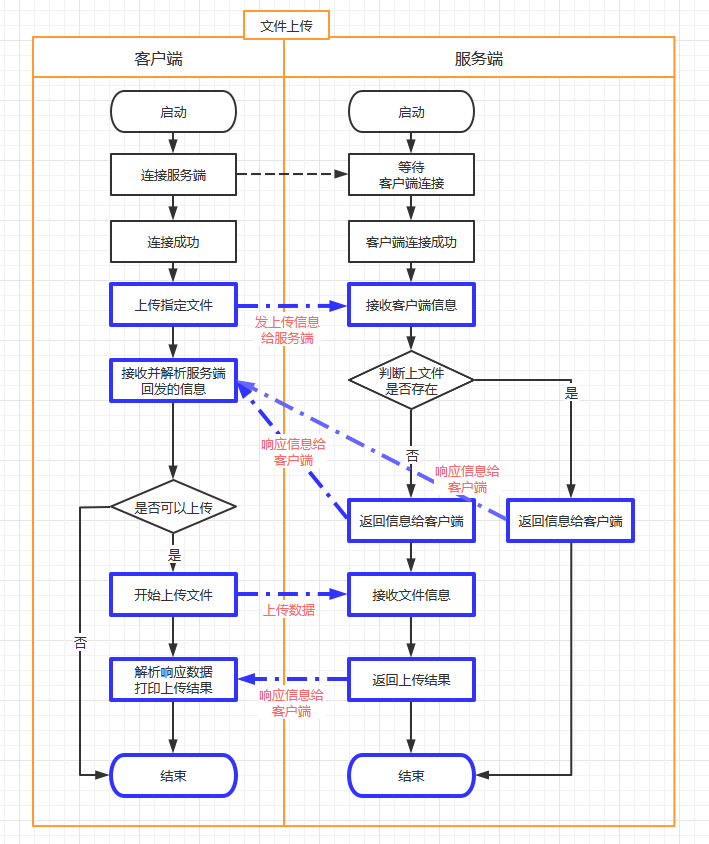
文件上传
-
文件上传交换流程
-
数据交互
请求:客户端 ---> 服务端
type=upload,fileName=要上传的文件,status=null,message=null,注意:文件要体现在服务端的位置。客户端看到的文件都是基于服务端某一个文件夹而存在的,我们把这个文件夹叫做root。
服务端开发时,可以任意指定一个合法的文件夹当做这个root。响应: 服务端 --->客户端
-
成功
告诉客户端,文件可以上传的
type=upload,fileName=要上传的文件,status=ok,message=null,客户端收到信息后,继续上传文件信息,文件接收完毕后继续响应
type=upload,fileName=要上传的文件,status=ok,message=文件上传成功, -
失败
如果发现服务端已经存在该文件,提示客户端不要上传
type=upload,fileName=要上传的文件,status=failed,message=文件已存在
-
【1】将客户端硬盘上任意位置的文件上传到服务器端的指定位置D:\abc

1.客户端
1)根据输入的序号和路径调用文件上传方法uploadFile进行文件的上传。
注意:需要获取上传的文件路径,判断是否存在和是否是文件夹,如果不存在和是文件夹都重新输入路径,只有是存在的文件路径才可以调用文件上传方法uploadFile进行文件的上传
//为了让程序一直运行
while (true) {
System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
System.out.println("1)浏览当前目录 \t2)浏览子目录 \t3)返回上一级目录 \t4)下载文件 \t5)上传文件");
System.out.println("***************************************************************************");
//获取键盘录入的选项
String choice = sc.nextLine();
switch (choice) {
case "1":
//1)浏览当前目录,效果和上述客户端刚连接服务端的效果一样,代码也一致
scanDirection(current);
break;
case "2":
//2)浏览子目录
/*
因为父目录是root目录,在父目录中存在多个子文件或者子目录,所以这里要提示下输入要浏览的子目录
*/
System.out.println("请输入要浏览的子目录:");
//获取输入的子目录
String dir = sc.nextLine();
try {
//扫描
/*
假设父目录root下面具有如下子文件和子目录:
test子目录
123.java子文件
假设输入的dir是test子目录。而父目录current是root
那么这里new File(current, dir) 就是root/test
*/
scanDirection(new File(current, dir));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case "3":
//3)返回上一级目录
/*
current表示: public File current = new File("root");
由于在scanDirection接收服务器端响应的时候修改了current值,代码如下:
current = new File(protocol.getFileName());
所以current值会改变,如果输入的路径是root/test,那么current就是root/test
如果浏览的是root目录,那么current就是root
*/
//判断是否是父目录root
if (current.getName().equals("root")) {
//说明是root目录
System.out.println("没有上一级了");
} else {
//说明不是root目录,例如是root/test。即current就是root/test
// File getParentFile() 方法表示获取父目录,例如当前路径是root/test,那么父目录是root
scanDirection(current.getParentFile());
}
break;
case "4":
//下载
System.out.println("请输入要下载的文件名(含后缀):");
//获取键盘输入要下载的文件名
String fileName = sc.nextLine();
/*
1.current表示当前路径,假设是 root 即服务器上面的D:\abc路径
2.fileName表示当前要下载的文件名:例如123.java
3.new File(current, fileName) 表示根据父目录和子文件创建File类对象:
root\123.java 在服务器上就是D:\abc\123.java
*/
//根据传递的路径执行下载文件方法
downloadFile(new File(current, fileName));
break;
case "5":
//文件上传
//使用死循环控制,如果输入的路径不正确就一直输入
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入在您的计算机中要上传的文件路径");
//获取键盘输入的文件上传的路径
String uploadFilePath = sc.nextLine();
//根据输入的路径创建File类的对象
File upFile = new File(uploadFilePath);
//判断用户输入的文件上传的路径是否存在
if (!upFile.exists()) {
//说明路径不存在
System.out.println("文件不存在,请重新输入!");
} else if (upFile.isDirectory()) {
//说明上传的是文件夹
System.out.println("抱歉,不支持目录上传!");
} else if (upFile.isFile()) {
//说明输入的是文件,将上传文件路径作为参数调用文件上传的方法
uploadFile(upFile);
break;
}
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("功能尚在开发中....");
}
}
2)客户端上传文件的方法
注意:别忘记书写结束标记.
a:和服务器建立连接
b:根据上传文件的路径结合当前路径current生成文件上传的协议
c:将文件上传的协议发送给服务器
d:获取服务器端响应的协议
e:判断响应协议的状态是否是ok
f:如果是ok,开始上传文件,根据键盘录入的路径创建字节输入流对象
g:使用IOUtil工具类将文件传递给服务器端
h:告知服务器,客户端文件上传完毕
i:接收服务端在接收到客户端上传完文件之后的响应
j:根据响应的内容,输出成功还是失败
/**
* 文件上传
*
* @param upFile
*/
@Override
public void uploadFile(File upFile) {//假设客户端上传的文件路径:D:\test\6.jpg
try (Socket socket = connect();
InputStream netIn = socket.getInputStream();
OutputStream netOut = socket.getOutputStream();) {
//【发】上传文件
//new File(current, upFile.getName()) ----"root\6.jpg"
//创建上传文件的协议
Protocol up = Protocol.getUploadProtocol(new File(current, upFile.getName()));
//将上传文件的协议发送给服务器端
send(netOut, up);
//【收】等待响应
//获取服务器端响应协议
Protocol protocol = Protocol.parseProtocol(netIn);
//判断是否可以上传
if (protocol.getStatus().equals(Protocol.Status.OK)) {
//【发】开始上传
try (FileInputStream localIn = new FileInputStream(upFile)) {//D:\test\6.jpg
System.out.println("开始上传");
//使用工具类将客户端文件上传到服务器端
IOUtil.copy(localIn, netOut);
//告知服务器,客户端上传文件结束
socket.shutdownOutput();
//上传结束
System.out.println("上传结束");
//【收】接收服务端在接收到客户端上传完文件之后的响应
protocol = Protocol.parseProtocol(netIn);
System.out.println(protocol.getMessage());
}
} else {
System.out.println("上传失败" + protocol.getMessage());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.服务器端
1)在任务方法run中根据客户端传递的内容来调用文件上传的方法
2)文件上传功能
a:将客户端传递默认的root替换为D:\abc,生成新的文件字符串路径
b:根据生成新的文件字符串路径创建File类的对象
c:判断文件路径是否存在,如果已经存在,则不能上传
d:如果文件不存在,可以上传,告知客户端可以上传,创建字节输出流,将客户端传递的内容进行读写
e:告知客户端上传成功
/**
* 文件上传功能
*
* @param protocol
* @param netIn
* @param netOut
*/
@Override
public void uploadFile(Protocol protocol, InputStream netIn, OutputStream netOut) throws IOException {
//"root\6.jpg" ---- fileName = "D:\abc\6.jpg"
String fileName = protocol.getFileName().replace("root", rootDir.toString());
//创建File对象:"D:\abc\6.jpg"
File file = new File(fileName);
//检测要上传的文件是否存在
if (file.exists()) {
//【发】文件已存在,不能上传
protocol.setStatus(Protocol.Status.FAILED);
protocol.setMessage("文件已存在");
//返回给客户端
send(netOut, protocol);
} else{
//说明不存在
//告诉客户端开始上传
protocol.setStatus(Protocol.Status.OK);
send(netOut, protocol);
try (FileOutputStream localOut = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
System.out.println("开始上传");
IOUtil.copy(netIn, localOut);//拷贝
}
protocol.setMessage(file + " 文件上传成功");
send(netOut, protocol);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号