1、Stream有几个特性:
stream不存储数据,而是按照特定的规则对数据进行计算,一般会输出结果。
stream不会改变数据源,通常情况下会产生一个新的集合或一个值。
stream具有延迟执行特性,只有调用终端操作时,中间操作才会执行。
2、Stream可以由数组或集合创建,对流的操作分为两种:
中间操作,每次返回一个新的流,可以有多个,所有中间操作都返回Stream(可以链接)。
终端操作,每个流只能进行一次终端操作,终端操作结束后不返回流。终端操作会产生非流(无法链接)结果,例如原始值,集合。
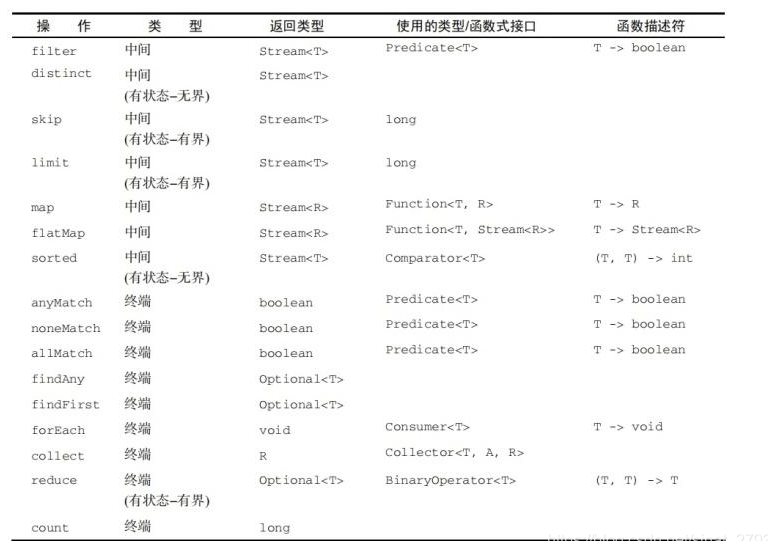
3、在 Java 8 中, 集合接口有两个方法来生成流:
- stream() :为集合创建串行流。
- parallelStream() :为集合创建并行流。
实战:https://yunfan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/111872756
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a","b","c");
Stream<String> streamList = list.stream();
streamList.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
int[] arrys = {1,2,3};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arrys.clone());
stream.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3);
//n的初始值为2,依次*3(无限流,配合limit使用)
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(2,n -> n * 3).limit(5);
//随机取8个Double(无限流,配合limit使用)
Stream<Double> stream = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(8);
stream.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7);
list.stream().filter(x -> x>5).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a","as","asf","asfg","asfdg");
Optional<String> list1 = list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(String::length));
System.out.println(list1.get());
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
Optional<Integer> min = list.stream().min(Integer::compareTo);
System.out.println(min.get());
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
//filter有返回值
System.out.println(list.stream().filter(e -> e>3).count());
//forEach无返回值
list.stream().forEach(e -> e++);
String[] arrys = {"a","ab","abc"};
List<String> list = Arrays.stream(arrys).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list.toString());
list.stream().forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
String[] arrys = {"a","ab","abc"};
Arrays.stream(arrys).map(String::toUpperCase).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e));
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("1,2,3","4,5,6");
List<String> listnew = list.stream().flatMap(s -> {
String[] ss = s.split(",");
Stream<String> sss = Arrays.stream(ss);
return sss;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
listnew.forEach(System.out::println);
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Optional<Integer> sum1 = list.stream().reduce((x,y) -> x+y);
Optional<Integer> sum4 = list.stream().reduce((x,y) -> x*y);
Integer sum2 = list.stream().reduce(0,Integer::sum);
Optional<Integer> sum3 = list.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println(sum1+"-----"+sum2+"-----"+sum3+"-----"+sum4);
Integer sum5 = list.stream().reduce(1,Integer::max);
Optional<Integer> sum6 = list.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x>y ? x : y);
System.out.println(sum5+"-----"+sum6.get()+"-----"+sum3+"-----"+sum4);
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6);
list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
String[] strArr = {"Java", "Python", "C++", "C", "PHP"};
Arrays.stream(strArr).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.of(list).toArray(Long[]::new)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号