MindSpore Reduce Sum 算子
简介
通过阅读文档,我们可以知道:Reduce Sum 规约和算子,作用是对向量元素求和,默认情况下是将整个向量进行求和,还可以指定维度进行规约。
例子:
import numpy as np
import mindspore
import mindspore.ops as ops
from mindspore import Tensor
x = Tensor(np.random.randn(3, 4, 5, 6).astype(np.float32))
op = ops.ReduceSum(keep_dims=True)
output = op(x, 1)
output.shape
# case 1: Reduces a dimension by summing all elements in the dimension.
x = Tensor(np.array([[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]],
[[4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4], [5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6]],
[[7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7], [8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8], [9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9]]]), mindspore.float32)
output = op(x)
print(output)
print(output.shape)
# case 2: Reduces a dimension along axis 0.
output = op(x, 0)
print(output)
# case 3: Reduces a dimension along axis 1.
output = op(x, 1)
print(output)
# case 4: Reduces a dimension along axis 2.
output = op(x, 2)
print(output)
# case 5: Reduces a dimension along axis 0, 2.
output = op(x, (0, 2))
print(output)
# case 6: Reduces a dimension along axis 0, 1.
output = op(x, [0, 1])
print(output)
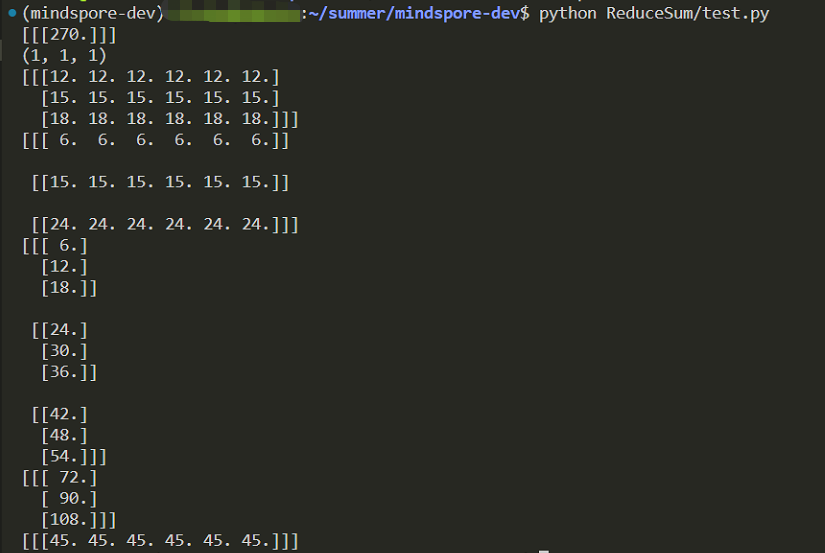
输出结果:
实现思路
Reduce Sum 算子和其他 Reduce 算子一样,使用同一个 CPU Reduce Kernel 计算出来的。
计算逻辑
第一,抽象出基本操作,比如规约求和的基本操作定义如下,给定输入和位置,将计算结果放到输出。
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out += input[pos]; };
第二,整体的计算逻辑分为了两种情况讨论,并且引入了两种优化。第一种情况是规约所有元素,直接遍历所有元素调用基本操作,引入的优化是长向量优化。第二种情况是老老实实算,针对二维矩阵且规约维度为第 1 维度的情况,引入了 AVX 指令集优化。
那么如何老老实实计算呢?首先是预处理,将需要规约的维度放到后面,比如 (x0, x1, a0, x3, a1) 变成 (x0, x1, x3, a0, a1),然后用这个新的维度去 transpose。使用 a0 x a1 作为 stride,然后每 stride 个元素进行规约,最后得到的输出大小是 (x0, x1, x3, 1, 1)。
1. 预处理
预处理给后续的 TransposeIterator 用的数据,方便计算下标。
// Calculate transpose axes and stride
int dimension = input_shape_.size();
size_t stride = 1;
std::vector<size_t> axes(input_shape_.size());
size_t j = 0;
size_t k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; ++i) {
if (j == axis_.size() || i != axis_[j]) {
axes[k] = i;
++k;
} else {
stride *= input_shape_[i];
++j;
}
}
for (auto &it : axis_) {
axes[k] = it;
++k;
}
// 以上过程的一个运算例子
// 输入的 input_shape_: [3, 2, 4, 5], axis_: [0, 2]
// 运算过程:
// i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; false[0 == 2] || false[0 != 0]; stride = 3
// i = 1, j = 1, k = 0; false[1 == 2] || true[1 != 2]; axes[0] = 1
// i = 2, j = 1, k = 1; true[1 == 2] || false[2 != 2]; stride = 12
// i = 3, j = 2, k = 1; true[2 == 2] || ?; axes[1] = 3
// 输出的 axes: [1, 3, 0, 2], stride = 12
2. 计算
使用 ParallelLaunchAutoSearch 自动并行,将 0 ~ output_size 切分成多个小任务,每个任务处理 start 到 end 之间的元素,借助 TransposeIterator 可以很方便找到需要规约的元素的下标。
std::vector<size_t> transpose_shape(input_shape_.size());
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; ++i) {
transpose_shape[i] = input_shape_[axes[i]];
}
TransposeIterator base_iter(std::move(transpose_shape), std::move(axes), input_shape_);
auto task = [this, &base_iter, input_addr, output_addr, stride](size_t start, size_t end) {
auto iter = base_iter;
iter.SetPos(start * stride);
for (size_t i = start; i < end; ++i) {
// output_addr 指向第一个元素
output_addr[i] = input_addr[iter.GetPos()];
iter.GenNextPos();
// 剩下的元素调用规约函数迭代计算即可
for (size_t j = 1; j < stride; ++j) {
reduce_func_(input_addr, iter.GetPos(), &output_addr[i]);
iter.GenNextPos();
}
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
output_addr[i] /= stride;
}
}
};
ParallelLaunchAutoSearch(task, output_size, this, ¶llel_search_info_);
优化
MindSpore 在实现 Reduce 算子的时候,针对一些特殊情况做了针对性优化。
优化1:长向量
一,针对规约所有元素且是长向量(元素个数大于 200000)的情况,使用自动并行来加速,其中需要加锁避免访问冲突。对于小向量,在计算的时候,直接单线程计算规约。
/**
AccelerateLongVector 为长向量专门优化:
使用 ParallelLaunchAutoSearch 自动并行,需要加锁避免可能存在的数据冲突
需要注意 AccelerateLongVector 只能对规约所有元素使用
在对小向量计算的时候,是单线程的;长向量是自动并行,多线程的。
*/
template <typename T>
void ReduceCpuKernelFunc<T>::AccelerateLongVector(T *input_addr, T *output_addr, size_t input_size) {
// init output_addr
*output_addr = input_addr[0];
std::mutex task_mutex;
auto task = [this, input_addr, output_addr, &task_mutex](size_t start, size_t end) {
// 跳过第 0 号元素,因为 output_addr 的初值设置为了 input_addr[0]
if (start == 0) {
++start;
}
if (start == end) {
return;
}
auto block_output = input_addr[start];
size_t i = start + 1;
while (i < end) {
reduce_func_(input_addr, i, &block_output);
++i;
}
{
// 将结果汇总到 output_addr,这里是规约了所有元素,所以 output_addr 只有一个元素
// 因此在访问同一个位置的时候,需要加锁
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> task_lock(task_mutex);
reduce_func_(&block_output, 0, output_addr);
}
};
ParallelLaunchAutoSearch(task, input_size, this, ¶llel_search_info_);
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
*output_addr /= input_size;
}
}
优化2:AVX 指令
二,针对规约 axis=1,input_shape.size=2 的情况:可以理解为二维矩阵按照行压成一维,利用了 AVX 指令加速计算。
// [A, B] -> [A]
int ReduceSumDim2Axis1(size_t col_len, const float *src_data, float *dst_data) {
if (src_data == NULL || dst_data == NULL) {
return NNACL_NULL_PTR;
}
size_t k = 0;
float tmp = 0;
#ifdef ENABLE_AVX
size_t block_mod = col_len % C8NUM;
size_t block_c8 = col_len - block_mod;
float tmp_arr[8] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
MS_FLOAT32X8 tmp_arr_8 = MS_MOV256_F32(tmp_arr[0]);
for (; k < block_c8; k += C8NUM) {
MS_FLOAT32X8 src_in = MS_LD256_F32(src_data + k);
tmp_arr_8 = MS_ADD256_F32(tmp_arr_8, src_in);
}
MS_ST256_F32(tmp_arr, tmp_arr_8);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
tmp += tmp_arr[i];
}
#endif
for (; k < col_len; k++) {
tmp += src_data[k];
}
dst_data[0] = tmp;
return NNACL_OK;
}
完整代码评注
/**
* Copyright 2021-2022 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#include "plugin/device/cpu/kernel/reduce_cpu_kernel.h"
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <utility>
#include <map>
#include "nnacl/fp32/reduce_fp32.h"
namespace mindspore {
namespace kernel {
namespace {
constexpr size_t kReduceSmallVectorSize = 200000;
constexpr size_t kReduceInputsNum = 1;
constexpr size_t kReduceOutputsNum = 1;
constexpr auto kReduceMeanName = "ReduceMean";
constexpr auto kReduceMaxName = "ReduceMax";
constexpr auto kReduceSumName = "ReduceSum";
constexpr auto kReduceMinName = "ReduceMin";
constexpr auto kReduceProdName = "ReduceProd";
constexpr auto kReduceAllName = "ReduceAll";
constexpr auto kReduceAnyName = "ReduceAny";
/**
提供统一的基类 Reduce,根据不同的 Reduce 类型进行特化
InitFunc 方法用于初始化相关参数,比如输入的 shape,axis,reduce_type,对应的函数等
RunFunc 执行 Kernel 的计算。
AccelerateLongVector 针对长向量做了针对性的优化
*/
template <typename T>
class ReduceCpuKernelFunc : public CpuKernelFunc {
public:
ReduceCpuKernelFunc() = default;
~ReduceCpuKernelFunc() override = default;
void InitFunc(const CNodePtr &kernel_node) override;
bool RunFunc(const std::vector<AddressPtr> &inputs, const std::vector<AddressPtr> &workspace,
const std::vector<AddressPtr> &outputs) override;
private:
void AccelerateLongVector(T *input_addr, T *output_addr, size_t input_size);
enum class ReduceFuncType {
kReduceAllType,
kReduceAnyType,
kReduceMaxType,
kReduceMinType,
kReduceSumType,
kReduceMeanType,
kReduceProdType
};
std::vector<size_t> input_shape_;
std::vector<int64_t> axis_;
ReduceFuncType reduce_type_{ReduceFuncType::kReduceAllType};
std::function<void(const T *, size_t, T *)> reduce_func_;
bool simple_execute_{false};
std::string kernel_name_;
};
/**
更新输入的参数 axis 为用户指定的需要保留规约的维度
*/
void UpdateAxis(const PrimitivePtr &prim, const CNodePtr &kernel_node, const std::string &kernel_name,
std::vector<int64_t> *axis) {
auto axis_addr = prim->GetAttr(AXIS);
if (axis == nullptr) {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "For '" << kernel_name << "', the 'axis' should be not null.";
}
if (axis_addr == nullptr) {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "For '" << kernel_name << "', the 'axis' should be not null, but got empty value.";
}
if (axis_addr->isa<ValueTuple>() || axis_addr->isa<ValueList>()) {
*axis = common::AnfAlgo::GetNodeAttr<std::vector<int64_t>>(kernel_node, AXIS);
} else if (axis_addr->isa<Int64Imm>()) {
(void)axis->emplace_back(common::AnfAlgo::GetNodeAttr<int64_t>(kernel_node, AXIS));
} else {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "For '" << kernel_name
<< "', the type of 'axis' should be tuple, list, or int, but got invalid type.";
}
}
template <typename T>
void ReduceCpuKernelFunc<T>::InitFunc(const CNodePtr &kernel_node) {
MS_EXCEPTION_IF_NULL(kernel_node);
kernel_name_ = common::AnfAlgo::GetCNodeName(kernel_node);
axis_.clear();
input_shape_ = AnfAlgo::GetInputDeviceShape(kernel_node, 0);
auto prim = common::AnfAlgo::GetCNodePrimitive(kernel_node);
MS_EXCEPTION_IF_NULL(prim);
UpdateAxis(prim, kernel_node, kernel_name_, &axis_);
size_t dimension = input_shape_.size();
// 这意味着输入 axis 有效范围只能在 [-dimension, dimension-1] 之间
(void)std::transform(axis_.begin(), axis_.end(), axis_.begin(),
[dimension](const auto &a) { return a < 0 ? dimension + a : a; });
// 为了后面可以取出重复元素,先排序,这样相同的元素就会连续放置,所以可以使用 unique
sort(axis_.begin(), axis_.end());
// Delete the duplicate axis.
auto last = std::unique(axis_.begin(), axis_.end());
axis_.erase(last, axis_.end());
auto kernel_name = common::AnfAlgo::GetCNodeName(kernel_node);
if constexpr (std::is_same<T, bool>::value) {
if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceAll->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceAllType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out &= input[pos]; };
} else if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceAny->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceAnyType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out |= input[pos]; };
} else {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "For '" << kernel_name_ << "', unsupported reduce operation for bool.";
}
} else {
if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceMax->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceMaxType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out = std::max(input[pos], *out); };
} else if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceMin->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceMinType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out = std::min(input[pos], *out); };
} else if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceSum->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceSumType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out += input[pos]; };
} else if (kernel_name_ == prim::kPrimReduceMean->name()) {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out += input[pos]; };
} else if (kernel_name == "ReduceProd") {
reduce_type_ = ReduceFuncType::kReduceProdType;
reduce_func_ = [](const T *input, size_t pos, T *out) { *out *= input[pos]; };
} else {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "For '" << kernel_name_ << "', unsupported reduce operation.";
}
}
// special accelerate for axis = 1 and input has 2 dims
if constexpr (std::is_same<T, float>::value) {
if ((reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType || reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceSumType) &&
axis_.size() == 1 && axis_[0] == 1 && input_shape_.size() == 2) {
simple_execute_ = true;
}
}
}
template <typename T>
bool ReduceCpuKernelFunc<T>::RunFunc(const std::vector<kernel::AddressPtr> &inputs,
const std::vector<kernel::AddressPtr> &,
const std::vector<kernel::AddressPtr> &outputs) {
CHECK_KERNEL_INPUTS_NUM(inputs.size(), kReduceInputsNum, kernel_name_);
CHECK_KERNEL_OUTPUTS_NUM(outputs.size(), kReduceOutputsNum, kernel_name_);
size_t input_size = inputs[0]->size / sizeof(T);
auto *input_addr = reinterpret_cast<T *>(inputs[0]->addr);
auto *output_addr = reinterpret_cast<T *>(outputs[0]->addr);
if (axis_.empty() || input_shape_.empty() || input_shape_.size() == 1) {
// 规约所有元素的条件:
// 1. 没有需要规约的 axis
// 2. 输入是一个没有 shape 的 tensor
// 3. 输入的 shape 只有一个维度,即一维向量
if (input_size < kReduceSmallVectorSize) {
// Get one ret
*output_addr = input_addr[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < input_size; ++i) {
reduce_func_(input_addr, i, output_addr);
}
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
*output_addr /= input_size;
}
} else {
// 特化,加速长向量的情况
AccelerateLongVector(input_addr, output_addr, input_size);
}
} else {
// Calculate transpose axes and stride
int dimension = input_shape_.size();
size_t stride = 1;
std::vector<size_t> axes(input_shape_.size());
size_t j = 0;
size_t k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; ++i) {
if (j == axis_.size() || i != axis_[j]) {
axes[k] = i;
++k;
} else {
stride *= input_shape_[i];
++j;
}
}
for (auto &it : axis_) {
axes[k] = it;
++k;
}
// 以上过程的一个运算例子
// 输入的 input_shape_: [3, 2, 4, 5], axis_: [0, 2]
// 运算过程:
// i = 0, j = 0, k = 0; false[0 == 2] || false[0 != 0]; stride = 3
// i = 1, j = 1, k = 0; false[1 == 2] || true[1 != 2]; axes[0] = 1
// i = 2, j = 1, k = 1; false[1 == 2] || false[2 != 2]; stride = 12
// i = 3, j = 2, k = 1; true[2 == 2] || ?; axes[1] = 3
// 输出的 axes: [1, 3, 0, 2], stride = 12
size_t output_size = outputs[0]->size / sizeof(T);
if constexpr (std::is_same<T, float>::value) {
if (simple_execute_) {
auto task = [&](size_t start, size_t end) {
for (size_t i = start; i < end; ++i) {
// 规约 axis=1 input_shape.size=2 的情况:可以理解为二维矩阵按照行压成一维
// 因此,input_addr 需要加上 i * stride 个元素,output_addr 的第 i 个位置是规约结果
(void)ReduceSumDim2Axis1(stride, input_addr + i * stride, output_addr + i);
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
output_addr[i] /= stride;
}
}
};
// 自动并行 [0, output_size) 自动切分,然后调用 task 执行
ParallelLaunchAutoSearch(task, output_size, this, ¶llel_search_info_);
return true;
}
}
// Calculate transpose shape
std::vector<size_t> transpose_shape(input_shape_.size());
for (int i = 0; i < dimension; ++i) {
transpose_shape[i] = input_shape_[axes[i]];
}
TransposeIterator base_iter(std::move(transpose_shape), std::move(axes), input_shape_);
auto task = [this, &base_iter, input_addr, output_addr, stride](size_t start, size_t end) {
auto iter = base_iter;
iter.SetPos(start * stride);
for (size_t i = start; i < end; ++i) {
// output_addr 指向第一个元素
output_addr[i] = input_addr[iter.GetPos()];
iter.GenNextPos();
// 剩下的元素调用规约函数迭代计算即可
for (size_t j = 1; j < stride; ++j) {
reduce_func_(input_addr, iter.GetPos(), &output_addr[i]);
iter.GenNextPos();
}
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
output_addr[i] /= stride;
}
}
};
ParallelLaunchAutoSearch(task, output_size, this, ¶llel_search_info_);
}
return true;
}
/**
AccelerateLongVector 为长向量专门优化:
使用 ParallelLaunchAutoSearch 自动并行,需要加锁避免可能存在的数据冲突
需要注意 AccelerateLongVector 只能对规约所有元素使用
在对短向量计算的时候,是单线程的;长向量是自动并行,多线程的。
*/
template <typename T>
void ReduceCpuKernelFunc<T>::AccelerateLongVector(T *input_addr, T *output_addr, size_t input_size) {
// init output_addr
*output_addr = input_addr[0];
std::mutex task_mutex;
auto task = [this, input_addr, output_addr, &task_mutex](size_t start, size_t end) {
// 跳过第 0 号元素,因为 output_addr 的初值设置为了 input_addr[0]
if (start == 0) {
++start;
}
if (start == end) {
return;
}
auto block_output = input_addr[start];
size_t i = start + 1;
while (i < end) {
reduce_func_(input_addr, i, &block_output);
++i;
}
{
// 将结果汇总到 output_addr,这里是规约了所有元素,所以 output_addr 只有一个元素
// 因此在访问同一个位置的时候,需要加锁
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> task_lock(task_mutex);
reduce_func_(&block_output, 0, output_addr);
}
};
ParallelLaunchAutoSearch(task, input_size, this, ¶llel_search_info_);
if (reduce_type_ == ReduceFuncType::kReduceMeanType) {
*output_addr /= input_size;
}
}
template <typename T>
std::shared_ptr<CpuKernelFunc> SpecializeReduceFunc() {
return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelFunc<T>>();
}
using SpecializeReduceFuncCreator = std::function<std::shared_ptr<CpuKernelFunc>()>;
static std::map<std::string, std::vector<std::pair<KernelAttr, SpecializeReduceFuncCreator>>> kernel_attr_list = {
{kReduceMeanName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32), SpecializeReduceFunc<float>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64), SpecializeReduceFunc<double>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32), SpecializeReduceFunc<int32_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64), SpecializeReduceFunc<int64_t>}}},
{kReduceMaxName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32), SpecializeReduceFunc<float>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64), SpecializeReduceFunc<double>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32), SpecializeReduceFunc<int32_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64), SpecializeReduceFunc<int64_t>}}},
{kReduceSumName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32), SpecializeReduceFunc<float>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64), SpecializeReduceFunc<double>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32), SpecializeReduceFunc<int32_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64), SpecializeReduceFunc<int64_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeBool).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeBool), SpecializeReduceFunc<bool>}}},
{kReduceMinName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32), SpecializeReduceFunc<float>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64), SpecializeReduceFunc<double>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32), SpecializeReduceFunc<int32_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64), SpecializeReduceFunc<int64_t>}}},
{kReduceProdName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat32), SpecializeReduceFunc<float>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeFloat64), SpecializeReduceFunc<double>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt32), SpecializeReduceFunc<int32_t>},
{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeInt64), SpecializeReduceFunc<int64_t>}}},
{kReduceAllName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeBool).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeBool), SpecializeReduceFunc<bool>}}},
{kReduceAnyName,
{{KernelAttr().AddInputAttr(kNumberTypeBool).AddOutputAttr(kNumberTypeBool), SpecializeReduceFunc<bool>}}}};
} // namespace
void ReduceCpuKernelMod::InitKernel(const CNodePtr &kernel_node) {
kernel_name_ = common::AnfAlgo::GetCNodeName(kernel_node);
if (kernel_name_ != kernel_type_) {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "Suppose to be " << kernel_type_ << " but got " << kernel_name_;
}
auto iter = kernel_attr_list.find(kernel_type_);
if (iter == kernel_attr_list.end()) {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "Reduce cpu does not support " << kernel_type_;
}
std::vector<KernelAttr> support_list;
(void)std::transform(iter->second.begin(), iter->second.end(), std::back_inserter(support_list),
[](const std::pair<KernelAttr, SpecializeReduceFuncCreator> &pair) { return pair.first; });
auto kernel_attr = GetKernelAttrFromNode(kernel_node);
auto [is_match, index] = MatchKernelAttr(kernel_attr, support_list);
if (!is_match) {
MS_LOG(EXCEPTION) << "Reduce does not support this kernel data type: " << kernel_attr;
}
func_obj_ = kernel_attr_list[kernel_type_][index].second();
func_obj_->InitFunc(kernel_node);
}
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceMean,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceMeanName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceMax,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceMaxName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceSum,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceSumName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceMin,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceMinName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceProd,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceProdName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceAll,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceAllName); });
MS_KERNEL_FACTORY_REG_BY_CREATOR(NativeCpuKernelMod, ReduceAny,
[]() { return std::make_shared<ReduceCpuKernelMod>(kReduceAnyName); });
} // namespace kernel
} // namespace mindspore


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号