pytorch数据操作
数据创建
torch.arange(1, 16)

torch.eyes(n)
对角线为1的矩阵,若n==m。
torch.eye(n, m=None, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) → Tensor

数据操纵
dim含义(以cat拼接为例):size=[256,50],dim=0就指的是256那一维,dim=1就指的是50那一维。
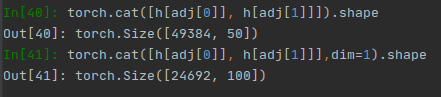
torch.cat
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, *, out=None) → Tensor
Example: (就是在第dim个维度上相加,先算shape,再推形状)
>>> x = torch.ones(4, 8, 10)
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 0).shape
torch.Size([12, 8, 10])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 1).shape
torch.Size([4, 24, 10])
>>> torch.cat((x, x, x), 2).shape
torch.Size([4, 8, 30])
torch.unsqueeze
torch.unsqueeze(input, dim, out=None)
挤压:扩展维度
对输入的tensor,在shape[4, 8, 10]的第dim个空缺处增加一个维度,[4, 1, 8, 10]
注意: 返回张量与输入张量共享内存,所以改变其中一个的内容会改变另一个。
如果dim为负,则将会被转化dim+input.dim()+1
Example:
>>> x = torch.ones(4, 8, 10)
>>> x.shape
torch.Size([4, 8, 10])
>>> x.dim()
3
>>> x.unsqueeze(1).shape
torch.Size([4, 1, 8, 10])
>>> x.unsqueeze(2).shape
torch.Size([4, 8, 1, 10])
>>> x.unsqueeze(-1).shape
torch.Size([4, 8, 10, 1])
参数:
tensor (Tensor)– 输入张量dim (int)– 插入维度的索引out (Tensor, optional)– 结果张量
torch.squeeze
作用:降维
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
将输入张量形状中的1 去除并返回。 如果输入是形如(A×1×B×1×C×1×D),那么输出形状就为: (A×B×C×D)
当给定dim时,那么挤压操作只在给定维度上。例如,输入形状为: (A×1×B), squeeze(input, 0) 将会保持张量不变,只有用 squeeze(input, 1),形状会变成 (A×B)。
注意: 返回张量与输入张量共享内存,所以改变其中一个的内容会改变另一个。
m = torch.zeros(2, 1, 2, 1, 2)
print(m.size()) # torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
n = torch.squeeze(m)
print(n.size()) # torch.Size([2, 2, 2])
n = torch.squeeze(m, 0) # 当给定dim时,那么挤压操作只在给定维度上
print(n.size()) # torch.Size([2, 1, 2, 1, 2])
n = torch.squeeze(m, 1)
print(n.size()) # torch.Size([2, 2, 1, 2])
torch.expand
expand(*sizes) -> Tensor
*sizes(torch.Size or int) - the desired expanded size 参数:扩充以后的形状,而非对每个维度的重复次数。
Returns a new view of the self tensor with singleton dimensions expanded to a larger size.
- size参数加不加[]号都是一样的
- 返回当前张量在某维扩展更大后的张量。扩展(expand)张量不会分配新的内存,只是在存在的张量上创建一个新的视图(view),一个大小(size)等于1的维度扩展到更大的尺寸。
- size参数的维度可以大于x的维度,其意义同repeat,扩充时在不存在的维度上看成1,再扩充。
(直观上,只能在值为1的维度上扩充,见例子)
>>> x = torch.randn(2, 1, 1, 4)
>>> x
tensor([[[[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404]]],
[[[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841]]]])
>>> x.expand(2,2,3,4) #-1表示不变,等价于x.expand(-1,2,3,-1) 扩充以后的数据为形状[2, 2, 3, 4]
tensor([[[[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404],
[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404],
[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404]],
[[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404],
[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404],
[ 1.3860, -1.0969, 1.4059, -1.0404]]],
[[[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841],
[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841],
[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841]],
[[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841],
[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841],
[ 0.9608, 1.0212, 1.7618, -0.4841]]]])
>>> x.expand(2,2,3,4).shape
torch.Size([2, 2, 3, 4])
torch.repeat
repeat(*sizes) -> Tensor
sizes参数:(设x的size为[33,55])
- x.repeat(3, 2):对每个维度复制的次数,在第0维复制3次,第1维复制2次。即最终得到的形状是[333,552]。size参数的维度可以大于x的维度,其意义见下。
*size(torch.Size or int) - The number of times to repeat this tensor along each dimension.
Repeats this tensor along the specified dimensions.
- size参数加不加[]号都是一样的,x.repeat([2,2,3])同x.repeat(2,2,3)。
- 沿着特定的维度重复这个张量,和expand()不同的是,这个函数拷贝张量的数据。
>> x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x
tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x.shape
torch.Size([3])
>> x.repeat(3, 2)
tensor([[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]])
size参数的维度可以大于x的维度,x为一维的([3]),此时x的维度可以看成([1,1,3]),3仍然与(4,3,2)的最后后1维2对齐相乘,其余维也对齐相乘,得:size[4,3,6]
>>> x.size()
torch.Size([3])
>>> x.repeat(4,3, 2).size()
torch.Size([4, 3, 6])
对比
- repeat会分配新的内存存储增加的数据,而expand不分配新内存。
- expand是直接作为期望的size()的,而repeat是对齐相乘:
>>> x
tensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> x.repeat(2,2,3).size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 9])
>>> x.expand(2,2,3).size()
torch.Size([2, 2, 3])
- repeat不能用-1表示该维度上不变,因为对于*size参数的逻辑,repeat是对齐相乘的,维度不能是负数。
>>> a = torch.randn(33, 55)
>>> a.repeat(2,-1).size()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
RuntimeError: Trying to create tensor with negative dimension -55: [66, -55]
- 为什么呢?因为x.repeat(3, 2)的逻辑是每个数字都对应了
torch.split
torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
Splits the tensor into chunks. Each chunk is a view of the original tensor.
如果参数为整数split_size,函数将把原tensor切成大小为split_size的块(切成了total/split_size[上取整]个块)。
If
split_size_or_sectionsis an integer type, thentensorwill be split into equally sized chunks (if possible). Last chunk will be smaller if the tensor size along the given dimensiondimis not divisible bysplit_size.
如果参数为一个列表split_sections,将按列表的规定切分。
If
split_size_or_sectionsis a list, thentensorwill be split intolen(split_size_or_sections)chunks with sizes indimaccording tosplit_size_or_sections.
>>> a = torch.arange(10).reshape(5,2)
>>> a
tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]])
>>> torch.split(a, 2)
(tensor([[0, 1],
[2, 3]]),
tensor([[4, 5],
[6, 7]]),
tensor([[8, 9]]))
>>> torch.split(a, [1,4])
(tensor([[0, 1]]),
tensor([[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]]))
torch.chunk
功能类似但不如split,用法只能为整数split_size。
不同:
- chunk只能用split_size,而不能用split_sections;即参数只能为整数,而不能为列表。
- chunk在dim<split_size时,方案为切成若干个dim为1的块,而split仍然采用固定规则切分(即不足的话单独成为一个块,不切)
数据比较
torch.equal
torch.equal(tensor1, tensor2) → bool
如果两个张量的尺寸和元素都相同,则返回True,否则返回False。
torch.gt(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
计算 input tensor > other{torch.lt}
torch.gt(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]]))
tensor([[False, True],
[False, False]])
torch.ge(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
计算 input tensor >= other{torch.le}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号