数据采集作业2
作业1
在中国气象网(http://www.weather.com.cn)给定城市集的7日天气预报,并保存在数据库。
代码和结果
打开网站查看每一个城市对应的代码,比如图片中武汉的代码为101200101,选取4个城市的代码用于编写我们的爬虫

代码:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
import time
# 目标城市配置(北京、杭州、武汉、重庆)
CITY_INFO = [
{"name": "北京", "code": "101010100"},
{"name": "杭州", "code": "101210101"},
{"name": "武汉", "code": "101200101"},
{"name": "重庆", "code": "101040100"}
]
# 请求头
HEADERS = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/129.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2",
"Referer": "http://www.weather.com.cn/"
}
# 初始化数据库
def init_db():
conn = sqlite3.connect("weather_db.db")
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS weather_data (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
area TEXT NOT NULL,
date TEXT NOT NULL,
weather_info TEXT NOT NULL,
temperature TEXT NOT NULL,
crawl_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
UNIQUE(area, date)
)
''')
conn.commit()
conn.close()
# 爬取单个城市的天气数据并存储到数据库
def crawl_and_save(city_name, city_code):
url = f"http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/{city_code}.shtml"
try:
time.sleep(3)
response = requests.get(url, headers=HEADERS, timeout=15)
response.encoding = "utf-8"
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser")
forecast_ul = soup.find("ul", class_="t clearfix")
if not forecast_ul:
print(f"[{city_name}] 未找到天气数据(页面结构可能变化)")
return
crawl_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
conn = sqlite3.connect("weather_db.db")
cursor = conn.cursor()
for index, li in enumerate(forecast_ul.find_all("li")[:7], 1):
date = li.find("h1").text.strip()
weather = li.find("p", class_="wea").text.strip()
temp = li.find("p", class_="tem").text.strip().replace("\n", "")
wind = li.find("p", class_="win").text.strip().replace("\n", "")
weather_info = f"{weather},{wind}" if wind else weather
cursor.execute('''
INSERT OR IGNORE INTO weather_data
(area, date, weather_info, temperature, crawl_time)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (city_name, date, weather_info, temp, crawl_time))
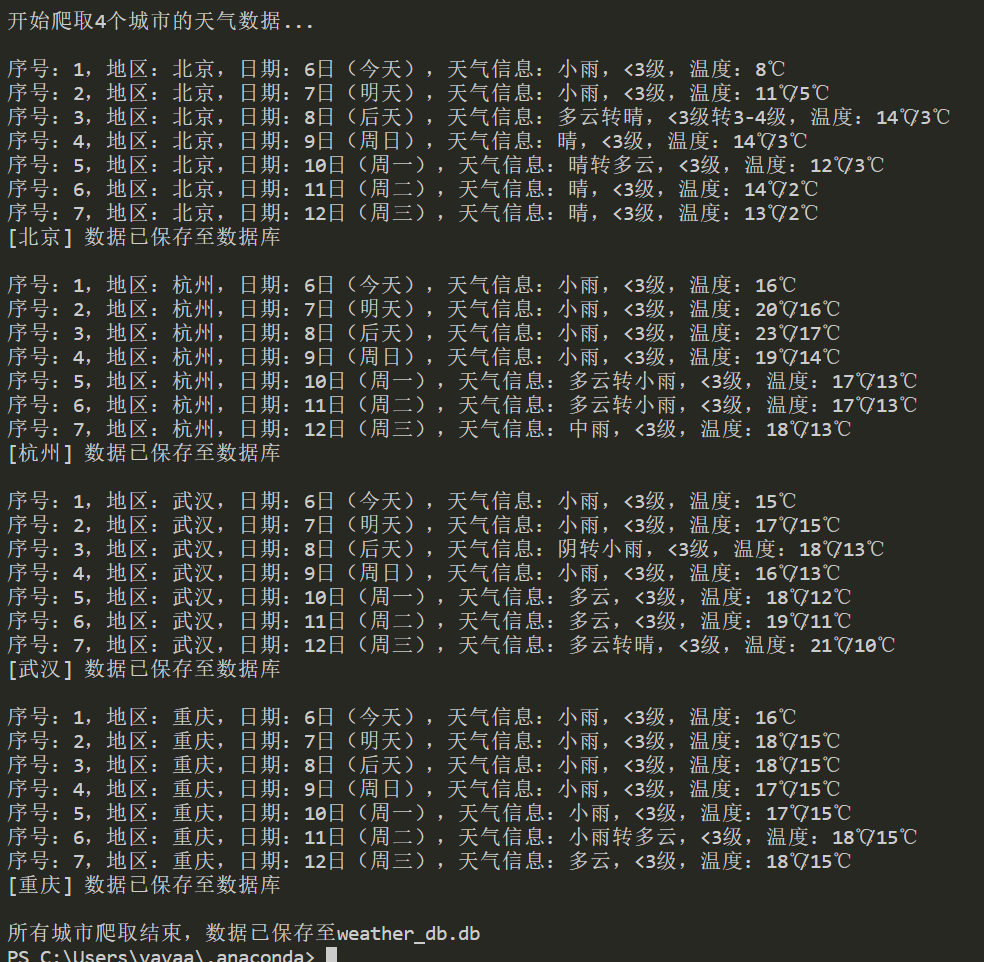
print(f"序号:{index},地区:{city_name},日期:{date},天气信息:{weather_info},温度:{temp}")
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print(f"[{city_name}] 数据已保存至数据库\n")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[{city_name}] 爬取失败:{str(e)}\n")
# 主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
init_db()
print("开始爬取4个城市的天气数据...\n")
for city in CITY_INFO:
crawl_and_save(city["name"], city["code"])
print("所有城市爬取结束,数据已保存至weather_db.db")
实验心得
这个实验我们通过预先配置目标城市名称及对应的天气网城市编码,以模拟真实浏览器的请求头向中国天气网发送 HTTP 请求,然后查看一下页面的各个信息都存在什么标签底下,然后用BeautifulSoup 解析 HTML 页面,定位一下存储预报数据的容器标签,提取日期、天气状况、温度等字段,获取 4 个城市的 7 天天气预报网页内容,让我明白了爬取页面时要注意不同url的变化
作业2
用requests和json解析方法定向爬取股票相关信息,并存储在数据库中。
代码和结果
代码:
点击查看代码
import requests
import time
from math import ceil
import pandas as pd
def get_single_page_data(page_num, page_size=50):
try:
# 1. 用params参数传递所有请求参数
url = "https://push2.eastmoney.com/api/qt/clist/get"
params = {
"np": 1,
"fltt": 1,
"invt": 2,
"fs": "m:0+t:6+f:!2,m:0+t:80+f:!2,m:1+t:2+f:!2,m:1+t:23+f:!2,m:0+t:81+s:262144+f:!2",
"fields": "f12,f14,f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f23", # 保留需要的字段
"fid": "f3",
"pn": page_num,
"pz": page_size,
"po": 1,
"dect": 1,
"ut": "fa5fd1943c7b386f172d6893dbfba10b",
"wbp2u": "|0|0|0|web"
}
# 2. 模拟浏览器请求,降低反爬概率
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"Referer": "https://quote.eastmoney.com/" # 增加来源页
}
time.sleep(0.8)
response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status() # 请求失败直接抛异常,便于排查
# 3. 解析JSON数据
stock_json = response.json()
# 4. 校验数据有效性
if stock_json.get("rc") != 0 or "data" not in stock_json:
print(f"第{page_num}页数据无效,跳过")
return None
return stock_json["data"]["diff"]
except Exception as e:
print(f"第{page_num}页请求失败:{str(e)},重试1次...")
# 失败重试1次,提升成功率
time.sleep(1)
try:
response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
stock_json = response.json()
if stock_json.get("rc") == 0 and "data" in stock_json:
return stock_json["data"]["diff"]
else:
print(f"第{page_num}页重试也失败,跳过")
return None
except Exception as retry_e:
print(f"第{page_num}页重试失败:{str(retry_e)},跳过")
return None
def get_total_stock_count():
"""获取总股票数,用于计算总页数"""
try:
url = "https://push2.eastmoney.com/api/qt/clist/get"
params = {
"np": 1,
"fltt": 1,
"invt": 2,
"fs": "m:0+t:6+f:!2,m:0+t:80+f:!2,m:1+t:2+f:!2,m:1+t:23+f:!2,m:0+t:81+s:262144+f:!2",
"fields": "f12", # 仅需股票代码,减少数据量
"fid": "f3",
"pn": 1,
"pz": 1, # 每页1条,快速获取总数量
"ut": "fa5fd1943c7b386f172d6893dbfba10b"
}
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"}
response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers, timeout=10)
stock_json = response.json()
if stock_json.get("rc") == 0 and "data" in stock_json:
total = stock_json["data"]["total"]
print(f" 检测到当前市场共{total}只股票")
return total
else:
print(" 无法获取总股票数,默认按5500只处理")
return 5500
except Exception as e:
print(f" 获取总股票数失败:{str(e)},默认按5500只处理")
return 5500
def crawl_all_stocks_save_excel():
"""全量爬取+去重+仅保存Excel文件"""
all_stocks = []
page_size = 50 # 每页50条,效率与稳定性平衡
total_count = get_total_stock_count()
total_pages = ceil(total_count / page_size) # 向上取整,确保爬完所有页
print(f" 爬取计划:共{total_pages}页,每页{page_size}条\n")
# 1. 循环爬取所有页面
for page_num in range(1, total_pages + 1):
print(f" 正在爬取第{page_num}/{total_pages}页...")
page_data = get_single_page_data(page_num, page_size)
if page_data:
# 2. 去重:用股票代码(f12,唯一标识)判断,避免重复添加
new_stock_count = 0
for stock in page_data:
stock_code = stock.get("f12")
# 检查该代码是否已在all_stocks中,不在则添加
if not any(existing_stock.get("f12") == stock_code for existing_stock in all_stocks):
all_stocks.append(stock)
new_stock_count += 1
print(f" 第{page_num}页爬取成功,新增{new_stock_count}只股票,累计{len(all_stocks)}只\n")
else:
print(f" 第{page_num}页无有效数据,累计{len(all_stocks)}只股票\n")
# 3. 数据格式化:转换为可读格式(修正原始数值÷100的问题)
formatted_data = []
for idx, stock in enumerate(all_stocks, start=1):
formatted_data.append({
"序号": idx,
"股票代码": stock.get("f12", "-"),
"股票名称": stock.get("f14", "-"),
"最新价(元)": round(stock.get("f2", 0)/100, 2) if stock.get("f2") != "-" else "-",
"涨跌幅(%)": round(stock.get("f3", 0)/100, 2) if stock.get("f3") != "-" else 0,
"涨跌额(元)": round(stock.get("f4", 0)/100, 2) if stock.get("f4") != "-" else "-",
"成交量(手)": stock.get("f5", "-"),
"成交额(万元)": round(stock.get("f6", 0)/10000, 1) if stock.get("f6") != "-" else "-",
"换手率(%)": round(stock.get("f23", 0)/100, 2) if stock.get("f23") != "-" else 0
})
# 4. 保存为Excel文件
if formatted_data:
excel_path = "全量A股股票数据.xlsx"
# 用pandas生成Excel,列顺序清晰
df = pd.DataFrame(formatted_data)
# 调整列顺序,与日常查看习惯一致
column_order = ["序号", "股票代码", "股票名称", "最新价(元)", "涨跌幅(%)", "涨跌额(元)", "成交量(手)", "成交额(万元)", "换手率(%)"]
df = df[column_order]
# 保存Excel(engine=openpyxl支持.xlsx格式)
df.to_excel(excel_path, index=False, engine="openpyxl")
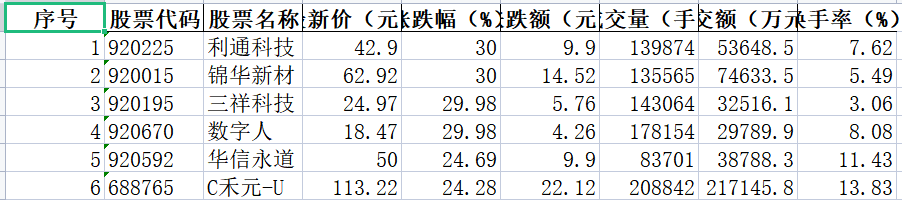
print(f" 爬取完成!共获取{len(formatted_data)}只无重复股票数据")
print(f" Excel文件已保存至:{excel_path}")
else:
print(" 未获取到任何有效股票数据,无法生成Excel文件")
return formatted_data
# ------------------- 主程序:直接运行即可 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 启动全量爬取并保存Excel
crawl_all_stocks_save_excel()

实验心得

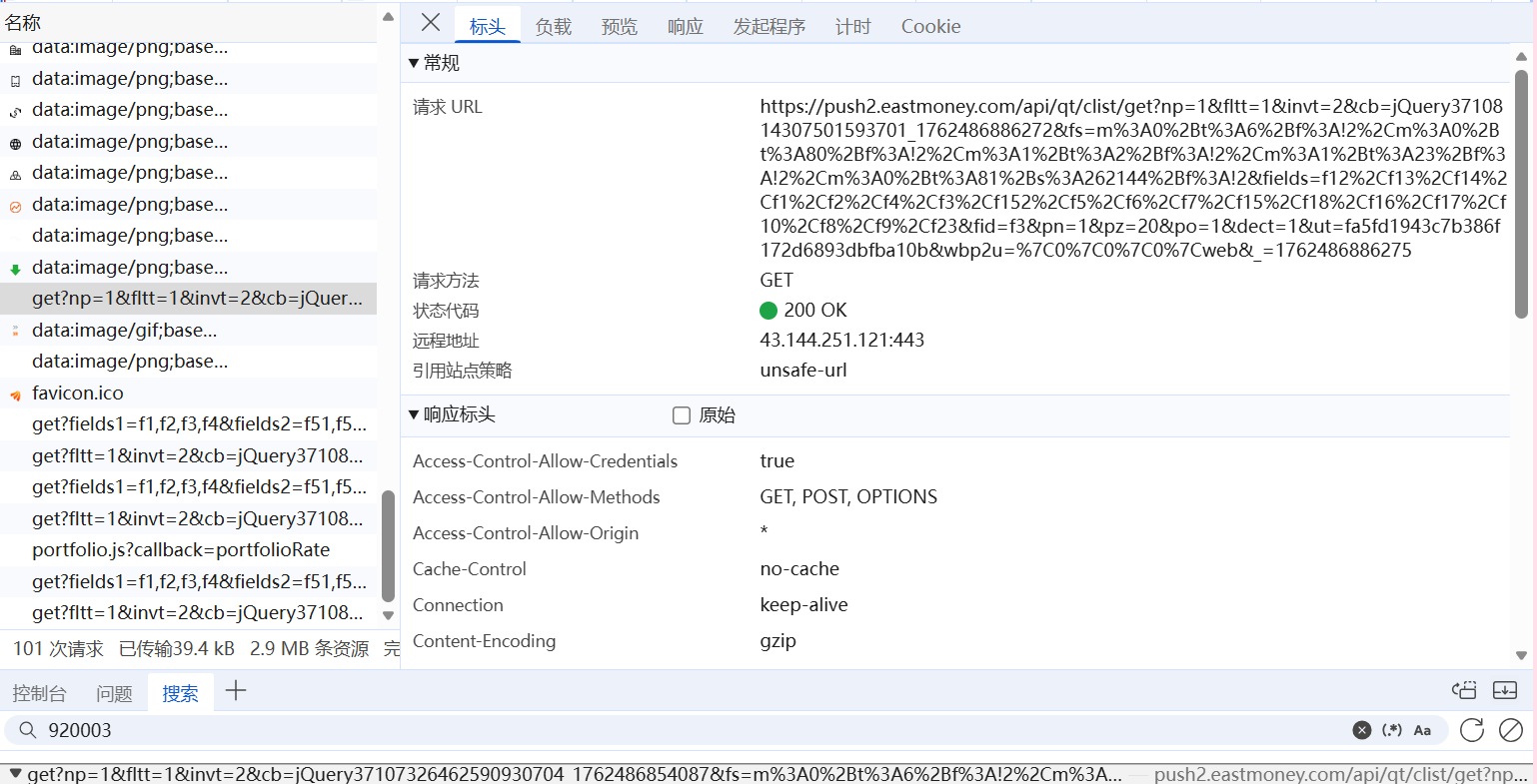
我们通过f12查看页面网络,然后搜索一下当天股票的代码,就能找到储存股票信息的js文件,我们可以看到股票信息
以及请求的url(有时候爬太多会被反爬)可以在可以爬的时候保存json文件或者用其他url(params参数)进行爬取,(也有尝试过保存json文件的方式)
保存json的方式
总结:这个任务让我深知F12开发者工具的价值——通过Network面板定位股票API,用requests携带参数请求,解析JSON数据并去重、换算单位,最终保存为Excel,比解析HTML简洁高效太多,核心就是找对接口、理清参数、做好数据清洗。
作业3
爬取中国大学2021主榜(https://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2021)所有院校信息,并存储在数据库中,同时将浏览器F12调试分析的过程录制Gif加入至博客中。
代码和结果
代码:
抓包寻找url的时候,我们可以看到其实网站的js文件储存了所有的学校信息,而且学校的一些信息是通过变量名——实际值这样的一个映射存在js文件中的,如果我们直接提取js文件,学校的省市什么的只能提取出一些英文字母的变量名,我们在js文件底部能找到映射字典,再通过正则表达式来提取信息的各个字段,保存在数据库里,为了方便直接查看,还保存了一个csv文件

点击查看代码
import requests
import re
import sqlite3
import csv
class UniversitySpider:
def __init__(self):
# 数据源URL - 包含所有大学排名信息的JS文件
self.url = "https://www.shanghairanking.cn/_nuxt/static/1762223212/rankings/bcur/2021/payload.js"
def get_js_content(self):
# 获取原始JS数据
response = requests.get(self.url)
return response.text
def build_mapping(self):
# 构建变量映射表:字母变量 → 实际含义
mapping = {
# 学校类型映射
'e': '理工', 'f': '综合', 'h': '师范', 'm': '农业', 'P': '林业',
# 省市地区映射
'q': '北京', 'N': '天津', 'p': '河北', 'G': '山西', 'L': '内蒙古',
'r': '辽宁', 'B': '黑龙江', 'C': '吉林', 'D': '上海', 'k': '江苏',
'x': '浙江', 'y': '安徽', 'z': '江西', 'F': '福建', 'n': '山东',
'o': '河南', 'v': '湖北', 'w': '湖南', 'u': '广东', 'I': '广西',
'Q': '海南', 't': '四川', 'J': '贵州', 'H': '云南', 'S': '青海',
'T': '西藏', 's': '陕西', 'K': '甘肃', 'R': '宁夏', 'O': '新疆',
'M': '重庆'
}
return mapping
def extract_data(self, content, mapping):
# 使用正则表达式提取各字段数据
school_names = re.findall(r'univNameCn:"([^"]+)"', content)
provinces = re.findall(r'province:([a-zA-Z])', content)
categories = re.findall(r'univCategory:([a-zA-Z])', content)
scores_raw = re.findall(r'score:([a-zA-Z\d.]+)', content)
universities = []
# 遍历所有学校,组装完整数据
for i in range(len(school_names)):
# 通过映射表将字母代码转换为实际值
province = mapping.get(provinces[i], '未知')
category = mapping.get(categories[i], '未知')
# 处理分数:
score_raw = scores_raw[i] if i < len(scores_raw) else '0.0'
try:
score = float(score_raw) if score_raw.replace('.', '').isdigit() else 0.0
except:
score = 0.0
universities.append({
'序号': i + 1,
'排名': i + 1,
'学校名称': school_names[i],
'省市': province,
'类型': category,
'总分': score
})
return universities
def save_data(self, universities):
# 保存到SQLite数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect('university_ranking_2021.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS universities')
cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE universities (序号 INTEGER, 排名 INTEGER, 学校名称 TEXT, 省市 TEXT, 类型 TEXT, 总分 REAL)')
for uni in universities:
cursor.execute('INSERT INTO universities VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)',
(uni['序号'], uni['排名'], uni['学校名称'], uni['省市'], uni['类型'], uni['总分']))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
# 同时保存到CSV文件
with open('university_ranking_2021.csv', 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8-sig') as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=['序号', '排名', '学校名称', '省市', '类型', '总分'])
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(universities)
print(f"已保存 {len(universities)} 所大学数据")
def display(self, universities, n=60):
# 以表格形式显示前n所大学数据
print("\n" + "=" * 100)
print(f"{'排名':<6}{'学校名称':<20}{'省市':<8}{'类型':<6}{'总分':<8}")
print("=" * 100)
for uni in universities[:n]:
print(f"{uni['排名']:<8}{uni['学校名称']:<22}{uni['省市']:<10}{uni['类型']:<8}{uni['总分']:<8.1f}")
print("=" * 100)
print(f"总共 {len(universities)} 所大学(显示前 {n} 所)")
def run(self):
# 主执行流程
content = self.get_js_content() # 1. 获取数据
mapping = self.build_mapping() # 2. 构建映射表
universities = self.extract_data(content, mapping) # 3. 提取数据
self.save_data(universities) # 4. 存储数据
self.display(universities) # 5. 显示结果
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 启动爬虫
UniversitySpider().run()

数据库和csv文件保存全部信息

实验心得
这一次我们通过构建映射表将字母变量转换为实际省市和类型信息,并使用正则表达式提取结构化数据,成功提取了582所学校的信息,了解到了映射这么一个js文件的保存方式,此外我发现原网站的js文件中分数有少部分采用两位字母的变量名储存,但是很奇怪没有一个有规律的映射关系,可能需要手动一个一个对应?,但总体还是顺利爬取了学校信息,学会了如何用抓包和读取js文件的方式实现爬虫。
gitee仓库链接
https://gitee.com/yaya-xuan/zyx_project/tree/master/数据采集/作业2




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号