Java--Thread--知识复习
![]()
-
线程开启:start()
-
// 1.开启线程:start() new Thread(() ->{ System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开启啦"); },"input thread name").start();
-
-
线程终止:
-
-
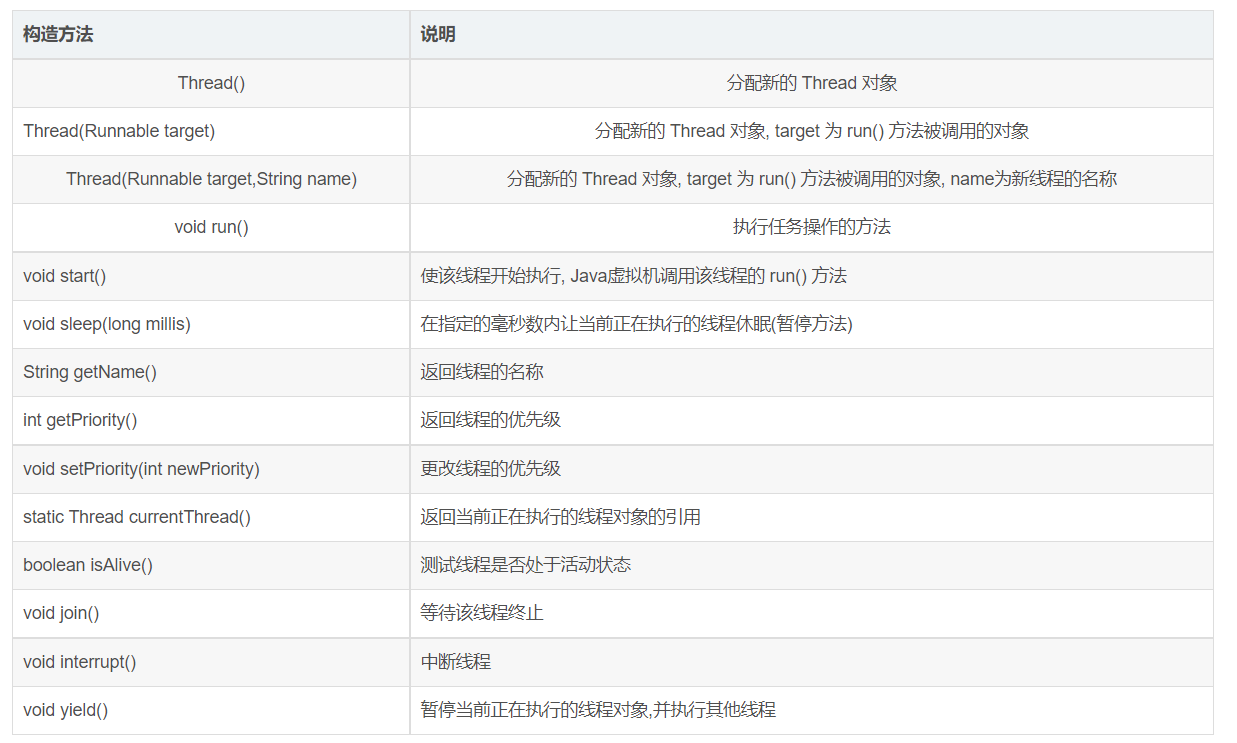
常用方法第一组:(wait())
![]()
-
![]()
-
package com.model.thread; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/22 19:04 * 线程的常用方法 */ public class ThreadDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 1.开启线程:start() new Thread(() ->{ System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开启啦"); },"A").start(); // 2.是当前的线程进入到休眠状态:Thread.sleep() // 3.Thread.currentThread():返回当前线程的一个引用 // 4.getName():获取当前线程的名字 // 5.interrupt():中断线程的休眠状态,使其继续运行 Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { // thread对象等价于Thread.currentThread() System.out.println("当前线程的名字" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { Thread.sleep(20000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "B"); thread.start(); System.out.println("获取线程的优先级:"+thread.getPriority()); Thread.sleep(2000); thread.interrupt();//中断线程,一般用于中断线程的休眠,可见线程 B 并没有休眠20秒 System.out.println("中断成功"); } }
-
线程常用方法第二组:
-
![]()
-
package com.model.thread; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/22 20:10 * 线程常用方法 */ public class ThreadDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 1.yield():将cpu的使用权交给其他的线程使用 // 2.join():再A线程执行过程中,插入B线程,使B先执行,B执行完毕之后A在执行 Thread A = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开启了"); try { Thread.sleep(10000); Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程结束啦"); }, "A"); Thread B = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开启了"); try { Thread.sleep(5000); Thread.yield();//将cpu的使用权交给 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程结束啦"); }, "B"); Thread c = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开启了"); try { System.out.println("C线程插队执行"); Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程结束啦"); }, "C"); // B.start();//B获得CPU的使用权,然后再执行过程中,将使用全让给A,A执行完毕之后就回轮到B执行 // A.start(); c.start(); System.out.println("主线程开始了"); Thread.sleep(2000); c.join();//主线程让C线程先执行,插队了 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行完毕了"); } }
-
-
守护线程:
-
当主线程结束后,我们也希望子线程结束,这是我们可以将子线程设置为守护线程
-
package com.model.thread; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/22 20:56 * 守护线程的使用 */ public class ThreadDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("main线程开始了"); Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程执行了一次"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "守护线程"); thread.setDaemon(true);//设置为守护线程,当主线程结束后,守护线程也会自动结束 thread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread.sleep(200); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了一次"); } System.out.println("main线程结束了"); } }
-
-
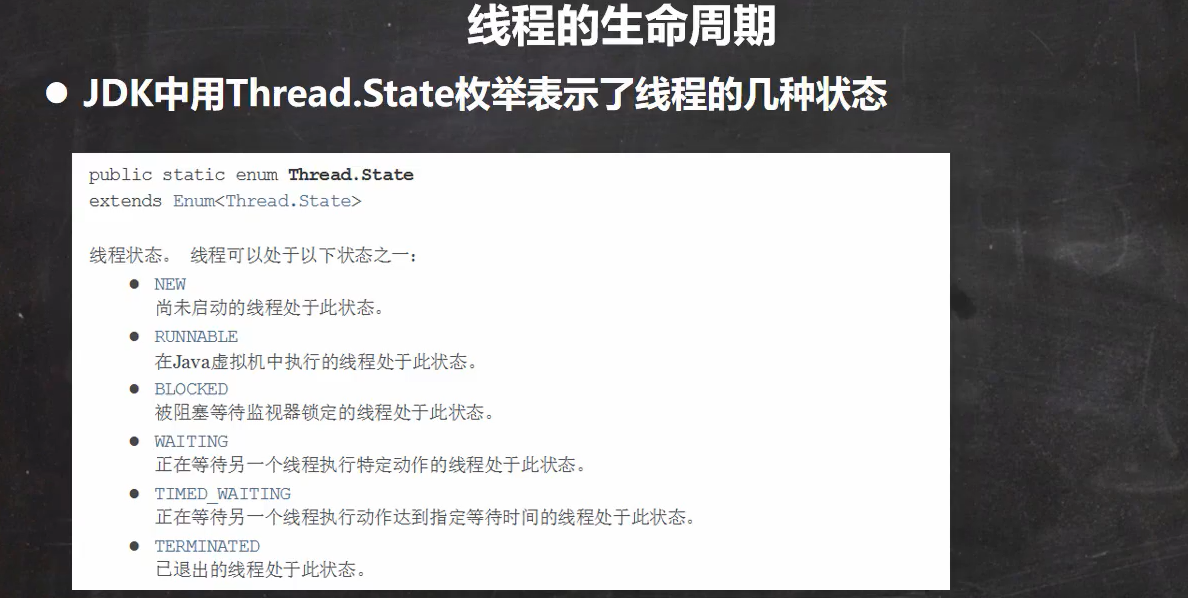
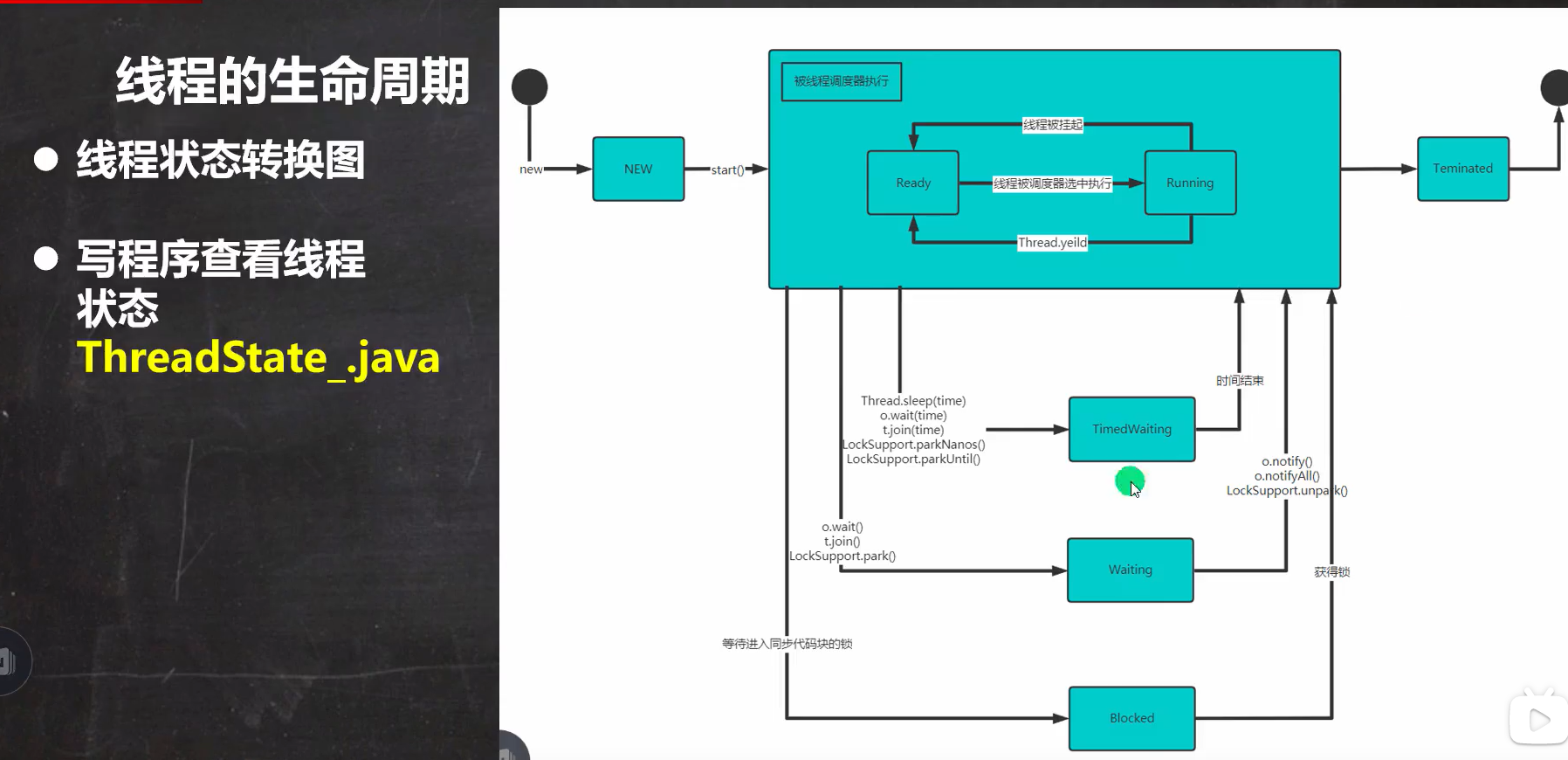
Thread的生命周期:
-
![]()
-
1. 初始(NEW):新创建了一个线程对象,但还没有调用start()方法。
2. 运行(RUNNABLE):Java线程中将就绪(ready)和运行中(running)两种状态笼统的称为“运行”。
线程对象创建后,其他线程(比如main线程)调用了该对象的start()方法。该状态的线程位于可运行线程池中,等待被线程调度选中,获取CPU的使用权,此时处于就绪状态(ready)。就绪状态的线程在获得CPU时间片后变为运行中状态(running)。
3. 阻塞(BLOCKED):表示线程阻塞于锁。
4. 等待(WAITING):进入该状态的线程需要等待其他线程做出一些特定动作(通知或中断)。
5. 超时等待(TIMED_WAITING):该状态不同于WAITING,它可以在指定的时间后自行返回。
6. 终止(TERMINATED):表示该线程已经执行完毕。 -
![]()
-
-
线程的同步机制:
-
-
互斥锁:
-
![]()
-
使用synchronized关键字实现了互斥锁
-
当我们synchronized修饰非静态方法时,它锁的时这个对象,this
- 当我门使用的synchronized修饰的是静态方法是,他锁的正个类对象
-
![]()
-
package com.model.thread; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/23 14:27 * 使用synchronized关键字实现互斥锁 */ public class ThreadDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { LockTest test = new LockTest(); Thread a = new Thread(() -> { try { System.out.println("A"); while (test.loop) { test.m1(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "A"); Thread b = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("B"); try { while (test.loop) { test.m1(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "B"); Thread c = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("C"); try { while (test.loop) { test.m1(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "C"); b.start(); a.start(); c.start(); } } class LockTest { public int num = 100; public boolean loop = true; public void m1() throws InterruptedException { if (num <= 0) { System.out.println("卖完了"); loop = false; return; } Thread.sleep(50); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买了一张票,还剩下" + --num); } public void m2() {//等价于上面的 synchronized (this) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "实现互斥锁,锁的这个对象this" + num--); } } public static synchronized void m3() { System.out.println("实现互斥锁,整个类对象"); } public static void m4() {//等价于上面的 synchronized (LockTest.class) { System.out.println("实现互斥锁,锁的是整个类对象"); } } }
-
-
死锁:两个资源,A线程需要 1,2资源才能执行,B线程需要1,2资源执行,当A的到了1,等待2,而B的到了2等代1,造成了死锁
-
package com.model.thread; import java.util.function.ObjDoubleConsumer; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/23 15:11 * 死锁的实现 */ public class ThreadDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { DeadLock deadLock = new DeadLock(); new Thread(() ->{ try { deadLock.m1(true); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(() ->{ try { deadLock.m1(false); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"B").start(); } } class DeadLock{ // static final DeadLock lock1 = new DeadLock(); //static保证多个线程共享一个对象,这里使用static修饰 // static final DeadLock lock2 = new DeadLock(); static DeadLock lock1= new DeadLock(); //static保证多个线程共享一个对象,这里使用static修饰 static DeadLock lock2 =new DeadLock(); public DeadLock() {//不能再构造方法里面new 对象使用本构造方,会构成反复一直调用,栈内存溢出 } public void m1(boolean flag) throws InterruptedException { if (flag){ synchronized (lock1){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的到了1,等待第2"); Thread.sleep(2000); synchronized (lock2){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的到了2"); } } }else { synchronized (lock2){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的到了2,等待第1"); Thread.sleep(1000); synchronized (lock1){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"得到了2"); } } } } }
-
-
释放锁:
-

















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号