第七次总结 文件操作 io
- 什么是数据流?
- FileInputStream的使用方法?
- FileOutputStream的使用方法?
- 如何完成一个文件的复制??
1.什么是数据流?
文件和内存之间数据的传输称之为数据流
数据流分为输入流和输出流(输入和输入的相对的)
字节输入流
InputStream
- FileInputStream 从文件中获得字节输入
- ByteArrayInputStream 从字节数组中获得字节输入
- BufferedInputStream 缓冲字节输入流
- DataInputStream 基本数据类型输入流
- ObjectInputStream 对象输入流
字节输出流
OutputStream
- FileOutputStream 将数据写到文件中
- ByteArrayOutputStream 将数据写到字节数组中
- BufferedOutputStream 将数据写到缓冲流中
- DataOutputStream 将数据以基本数据类型的方式写出
- ObjectOutputStream 将数据以对象的方式写出
2.FileInputStream的使用方法?
文件字节输入流
常用的构造方法
new FileInputStream(文件路径)
String pate ="D:\\11\\file.txt"; try { FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream(pate); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
常用方法
从输入流中读取一个字节,如果返回的是-1。说明已经读到的文件末尾
否则返回读取到的字节
int t = fis.read();.
int i = fis.read(); while (i!=-1){ i=fis.read(); }
从输入流中读取字节,填充到字节数组中,直到填满字节数组或者达到文件末尾
返回值表示本次总共读取了字节数
int len= fis.read(byte[]).
File f =new File(pate); //length是long类型,强制转换成int类型 此方法只使用于小文件 int len = (int) f.length(); byte [] bytes =new byte[len]; fis.read(bytes);
从输入流中最多读取length个字节,填充到字节数组中,从start下标位置开始填充
fis.read(byte[],int start,int length)
File f =new File(pate); //length是long类型,强制转换成int类型 此方法只使用于小文件 int len = (int) f.length(); byte [] bytes =new byte[len]; fis.read(bytes,3,3);
获得输入流中的估计剩余字节数
int t = fis.available();
读取3个字符后对比
int i = fis.available(); System.out.println(i); fis.read(bytes, 3, 3); i = fis.available();
输出结果:

跳过指定的字节数
fis.skip(3);
获得全部字节:
fis.read(bytes); String s = new String(bytes); System.out.println(s);
输出结果:
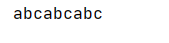
跳过2个字节:
fis.skip(2); String s = new String(bytes); System.out.println(s);
输出结果:
![]()
关闭输入流
fis.close()
3.FileOutputStream的使用方法?
文件字节输出流 输出会覆盖原本的内容
构造方法
new FileOutputStream(String path)
String pate = "D:\\11\\file1.txt"; try { //如果没有该路径文件,将自动创建 FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream(pate); }catch (Exception ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); }
追加模式的构造方法
new FileOutputStream(String path,boolean append)
String path = "D:\\aa\\aa.log"; //创建文件输出流 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path,true); String msg = "2020-07-22 17:00:20 zhangsan loginOut"; //将要写的内容转换成字节数组 byte[] bs = msg.getBytes(); //写到输出流中 fos.write(bs); fos.flush(); fos.close();
常用方法
将指定的字节写到输出流
write(int t)
FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream(pate); //输出a fos.write(97);
将数组中的所有字节写到输出流
write(byte[] bs)
FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream(pate); String s ="One World, One Dream"; //将字符串类型转换成byte数组 byte [] by =s.getBytes(); fos.write(by);
从数组的指定位置开始,将最多len个字节写到输出流
write(byte[] bs,int start,int len)
FileOutputStream fos =new FileOutputStream(pate); String s ="One World, One Dream"; //将字符串类型转换成byte数组 byte [] by =s.getBytes(); fos.write(by,2,6);
输出结果:
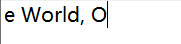
强制输出流中的数据
flush()
fos.close();
关闭输出流
close()
4.如何完成一个文件的复制??
copy方法实现文件复制
//src 要复制的源文件
//dest 要复制的目标文件
public void copy(String src,String dest) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { //创建文件输入和输出流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest); //通过输入流来读取元原文件中的字节数据 int t = fis.read(); //如果没有读到文件末尾,就不停的读取 while(t!=-1){ //每读取一个,就将读取到的字节写到输出流中 fos.write(t); //继续读取下一个字节 t = fis.read(); } //强制输出 fos.flush(); //关闭数据里 fis.close(); fos.close(); }
mian方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ FileCopy fc = new FileCopy(); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { fc.copy("D:\\aa\\Web.rar", "D:\\aa\\Web_fujian.rar"); }catch (Exception ef){ ef.printStackTrace(); } long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制完毕,耗时:"+(t2-t1)+"ms");
测试发现 该方法运行效率低
改进办法 一次多输出一些字节
copy2优化复制的方法
/** * 优化复制的方法 * 每次多读几个字节,再一次性写出去 * @param src * @param dest * @throws FileNotFoundException0 * @throws IOException */ public void copy2(String src,String dest) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{ //创建文件输入和输出流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest); //定义一个字节数组,作为字节缓冲区 //现将这个数组读满,再将整个数组写到输出流 byte[] bs = new byte[1024]; //将数据读取到字节数组中,直到填满整个数组或者读取到末尾 //返回值表示读取到了多少个字节,如果是-1,说明已经到达文件末尾 int t = fis.read(bs); while(t!=-1){ //如果没有到达末尾,就将读取到的字节写到输出流中 fos.write(bs,0,t); //继续读取下一次 t = fis.read(bs); } //强制输出 fos.flush(); //关闭资源 fos.close(); fis.close(); }
copy3使用系统提供的缓冲流来复制文件
/** * 使用系统提供的缓冲流来复制文件 * @param src * @param dest * @throws FileNotFoundException * @throws IOException */ public void copy3(String src,String dest) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { //创建文件输入和输出流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest); //将文件流包装成缓冲流 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); int t = bis.read(); while(t!=-1){ bos.write(t); t = bis.read(); } //强制输出 bos.flush(); //关闭资源 bos.close(); bis.close(); fis.close(); fos.close(); }
将三个记事本文件中的数据合并到一个记事本文件中
public class Test { /* *将三个记事本文件中的数据合并到一个记事本文件中 * */ public static void main(String[] args) { /* patea记事本a pateb记事本b pateb记事本c */ try { String patea = "D:\\11\\a.txt"; FileInputStream fisa = new FileInputStream(patea); File filea = new File(patea); //filea.length()是long类型 强转int类型 只可用于小文件小于int int len1 = (int) filea.length(); String pateb = "D:\\11\\b.txt"; FileInputStream fisb = new FileInputStream(pateb); File fileb = new File(patea); int len2 = (int) fileb.length(); String patec = "D:\\11\\c.txt"; FileInputStream fisc = new FileInputStream(patec); File filec = new File(patea); int len3 = (int) filec.length(); byte[] bytesa = new byte[len1]; byte[] bytesb = new byte[len2]; byte[] bytesc = new byte[len3]; fisa.read(bytesa); fisb.read(bytesb); fisc.read(bytesc); //输出流 String s ="D:\\11\\d.txt"; FileOutputStream file =new FileOutputStream(s); file.write(bytesa); file.write(bytesb); file.write(bytesc); //受检查异常 }catch (Exception ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号