vuex是什么,及里面的属性详解
Vuex是什么?
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。Vuex背后的基本思想,就是前面所说的单向数据流。下图就是Vuex实现单向数据流的示意图。
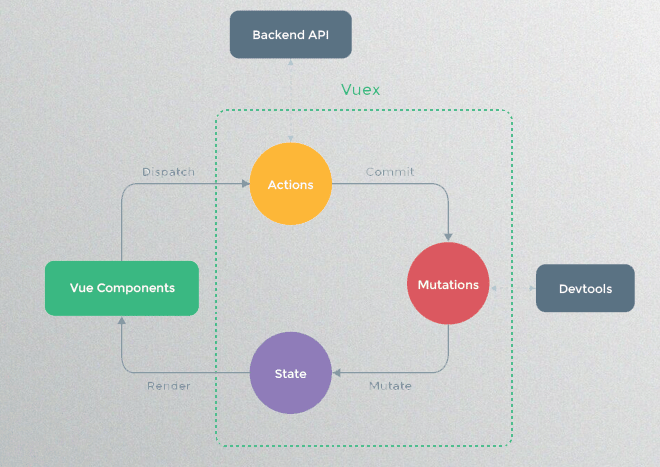
Vuex状态管理跟使用传统全局变量的不同之处
1.Vuex的状态存储是响应式的:就是当你的组件使用到了这个Vuex的状态,一旦它改变了,所有关联的组件都会自动更新相对应的数据,这样开发者省事很多。
2.不能直接修改Vuex的状态:如果是个全局对象变量,要修改很容易,但是在Vuex中不能这样做,想修改就得使用Vuex提供的唯一途径:显示地提交(commint)mutations来实现修改。这样做的好处就是方便我们跟踪每一个状态的变化,在开发过程中调试的时候,非常实用。
使用步骤
1 .安装Vuex
npm install vuex --save
- 1
2 . 引用vuex,创建仓库store。 创建 store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
//数据
const state={
count:10
}
//action 执行异步操作,不可以修改state数据
const actions={
getParamSync (context,Object) {
//处理异步操作
setTimeout(()=>{
//3.通过commit提交一个名为getParam的mutation
//action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation
context.commit('increment',Object)
},3000)
}
}
//mutation 可直接修改state数据
const mutations={
increment(state,value){
state.count += value;
},
decrement(state,value){
state.count -=value;
}
}
//getter
const getters = {
newCount:state => state.count * 3
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
})
3 . 在 main.js中注册到根组件中
import store from './store/store.js'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
action
action:
用来解决异步流程来改变state数据。
而matution是直接进行同步操作的,如果你在mutations里进行异步操作,你会发现没用,并不会起任何效果
只有通过action=>mutations=>states,这个流程进行操作,具体步骤如下:
export default new Vuex.Store({
//存放数据
state: {
count: 5,
},
//2.接受dispatch传递过来的方法和参数
actions: {
getParamSync (context,val) {
//处理异步操作
setTimeout(()=>{
//3.通过commit提交一个名为getParam的mutation
//action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation
context.commit('increment',val)
},3000)
}
}
})
vue组件中通过事件触发action
methods: {
getVal() {
//1.通过dispatch将方法getParamSync和多个参数{name,age,sex}传递给actions
this.$store.dispatch('getParamSync',1)
}
}
Mutations:
Vuex给我们提供修改仓库 store中的状态的唯一办法就是通过提交mutation
我们在 mutations中定义了一个叫increment的函数,函数体就是我们要进行更改的地方
会接受 state作为第一个参数,第二个是自定义传参
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//state存储应用层的状态
state:{
count:5 //总数:5
},
mutations:{
increment(state,value){
state.count += value;
}
}
});
我们在提交commit时候,字符串参数increment,就是对应在 mutations中的increment。
一般通过方法或钩子触发,例如:
methods: {
getVal(event) {
//获取当前的按键的值
let value = event.target.dataset.value;
//通过commit提交一个名为increment的mutation
this.$store.commit("increment", value);
}
}
在组件中获取{{count}}方式:
export default {
computed: {
count(){
return this.$store.state.count;
}
}
};
1.increment官方说是type,其实就是注册的事件名
2.可以是单个参数
3.如果是多个参数,我们则用对象放入,否则会报错
Getters
可以认为,getters 是store的计算属性,类似于computed,对state里的数据进行一些过滤,改造等等
假设我们要在state.count的基础上派生出一个新的状态newCount出来,就适合使用我们的 getters
getters 接受 state 作为其第一个参数
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//state存储应用层的状态
state:{
count:5 //总数:5
},
getters:{
newCount:state => state.count * 3
}
});
在组件中获取{{newCount}}方式:
export default {
computed: {
newCount(){
return this.$store.getters.newCount;
}
}
};
组件中触发action、mutation
methods:{
jia(){
console.log(this.$store)
this.$store.commit("increment", 1);
},
jian(){
this.$store.commit('decrement',1)
},
twojia(){
this.$store.dispatch('getParamSync',1)
}
},
推荐大家用一下方式,将vuex每个部分拆分
运用vuex语法糖mapMutations
mutations.js
const mutations = {
SET_NEWS(state, val) {
state.news = val
}
}
export default mutations
1.存储数据( a.vue文件 )
import { mapMutations } from "vuex"; // 引入mapMutations
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations({
// 将changeNews与mutations中的SET_NEWS关联
changeNews: "SET_NEWS"
}),
submit(){
// 提交一个名为changeNews的mutation,并传入参数val
let val = 'test news';
this.changeNews(val);// 相当于this.$store.commit("changeNews", val);
}
}
}
2.获取数据( b.vue文件 )
import { mapGetters } from "vuex"; // 引入mapGetters
export default {
computed: {
// 用vuex读取数据(读取的是getters.js中的数据)
// 相当于this.$store.getters.news(vuex语法糖)
...mapGetters(["news"])
},
created() {
// 获取getters中news数据
console.log(this.news);
}
}
3.store文件目录结构
index.js:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import * as actions from './actions'
import * as getters from './getters'
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
//每次修改state都会在控制台打印log
import createLogger from 'vuex/dist/logger'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const debug = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
getters,
state,
mutations,
strict: debug, // 当debug=true时开启严格模式(性能有损耗)
plugins: debug ? [createLogger()] : []
})
state.js:
const state = {
news: {}
}
export default statemutations.js:
const mutations = {
SET_NEWS(state, val) {
state.news= val
}
}
export default mutationsgetters.js:
// 通常通过getters取数据 (this.$store.getters.news;)
export const news = state => state.news // 不做其他处理 直接映射出去
actions.js:
//异步处理
...
4.使用store
在main.js中引用
import store from './store' //vuex存储文件
...
...
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: {
App
},
template: '<App/>'
})
什么是module?
背景:在Vue中State使用是单一状态树结构,应该的所有的状态都放在state里面,如果项目比较复杂,那state是一个很大的对象,store对象也将对变得非常大,难于管理。
module:可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理。
二、怎么用module?
一般结构
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB})
使用
// computed属性,从store 中获取状态state,不要忘记login命名空间。
computed: {
useName: function() {
//return store.state.login.useName
return this.$store.state.moduleA.useName
}
},
methods:{
changeName(){
this.$store.dispatch("changeName",'jason');
}
}
}
module综合用法
store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const test1 = {
namespaced: true,
state: {
name: 'moduleA',
type: 'module A'
},
mutations: {
updateNameByMutation(state, appendStr){
state.name = state.name + " append Str: " + appendStr
}
},
actions: {
udpateNameByAction({commit}, appendStr) {
commit("updateNameByMutation", appendStr)
}
},
getters: {
getNameA(state){
return state.name
}
}
}
const test2 = {
// 当namespaced=true 时, vuex, 将会自动给各自module 添加访问路径名。 方便区分moduel
namespaced: true,
state:{
name: 'moduleB',
type: 'module B'
},
mutations: {
updateNameByMutation(state, appendStr){
state.name = state.name + " append Str: " + appendStr
}
},
actions: {
// 如果不使用命名空间, 那么view 指向actions 的该方法时,会执行所有与指定action名相同的函数(即:这里module A,B 中该action都会执行)
udpateNameByAction({commit}, appendStr){
commit("updateNameByMutation", appendStr)
}
},
getters: {
getNameB(state){
return state.name
}
}
}
const storeInstall = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
name: 'i am root state name'
},
modules:{
// 这里的路径名: test1, test2, 在view 中 通过 mapActions('test1', [actionName]) 使用并区分需要使用的module
test1,
test2
}
})
export default storeInstall
store.js 几个简单的vuex 使用场景模拟。 我们有多个模块,分别为: test1, test2… 。
我们发现开发中可能会存在相同的stateName/ actionName/ mutaionName /。 (实际开发中,getterName 如果有重名编译会提示 getter 重名....)
我们使用vuex 需要实例化一个Vuex的Store构造函数。 这里storeInstall 中第一个state, 我们可以理解为根 state, 它全局可访问。 modules 中则是我们自定义注册的module. 每个module 中都有自己独立的state, action, mutation, getter...
需要注意的是,这里通过给每个module 对象添加namespaced: true, 来达到命名空间来区分Module的效果。也是通过它来区分更新/调用 对应的vuex 方法来隔离未知数据更新等数据相关问题
vue组件
<template>
<div>
<div>
<h2>Page Test1</h2>
</div>
<div>
<a href="javascript:" @click="changeName">udpate: 名称Name</a>
<a href="javascript:" @click="showName">显示更新后的Name</a>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
data(){
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState('test1', {
state: state => state
})
},
methods: {
// test1 模块路径名
...mapActions('test1', [
'udpateNameByAction'
]),
changeName(){
this["udpateNameByAction"]('ha ha test1 udpate !!')
},
showName(){
console.log(this.$store.state)
},
},
mounted() {
console.log("store name: ", this.$store)
console.log("namespace test1 state: ", this.state)
}
}
</script>
关于vuex module 这里只是个基本讲解。 总结下来就是module 给了我们一种隔离vuex store 各个 state及相关api 的方法,让数据相关操作在复杂的项目场景可以更清晰,易追踪。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号