笨办法学python习题21-30
习题21:函数可以返回某些东西
代码展示
def add(a,b):
print(f"ADDING {a} + {b}")
return a + b
def subtract(a,b):
print(f"SUNTRACTING {a} - {b}")
return a - b
def multiply(a,b):
print(f"MULTIPLYING {a} * {b}")
return a * b
def divide(a,b):
print(f"DIVIDING {a} / {b}")
return a / b
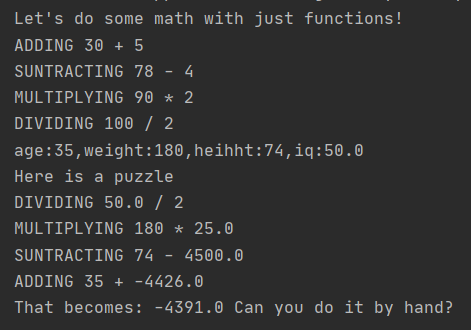
print("Let's do some math with just functions!")
age = add(30,5)
height = subtract(78,4)
weight = multiply(90,2)
iq = divide(100,2)
print(f"age:{age},weight:{weight},heihht:{height},iq:{iq}")
#A puzzle for the extra credit,type it in anyway
print("Here is a puzzle")
what = add(age,subtract(height,multiply(weight,divide(iq,2))))
print("That becomes:",what,"Can you do it by hand?")
运行结果
习题23:字符串、字节串和字符编码
代码展示
import sys
script,encoding,error = sys.argv
def main(language_file,encoding,errors):
line = language_file.readline()
if line:
print_line(line,encoding,eooros)
return main(language_file,encoding,errors)
def print_line(line,encoding,errors):
next_lang = line.strip()
raw_bytes = next_lang.encode(encoding,errors = errors)
cooked_string = raw_bytes.decode(encoding,errors = errors)
print(raw_bytes,"<===>",cooked_string)
languages = open("languages.txt",encoding = "utf-8")
main(languages,encoding,error)
运行截图:
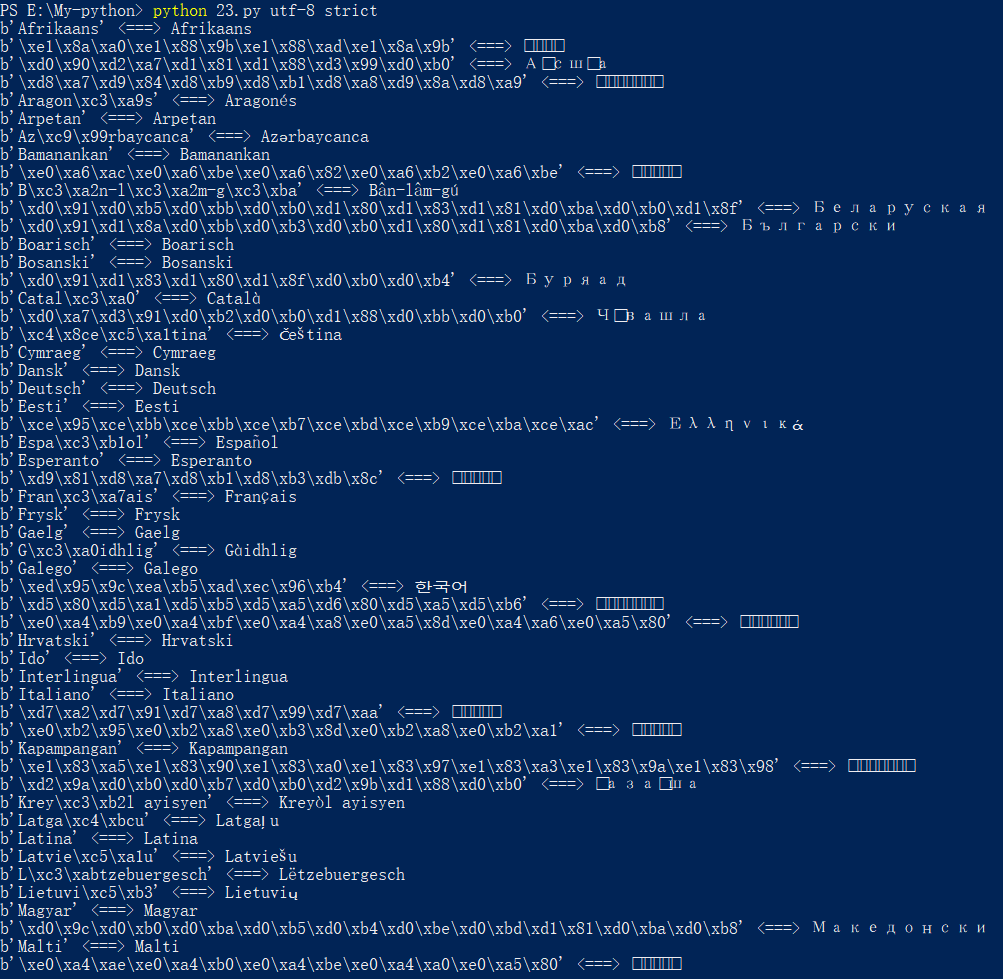
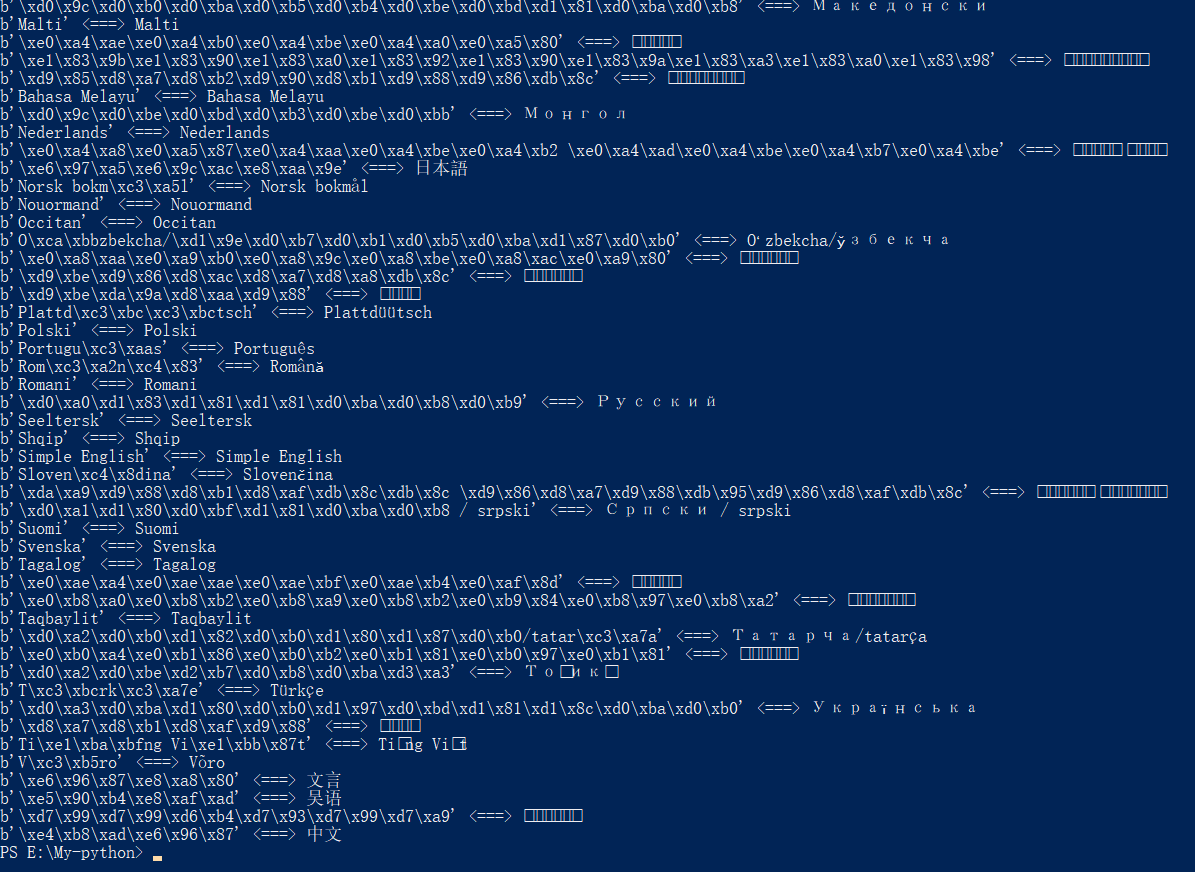
·<===>符号左侧的utf-8每一个字节的数字(十六进制),右侧是输出的字符
·当运行到文件的结尾时,readline函数会返回一个空字符串,if会检查这个空字符串,只要readline函数返回了内容这里就为真
·在main函数的最后调用了main函数,形成循环重复main函数功能,直到if语句结束循环
·print_line函数实质是对language.txt文件中的每一行进行编码
·python中strip的函数详解
·next_lang变量是一个字符串,要获取原始字节串,必须调用.encode()来编码字符串,此时需要把编码的方式和处理错误的方式传入传入encode()函数
习题24:
代码展示
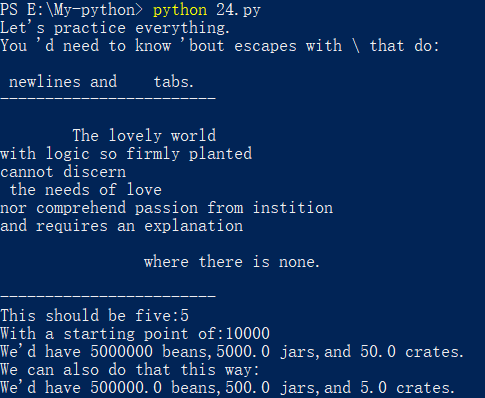
print("Let's practice everything.")
print('You \'d need to know \'bout escapes with \\ that do:')
print('\n newlines and \t tabs.')
poem = """
\tThe lovely world
with logic so firmly planted
cannot discern \n the needs of love
nor comprehend passion from instition
and requires an explanation
\n\t\twhere there is none.
"""
print("------------------------")
print(poem)
print("------------------------")
five = 10-2+3-6
print(f"This should be five:{five}")
def secret_formula(started):
jelly_beans = started * 500
jars = jelly_beans / 1000
crates = jars / 100
return jelly_beans,jars,crates
start_point = 10000
beans,jars,crates = secret_formula(start_point)
#remember that this is another way to format a string
print("With a starting point of:{}".format(start_point))
#it's just like with an f"" string
print(f"We'd have {beans} beans,{jars} jars,and {crates} crates.")
start_point = start_point / 10
print("We can also do that this way:")
formula = secret_formula(start_point)
#this is a easy way to apply a list to a format string
print("We'd have {} beans,{} jars,and {} crates.".format(*formula))
运行结果
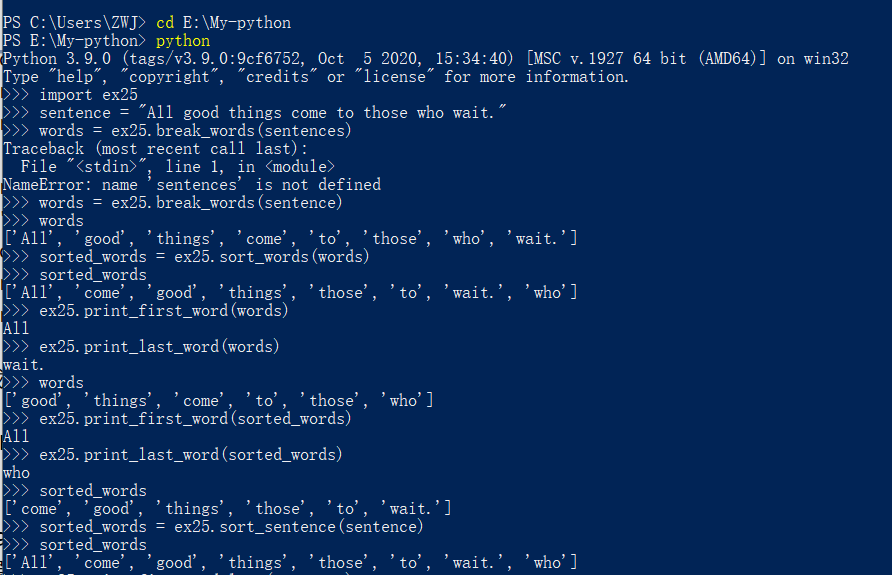
习题25:更多更多的练习
代码展示
def break_words(stuff):
"""This function will break up words for us"""
words = stuff.split('')
return words
def sort_words(words):
"""Sorts the words."""
return sorted(words)
def print_first_word(words):
"""Prints the first word after popping it off."""
word = words.pop(0)
print(word)
def print_last_word(words):
"""Prints the last word after popping it off."""
word = words.pop(-1)
print(word)
def sort_sentence(sentence):
"""Take in a full sentence and returns the sorted words"""
words = break_words(sentence)
return sort_words(words)
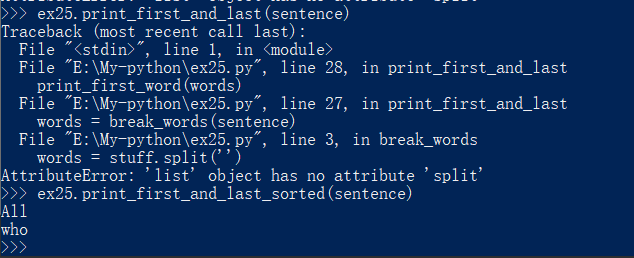
def print_first_and_last(sentence):
"""Prints the first and last words of the sentence."""
words = break_words(sentence)
print_first_word(words)
print_last_word(words)
def print_first_and_last_sorted(sentence):
"""Sorts the words then prints the first and last one."""
words = sort_sentence(sentence)
print_first_word(words)
print_last_word(words)
运行截图
习题29:if语句
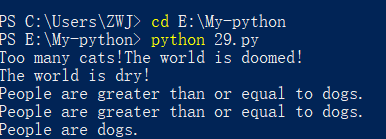
代码展示
people = 20
cats = 30
dogs = 15
if people < cats:
print("Too many cats!The world is doomed!")
if people > cats:
print("Not many cats!The world is saved!")
if people < dogs:
print("The world is drooled on!")
if people > dogs:
print("The world is dry!")
dogs += 5
if people >= dogs:
print("People are greater than or equal to dogs.")
if people <= dogs:
print("People are greater than or equal to dogs.")
if people == dogs:
print("People are dogs.")
运行截图
习题30:else和if
代码展示
people = 30
cars =40
trucks = 15
if cars > people:
print("We should take the cars.")
elif cars < people:
print("We should not take the cars.")
else:
print("We can't decide")
if trucks > cars:
print("That's too many trucks.")
elif trucks < cars:
print("Maybe we should take the trucks.")
else:
print("We still can't decide.")
if people > trucks:
print("Alright,let's just take the trucks.")
else:
print("Fine,let's stay home then.")
运行截图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号