JS面向对象高级特性
本篇是通过学习视频《一头扎进javascirpt高级篇》整理的一些相关知识,大致包括下面几个方面:
1 对象的创建方法
2 对象的对象属性、私有属性、类属性
3 对象的对象方法、私有方法、类方法
4 javascirpt的继承、封装、与多态
对象的创建方法:
对象的创建可以通过两种方式,第一种通过对象初始化的方法:
var person={ name:"xingoo", age:26, say:function(){ console.log("say something"); }, action:function(){ console.log("do something"); } }; console.log(person.name); console.log(person.age); person.say(); person.action();
第二种方式通过构造函数创建:
function student(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; this.say = function(){ console.log("say something"); } this.action = function(){ console.log("do something"); } } var xingoo = new student("xingoo",27); console.log(xingoo.name); console.log(xingoo.age); xingoo.say(); xingoo.action();
对象的属性
对象的属性分为对象属性、私有属性和类属性。
对象属性需要创建对象后才能使用;
私有属性在内部可以直接使用,在外部需要通过闭包才能使用。
类属性可以通过对象名称直接使用。
function func(){ this.objPro1 = "对象属性"; func.prototype.objPro2 = "对象属性"; var privatePro = "私有属性"; } func.classPro = "类属性"; console.log(func.classPro); var f = new func(); console.log(f.objPro1); console.log(f.objPro2); <!-- 私有属性可以通过闭包获取 -->
对象的方法
对象方法包括:对象方法,私有方法和类方法,使用类似前面的属性。
function demoFunc1(){ var privateFunc = function(){ console.log("this is privateFunc"); }; privateFunc(); this.objFunc1 = function(){ console.log("this is objFunc1"); }; demoFunc1.prototype.objFunc2 = function(){ console.log("this is objFunc2"); }; } demoFunc1.classFunc = function(){ console.log("this is classFunc"); }; demoFunc1.classFunc(); var f = new demoFunc1(); f.objFunc1(); f.objFunc2();
继承、封装与多态
JS要想实现继承,需要通过apply方法或者prototype实现。
如果单纯的使用apply方法,子类的原型是子类;如果使用prototype,那么子类的原型也将继承父类。
例如下面的代码:
function Animal(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age =age; this.say = function(){ console.log("animal say something"); } } function Cat(name,age){ Animal.apply(this,[name,age]); } <!-- Cat.prototype = new Animal();--> var cat1 = new Cat("xingoo",3); console.log(cat1.name); console.log(cat1.age); cat1.say();
上面代码中,cat的原型是cat;
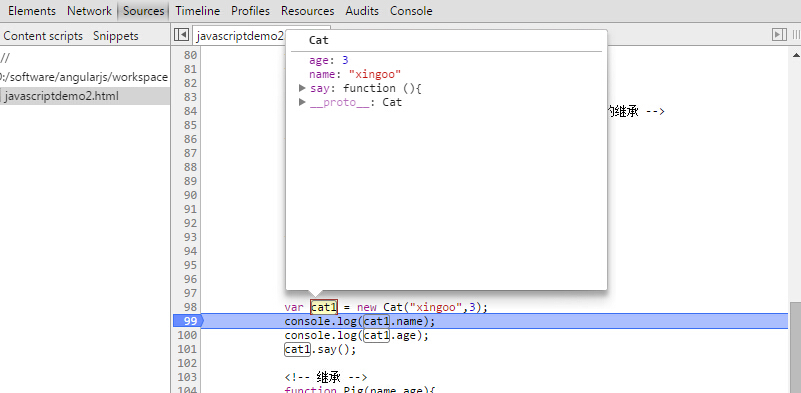
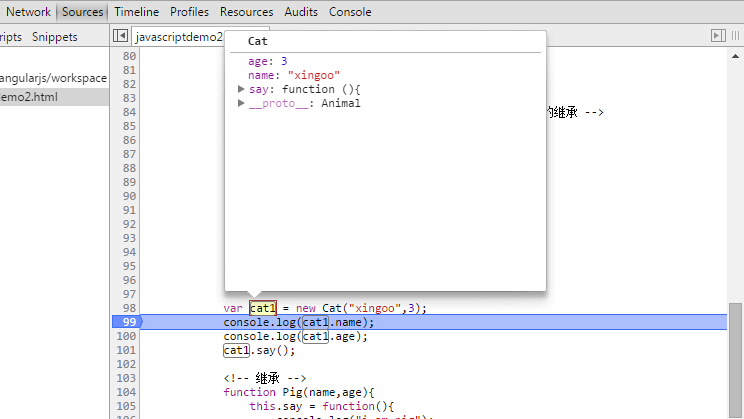
如果开启注释的部分,可以发现,cat类的原型也变成了Animal。
子类的方法会覆盖父类的方法,即表现出多态性:
function Pig(name,age){ this.say = function(){ console.log("i am pig"); } } Pig.prototype = new Animal(); function Dog(name,age){ this.say = function(){ console.log("i am dog"); } } Dog.prototype = new Animal(); function say(animal){ if(animal instanceof Animal){ animal.say(); } } var dog = new Dog(); var pig = new Pig(); say(dog); say(pig);
使用到的全部代码:

<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
<!-- 对象初始化器方式 -->
var person={
name:"xingoo",
age:26,
say:function(){
console.log("say something");
},
action:function(){
console.log("do something");
}
};
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
person.say();
person.action();
<!-- 构造函数方式 -->
function student(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("say something");
}
this.action = function(){
console.log("do something");
}
}
var xingoo = new student("xingoo",27);
console.log(xingoo.name);
console.log(xingoo.age);
xingoo.say();
xingoo.action();
<!-- 对象属性 私有属性,对象属性,类属性 -->
function func(){
this.objPro1 = "对象属性";
func.prototype.objPro2 = "对象属性";
var privatePro = "私有属性";
}
func.classPro = "类属性";
console.log(func.classPro);
var f = new func();
console.log(f.objPro1);
console.log(f.objPro2);
<!-- 私有属性可以通过闭包获取 -->
<!-- 私有方法,对象方法,类方法 -->
function demoFunc1(){
var privateFunc = function(){
console.log("this is privateFunc");
};
privateFunc();
this.objFunc1 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc1");
};
demoFunc1.prototype.objFunc2 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc2");
};
}
demoFunc1.classFunc = function(){
console.log("this is classFunc");
};
demoFunc1.classFunc();
var f = new demoFunc1();
f.objFunc1();
f.objFunc2();
<!-- 封装性,继承性,多态性 -->
<!-- apply()实现属性和方法的集成,prototype实现原型的继承 -->
function Animal(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age =age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("animal say something");
}
}
function Cat(name,age){
Animal.apply(this,[name,age]);
}
<!-- Cat.prototype = new Animal();-->
var cat1 = new Cat("xingoo",3);
console.log(cat1.name);
console.log(cat1.age);
cat1.say();
<!-- 继承 -->
function Pig(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am pig");
}
}
Pig.prototype = new Animal();
function Dog(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am dog");
}
}
Dog.prototype = new Animal();
function say(animal){
if(animal instanceof Animal){
animal.say();
}
}
var dog = new Dog();
var pig = new Pig();
say(dog);
say(pig);
</script>
</body>
</html>
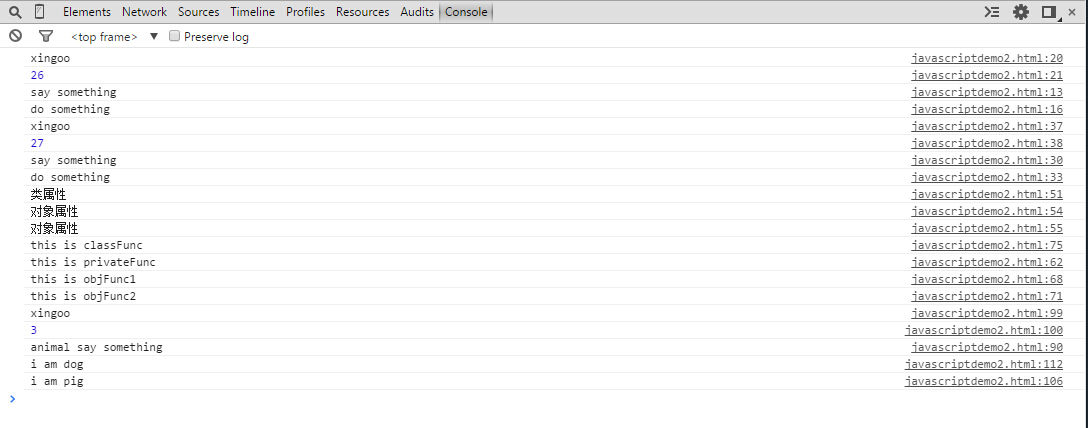
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号