0201 可变参数 collections集合常用工具类 集合嵌套 斗地主发牌器
1、可变参数
比如我们想定义一个方法去求和,但是个数不确定,首先想到的是方法重载,那也可以实现,但是是不是很麻烦呢。来看一下可变参数发方法
格式:修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型... 形参名){ }
上述格式其实等价于:修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型[] 形参名){ }。底层封装了一个数组
例:代码展示
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(add(1,2));
System.out.println(add(1,2,3));
}
//计算整数和
public static int add(int...a){
int sum=0;
for(int s:a){
sum=sum+s;
}
return sum;
}
}
注:如果想在可变参数中再传其他参数,一定要方法可变参数前边,因为如果方法后边会有不确定因素产生。
2、collections集合常用工具类
(1)shuffle();用来打乱顺序的
(2)sort();排序
代码展示:
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(10);
list.add(11);
list.add(16);
//打乱list集合中的元素
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
//排序
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
3、集合嵌套
嵌套集合遍历,代码展示,四种方法
public class Work2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HashMap<String,HashMap<Person,String>> bigmap=new HashMap<String,HashMap<Person,String>>();
HashMap<Person, String> smap1=new HashMap<Person, String>();
HashMap<Person, String> smap2=new HashMap<Person, String>();
//小map存值
smap1.put(new Person("小白",20), "学习号");
smap1.put(new Person("小黑",21), "学习不好");
smap2.put(new Person("小率",22), "体育号");
smap2.put(new Person("小白",23), "垃圾");
//想大map中存值
bigmap.put("java1127",smap1);
bigmap.put("java1128",smap2);
//keyset 增强for
//获取大map的key所在的set集合
/*Set<String> bigset=bigmap.keySet();
//遍历获得每一个大map的key
for(String bigkey:bigset){
//根据大map的key值获得小map
HashMap<Person,String> smallmap=bigmap.get(bigkey);
//获得小map的key所在的set集合
Set<Person> smallset=smallmap.keySet();
//遍历获得每一个小map的key值
for(Person smallkey:smallset){
//根据小map的key值获得小map的value值
String value=smallmap.get(smallkey);
System.out.println(bigkey+".."+smallkey+".."+value);
}
}*/
//keyset 迭代器
//获取大map的key所在的set集合
/*Set<String> bigset=bigmap.keySet();
//获得大map的迭代器对象
Iterator<String> bigit=bigset.iterator();
while(bigit.hasNext()){
//获得大map的key值
String bigkey=bigit.next();
//根据大map的key值获得小map
HashMap<Person,String> smallmap=bigmap.get(bigkey);
//获得小map的key值所在的set集合
Set<Person> smallset=smallmap.keySet();
//获得小map的迭代器对象
Iterator<Person> smallit=smallset.iterator();
while(smallit.hasNext()){
//获得小map的key值
Person smallkey=smallit.next();
//根据小map的key值获得小map的value值
String value=smallmap.get(smallkey);
System.out.println(bigkey+"..."+smallkey+"..."+value);
}
}*/
//entryset 增强for
//获得大map的结婚证对象所在的set集合
/*Set<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Person,String>>> set=bigmap.entrySet();
//循环遍历获得大map的键值对对象
for(Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Person,String>> bigentry:set){
//根据键值对对象的getkey方法获得大map的key值
String bigkey=bigentry.getKey();
//根据大map的key、值获得小map
HashMap<Person,String> smallmap=bigmap.get(bigkey);
//获得小map的结婚证对象所在的set集合
Set<Map.Entry<Person, String>> smallset=smallmap.entrySet();
//循环遍历小map获得键值对对象
for(Map.Entry<Person, String> smallentry:smallset){
//根据键值对对象的getkey方法获得小map的key值
Person smallkey=smallentry.getKey();
//根据小map的key值获得value值
String value=smallentry.getValue();
System.out.println(bigkey+".."+smallkey+".."+value);
}
}*/
//entryset 迭代器
//获得大map键值对对象所在的set集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Person,String>>> set=bigmap.entrySet();
//获得大map的键值对对象的迭代器对象
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Person,String>>> bigit=set.iterator();
while(bigit.hasNext()){
//获得大map的键值对对象
Map.Entry<String, HashMap<Person,String>> bigentry=bigit.next();
//根据键值对对象的方法getkey得到大map的key值
String bigkey=bigentry.getKey();
//根据大map中的key值获得小map
HashMap<Person,String> smallmap=bigmap.get(bigkey);
//获得小map键值对对象所在的set集合
Set<Map.Entry<Person, String>> smallset=smallmap.entrySet();
//获得小map键值对对象的迭代器对象
Iterator<Map.Entry<Person, String>> smallit=smallset.iterator();
while(smallit.hasNext()){
//获得小map的键值对对象
Map.Entry<Person, String> smallentry=smallit.next();
//根据键值对对象的getkey方法获得小map的key值
Person smallkey=smallentry.getKey();
//根据小map的key值获得小map的value值
String value=smallentry.getValue();
System.out.println(bigkey+".."+smallkey+".."+value);
}
}
}
}
4、斗地主发牌器
案例需求:
具体规则:
1、组装54张扑克牌
2、将54张牌顺序打乱
3、三个玩家参与游戏,三人交替摸牌,每人17张牌,最后三张留作底牌。
4、查看三人各自手中的牌(按照牌的大小排序)、底牌
5、手中扑克牌从大到小的摆放顺序:大王,小王,2,A,K,Q,J,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3
图解:
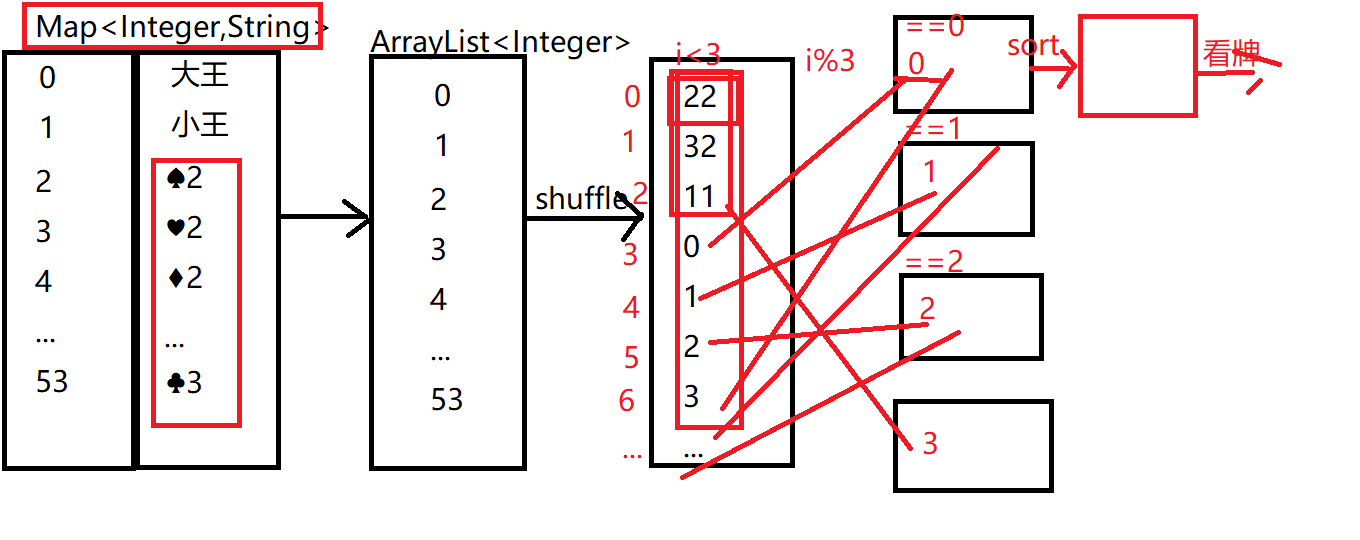
首先选择双列集合 Map集合作为主要存储这个54张扑克牌,key值存放的是0-53位整数,value值存的是花色和数字(花色和数字分别存放在两个数组中,经过遍历让花色和数字一一拼接)。题目中还涉及到了排序和打乱这两个要求,但是这两个需求单纯用map双列集合时很难做到的,所以要创建一个Arraylist集合存储双列集合中的key值,用Arraylist集合将其打乱和排序。然后将牌发给三维玩家和底牌,那么我们将打乱后的key值进行遍历,如果是前三张就把这三张给底牌,剩下的数与3取余如果余数为0,则给玩家1,如果余数为2,则给玩家2,如果余数为3,则发给玩家3,
代码展示:
public class Doudizhu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//创建装有扑克牌的map集合
Map<Integer, String> pooker=new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//再创建key值的arraylist集合
List<Integer> pookernum=new ArrayList<Integer>();
//封装花色和牌号数组
String[] color={"♥","♣","♠","♦"};
String[] number={"2","A","K","Q","J","10","9","8","7","6","5","4","3"};
//封装遍历
int index=2;
for(String n:number){
for(String c:color){
//将组合好的牌号封装到map集合中
pooker.put(index, c+n);
//将key封装到集合中
pookernum.add(index);
index++;
}
}
//封装大小王
pooker.put(0, "大王");
pookernum.add(0);
pooker.put(1,"小王");
pookernum.add(1);
//洗牌
Collections.shuffle(pookernum);
//创建三个玩家加底牌集合
ArrayList<Integer> player1=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> player2=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> player3=new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> bottom=new ArrayList<Integer>();
//循环遍pkkoernum 所有key 发牌
for(int i=0;i<pookernum.size();i++){
//将前三张拍发给底牌
if(i<3){
bottom.add(pookernum.get(i));
}else if(i%3==0){
player1.add(pookernum.get(i));
}else if(i%3==1){
player2.add(pookernum.get(i));
}else if(i%3==2){
player3.add(pookernum.get(i));
}
}
//排序
Collections.sort(player1);
Collections.sort(player2);
Collections.sort(player3);
Collections.sort(bottom);
//看牌 写方法
look("玩家1",pooker,player1);
look("玩家2",pooker,player2);
look("玩家3",pooker,player3);
look("底牌",pooker,bottom);
}
public static void look(String name,Map<Integer, String> pooker,ArrayList<Integer> player1){
//遍历渠道集合中的每一个key值
System.out.print(name+":");
for(int key:player1){
System.out.print(pooker.get(key)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号