刷题笔记5.树、二叉树、二叉搜索树
树、二叉树、二叉搜索树
树

二叉树

LinkedList是特殊化的Tree,Tree是特殊化的Graph
Public class TreeNode{
public int val;
public TreeNode left,right;
public TreeNode(int val){
this.val=val;
this.left=null;
this.right=null;
}
}
二叉树遍历
史上最全遍历二叉树详解 - 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)


中左右
左中右
左右中
1.递归方式


递归序

先序:打印第一次出现

2.非递归方式
前序遍历:
首先我们应该创建一个Stack用来存放节点,首先我们想要打印根节点的数据,此时Stack里面的内容为空,所以我们优先将头结点加入Stack,然后打印。
之后我们应该先打印左子树,然后右子树。所以先加入Stack的就是右子树,然后左子树。
此时你能得到的流程如下



public static void preOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
}
后序遍历:头右左是左右头的逆序,先压左再压右,准备一个新的栈逆序打印。两个栈
中序遍历:
1.同理创建一个Stack,然后按 左 中 右的顺序输出节点。
2.尽可能的将这个节点的左子树压入Stack,此时栈顶的元素是最左侧的元素,其目的是找到一个最小单位的子树(也就是最左侧的一个节点),并且在寻找的过程中记录了来源,才能返回上层,同时在返回上层的时候已经处理完毕左子树了。
3.当处理完最小单位的子树时,返回到上层处理了中间节点。(如果把整个左中右的遍历都理解成子树的话,就是处理完 左子树->中间(就是一个节点)->右子树)
4.如果有右节点,其也要进行中序遍历

public static void inOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
TreeNode cur = head;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
if (node.right != null) {
cur = node.right;
}
}
}


后序遍历:
左右中 左树处理完了处理右树,一个栈搞定。利用h
前序遍历的过程 是 中左右。
将其转化成 中右左。也就是压栈的过程中优先压入左子树,在压入右子树。
然后将这个结果返回来,这里是利用栈的先进后出倒序打印。
public static void postOrderIteration(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(head);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(node);
if (node.left != null) {
stack1.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
stack1.push(node.right);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
宽度优先遍历


按层遍历,一个队列。
public static void level(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println(cur.value);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
}
求树的最大宽度

使用map的方式
public static int maxWidthUseMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
// key 在 哪一层,value
HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>();
levelMap.put(head, 1);
int curLevel = 1; // 当前你正在统计哪一层的宽度
int curLevelNodes = 0; // 当前层curLevel层,宽度目前是多少
int max = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
int curNodeLevel = levelMap.get(cur);
if (cur.left != null) {
levelMap.put(cur.left, curNodeLevel + 1);
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
levelMap.put(cur.right, curNodeLevel + 1);
queue.add(cur.right);
}
if (curNodeLevel == curLevel) {
curLevelNodes++;
} else {
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes);
curLevel++;
curLevelNodes = 1;
}
}
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes);
return max;
}

public static int maxWidthNoMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
Node curEnd = head; // 当前层,最右节点是谁
Node nextEnd = null; // 下一层,最右节点是谁
int max = 0;
int curLevelNodes = 0; // 当前层的节点数
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
nextEnd = cur.left;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
nextEnd = cur.right;
}
curLevelNodes++;
if (cur == curEnd) {
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes);
curLevelNodes = 0;
curEnd = nextEnd;
}
}
return max;
}
二叉搜索树


复杂度分析

二叉树搜索树的递归套路
本质是利用二叉树的遍历性
二叉树的递归套路
1)假设以X节点为头,假设可以向X左树和X右树要任何信息
2)在上一步的假设下,讨论以X为头节点的树,得到答案的可能性(最重要)
3)列出所有可能性后,确定到底需要向左树和右树要什么样的信息
4)把左树信息和右树信息求全集,就是任何一-棵子树都需要返回的信息S
5)递归函数都返回S,每一棵子树都这么要求
6)写代码,在代码中考虑如何把左树的信息和右树信息整合出整棵树的信息
实践
1.给定一颗二叉树的头节点head,返回这棵树是不是平衡二叉树。
平衡性:

2.给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,任何两个节点之间都存在距离,返回整棵二叉树的最大距离
可能性1:与头节点x无关

可能性二:与x有关

<img src="%E6%9E%81%E5%AE%A2%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95.assets/image-20210708094614373.png" alt="image-20210708094614373" style="zoom:50%;" /
动态规划,

得到左节点f(d)的信息,返回,在到右节点

public static int maxDistance2(Node head) {
return process(head).maxDistance;
}
public static class Info {
public int maxDistance;
public int height;
public Info(int m, int h) {
maxDistance = m;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
int p1 = leftInfo.maxDistance;
int p2 = rightInfo.maxDistance;
int p3 = leftInfo.height + rightInfo.height + 1;
int maxDistance = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), p3);
return new Info(maxDistance, height);
}
3.给定头节点,返回这颗二叉搜索树子树的头节点

搜索二叉树,所有子树都满足左<头<右;


public static int maxSubBSTSize2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(head).maxSubBSTSize;
}
// 任何子树
public static class Info {
public boolean isAllBST;
public int maxSubBSTSize;
public int min;
public int max;
public Info(boolean is, int size, int mi, int ma) {
isAllBST = is;
maxSubBSTSize = size;
min = mi;
max = ma;
}
}
public static Info process(Node X) {
if(X == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(X.left);
Info rightInfo = process(X.right);
int min = X.value;
int max = X.value;
if(leftInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, leftInfo.min);
max = Math.max(max, leftInfo.max);
}
if(rightInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, rightInfo.min);
max = Math.max(max, rightInfo.max);
}
int maxSubBSTSize = 0;
if(leftInfo != null) {
maxSubBSTSize = leftInfo.maxSubBSTSize;
}
if(rightInfo !=null) {
maxSubBSTSize = Math.max(maxSubBSTSize, rightInfo.maxSubBSTSize);
}
boolean isAllBST = false;
if(
// 左树整体需要是搜索二叉树
( leftInfo == null ? true : leftInfo.isAllBST )
&&
( rightInfo == null ? true : rightInfo.isAllBST )
&&
// 左树最大值<x
(leftInfo == null ? true : leftInfo.max < X.value)
&&
(rightInfo == null ? true : rightInfo.min > X.value)
) {
maxSubBSTSize =
(leftInfo == null ? 0 : leftInfo.maxSubBSTSize)
+
(rightInfo == null ? 0 : rightInfo.maxSubBSTSize)
+
1;
isAllBST = true;
}
return new Info(isAllBST, maxSubBSTSize, min, max);
}
4.派对的最大快乐值
员工信息的定义如下:
class Employee{
public int happy;//这名员工可以带来的快乐值
List<Employee>subordinates;//这名员工有哪些直接下级
}
派对的最大快乐值
这个公司现在要办party,你可以决定哪些员工来,哪些员工不来,规则:
1.如果某个员工来了,那么这个员工的所有直接下级都不能来
2.派对的整体快乐值是所有到场员工快乐值的累加
3.你的目标是让派对的整体快乐值尽量大给定一棵多叉树的头节点boss,请返回派对的最大快乐值。


头节点来情况下,不来情况下的最大快乐值
public static int maxHappy2(Employee head) {
Info allInfo = process(head);
return Math.max(allInfo.no, allInfo.yes);
}
public static class Info {
public int no;
public int yes;
public Info(int n, int y) {
no = n;
yes = y;
}
}
public static Info process(Employee x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
int no = 0;
int yes = x.happy;
for (Employee next : x.nexts) {
Info nextInfo = process(next);
no += Math.max(nextInfo.no, nextInfo.yes);
yes += nextInfo.no;
}
return new Info(no, yes);
}
二叉树实战题目:
二叉树/N叉树的遍历

非递归遍历
1.迭代法
前序遍历:中左右
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root==null) return ans;
Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node=stack.pop();
ans.add(node.val);
if(node.right!=null) stack.push(node.right);
if(node.left!=null) stack.push(node.left);
}
return ans;
}
}
中序遍历:左中右
递归的调用过程是不断往左边走,当左边走不下去了,就打印节点,并转向右边,然后右边继续这个过程。
我们在迭代实现时,就可以用栈来模拟上面的调用过程。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(stack.size()>0 || root!=null) {
//不断往左子树方向走,每走一次就将当前节点保存到栈中
//这是模拟递归的调用
if(root!=null) {
stack.add(root);
root = root.left;
//当前节点为空,说明左边走到头了,从栈中弹出节点并保存
//然后转向右边节点,继续上面整个过程
} else {
TreeNode tmp = stack.pop();
res.add(tmp.val);
root = tmp.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
}
后序遍历:中左右
- 前序遍历的过程 是 中左右。
- 将其转化成 中右左。也就是压栈的过程中优先压入左子树,在压入右子树。
- 然后将这个结果返回来,这里是利用栈的先进后出倒序打印。
public List postorder(TreeNode root){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode();
Stack stack = new Stack();
List list = new LinkedList();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root!=null){
if(root!=null){
//头插法
List.addFirst(root.val);
if(root.left!=null)
stack.push(root.left);
//优先访问右子树
root = root.right;
}else {
root = stack.pop();
}
}
return list;
}
2. 颜色法
其核心思想如下:
使用颜色标记节点的状态,新节点为白色,已访问的节点为灰色。
如果遇到的节点为白色,则将其标记为灰色,然后将其右子节点、自身、左子节点依次入栈。
如果遇到的节点为灰色,则将节点的值输出。
前序遍历:中,左,右
中序遍历:左,中,右
后序遍历:左,右,中
对于不同遍历调整顺序,倒序入栈即可
class Solution {
class ColorNode {
TreeNode node;
String color;
public ColorNode(TreeNode node,String color){
this.node = node;
this.color = color;
}
}
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<ColorNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new ColorNode(root,"white"));
while(!stack.empty()){
ColorNode cn = stack.pop();
if(cn.color.equals("white")){
if(cn.node.right != null) stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node.right,"white"));
stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node,"gray"));
if(cn.node.left != null)stack.push(new ColorNode(cn.node.left,"white"));
}else{
res.add(cn.node.val);
}
}
return res;
}
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
一套拳法👊刷掉n个遍历树的问题 - N 叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode head){
if(head==null) return;
//前序
dfs(head.left);
ans.add(head.val);//中序
dfs(head.right);
//后序
}
}
590. N 叉树的后序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
N 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
进阶:
递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?

1.递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
if(root==null) return ans;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(Node root){
if(root.children==null) return;
for(Node child:root.children){
dfs(child);
}
ans.add(root.val);
}
}
2.非递归,栈
从左到右 子节点入栈
class Solution {
List<Integer> list ;
Deque<Node> stack ;
public List<Integer> postorder(Node root) {
list = new ArrayList<>() ;
stack = new LinkedList<>() ;
if(root == null) return list;
stack.push(root) ;
Node current ;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
current = stack.pop() ;
list.add(current.val) ;
for(Node child : current.children)
{
stack.push(child) ;
}
}
Collections.reverse(list) ;
return list ;
}
}
589. N 叉树的前序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的 前序遍历 。
N 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
进阶:
递归法很简单,你可以使用迭代法完成此题吗?
方法:迭代
由于递归实现 N 叉树的前序遍历较为简单,因此我们只讲解如何使用迭代的方法得到 N 叉树的前序遍历。
我们使用栈来帮助我们得到前序遍历,需要保证栈顶的节点就是我们当前遍历到的节点。
我们首先把根节点入栈,因为根节点是前序遍历中的第一个节点。随后每次我们从栈顶取出一个节点 u,它是我们当前遍历到的节点,并把 u 的所有子节点逆序推入栈中。例如 u 的子节点从左到右为 v1, v2, v3,那么推入栈的顺序应当为 v3, v2, v1,这样就保证了下一个遍历到的节点(即 u 的第一个子节点 v1)出现在栈顶的位置。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
LinkedList<Integer> output = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return output;
}
LinkedList<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.add(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.pollLast();
output.add(node.val);
Collections.reverse(node.children);
for (Node item : node.children) {
stack.add(item);
}
}
return output;
}
}
590. N 叉树的后序遍历
1.迭代,比较简单
2,
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
LinkedList<Integer> output = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return output;
}
LinkedList<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.add(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.pollLast();
output.add(node.val);
Collections.reverse(node.children);
for (Node item : node.children) {
stack.add(item);
}
}
return output;
}
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
难度中等
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。

API
//双向队列:
Deque<Integer> levelList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
levelList.offerLast(curNode.val);//尾插
levelList.offerFirst(curNode.val);//头插
//队列:
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode tmp = queue.poll();
queue.offer(root);
//双向链表:
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
path.addFirst(tmp.val);//头插
path.addLast(tmp.val);//尾插
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//结果
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
//层次便利需要的队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
//用于计数,奇数的时候反转,偶数的时候不反转
int count = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
//保存每一层的结果,用LinkedList实现
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){
TreeNode tmp = queue.poll();
if (tmp.left != null) queue.add(tmp.left);
if (tmp.right != null) queue.add(tmp.right);
if (count % 2 == 1){
//奇数层,头插
path.addFirst(tmp.val);
}else{
//偶数层,正常从前往后加入
path.addLast(tmp.val);
}
}
//一层遍历结束之后,添加到结果,count++
count++;
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return res;
}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
难度中等596收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:

输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
1.BFS
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return res;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
res.add(queue.peek().val);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node= queue.poll();
if(node.right!=null) queue.offer(node.right);
if(node.left!=null) queue.offer(node.left);
}
}
return res;
}
}
2.dfs深度
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0); // 从根节点开始访问,根节点深度是0
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 先访问 当前节点,再递归地访问 右子树 和 左子树。
if (depth == res.size()) { // 如果当前节点所在深度还没有出现在res里,说明在该深度下当前节点是第一个被访问的节点,因此将当前节点加入res中。
res.add(root.val);
}
depth++;
dfs(root.right, depth);
dfs(root.left, depth);
}
}
二叉树层序遍历登场
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
- 199.二叉树的右视图
- 637.二叉树的层平均值
- 429.N叉树的前序遍历
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
二叉树的属性
101. 对称二叉树
104. 二叉树的最大深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度
未做题解
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
未做题解
110. 平衡二叉树
257. 二叉树的所有路径
未做题解
404. 左叶子之和
未做题解
513. 找树左下角的值
未做题解
二叉树路径问题(问题分析+分类模板+题目剖析)
二叉树路径的问题大致可以分为两类:
1、自顶向下:
顾名思义,就是从某一个节点(不一定是根节点),从上向下寻找路径,到某一个节点(不一定是叶节点)结束
具体题目如下:
257. 二叉树的所有路径
面试题 04.12. 求和路径
112. 路径总和
113. 路径总和 II
437. 路径总和 III
988. 从叶结点开始的最小字符串
而继续细分的话还可以分成一般路径与给定和的路径
2、非自顶向下:
就是从任意节点到任意节点的路径,不需要自顶向下
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
687. 最长同值路径
543. 二叉树的直径
二叉树的修改和构造
114. 二叉树展开为链表
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉
617. 合并二叉树
654. 最大二叉树
未做题解
100. 相同的树
简单
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
DFS
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
} else if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
} else if (p.val != q.val) {
return false;
} else {
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}
}
BFS
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
} else if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue1.offer(p);
queue2.offer(q);
while (!queue1.isEmpty() && !queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node1 = queue1.poll();
TreeNode node2 = queue2.poll();
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
TreeNode left1 = node1.left, right1 = node1.right, left2 = node2.left, right2 = node2.right;
if (left1 == null ^ left2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (right1 == null ^ right2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (left1 != null) {
queue1.offer(left1);
}
if (right1 != null) {
queue1.offer(right1);
}
if (left2 != null) {
queue2.offer(left2);
}
if (right2 != null) {
queue2.offer(right2);
}
}
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。

这道题目背后有一个让程序员心酸的故事,听说 Homebrew的作者Max Howell,就是因为没在白板上写出翻转二叉树,最后被Google拒绝了。
利用前序遍历
class Solution {
// 先序遍历--从顶向下交换
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
// 保存右子树
TreeNode rightTree = root.right;
// 交换左右子树的位置
root.right = invertTree(root.left);
root.left = invertTree(rightTree);
return root;
}
}
利用中序遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
invertTree(root.left); // 递归找到左节点
TreeNode rightNode= root.right; // 保存右节点
root.right = root.left;
root.left = rightNode;
// 递归找到右节点 继续交换 : 因为此时左右节点已经交换了,所以此时的右节点为root.left
invertTree(root.left);
}
}
利用后序遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// 后序遍历-- 从下向上交换
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode leftNode = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode rightNode = invertTree(root.right);
root.right = leftNode;
root.left = rightNode;
return root;
}
}
利用层次遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// 层次遍历--直接左右交换即可
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
TreeNode rightTree = node.right;
node.right = node.left;
node.left = rightTree;
if (node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
二叉搜索树的属性
98. 验证二叉搜索树
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
未做题解
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
未做题解
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
难度简单224收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k大的节点。
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
3
/ \
1 4
\
2
输出: 4
到这里又有疑问了,为什么k作为参数传递出现了两个不同的k?int作为基本类型传参,只要修改就会重新在内存中开辟新的地址,而引用类型传参栈中地址会指向堆内的实际对象,修改的时候是同一个;所以这里k必须用类变量保证其唯一性防止判断出错
题目指出:1≤k≤N (二叉搜索树节点个数);因此无需考虑 k > N 的情况。
若考虑,可以在中序遍历完成后判断 k > 0k>0 是否成立,若成立则说明 k > Nk>N 。
class Solution {
int res, k;
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null||k==0) return;
dfs(root.right);
if(--k == 0) res = root.val;
dfs(root.left);
}
}
二叉搜索树的修改和构造
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
未做题解
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
未做题解
669. 修剪二叉搜索树
未做题解
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
难度简单945
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。
高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
示例 1:

输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
根据中序遍历结果构造二叉树
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
public TreeNode dfs(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return null;
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=dfs(nums,left,mid-1);
root.right=dfs(nums,mid+1,right);
return root;
}
}
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
难度中等666
给定一个单链表,其中的元素按升序排序,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
给定的有序链表: [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9],
一个可能的答案是:[0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], 它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
类似于108,链表找中点使用快慢指针
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
return dfs(head,null);
}
public TreeNode dfs(ListNode left,ListNode right){
if(left==right) return null;
ListNode mid=getMedian(left,right);
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(mid.val);
root.left=dfs(left,mid);
root.right=dfs(mid.next,right);
return root;
}
public ListNode getMedian(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
ListNode fast = left;
ListNode slow = left;
while (fast != right && fast.next != right) {
fast = fast.next;
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
难度中等360收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。
为了让您更好地理解问题,以下面的二叉搜索树为例:
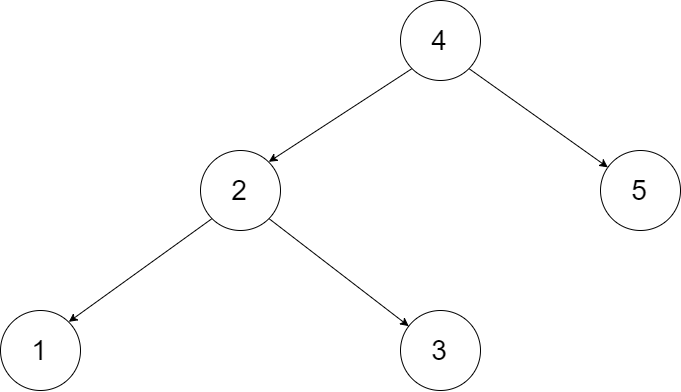
我们希望将这个二叉搜索树转化为双向循环链表。链表中的每个节点都有一个前驱和后继指针。对于双向循环链表,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
下图展示了上面的二叉搜索树转化成的链表。“head” 表示指向链表中有最小元素的节点。
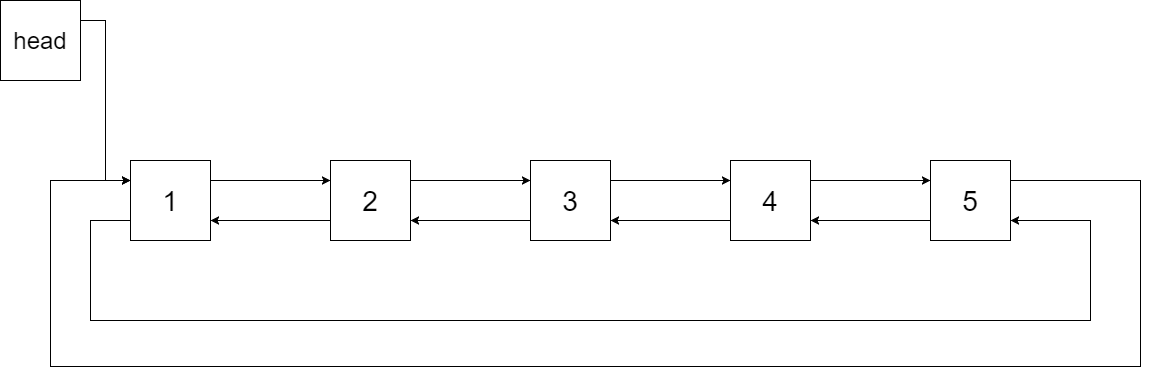
特别地,我们希望可以就地完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。
中序遍历
- 排序链表: 节点应从小到大排序,因此应使用 中序遍历 “从小到大”访问树的节点。
- 双向链表: 在构建相邻节点的引用关系时,设前驱节点 pre 和当前节点 cur ,不仅应构建 pre.right = cur ,也应构建 cur.left = pre
- 循环链表: 设链表头节点
head和尾节点tail,则应构建head.left = tail和tail.right = head。
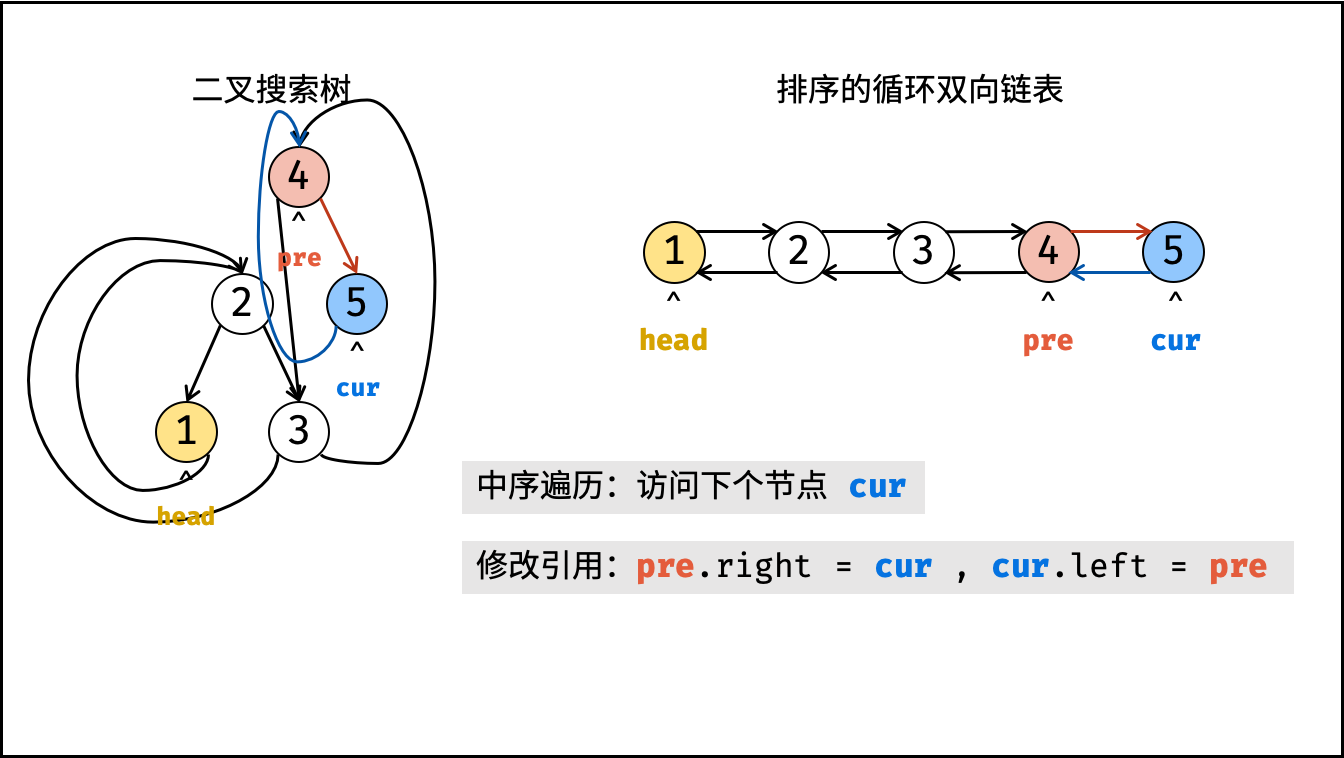
算法流程:
dfs(cur): 递归法中序遍历;
- 终止条件: 当节点
cur为空,代表越过叶节点,直接返回; - 递归左子树,即
dfs(cur.left); - 构建链表:
- 当
pre为空时: 代表正在访问链表头节点,记为head; - 当 pre 不为空时: 修改双向节点引用,即 pre.right = cur , cur.left = pre ;
- 保存 cur : 更新 pre = cur ,即节点 cur 是后继节点的 pre ;
- 当
构建循环链表: 中序遍历完成后,head 指向头节点, pre 指向尾节点,因此修改 head 和 pre 的双向节点引用即可
class Solution {
Node head, pre;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null) return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right = head;
head.left =pre;//进行头节点和尾节点的相互指向,这两句的顺序也是可以颠倒的
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
//pre用于记录双向链表中位于cur左侧的节点,即上一次迭代中的cur,当pre==null时,cur左侧没有节点,即此时cur为双向链表中的头节点
if(pre==null) head = cur;
//反之,pre!=null时,cur左侧存在节点pre,需要进行pre.right=cur的操作。
else pre.right = cur;
cur.left = pre;//pre是否为null对这句没有影响,且这句放在上面两句if else之前也是可以的。
pre = cur;//pre指向当前的cur
dfs(cur.right);//全部迭代完成后,pre指向双向链表中的尾节点
}
}
二叉树的公共祖先
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
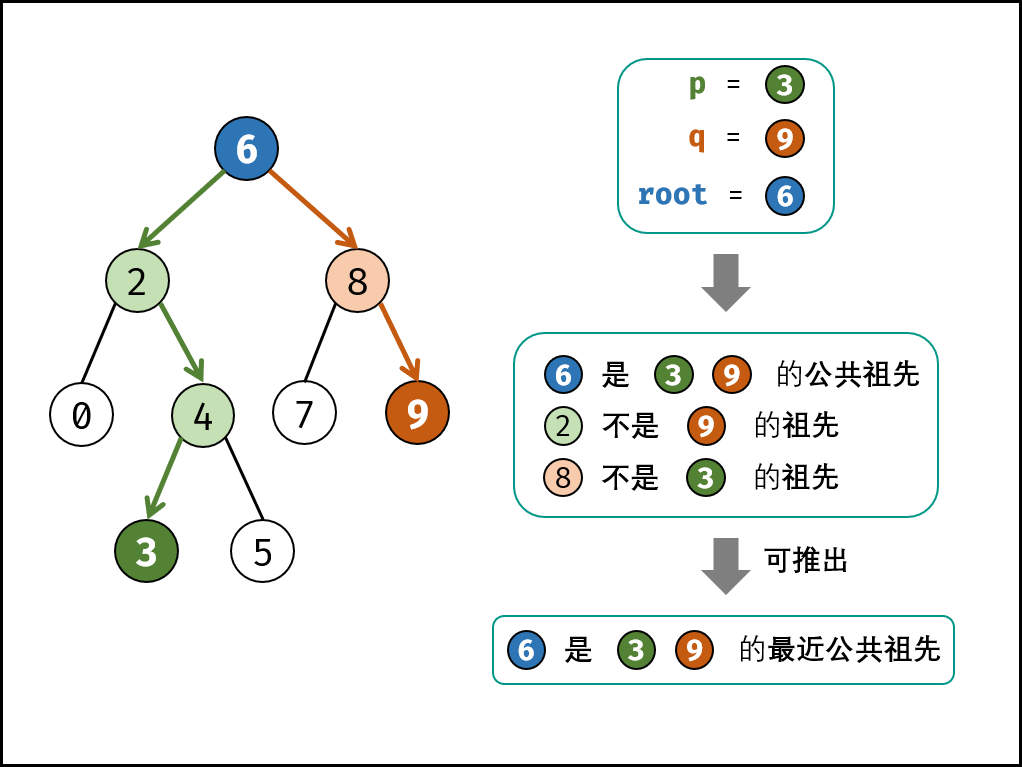
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
方法一:迭代
若 root.val < p.val ,则 pp 在 root 右子树 中;
若 root.val > p.val ,则 pp 在 root 左子树 中;
若 root.val = p.val ,则 pp 和 root 指向 同一节点 。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while(root != null) {
if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) // p,q 都在 root 的右子树中
root = root.right; // 遍历至右子节点
else if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) // p,q 都在 root 的左子树中
root = root.left; // 遍历至左子节点
else break;
}
return root;
}
}
优化:若可保证 p.val < q.valp.val<q.val ,则在循环中可减少判断条件。
方法二:递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
return root;
}
}
递归模板
public void recur(int level,int param){
//terminator1.终止条件
if(level > Max_Level){
// process result
return;
}
// process current logic 2.每一层的逻辑
process(level, param);
//drill down
recur(level:level+1, newParam);
//restore current status
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号