基于mykernel 2.0编写一个操作系统内核
2020-05-12 14:59 微光~ 阅读(175) 评论(0) 收藏 举报实验准备(参考https://github.com/mengning/mykernel)
实验要求:
- 按照https://github.com/mengning/mykernel 的说明配置mykernel 2.0,熟悉Linux内核的编译;
- 基于mykernel 2.0编写一个操作系统内核,参照https://github.com/mengning/mykernel 提供的范例代码
- 简要分析操作系统内核核心功能及运行工作机制
实验环境:
Ubuntu版本:ubuntu-18.04.4-desktop-amd64
配置mykernel 2.0
配置命令:
在ubuntu虚拟机中,打开终端,输入如下指令:
wget https://raw.github.com/mengning/mykernel/master/mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch sudo apt install axel axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz //解压 tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar cd linux-5.4.34 patch -p1 < ../mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch sudo apt install build-essential libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev make defconfig 10 make -j$(nproc) sudo apt install qemu 12 qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
配置成功后结果如下,从qemu窗口中可以看到my_start_kernel在执行:
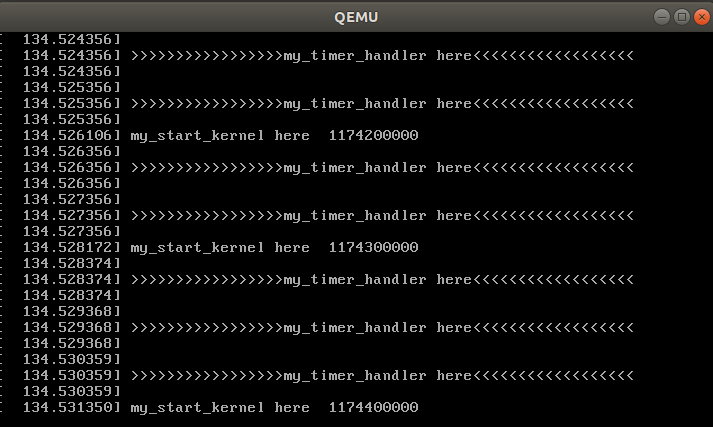
同时my_timer_handler时钟中断处理程序周期性执行,my_start_kernel是在mymain.c中循环运行的输出,因为是while(1),它将不断运行输出。
编写内核
1. 首先在mykernel目录下增加一个mypcb.h头文件,用来定义进程控制块(Process Control Block),也就是进程结构体的定义。
主要有进程号、进程状态、分配存储区、保存进程的现场、进程入口等。
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4 #define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*2 /* CPU-specific state of this task */ struct Thread { unsigned long ip; unsigned long sp; }; typedef struct PCB{ int pid; volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ unsigned long stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE]; /* CPU-specific state of this task */ struct Thread thread; unsigned long task_entry; struct PCB *next; }tPCB; void my_schedule(void);
2. 对mymain.c中的my_start_kernel函数进行修改,并在mymain.c中实现了my_process函数,用来作为进程的代码模拟一个个进程,时间片轮转调度。
#include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/string.h> #include <linux/ctype.h> #include <linux/tty.h> #include <linux/vmalloc.h> #include "mypcb.h" tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM]; tPCB * my_current_task = NULL; volatile int my_need_sched = 0; void my_process(void); void __init my_start_kernel(void) { int pid = 0; int i; /* Initialize process 0*/ task[pid].pid = pid; task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process; task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]; task[pid].next = &task[pid]; /*fork more process */ for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++) { memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB)); task[i].pid = i; task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)(&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]); task[i].next = task[i-1].next; task[i-1].next = &task[i]; } /* start process 0 by task[0] */ pid = 0; my_current_task = &task[pid]; asm volatile( "movq %1,%%rsp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to rsp */ "pushq %1\n\t" /* push rbp */ "pushq %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */ "ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to rip */ : : "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/ ); } int i = 0; void my_process(void) { while(1) { i++; if(i%10000000 == 0) { printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -\n",my_current_task->pid); if(my_need_sched == 1) { my_need_sched = 0; my_schedule(); } printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +\n",my_current_task->pid); } } }
在my_process函数的while循环里面可见,会不断检测全局变量my_need_sched的值,当my_need_sched的值从0变成1的时候,就需要发生进程调度,全局变量my_need_sched重新置为0,执行my_schedule()函数进行进程切换。
3.对myinterrupt.c的修改,my_timer_handler用来记录时间片,时间片消耗完之后完成调度。并在该文件中完成,my_schedule(void)函数的实现
#include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/string.h> #include <linux/ctype.h> #include <linux/tty.h> #include <linux/vmalloc.h> #include "mypcb.h" extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM]; extern tPCB * my_current_task; extern volatile int my_need_sched; volatile int time_count = 0; /* * Called by timer interrupt. * it runs in the name of current running process, * so it use kernel stack of current running process */ void my_timer_handler(void) { if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1) { printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<\n"); my_need_sched = 1; } time_count ++ ; return; } void my_schedule(void) { tPCB * next; tPCB * prev; if(my_current_task == NULL || my_current_task->next == NULL) { return; } printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<\n"); /* schedule */ next = my_current_task->next; prev = my_current_task; if(next->state == 0)/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ { my_current_task = next; printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<\n",prev->pid,next->pid); /* switch to next process */ asm volatile( "pushq %%rbp\n\t" /* save rbp of prev */ "movq %%rsp,%0\n\t" /* save rsp of prev */ "movq %2,%%rsp\n\t" /* restore rsp of next */ "movq $1f,%1\n\t" /* save rip of prev */ "pushq %3\n\t" "ret\n\t" /* restore rip of next */ "1:\t" /* next process start here */ "popq %%rbp\n\t" : "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip) : "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip) ); } return; }
4.重新编译运行内核后,效果如下图所示
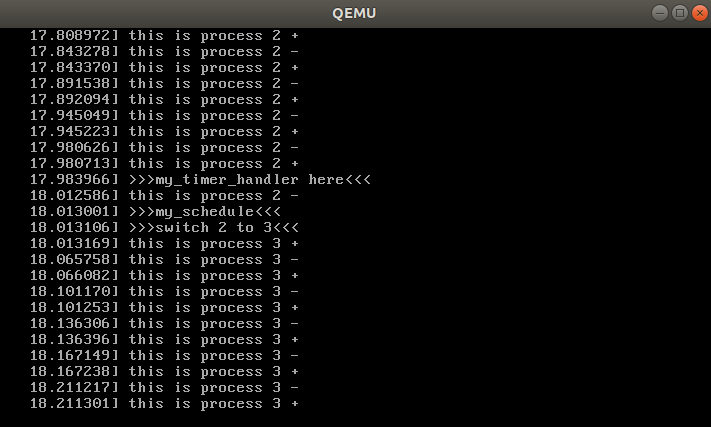
简要分析操作系统内核核心功能及运行工作机制
操作系统运行工作机制:操作系统中的进程在执⾏过程中,当进程的一个时间⽚⽤完操作系统需要进⾏进程切换时,需要先保存当前的进程上下⽂环境,下次进程被调度执⾏时,需要恢复进程上下⽂环境。我们通过Linux内核代码模拟 了⼀个具有时钟中断和C代码执⾏环境的硬件平台,mymain.c中的代码在不停地执⾏。同时有⼀个中断处理程序的上下⽂环境,周期性地产⽣的时钟中断信号,能够触发myinterrupt.c中的代码,产生进程切换。

asm volatile( "pushq %%rbp\n\t" /* save rbp of prev */ "movq %%rsp,%0\n\t" /* save rsp of prev */ "movq %2,%%rsp\n\t" /* restore rsp of next */ "movq $1f,%1\n\t" /* save rip of prev */ "pushq %3\n\t" "ret\n\t" /* restore rip of next */ "1:\t" /* next process start here */ "popq %%rbp\n\t" : "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip) : "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip) );
pushq %%rbp: 保存prev进程当前RBP寄存器的值到堆栈;
movq %%rsp,%0 :保存prev进程当前RSP寄存器的值到prev->thread.sp,这时RSP寄存器指向进程的栈顶地址,实际上就是将prev进程的栈顶地址保存;
movq %2,%%rsp: 将next进程的栈顶地址next->thread.sp放⼊RSP寄存器,完成了进程0和进程1的堆栈切换。
movq $1f,%1 :保存prev进程当前RIP寄存器值到prev->thread.ip,这⾥$1f是指标号1。
pushq %3 :把即将执⾏的next进程的指令地址next->thread.ip⼊栈,这时的next->thread.ip可能是进程1的起点my_process(void)函数,也可能是$1f(标号1)。第⼀次被执⾏从头开始为进程1的起点my_process(void)函数,其余的情况均为$1f(标号1),因为next进程如果之前运⾏过那么它就⼀定曾经也作为prev进程被进程切换过。rip寄存器程序员没有权限进行写入,需要多一个步骤
ret :就是将压⼊栈中的next->thread.ip放⼊RIP寄存器,
1: 标号1是⼀个特殊的地址位置,该位置的地址是$1f。
popq %%rbp :将next进程堆栈基地址从堆栈中恢复到RBP寄存器中。
自此,就完成了进程与进程的切换,其他两个相邻进程的切换过程也和这个相同。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号