java 集合系列目录:
Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 04 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 05 Vector详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 06 Stack详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 07 List总结(LinkedList, ArrayList等使用场景和性能分析)
Java 集合系列 09 HashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 10 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
Java 集合系列 11 hashmap 和 hashtable 的区别
概要
和学习ArrayList一样,接下来呢,我们先对LinkedList有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码;最后再通过实例来学会使用LinkedList。内容包括:
第1部分 LinkedList介绍
第2部分 LinkedList数据结构
第3部分 LinkedList源码解析(基于JDK1.7)
第4部分 LinkedList遍历方式
第1部分 LinkedList介绍
LinkedList简介
LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
LinkedList 是非同步的。
LinkedList构造函数
// 默认构造函数 LinkedList() // 创建一个LinkedList,保护Collection中的全部元素。 LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> collection)
LinkedList的API
LinkedList的API boolean add(E object) void add(int location, E object) boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) void addFirst(E object) void addLast(E object) void clear() Object clone() boolean contains(Object object) Iterator<E> descendingIterator() E element() E get(int location) E getFirst() E getLast() int indexOf(Object object) int lastIndexOf(Object object) ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) boolean offer(E o) boolean offerFirst(E e) boolean offerLast(E e) E peek() E peekFirst() E peekLast() E poll() E pollFirst() E pollLast() E pop() void push(E e) E remove() E remove(int location) boolean remove(Object object) E removeFirst() boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) E removeLast() boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) E set(int location, E object) int size() <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) Object[] toArray()
AbstractSequentialList简介
在介绍LinkedList的源码之前,先介绍一下AbstractSequentialList。毕竟,LinkedList是AbstractSequentialList的子类。
AbstractSequentialList 实现了get(int index)、set(int index, E element)、add(int index, E element) 和 remove(int index)这些函数。这些接口都是随机访问List的,LinkedList是双向链表;既然它继承于AbstractSequentialList,就相当于已经实现了“get(int index)这些接口”。
此外,我们若需要通过AbstractSequentialList自己实现一个列表,只需要扩展此类,并提供 listIterator() 和 size() 方法的实现即可。若要实现不可修改的列表,则需要实现列表迭代器的 hasNext、next、hasPrevious、previous 和 index 方法即可。
第2部分 LinkedList数据结构
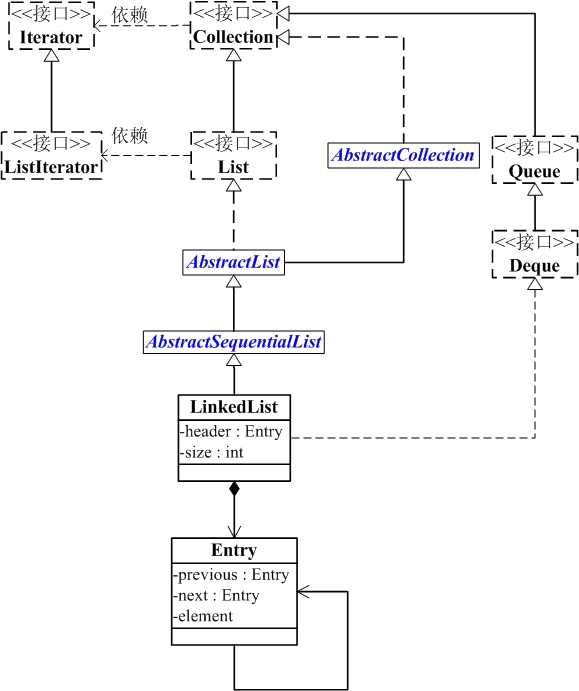
LinkedList的继承关系
java.lang.Object ↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E> ↳ java.util.AbstractList<E> ↳ java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E> ↳ java.util.LinkedList<E> public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
LinkedList与Collection关系如下图:
第3部分 LinkedList源码解析(基于JDK1.7)
为了更了解LinkedList的原理,下面对LinkedList源码代码作出分析。
在阅读源码之前,我们先对LinkedList的整体实现进行大致说明:
LinkedList实际上是通过双向链表去实现的。既然是双向链表,那么它的顺序访问会非常高效,而随机访问效率比较低。
既然LinkedList是通过双向链表的,但是它也实现了List接口{也就是说,它实现了get(int location)、remove(int location)等“根据索引值来获取、删除节点的函数”}。LinkedList是如何实现List的这些接口的,如何将“双向链表和索引值联系起来的”?
实际原理非常简单,它就是通过一个计数索引值来实现的。例如,当我们调用get(int location)时,首先会比较“location”和“双向链表长度的1/2”;若前者大,则从链表头开始往后查找,直到location位置;否则,从链表末尾开始先前查找,直到location位置。
这就是“双线链表和索引值联系起来”的方法。
好了,接下来开始阅读源码(只要理解双向链表,那么LinkedList的源码很容易理解的)。
有关LinkedList在JDK1.6和JDK1.7的区别以及优化,参看 JDK1.7-LinkedList循环链表优化,这里列出是1.7的源码
其中 Node:
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
1 public class LinkedList<E> 2 extends AbstractSequentialList<E> 3 implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 4 { 5 transient int size = 0; 6 7 /** 8 * Pointer to first node. 9 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || 10 * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) 11 */ 12 transient Node<E> first; 13 14 /** 15 * Pointer to last node. 16 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || 17 * (last.next == null && last.item != null) 18 */ 19 transient Node<E> last; 20 21 /** 22 * Constructs an empty list. 23 */ 24 public LinkedList() { 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified 29 * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's 30 * iterator. 31 * 32 * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list 33 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 34 */ 35 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 36 this(); 37 addAll(c); 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * Links e as first element. 42 */ 43 private void linkFirst(E e) { 44 final Node<E> f = first; 45 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); 46 first = newNode; 47 if (f == null) 48 last = newNode; 49 else 50 f.prev = newNode; 51 size++; 52 modCount++; 53 } 54 55 /** 56 * Links e as last element. 57 */ 58 void linkLast(E e) { 59 final Node<E> l = last; 60 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); 61 last = newNode; 62 if (l == null) 63 first = newNode; 64 else 65 l.next = newNode; 66 size++; 67 modCount++; 68 } 69 70 /** 71 * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. 72 */ 73 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { 74 // assert succ != null; 75 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; 76 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); 77 succ.prev = newNode; 78 if (pred == null) 79 first = newNode; 80 else 81 pred.next = newNode; 82 size++; 83 modCount++; 84 } 85 86 /** 87 * Unlinks non-null first node f. 88 */ 89 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { 90 // assert f == first && f != null; 91 final E element = f.item; 92 final Node<E> next = f.next; 93 f.item = null; 94 f.next = null; // help GC 95 first = next; 96 if (next == null) 97 last = null; 98 else 99 next.prev = null; 100 size--; 101 modCount++; 102 return element; 103 } 104 105 /** 106 * Unlinks non-null last node l. 107 */ 108 private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { 109 // assert l == last && l != null; 110 final E element = l.item; 111 final Node<E> prev = l.prev; 112 l.item = null; 113 l.prev = null; // help GC 114 last = prev; 115 if (prev == null) 116 first = null; 117 else 118 prev.next = null; 119 size--; 120 modCount++; 121 return element; 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * Unlinks non-null node x. 126 */ 127 E unlink(Node<E> x) { 128 // assert x != null; 129 final E element = x.item; 130 final Node<E> next = x.next; 131 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; 132 133 if (prev == null) { 134 first = next; 135 } else { 136 prev.next = next; 137 x.prev = null; 138 } 139 140 if (next == null) { 141 last = prev; 142 } else { 143 next.prev = prev; 144 x.next = null; 145 } 146 147 x.item = null; 148 size--; 149 modCount++; 150 return element; 151 } 152 153 /** 154 * Returns the first element in this list. 155 * 156 * @return the first element in this list 157 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 158 */ 159 public E getFirst() { 160 final Node<E> f = first; 161 if (f == null) 162 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 163 return f.item; 164 } 165 166 /** 167 * Returns the last element in this list. 168 * 169 * @return the last element in this list 170 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 171 */ 172 public E getLast() { 173 final Node<E> l = last; 174 if (l == null) 175 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 176 return l.item; 177 } 178 179 /** 180 * Removes and returns the first element from this list. 181 * 182 * @return the first element from this list 183 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 184 */ 185 public E removeFirst() { 186 final Node<E> f = first; 187 if (f == null) 188 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 189 return unlinkFirst(f); 190 } 191 192 /** 193 * Removes and returns the last element from this list. 194 * 195 * @return the last element from this list 196 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 197 */ 198 public E removeLast() { 199 final Node<E> l = last; 200 if (l == null) 201 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 202 return unlinkLast(l); 203 } 204 205 /** 206 * Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. 207 * 208 * @param e the element to add 209 */ 210 public void addFirst(E e) { 211 linkFirst(e); 212 } 213 214 /** 215 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 216 * 217 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}. 218 * 219 * @param e the element to add 220 */ 221 public void addLast(E e) { 222 linkLast(e); 223 } 224 225 /** 226 * Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element. 227 * More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains 228 * at least one element {@code e} such that 229 * <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>. 230 * 231 * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested 232 * @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element 233 */ 234 public boolean contains(Object o) { 235 return indexOf(o) != -1; 236 } 237 238 /** 239 * Returns the number of elements in this list. 240 * 241 * @return the number of elements in this list 242 */ 243 public int size() { 244 return size; 245 } 246 247 /** 248 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 249 * 250 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. 251 * 252 * @param e element to be appended to this list 253 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 254 */ 255 public boolean add(E e) { 256 linkLast(e); 257 return true; 258 } 259 260 /** 261 * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, 262 * if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is 263 * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index 264 * {@code i} such that 265 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> 266 * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list 267 * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list 268 * changed as a result of the call). 269 * 270 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 271 * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element 272 */ 273 public boolean remove(Object o) { 274 if (o == null) { 275 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 276 if (x.item == null) { 277 unlink(x); 278 return true; 279 } 280 } 281 } else { 282 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 283 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 284 unlink(x); 285 return true; 286 } 287 } 288 } 289 return false; 290 } 291 292 /** 293 * Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of 294 * this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified 295 * collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if 296 * the specified collection is modified while the operation is in 297 * progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is 298 * this list, and it's nonempty.) 299 * 300 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 301 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 302 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 303 */ 304 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 305 return addAll(size, c); 306 } 307 308 /** 309 * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this 310 * list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element 311 * currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to 312 * the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear 313 * in the list in the order that they are returned by the 314 * specified collection's iterator. 315 * 316 * @param index index at which to insert the first element 317 * from the specified collection 318 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 319 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 320 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 321 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 322 */ 323 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 324 checkPositionIndex(index); 325 326 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 327 int numNew = a.length; 328 if (numNew == 0) 329 return false; 330 331 Node<E> pred, succ; 332 if (index == size) { 333 succ = null; 334 pred = last; 335 } else { 336 succ = node(index); 337 pred = succ.prev; 338 } 339 340 for (Object o : a) { 341 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; 342 Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); 343 if (pred == null) 344 first = newNode; 345 else 346 pred.next = newNode; 347 pred = newNode; 348 } 349 350 if (succ == null) { 351 last = pred; 352 } else { 353 pred.next = succ; 354 succ.prev = pred; 355 } 356 357 size += numNew; 358 modCount++; 359 return true; 360 } 361 362 /** 363 * Removes all of the elements from this list. 364 * The list will be empty after this call returns. 365 */ 366 public void clear() { 367 // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: 368 // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit 369 // more than one generation 370 // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator 371 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { 372 Node<E> next = x.next; 373 x.item = null; 374 x.next = null; 375 x.prev = null; 376 x = next; 377 } 378 first = last = null; 379 size = 0; 380 modCount++; 381 } 382 383 384 // Positional Access Operations 385 386 /** 387 * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. 388 * 389 * @param index index of the element to return 390 * @return the element at the specified position in this list 391 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 392 */ 393 public E get(int index) { 394 checkElementIndex(index); 395 return node(index).item; 396 } 397 398 /** 399 * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the 400 * specified element. 401 * 402 * @param index index of the element to replace 403 * @param element element to be stored at the specified position 404 * @return the element previously at the specified position 405 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 406 */ 407 public E set(int index, E element) { 408 checkElementIndex(index); 409 Node<E> x = node(index); 410 E oldVal = x.item; 411 x.item = element; 412 return oldVal; 413 } 414 415 /** 416 * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. 417 * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any 418 * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). 419 * 420 * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted 421 * @param element element to be inserted 422 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 423 */ 424 public void add(int index, E element) { 425 checkPositionIndex(index); 426 427 if (index == size) 428 linkLast(element); 429 else 430 linkBefore(element, node(index)); 431 } 432 433 /** 434 * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any 435 * subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). 436 * Returns the element that was removed from the list. 437 * 438 * @param index the index of the element to be removed 439 * @return the element previously at the specified position 440 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 441 */ 442 public E remove(int index) { 443 checkElementIndex(index); 444 return unlink(node(index)); 445 } 446 447 /** 448 * Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element. 449 */ 450 private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { 451 return index >= 0 && index < size; 452 } 453 454 /** 455 * Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an 456 * iterator or an add operation. 457 */ 458 private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { 459 return index >= 0 && index <= size; 460 } 461 462 /** 463 * Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message. 464 * Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code, 465 * this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs. 466 */ 467 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { 468 return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; 469 } 470 471 private void checkElementIndex(int index) { 472 if (!isElementIndex(index)) 473 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 474 } 475 476 private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { 477 if (!isPositionIndex(index)) 478 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 479 } 480 481 /** 482 * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. 483 */ 484 Node<E> node(int index) { 485 // assert isElementIndex(index); 486 487 if (index < (size >> 1)) { 488 Node<E> x = first; 489 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) 490 x = x.next; 491 return x; 492 } else { 493 Node<E> x = last; 494 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) 495 x = x.prev; 496 return x; 497 } 498 } 499 500 // Search Operations 501 502 /** 503 * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element 504 * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. 505 * More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that 506 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, 507 * or -1 if there is no such index. 508 * 509 * @param o element to search for 510 * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in 511 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 512 */ 513 public int indexOf(Object o) { 514 int index = 0; 515 if (o == null) { 516 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 517 if (x.item == null) 518 return index; 519 index++; 520 } 521 } else { 522 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 523 if (o.equals(x.item)) 524 return index; 525 index++; 526 } 527 } 528 return -1; 529 } 530 531 /** 532 * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element 533 * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. 534 * More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that 535 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, 536 * or -1 if there is no such index. 537 * 538 * @param o element to search for 539 * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in 540 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 541 */ 542 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 543 int index = size; 544 if (o == null) { 545 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 546 index--; 547 if (x.item == null) 548 return index; 549 } 550 } else { 551 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 552 index--; 553 if (o.equals(x.item)) 554 return index; 555 } 556 } 557 return -1; 558 } 559 560 // Queue operations. 561 562 /** 563 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. 564 * 565 * @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty 566 * @since 1.5 567 */ 568 public E peek() { 569 final Node<E> f = first; 570 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 571 } 572 573 /** 574 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. 575 * 576 * @return the head of this list 577 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 578 * @since 1.5 579 */ 580 public E element() { 581 return getFirst(); 582 } 583 584 /** 585 * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. 586 * 587 * @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty 588 * @since 1.5 589 */ 590 public E poll() { 591 final Node<E> f = first; 592 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 593 } 594 595 /** 596 * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. 597 * 598 * @return the head of this list 599 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 600 * @since 1.5 601 */ 602 public E remove() { 603 return removeFirst(); 604 } 605 606 /** 607 * Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list. 608 * 609 * @param e the element to add 610 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer}) 611 * @since 1.5 612 */ 613 public boolean offer(E e) { 614 return add(e); 615 } 616 617 // Deque operations 618 /** 619 * Inserts the specified element at the front of this list. 620 * 621 * @param e the element to insert 622 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst}) 623 * @since 1.6 624 */ 625 public boolean offerFirst(E e) { 626 addFirst(e); 627 return true; 628 } 629 630 /** 631 * Inserts the specified element at the end of this list. 632 * 633 * @param e the element to insert 634 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast}) 635 * @since 1.6 636 */ 637 public boolean offerLast(E e) { 638 addLast(e); 639 return true; 640 } 641 642 /** 643 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list, 644 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 645 * 646 * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} 647 * if this list is empty 648 * @since 1.6 649 */ 650 public E peekFirst() { 651 final Node<E> f = first; 652 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 653 } 654 655 /** 656 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list, 657 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 658 * 659 * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} 660 * if this list is empty 661 * @since 1.6 662 */ 663 public E peekLast() { 664 final Node<E> l = last; 665 return (l == null) ? null : l.item; 666 } 667 668 /** 669 * Retrieves and removes the first element of this list, 670 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 671 * 672 * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if 673 * this list is empty 674 * @since 1.6 675 */ 676 public E pollFirst() { 677 final Node<E> f = first; 678 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 679 } 680 681 /** 682 * Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, 683 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 684 * 685 * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if 686 * this list is empty 687 * @since 1.6 688 */ 689 public E pollLast() { 690 final Node<E> l = last; 691 return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); 692 } 693 694 /** 695 * Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other 696 * words, inserts the element at the front of this list. 697 * 698 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}. 699 * 700 * @param e the element to push 701 * @since 1.6 702 */ 703 public void push(E e) { 704 addFirst(e); 705 } 706 707 /** 708 * Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other 709 * words, removes and returns the first element of this list. 710 * 711 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}. 712 * 713 * @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top 714 * of the stack represented by this list) 715 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 716 * @since 1.6 717 */ 718 public E pop() { 719 return removeFirst(); 720 } 721 722 /** 723 * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this 724 * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list 725 * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. 726 * 727 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 728 * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element 729 * @since 1.6 730 */ 731 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { 732 return remove(o); 733 } 734 735 /** 736 * Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this 737 * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list 738 * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. 739 * 740 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 741 * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element 742 * @since 1.6 743 */ 744 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { 745 if (o == null) { 746 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 747 if (x.item == null) { 748 unlink(x); 749 return true; 750 } 751 } 752 } else { 753 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 754 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 755 unlink(x); 756 return true; 757 } 758 } 759 } 760 return false; 761 } 762 763 /** 764 * Returns a list-iterator of the elements in this list (in proper 765 * sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. 766 * Obeys the general contract of {@code List.listIterator(int)}.<p> 767 * 768 * The list-iterator is <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is structurally 769 * modified at any time after the Iterator is created, in any way except 770 * through the list-iterator's own {@code remove} or {@code add} 771 * methods, the list-iterator will throw a 772 * {@code ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of 773 * concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather 774 * than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined 775 * time in the future. 776 * 777 * @param index index of the first element to be returned from the 778 * list-iterator (by a call to {@code next}) 779 * @return a ListIterator of the elements in this list (in proper 780 * sequence), starting at the specified position in the list 781 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 782 * @see List#listIterator(int) 783 */ 784 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 785 checkPositionIndex(index); 786 return new ListItr(index); 787 } 788 789 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { 790 private Node<E> lastReturned = null; 791 private Node<E> next; 792 private int nextIndex; 793 private int expectedModCount = modCount; 794 795 ListItr(int index) { 796 // assert isPositionIndex(index); 797 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); 798 nextIndex = index; 799 } 800 801 public boolean hasNext() { 802 return nextIndex < size; 803 } 804 805 public E next() { 806 checkForComodification(); 807 if (!hasNext()) 808 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 809 810 lastReturned = next; 811 next = next.next; 812 nextIndex++; 813 return lastReturned.item; 814 } 815 816 public boolean hasPrevious() { 817 return nextIndex > 0; 818 } 819 820 public E previous() { 821 checkForComodification(); 822 if (!hasPrevious()) 823 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 824 825 lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; 826 nextIndex--; 827 return lastReturned.item; 828 } 829 830 public int nextIndex() { 831 return nextIndex; 832 } 833 834 public int previousIndex() { 835 return nextIndex - 1; 836 } 837 838 public void remove() { 839 checkForComodification(); 840 if (lastReturned == null) 841 throw new IllegalStateException(); 842 843 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; 844 unlink(lastReturned); 845 if (next == lastReturned) 846 next = lastNext; 847 else 848 nextIndex--; 849 lastReturned = null; 850 expectedModCount++; 851 } 852 853 public void set(E e) { 854 if (lastReturned == null) 855 throw new IllegalStateException(); 856 checkForComodification(); 857 lastReturned.item = e; 858 } 859 860 public void add(E e) { 861 checkForComodification(); 862 lastReturned = null; 863 if (next == null) 864 linkLast(e); 865 else 866 linkBefore(e, next); 867 nextIndex++; 868 expectedModCount++; 869 } 870 871 final void checkForComodification() { 872 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 873 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 874 } 875 } 876 877 private static class Node<E> { 878 E item; 879 Node<E> next; 880 Node<E> prev; 881 882 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { 883 this.item = element; 884 this.next = next; 885 this.prev = prev; 886 } 887 } 888 889 /** 890 * @since 1.6 891 */ 892 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { 893 return new DescendingIterator(); 894 } 895 896 /** 897 * Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous 898 */ 899 private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> { 900 private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size()); 901 public boolean hasNext() { 902 return itr.hasPrevious(); 903 } 904 public E next() { 905 return itr.previous(); 906 } 907 public void remove() { 908 itr.remove(); 909 } 910 } 911 912 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 913 private LinkedList<E> superClone() { 914 try { 915 return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone(); 916 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 917 throw new InternalError(); 918 } 919 } 920 921 /** 922 * Returns a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList}. (The elements 923 * themselves are not cloned.) 924 * 925 * @return a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList} instance 926 */ 927 public Object clone() { 928 LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); 929 930 // Put clone into "virgin" state 931 clone.first = clone.last = null; 932 clone.size = 0; 933 clone.modCount = 0; 934 935 // Initialize clone with our elements 936 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 937 clone.add(x.item); 938 939 return clone; 940 } 941 942 /** 943 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list 944 * in proper sequence (from first to last element). 945 * 946 * <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are 947 * maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate 948 * a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array. 949 * 950 * <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based 951 * APIs. 952 * 953 * @return an array containing all of the elements in this list 954 * in proper sequence 955 */ 956 public Object[] toArray() { 957 Object[] result = new Object[size]; 958 int i = 0; 959 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 960 result[i++] = x.item; 961 return result; 962 } 963 964 /** 965 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in 966 * proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of 967 * the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits 968 * in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new 969 * array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and 970 * the size of this list. 971 * 972 * <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e., 973 * the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array 974 * immediately following the end of the list is set to {@code null}. 975 * (This is useful in determining the length of the list <i>only</i> if 976 * the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.) 977 * 978 * <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between 979 * array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows 980 * precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may, 981 * under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs. 982 * 983 * <p>Suppose {@code x} is a list known to contain only strings. 984 * The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly 985 * allocated array of {@code String}: 986 * 987 * <pre> 988 * String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);</pre> 989 * 990 * Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to 991 * {@code toArray()}. 992 * 993 * @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to 994 * be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the 995 * same runtime type is allocated for this purpose. 996 * @return an array containing the elements of the list 997 * @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array 998 * is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in 999 * this list 1000 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null 1001 */ 1002 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 1003 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 1004 if (a.length < size) 1005 a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( 1006 a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); 1007 int i = 0; 1008 Object[] result = a; 1009 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1010 result[i++] = x.item; 1011 1012 if (a.length > size) 1013 a[size] = null; 1014 1015 return a; 1016 } 1017 1018 private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L; 1019 1020 /** 1021 * Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream 1022 * (that is, serializes it). 1023 * 1024 * @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it 1025 * contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its 1026 * elements (each an Object) in the proper order. 1027 */ 1028 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 1029 throws java.io.IOException { 1030 // Write out any hidden serialization magic 1031 s.defaultWriteObject(); 1032 1033 // Write out size 1034 s.writeInt(size); 1035 1036 // Write out all elements in the proper order. 1037 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1038 s.writeObject(x.item); 1039 } 1040 1041 /** 1042 * Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream 1043 * (that is, deserializes it). 1044 */ 1045 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 1046 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 1047 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 1048 // Read in any hidden serialization magic 1049 s.defaultReadObject(); 1050 1051 // Read in size 1052 int size = s.readInt(); 1053 1054 // Read in all elements in the proper order. 1055 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 1056 linkLast((E)s.readObject()); 1057 } 1058 }
总结:
(01) LinkedList 实际上是通过双向链表去实现的。
它包含一个非常重要的内部类:Entry。Entry是双向链表节点所对应的数据结构,它包括的属性有:当前节点所包含的值,上一个节点,下一个节点。
(02) 从LinkedList的实现方式中可以发现,它不存在LinkedList容量不足的问题。
(03) LinkedList的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个新的LinkedList对象中。
(04) LinkedList实现java.io.Serializable。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写入“每一个节点保护的值”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
(05) 由于LinkedList实现了Deque,而Deque接口定义了在双端队列两端访问元素的方法。提供插入、移除和检查元素的方法。每种方法都存在两种形式:一种形式在操作失败时抛出异常,另一种形式返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。
总结起来如下表格:
第一个元素(头部) 最后一个元素(尾部)
抛出异常 特殊值 抛出异常 特殊值
插入 addFirst(e) offerFirst(e) addLast(e) offerLast(e)
移除 removeFirst() pollFirst() removeLast() pollLast()
检查 getFirst() peekFirst() getLast() peekLast()
(06) LinkedList可以作为FIFO(先进先出)的队列,作为FIFO的队列时,下表的方法等价:
队列方法 等效方法
add(e) addLast(e)
offer(e) offerLast(e)
remove() removeFirst()
poll() pollFirst()
element() getFirst()
peek() peekFirst()
(07) LinkedList可以作为LIFO(后进先出)的栈,作为LIFO的栈时,下表的方法等价:
栈方法 等效方法
push(e) addFirst(e)
pop() removeFirst()
peek() peekFirst()
- 增
- addFirst(e)和offerFirst(e): 查的, 说addXxx是继承自List的, offerXxx是来自Queue.
- addLast(e)和offerLast(e)
- 获取: 获取,但不删除元素。
- getFirst()和peakFirst(): 如果集合为空, 前者抛异常, 后者获取null.
- getLast()和peakLast(): 同上
- 删: 获取,且删除元素。
- removeFirst()和pollFirst(): 如果集合为空, 前者抛异常, 后者获取null.
- remove()和poll(): 同上
- removeLast()和pollLast(): 同上
第4部分 LinkedList遍历方式
LinkedList遍历方式
LinkedList支持多种遍历方式。建议不要采用随机访问的方式去遍历LinkedList,而采用逐个遍历的方式。
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) iter.next();
(02) 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
int size = list.size(); for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { list.get(i); }
(03) 通过另外一种for循环来遍历LinkedList
for (Integer integ:list) ;
(04) 通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList
while(list.pollFirst() != null) ;
(05) 通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList
while(list.pollLast() != null) ;
(06) 通过removeFirst()来遍历LinkedList
try { while(list.removeFirst() != null) ; } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { }
(07) 通过removeLast()来遍历LinkedList
try { while(list.removeLast() != null) ; } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { }
测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下:
1 /** 2 * linkedList 3 * @ClassName: LinkedList_test_1 4 * @Description: 5 * @author Xingle 6 * @date 2014-5-20 上午9:48:33 7 * 8 */ 9 public class LinkedList_test_1 { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 13 // 通过Iterator遍历LinkedList 14 iteratorLinkedListThruIterator((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 15 // 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList 16 iteratorLinkedListThruForeach((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 17 // 通过for循环的变种来访问遍历LinkedList 18 iteratorThroughFor2((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 19 // 通过PollFirst()遍历LinkedList 20 iteratorThroughPollFirst((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 21 // 通过PollLast()遍历LinkedList 22 iteratorThroughPollLast((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 23 // 通过removeFirst()遍历LinkedList 24 iteratorThroughRemoveFirst((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 25 // 通过removeLast()遍历LinkedList 26 iteratorThroughRemoveLast((LinkedList<Integer>) getLinkedList()); 27 } 28 29 /** 30 * 通过RemoveLast()来遍历LinkedList 31 * @param 32 * @return 33 * @author xingle 34 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:59:11 35 */ 36 private static void iteratorThroughRemoveLast(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 37 String name = "iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:"; 38 if (list == null) 39 return; 40 long start = getCurrentTime(); 41 try { 42 while (list.removeLast() != null) 43 ; 44 } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { 45 46 } 47 long end = getCurrentTime(); 48 long interval = end - start; 49 getPrint(name, interval); 50 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * 通过RemoveFirst()来遍历LinkedList 55 * @param 56 * @return 57 * @author xingle 58 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:58:36 59 */ 60 private static void iteratorThroughRemoveFirst(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 61 String name = "iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:"; 62 if (list == null) 63 return; 64 long start = getCurrentTime(); 65 try { 66 while (list.removeFirst() != null) 67 ; 68 } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { 69 } 70 long end = getCurrentTime(); 71 long interval = end - start; 72 getPrint(name, interval); 73 74 } 75 76 77 78 /** 79 * 通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList 80 * @param 81 * @return 82 * @author xingle 83 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:57:37 84 */ 85 private static void iteratorThroughPollLast(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 86 String name = "iteratorThroughPollLast:"; 87 if (list == null) 88 return; 89 long start = getCurrentTime(); 90 while (list.pollLast() != null) 91 ; 92 long end = getCurrentTime(); 93 long interval = end - start; 94 getPrint(name, interval); 95 96 } 97 98 /** 99 * 通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList 100 * @param 101 * @return 102 * @author xingle 103 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:48:59 104 */ 105 private static void iteratorThroughPollFirst(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 106 String name = "iteratorThroughPollFirst:"; 107 if (list == null) 108 return; 109 long start = getCurrentTime(); 110 while (list.pollFirst() != null) 111 ; 112 long end = getCurrentTime(); 113 long interval = end - start; 114 getPrint(name, interval); 115 } 116 117 /** 118 * 119 * @Description: 120 * @param 121 * @return 122 * @author xingle 123 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:54:10 124 */ 125 private static void getPrint(String name, long interval) { 126 System.out.println(name + interval + " ms"); 127 128 } 129 130 /** 131 * 获取当前时间 132 * @Description: 133 * @param 134 * @return 135 * @author xingle 136 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:50:29 137 */ 138 private static long getCurrentTime() { 139 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 140 return start; 141 } 142 143 /** 144 * 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList 145 * 146 * @Description: 147 * @param 148 * @return 149 * @author xingle 150 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:32:33 151 */ 152 private static void iteratorThroughFor2(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 153 String name = "iteratorLinkedListByForeachRandomAccess:"; 154 if (list == null) 155 return; 156 long start = getCurrentTime(); 157 int size = list.size(); 158 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 159 list.get(i); 160 } 161 long end = getCurrentTime(); 162 long interval = end - start; 163 getPrint(name, interval); 164 } 165 166 /** 167 * 通过另外一种for循环来遍历LinkedList 168 * 169 * @Description: 170 * @param 171 * @return 172 * @author xingle 173 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:32:31 174 */ 175 private static void iteratorLinkedListThruForeach(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 176 String name = "iteratorThroughForEach:"; 177 if (list == null) 178 return; 179 long start = getCurrentTime(); 180 for (Integer i : list) 181 ; 182 long end = getCurrentTime(); 183 long interval = end - start; 184 getPrint(name, interval); 185 } 186 187 /** 188 * 通过快迭代器遍历LinkedList 189 * 190 * @Description: 191 * @param 192 * @return 193 * @author xingle 194 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:32:23 195 */ 196 private static void iteratorLinkedListThruIterator(LinkedList<Integer> list) { 197 String name = "iteratorLinkedListThruIterator:"; 198 if (list == null) 199 return; 200 long start = getCurrentTime(); 201 202 for (Iterator<Integer> iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) 203 iter.next(); 204 long end = getCurrentTime(); 205 long interval = end - start; 206 getPrint(name, interval); 207 } 208 209 /** 210 * 211 * @Description: 212 * @param 213 * @return 214 * @author xingle 215 * @data 2014-5-22 上午11:31:58 216 */ 217 private static Object getLinkedList() { 218 LinkedList<Integer> ls = new LinkedList<>(); 219 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) 220 ls.addLast(i); 221 222 return ls; 223 } 224 225 }
执行结果:
iteratorLinkedListThruIterator:13 ms
iteratorThroughForEach:9 ms
iteratorLinkedListByForeachRandomAccess:6886 ms
iteratorThroughPollFirst:7 ms
iteratorThroughPollLast:7 ms
iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:5 ms
iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:5 ms
由此可见,遍历LinkedList时,使用removeFist()或removeLast()效率最高。但用它们遍历时,会删除原始数据;若单纯只读取,而不删除,应该使用第3种遍历方式。
无论如何,千万不要通过随机访问去遍历LinkedList!
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308807.html





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号