MySQL高级--索引案例分析
- 建表
-
create table if not exists article( id int(10) unsigned not null primary key auto_increment, auther_id int(10) unsigned not null, category_id int(10) not null, views int(10) not null, comments int(10) not null, title varchar(255) not null, content text not null);
-
INSERT INTO article ( author_id,category_id,views,comments,title,content )
VALUES
(1, 1, 1,1,'1','1'),
(2, 2, 2,2, '2', '2'),
(1, 1, 3,3, '3', '3'); -
SEL ECT * FROM article;
-
-
-
案例1单表优化案例分析:
-
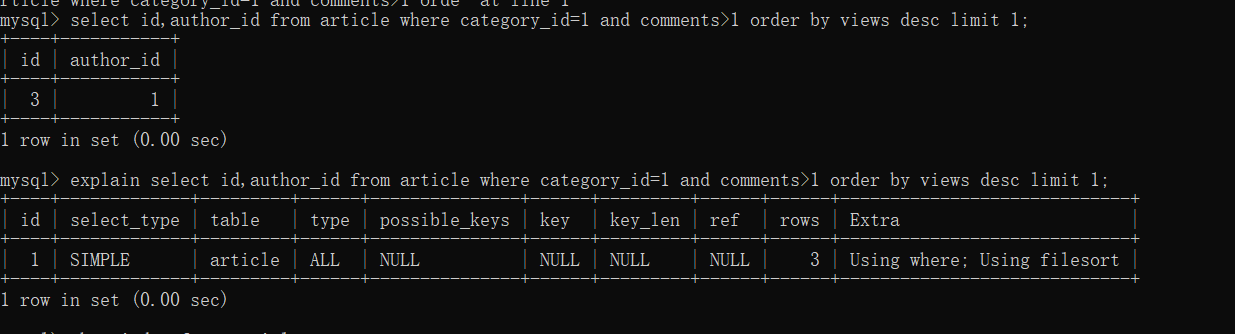
select id,author_id from article where category_id=1 and comments>1 order by views desc limit 1;
-
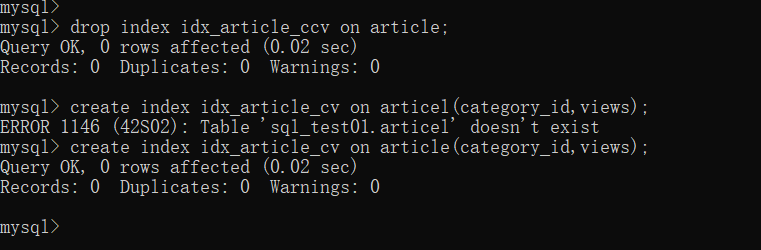
explain select id,author_id from article where category_id=1 and comments>1 order by views desc limit 1;
![]()
-
结论:很显然,type类型是all最坏的类型,extra也出现了Using filesort也是最坏的情况必须优化。
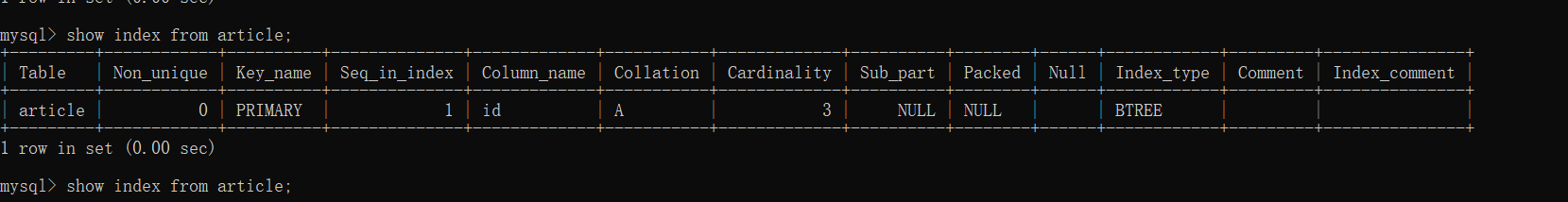
- 查看表的索引:show index from article;
-
首先查询中用到了 category_id,comments,views三个字段,先试试为这三个字段建立索引
-
查看语句的执行情况:explain select id,author_id from article where category_id=1 and comments>1 order by views desc limit 1;
-
解决了全表扫描,但是using fulesort 并未解决,删除索引:drop index idx_artecle_ccv on article;
-
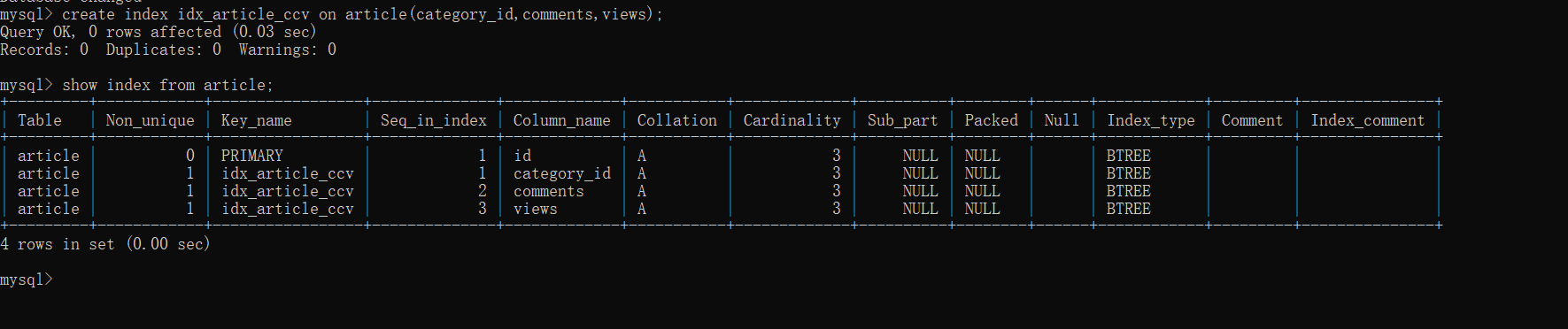
建立新的索引:create index idx_article_cv on article(category_id,views);
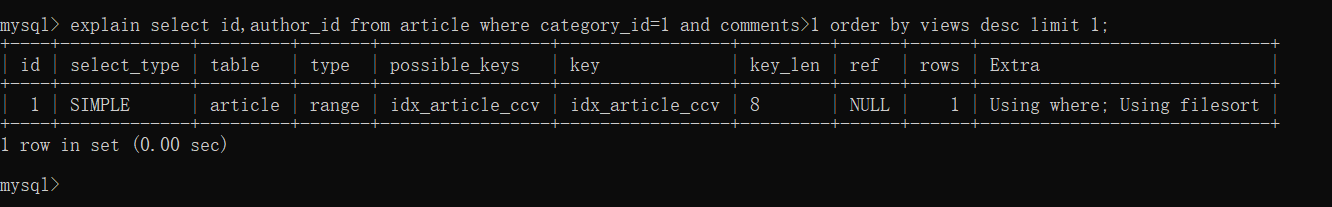
- 继续查看你sql语句的执行情况:explain select id,author_id from article where category_id=1 and comments>1 order by views desc limit 1;
-
结论:可以看到,type变为了ref,Extra 中的Using filesort 也消失了,结果非常理想。
-
- 案例2两表优化:
- 建表:
-
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS class(
id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS book(
bookid INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (bookid)
);
-
- 插入数据:
-
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND()* 20)));
-
- 查询两表中的数据:
-
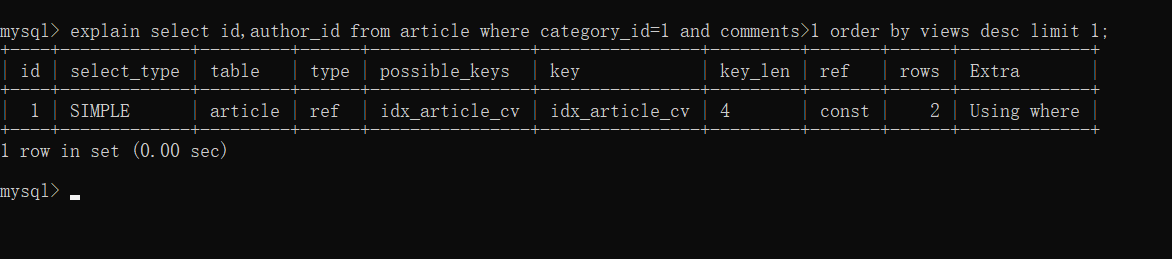
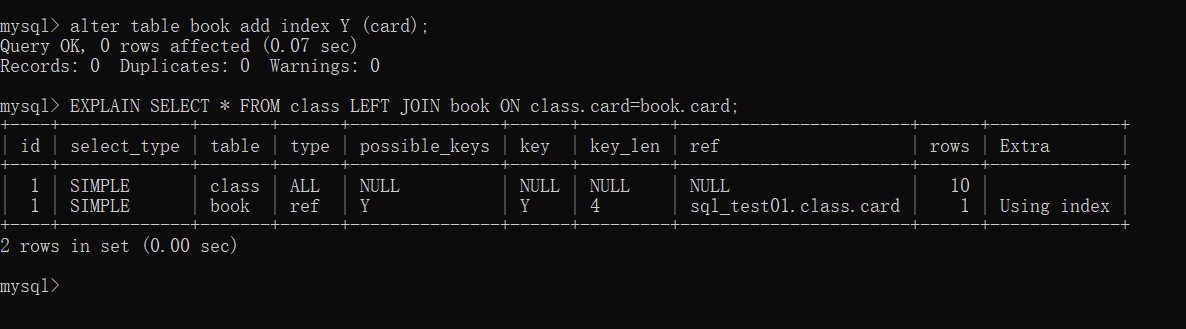
析sql语句 :EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM class LEFT JOIN book ON class.card=book.card;
-
结论是:type是all全表扫描,很显然我们需要进行优化。
-
显示着为右表建立索引:alter table book add index Y (card);
-
继续查看sql语句执行情况:EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM class LEFT JOIN book ON class.card=book.card;
-
![]()
- 可以看出我们的sql语句使用了索引,type由all变为ref。
-
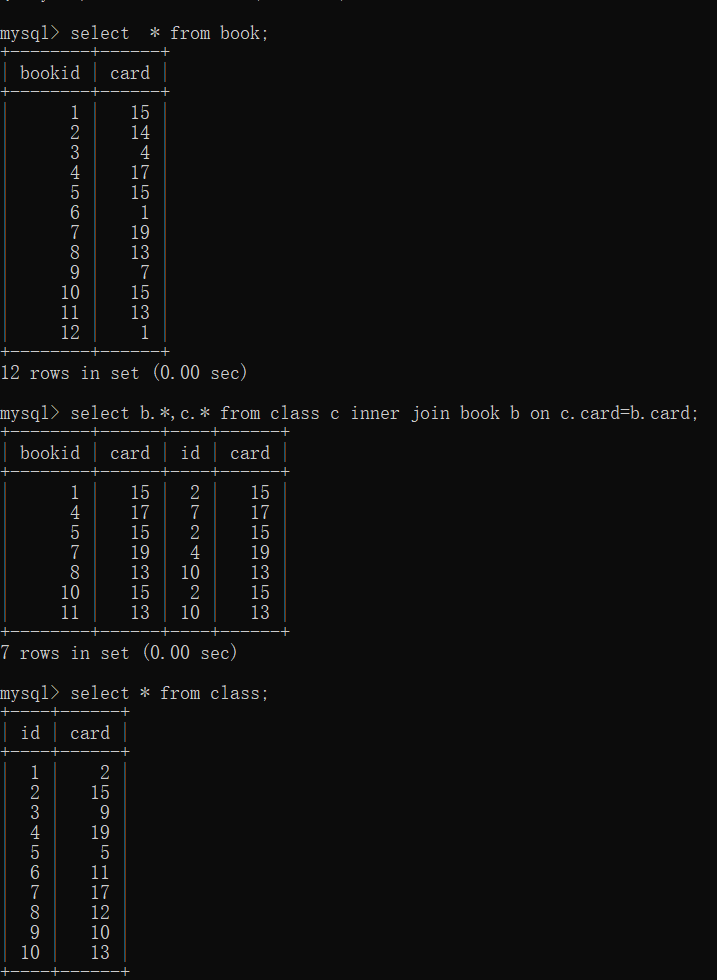
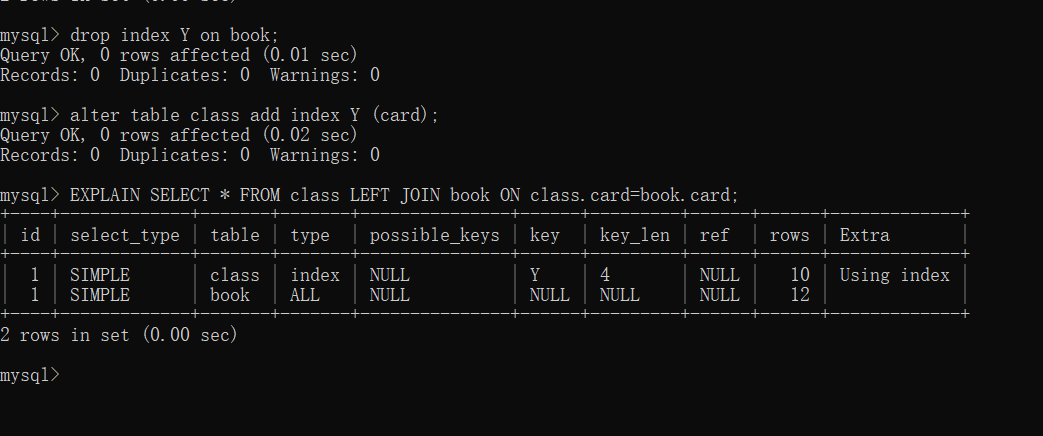
下面我们试试在左表中建立索引:drop index Y on book; alter table class add index Y (card);
-
继续执行sql 语句:EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM class LEFT JOIN book ON class.card=book.card;
![]()
-
#可以看到第二行的type变为了ref,rows 也变成了优化比较明显。#这是由左连接特性决定的。LEFT JOIN条件用于确定如何从右表搜索行,左边一定都有,#所以右边是我们的关键点,一定需要建立索引。
-
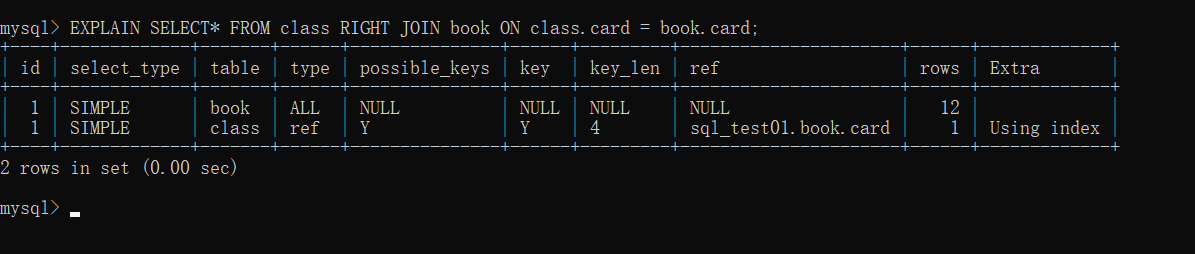
#然后来看一个右连接查询:
-
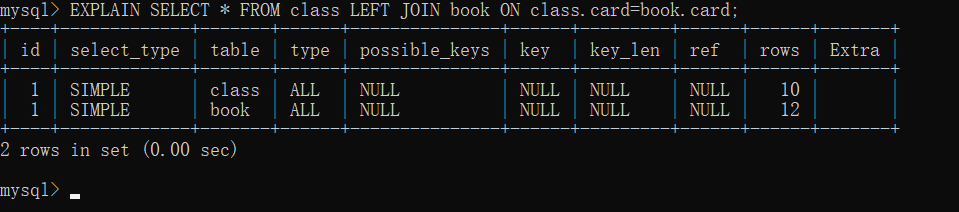
#优化较明显。这是因为RIGHT JOIN条件用于确定如何从左表搜索行,右边- -定都有,所以左边是我们的关键点,一定需要建立索引。
-
EXPLAIN SELECT* FROM class RIGHT JOIN book ON class.card = book.card;
![]()
-
-
总结:左连接我们的右表是关键,所以我们在右表建立索引,右连接我们的左表是关键,我们在左表建立索引。
-
- 建表:
-
案例分析3三表优化方案:
-
见表插入数据:
-
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS phone (
phoneid INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ( phoneid)
) ENGINE = INNODB; -
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20)));
insert into phone (card) values (floor (1+ (rand ()*20))); -
将class表中的索引删掉:drop index Y on class;
-
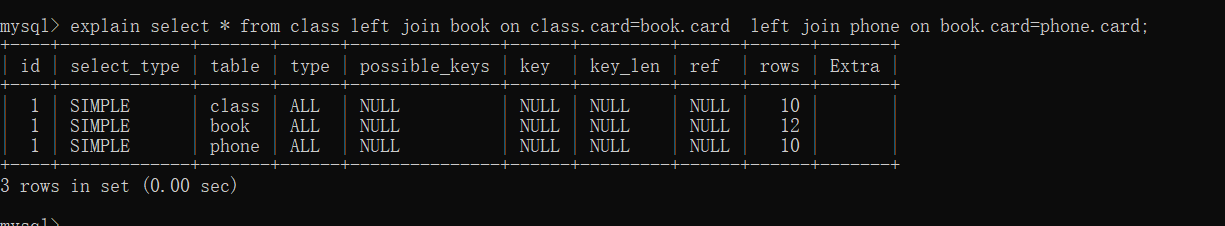
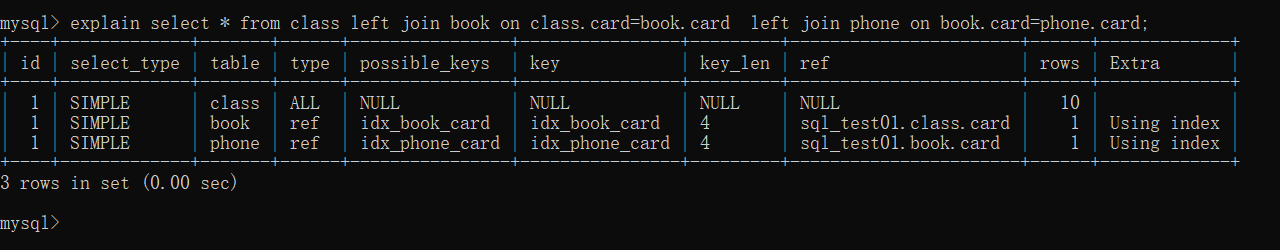
分析sql语句:explain select * from class left join book on class.card=book.card left join phone on book.card=phone.card;
![]()
- 全部都是全表扫描,很显然我们需要进行优化:
- 首先试着为两个从表建立索引:alter table book add index idx_book_card (card); alter table phone add index idx_phone_card (card);
- 继续执行sql语句:explain select * from class left join book on class.card=book.card left join phone on book.card=phone.card;
![]()
-
总结:后2行的type都是ref且总rows优化很好,效果不错。因此索引最好设置在需要经常查询的字段中。
-
Join语句的优化
尽可能减少Join语句中的NestedLoop的循环总次数;“ 永远用小结果集驱动大的结果集”。 - 优先优化NestedLoop的内循环;
- 保证join语句中被驱动表上join 条件字段已被索引;
- 当无法保证被驱动表的join条件字段被索引 且内存资源充足的情况下,不要太吝啬joinBuffer 的设置
-





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号