实验二
task1
T.h
点击查看代码
#include <string>
// 类T: 声明
class T {
// 对象属性、方法
public:
T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数
T(const T &t); // 复制构造函数
T(T &&t); // 移动构造函数
~T(); // 析构函数
void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据
void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息
private:
int m1, m2;
// 类属性、方法
public:
static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数
public:
static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息
static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限
private:
static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目
// 类T友元函数声明
friend void func();
};
// 普通函数声明
void func();
T.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "T.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// 类T实现
// static成员数据类外初始化
const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"};
const int T::max_cnt = 999;
int T::cnt = 0;
// 类方法
int T::get_cnt() {
return cnt;
}
// 对象方法
T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T copy constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T move constructor called.\n";
}
T::~T() {
--cnt;
std::cout << "T destructor called.\n";
}
void T::adjust(int ratio) {
m1 *= ratio;
m2 *= ratio;
}
void T::display() const {
std::cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ;
}
// 普通函数实现
void func() {
T t5(42);
t5.m2 = 2049;
std::cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "func: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << std::endl;
}
task1.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "T.h"
#include <iostream>
void test_T();
int main() {
std::cout << "test Class T: \n";
test_T();
std::cout << "\ntest friend func: \n";
func();
}
void test_T() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl;
cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl;
cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl;
T t1;
cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl;
T t2(3, 4);
cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl;
T t3(t2);
t3.adjust(2);
cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl;
T t4(std::move(t2));
cout << "t4 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl;
cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl;
}
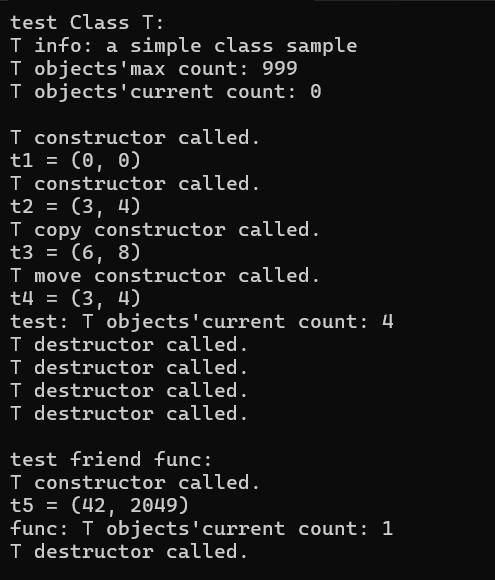
问题1
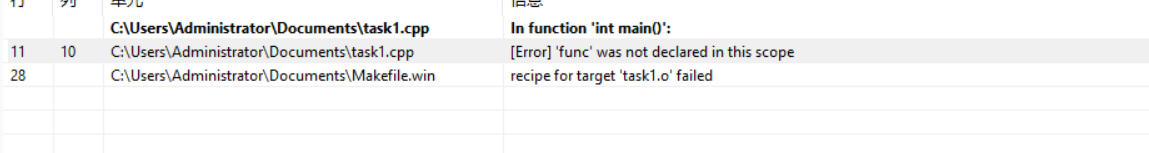
报错原因:func()函数未在T类友元声明里作为T类的成员函数,缺少函数声明,编译报错
问题2
普通构造函数功能是创建新对象时候初始化数据成员,在具体数据初始化或者不提供参数用默认参数初始化的时候调用
复制构造函数功能是用类对象来初始化创建新的类对象,在类对象初始化新的类对象或者值传递时调用
移动构造函数是把目标类对象的数据直接移动到创建的新类对象,从临时对象转移资源的时候调用
析构函数对象销毁时自动调用,释放对象占用资源,在对象销毁时候自动调用
问题3

报错原因:类的静态成员需要在类外定义,如果头文件中定义静态成员变量,那每个包含该头文件的源文件都会定义一次,就会产生多重定义的错误,因此检查定义位置应该确保只定义一次。
task2
complex.h
点击查看代码
#ifndef MY_COMPLEX_H_
#define MY_COMPLEX_H_
#include <string>
class Complex
{
// 对象属性、方法
private:
double real, imag;
public:
Complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0); // 普通构造函数
Complex(const Complex&); // 复制构造函数
Complex(const Complex&&) noexcept; // 移动构造函数
double get_real() const; // 显示Complex类对象实部
double get_imag() const; // 显示Complex类对象虚部
Complex& operator=(const Complex&);
Complex& operator=(const Complex&&) noexcept; // 重载=运算符
void add(const Complex&); // 将一个Complex类对象加到另一个Complex类对象上
// 类属性、方法
public:
static const std::string doc; // 用于类说明
// 类Complex友元函数声明
friend void output(const Complex&); // 以a+bi的形式显示Complex类对象的信息
friend double abs(const Complex&); // 对Complex类对象取模
friend Complex add(const Complex&, const Complex&); // 实现两个Complex类对象相加,返回Complex类对象
friend bool is_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&); // 判断两个Complex类对象是否相等
friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&); // 判断两个Complex类对象是否相等
};
void output(const Complex&);
double abs(const Complex&);
Complex add(const Complex&, const Complex&);
bool is_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
bool is_not_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
#endif
complex.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
const std::string Complex::doc = "a smplified complex class";
Complex::Complex(double r, double i): real(r), imag(i)
{
}
Complex::Complex(const Complex &c): real(c.real), imag(c.imag)
{
}
Complex::Complex(const Complex &&c) noexcept : real(c.real), imag(c.imag)
{
}
Complex& Complex::operator=(const Complex &c)
{
if (this != &c)
{
real = c.real;
imag = c.imag;
}
return *this;
}
Complex& Complex::operator=(const Complex &&c) noexcept
{
if (this != &c)
{
real = c.real;
imag = c.imag;
}
return *this;
}
double Complex::get_real() const
{
return real;
}
double Complex::get_imag() const
{
return imag;
}
void Complex::add(const Complex &c)
{
real += c.real;
imag += c.imag;
}
void output(const Complex &c)
{
std::cout << c.get_real()
<< (c.get_imag() < 0 ? " - " : " + ")
<< std::abs(c.get_imag()) << 'i';
}
double abs(const Complex &c)
{
return std::sqrt(c.get_real() * c.get_real() + c.get_imag() * c.get_imag());
}
Complex add(const Complex &c1, const Complex &c2)
{
Complex c;
c.add(c1);
c.add(c2);
return c;
}
bool is_equal(const Complex &c1, const Complex &c2)
{
return((c1.get_real() == c2.get_real()) && (c1.get_imag() == c2.get_imag()));
}
bool is_not_equal(const Complex &c1, const Complex &c2)
{
return !is_equal(c1, c2);
}
task2.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <complex>
void test_Complex();
void test_std_complex();
int main() {
std::cout << "*******测试1: 自定义类Complex*******\n";
test_Complex();
std::cout << "\n*******测试2: 标准库模板类complex*******\n";
test_std_complex();
}
void test_Complex() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
cout << "类成员测试: " << endl;
cout << Complex::doc << endl << endl;
cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl;
Complex c1;
Complex c2(3, -4);
Complex c3(c2);
Complex c4 = c2;
const Complex c5(3.5);
cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl;
cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl;
cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
cout << "c5.real = " << c5.get_real()
<< ", c5.imag = " << c5.get_imag() << endl << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c2 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
c4 = add(c2, c3);
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
}
void test_std_complex() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
cout << "std::complex<double>对象测试: " << endl;
std::complex<double> c1;
std::complex<double> c2(3, -4);
std::complex<double> c3(c2);
std::complex<double> c4 = c2;
const std::complex<double> c5(3.5);
cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
cout << "c5.real = " << c5.real()
<< ", c5.imag = " << c5.imag() << endl << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2)<< endl;
cout << "c1 != c2 : " << (c1 != c2) << endl;
c4 = c2 + c3;
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl;
}

问题1
标准库模板类complex的形式更加简洁。运算符重载使得复数运算可以像内置类型一样使用自然运算符,符合数学表达习惯,而自定义需要显式调用函数名,不够直观。
函数和运算内在有关联,标准库的运算符重载本质是将调用隐藏在运算符后,使得代码更易读
问题2
2-1:不需要,这些功能可以通过公有成员函数实现,无需直接访问私有数据,过度使用友元会破坏封装性
2-2:否,标准库通过提供公有接口访问数据,不用直接访问私有数据,避免友元使用破坏封装性
2-3:当两个类需要相互访问对方私有成员,重载输入输出符,非成员函数无法通过公有接口实现访问类私有数据时
问题3
要禁用复制初始化,可以将复制构造函数声明explicit,或者直接删除复制构造函数
task3
PlayerControl.h
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <string>
enum class ControlType {Play, Pause, Next, Prev, Stop, Unknown};
class PlayerControl {
public:
PlayerControl();
ControlType parse(const std::string& control_str); // 实现std::string --> ControlType转换
void execute(ControlType cmd) const; // 执行控制操作(以打印输出模拟)
static int get_cnt();
private:
static int total_cnt;
};
player.control.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "PlayerControl.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0;
PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {}
ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) {
std::string trans_result;
for (auto &c : control_str)
trans_result += std::tolower(c);
ControlType result = ControlType::Unknown; // 先设为Unknown
if ("play" == trans_result)
result = ControlType::Play;
else if ("next" == trans_result)
result = ControlType::Next;
else if ("prev" == trans_result)
result = ControlType::Prev;
else if ("stop" == trans_result)
result = ControlType::Stop;
else if ("pause" == trans_result)
result = ControlType::Pause;
// 只有成功调用(匹配到有效命令)时才递增total_cnt
if (result != ControlType::Unknown) {
++total_cnt;
}
return result;
}
void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const {
switch (cmd) {
case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[play] Playing music...\n"; break;
case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break;
case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break;
case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break;
case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break;
default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break;
}
}
int PlayerControl::get_cnt() {
return total_cnt;
}
task3
点击查看代码
#include "PlayerControl.h"
#include <iostream>
void test() {
PlayerControl controller;
std::string control_str;
std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n";
while(std::cin >> control_str) {
if(control_str == "quit")
break;
ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str);
controller.execute(cmd);
std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n";
}
}
int main() {
test();
}
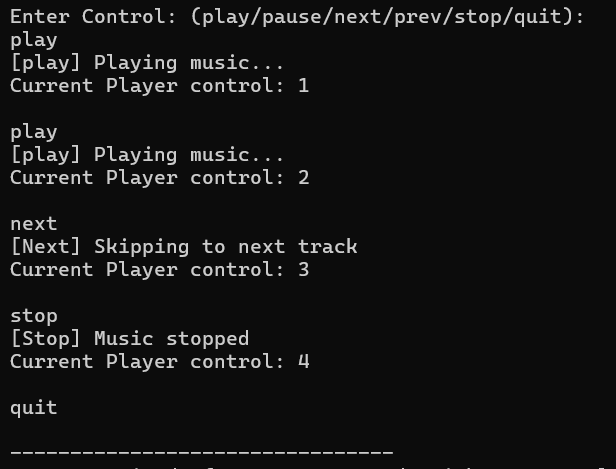
task4
Fraction.h
点击查看代码
#ifndef FRACTION_H
#define FRACTION_H
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Fraction {
public:
// 类属性
static const std::string doc;
// 构造函数
Fraction(int up = 0, int down = 1);
Fraction(const Fraction& other);
// 接口函数
int get_up() const { return up_; }
int get_down() const { return down_; }
Fraction negative() const;
private:
int up_; // 分子
int down_; // 分母
// 内部工具函数
void simplify();
static int gcd(int a, int b);
};
// 工具函数声明 - 使用命名空间自由函数方案
void output(const Fraction& f);
Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2);
Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2);
Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2);
Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2);
#endif
Fraction.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <stdexcept>
#include <cmath>
// 类属性定义
const std::string Fraction::doc =
"Fraction类 v0.01版。\n"
"目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算。";
// 构造函数实现
Fraction::Fraction(int up, int down) : up_(up), down_(down) {
if (down_ == 0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("分母不能为0");
}
// 处理负号:确保分母为正,负号在分子
if (down_ < 0) {
up_ = -up_;
down_ = -down_;
}
simplify();
}
Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& other)
: up_(other.up_), down_(other.down_) {
// 拷贝构造,对象已经是最简形式
}
// 求最大公约数
int Fraction::gcd(int a, int b) {
a = std::abs(a);
b = std::abs(b);
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
// 化简分数
void Fraction::simplify() {
if (up_ == 0) {
down_ = 1;
return;
}
int common_divisor = gcd(up_, down_);
up_ /= common_divisor;
down_ /= common_divisor;
// 确保分母为正
if (down_ < 0) {
up_ = -up_;
down_ = -down_;
}
}
// 求负运算
Fraction Fraction::negative() const {
return Fraction(-up_, down_);
}
// 工具函数实现
void output(const Fraction& f) {
if (f.get_down() == 1) {
std::cout << f.get_up();
} else {
std::cout << f.get_up() << "/" << f.get_down();
}
}
Fraction add(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) {
int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down() + f2.get_up() * f1.get_down();
int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down();
return Fraction(new_up, new_down);
}
Fraction sub(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) {
int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down() - f2.get_up() * f1.get_down();
int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down();
return Fraction(new_up, new_down);
}
Fraction mul(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) {
int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_up();
int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_down();
return Fraction(new_up, new_down);
}
Fraction div(const Fraction& f1, const Fraction& f2) {
if (f2.get_up() == 0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("分母不能为0");
}
int new_up = f1.get_up() * f2.get_down();
int new_down = f1.get_down() * f2.get_up();
return Fraction(new_up, new_down);
}
task4.cpp
点击查看代码
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
std::cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试:\n";
test2();
}
void test1() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "Fraction类测试:" << endl;
cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl;
Fraction f1(5);
Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12);
Fraction f4(f3);
cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl;
cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl;
cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl;
Fraction f5 = f4.negative();
cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl;
cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up()
<< ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl;
cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl;
}
void test2() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
try {
Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3);
cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl;
cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl;
cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}

选择命名空间自由函数的方案,因为可以通过公有接口访问,保持封装性,代码可读性更强
友元方案虽然可以直接访问类的私有成员,但是破坏封装性,需要修改类声明。
静态成员函数方案适合作为类的辅助函数,需要访问类的私有细节。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号