Python入门-import导入模块功能
1.啥是模块
模块(module):用来实现或者多个功能的Python代码,(包含变量、函数、类),本质就是*.py后缀文件。
包(package):定义了一个由模块和子包组成的Python应用程序执行环境,本质就是一个有层次的文件目录结构(必须带有一个__init__.py文件)。
2.模块导入方法
# 导入一个模块 import model_name # 导入多个模块,请多次导入,不要一行导入多个 import module_name1 import module_name2 import module_name3 # 导入模块中的指定的属性、方法(不加括号)、类,一般import后面的都是类名,是大写 from moudule_name import Moudule_Element #导入后的类名太长,为了方便引用,指定别名 from moudule_name import Moudule_Element as new_name
3.import的本质-路径搜索
#import演示 #模块1:test====================== def hello(): #定义一个简单函数 print("hello") #模块2:========================= import test print(type(test)) print(test) """ <class 'module'> <module 'test' from 'E:\\code\\hunjia_16\\day13_0826\\duojincheng\\test.py'>返回代码路径 """ 1.在导入模块的时候,在执行文件后,会在模块当前目录下,新建一个__pycache__目录,并在该目录下生成对应的【.cpython-38.pyc】文件,其中38是python版本号。 2.将py模块的全部代码,加载到内存并赋值给与模块同名的变量,写在当前文件中,这个变量的类型是'module';<module 'module_name' from 'E:\\PythonImport\\module_name.py'>

#from..import..演示 #模块1:test====================== def hello(): #定义一个简单函数 print("hello") #模块2:========================= from test import hello print(type(hello)) print(hello) """ from test import hello print(type(hello)) print(hello) """ 本质是导入指定的变量或方法到当前文件中。
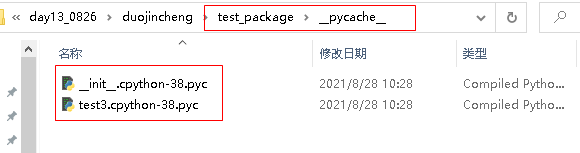
#from..import 包 #包1:test_package================= def hello(): #定义一个简单函数 print("hello") #模块2:========================= from test_package import test3 print(type(test3)) print(test3) """ <class 'module'> <module 'test_package.test3' from 'E:\\code\\hunjia_16\\day13_0826\\duojincheng\\test_package\\test3.py'> """ 导入包的本质就是执行该包下的__init__.py文件,在执行文件后,会在包目录下,新建一个__pycache__目录,并在该目录下生成对应的【.cpython-38.pyc】文件,其中38是python版本号。
4.import使用建议
#在模块导入的时候,默认现在当前目录下查找,然后再在系统中查找。系统查找的范围是:sys.path下的所有路径,依次按顺序查找。 1.导入时,系统模块在前,第三方模块在后面 2.尽量使用from..import方便系统查找,减少查找过程 3.非内建函数需要使用"import"导入。Python中的模块文件在"安装路径\Lib"目录下。 4.通过"pip install "命令安装的模块,以及自己在网站上下载的模块。一般第三方模块在"安装路径\Lib\site-packages"目录下 5.多个函数重复调用同一方法,每次都需要反复查找模块,可以自定义一个函数,直接反复用自定义函数即可,例如 def a(): hello() print("fun a")
5.疑问解答
1.导入模块,有了别名之后,原有名称是否可以继续使用?---可以正常使用
6.动态导入importlib
#https://www.cnblogs.com/zhbzz2007/p/6715516.html #coding:utf-8 import importlib.util def import_source(module_name):
#获取文件,路径和名称 module_file_path = module_name.__file__ module_name = module_name.__name__ module_spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location(module_name,module_file_path) module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(module_spec) module_spec.loader.exec_module(module) print(dir(module)) msg = "The {module_name} module has the following methods:{methods}" print(msg.format(module_name = module_name,methods = dir(module))) if __name__ == "__main__": import logging import_source(logging)
7.查找文件,方法,类-inspect
#https://www.cnblogs.com/yaohong/p/8874154.html #获取当前文件绝对路径 print(__file__) #获取当前文件名称 print(inspect.getmodulename(__file__)) #获取对应方法的,所在哪个文件 print(inspect.getfile(A.a))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号