使用Redis分布式锁处理并发,解决超卖问题
一、synchronized处理并发
首先,synchronized的确是一个解决办法,而且也很简单,在方法前面加一个synchronized关键字。
但是通过压测,发现请求变的很慢,因为:synchronized就用一个锁把这个方法锁住了,每次访问这个方法,只会有一个线程,所以这就是它导致慢的原因。通过这种方式,保证这个方法中的代码都是单线程来处理,不会出什么问题。
同时,使用synchronized还是存在一些问题的,首先,它无法做到细粒度的控制,比如同一时间有秒杀A商品和B商品的请求,都进入到了这个方法,虽然秒杀A商品的人很多,但是秒杀B商品的人很少,但是即使是买B商品,进入到了这个方法,也会一样的慢。
最重要的是,synchronized是jvm进程锁,它只适合单点的情况。如果以后程序水平扩展了,弄了个集群,很显然,负载均衡之后,不同的用户看到的结果一定是五花八门的。
所以,还是使用更好的办法,使用redis分布式锁。
二、redis分布式锁
1、两个redis的命令
setnx key value 简单来说,setnx就是,如果没有这个key,那么就set一个key-value, 但是如果这个key已经存在,那么将不会再次设置,get出来的value还是最开始set进去的那个value.
网站中还专门讲到可以使用!SETNX加锁,如果获得锁,返回1,如果返回0,那么该键已经被其他的客户端锁定。
并且也提到了如何处理死锁。
getset key value 这个就更简单了,先通过key获取value,然后再将新的value set进去。
2、redis分布式锁的实现
我们希望的,无非就是这一段代码,能够单线程的去访问,因此在这段代码之前给他加锁,相应的,这段代码后面要给它解锁:
2.1 引入redis依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
2.2 配置redis
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
package app;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.http.client.SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.TaskScheduler;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TaskScheduler taskScheduler() {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(500);
return taskScheduler;
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(ClientHttpRequestFactory factory){
return new RestTemplate(factory);
}
@Bean
public ClientHttpRequestFactory simpleClientHttpRequestFactory(){
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory factory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
factory.setReadTimeout(180000);//单位为ms1
factory.setConnectTimeout(5000);//单位为ms
return factory;
}
}
2.3 编写加锁和解锁的方法
package app.configuration;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
*feng
*/
@Component
public class RedisLock {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 加锁
* @param key id
* @param value 当前时间+超时时间
* @return
*/
public boolean lock(String key, String value) {
if (redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value)) { //这个其实就是setnx命令,只不过在java这边稍有变化,返回的是boolea
return true;
}
//避免死锁,且只让一个线程拿到锁
String currentValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
//如果锁过期了
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(currentValue) && Long.parseLong(currentValue) < System.currentTimeMillis()) {
//获取上一个锁的时间
String oldValues = redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndSet(key, value);
/*
只会让一个线程拿到锁
如果旧的value和currentValue相等,只会有一个线程达成条件,因为第二个线程拿到的oldValue已经和currentValue不一样了
*/
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(oldValues) && oldValues.equals(currentValue)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 解锁
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void unlock(String key, String value) {
try {
String currentValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(currentValue) && currentValue.equals(value)) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().getOperations().delete(key);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("『redis分布式锁』解锁异常,{}", e);
}
}
}
为什么要有避免死锁的一步呢?
假设没有『避免死锁』这一步,结果在执行到下单代码的时候出了问题,毕竟操作数据库、网络、io的时候抛了个异常,这个异常是偶然抛出来的,就那么偶尔一次,那么会导致解锁步骤不去执行,这时候就没有解锁,后面的请求进来自然也或得不到锁,这就被称之为死锁。
而这里的『避免死锁』,就是给锁加了一个过期时间,如果锁超时了,就返回true,解开之前的那个死锁。
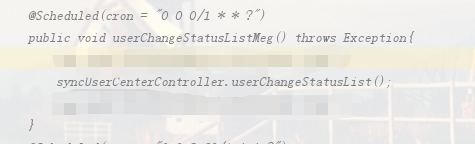
2.4 下单代码中引入加锁和解锁,确保只有一个线程操作
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 0/1 * * ?")
public void findUserCenterSyncTrialMeg(){
log.info("定时任务启动");
//加锁
long time = System.currentTimeMillis() + 1000*10; //超时时间:10秒,最好设为常量
boolean isLock = redisLock.lock(Const.SynchronousProbationaryEmployee.SYNCHRONOUS_PROBATIONARY_EMPLOYEE,
String.valueOf(time));
try {
if(isLock){
Thread.sleep ( 12000 );
syncUserCenterController.findUserCenterSyncTrial();
syncUserCenterController.findUserCenterSyncTrialOutsourcing();
log.info ( "执行成功---------------" );
}else{
log.info ( "人太多了,换个姿势再试试~---" );
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("Redisson 分布式锁获取异常 ");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("程序获取异常 ");
} finally {
if (!isLock) {
return;
}
//解锁
redisLock.unlock(Const.SynchronousProbationaryEmployee.SYNCHRONOUS_PROBATIONARY_EMPLOYEE, String.valueOf(time));
log.error("Redisson 分布式锁 解锁 ");
}
}
输出完成,成功成功成功!!!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号