虚树
虚树
概念
对于一棵树,我们把这棵树上的一些点拿出来,那么这个点集的虚树就是这些点及其在原树上的 lca 所组成的点集连边所构成的树。举个例子:
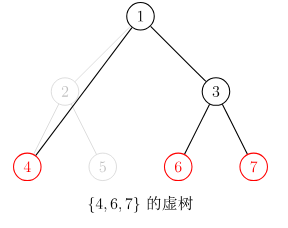
建树
考虑用单调栈建树。下文称需要建虚树的这个点集为关键点。
在此之前,我们先将所有关键点按 dfs 序排序。
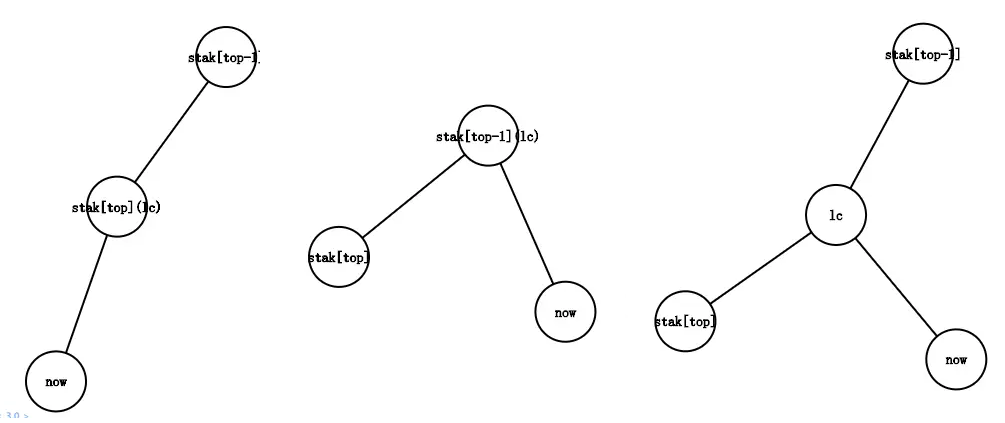
考虑用单调栈维护虚树上的一条链。首先将第一个关键点直接加入。然后我们依次考虑加入每一个关键点。设当前加入的关键点为 \(x\)。记栈顶的元素是 \(y\),栈中的第二个元素是 \(p\)。记 \(l\) 为 \(lca(x,y)\)。
那么我们要加入这个点,就要弹出栈顶的一写元素。就是说,如果 \(dfn_p \le dfn_l\),那么就表明此时可以停止弹栈。
考虑分三类讨论:
- 当 \(l = y\) 时,说明 \(y\) 是 \(x\) 的祖先,直接把 \(x\) 加入即可。
- 当 \(l=p\) 时,说明 \(l\) 在栈内,那让 \(y\) 出栈,再加入 \(x\) 即可。
- 当 \(l \ne p\) 时,说明 \(l\) 没有进栈内,那么需要将 \(y\) 与 \(l\) 连边并将 \(y\) 出栈,然后加入 \(l\) 和 \(x\) 即可。
那么在这个栈中,每个点在虚树上的父亲就是他在栈中的下一个点(更接近栈底的那边)。
然后就是建出虚树在上面做树形 dp 了。
例题
[P2495 SDOI2011] 消耗战 /【模板】虚树
给出一棵 \(n\) 个点的树以及 \(m\) 次询问,每次询问给出 \(k\) 以及 \(h_i,i \in[1,k],h_i \in[2,n]\)。对于每次询问,要求删掉一些边后 \(1\) 与任意的 \(h_i\) 不连通,求删掉的边的边权和的最小值。\(\sum k \le 5 \times 10^5\)。
对于这道题而言,如果只有一次询问,我们可以考虑一个简单的树形 dp \(O(n)\) 求解。
但是加上了 \(m\) 次询问,显然不能每次去 \(O(n)\) 跑。
考虑建立对于 \(h_i\) 建虚树。那么我们实际上得到的信息是没有少掉什么的,该有的都有,并不影响正常的 dp 转移,也没有落下哪一个点。
就相当于把无用的点都去掉了,而且把一次 dp 的时间复杂度降到了 \(O(S)\),\(S\) 为虚树的大小。可以证明,\(S \le 2 \times k\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define il inline
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int bufsz = 1 << 20;
char ibuf[bufsz], *p1 = ibuf, *p2 = ibuf;
#define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = ibuf) + fread(ibuf, 1, bufsz, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
il int read() {
int x = 0; char ch = getchar(); bool t = 0;
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {t ^= ch == '-'; ch = getchar();}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48); ch = getchar();}
return t ? -x : x;
}
bool Beg;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 250000 + 10, M = 20;
int n, m, k, h[N];
struct edge {
int y, w;
};
vector<edge> G[N];
int dfn[N], id[N << 1], tot, mn[N << 1][M], Log2[N << 1];
int dis[N];
il void dfs1(int x, int fa) {
id[++tot] = x;
dfn[x] = tot;
for (edge i : G[x]) {
if (i.y == fa) continue;
dis[i.y] = min(dis[x], i.w);
dfs1(i.y, x);
id[++tot] = x;
}
}
il void init() {
for (int i = 2; i <= tot; i++) Log2[i] = Log2[i / 2] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) mn[i][0] = dfn[id[i]];
for (int j = 1; j <= Log2[tot]; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= tot; i++) {
mn[i][j] = min(mn[i][j - 1], mn[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
}
il int getlca(int x, int y) {
if (dfn[x] > dfn[y]) swap(x, y);
int s = Log2[dfn[y] - dfn[x] + 1];
return id[min(mn[dfn[x]][s], mn[dfn[y] - (1 << s) + 1][s])];
}
il bool cmp(int a, int b) {return dfn[a] < dfn[b];}
vector<int> E[N];
int st[N], head;
vector<int> Del;
il void build() { // 建虚树
for (int i : Del) E[i].clear();
Del.clear();
head = 0;
st[++head] = h[1];
for (int i = 2; i <= k; i++) {
int x = h[i], y = st[head];
int l = getlca(x, y);
if (l == y) {
st[++head] = x;
continue;
}
while (dfn[st[head - 1]] > dfn[l]) {
E[st[head - 1]].push_back(st[head]);
head--;
}
if (l != st[head - 1]) {
E[l].push_back(st[head--]);
st[++head] = l;
} else {
E[l].push_back(st[head--]);
}
st[++head] = x;
}
for (int i = 1; i < head; i++) {
E[st[i]].push_back(st[i + 1]);
}
}
int f[N], a[N];
il void dfs(int x) { // 正常跑树形 dp
Del.push_back(x);
f[x] = 0;
for (int y : E[x]) {
dfs(y);
f[x] += f[y];
}
if (a[x]) f[x] = dis[x];
else f[x] = min(f[x], dis[x]);
}
il int solve() {
k = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
h[i] = read();
a[h[i]] = 1;
}
sort(h + 1, h + 1 + k, cmp);
build();
dfs(st[1]);
printf("%lld\n", f[st[1]]);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) a[h[i]] = 0;
return 0;
}
bool End;
il void Usd() {cerr << "\nUse: " << (&Beg - &End) / 1024.0 / 1024.0 << " MB" << (double)clock() * 1000.0 / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "ms\n";}
signed main() {
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x = read(), y = read(), w = read();
G[x].push_back({y, w});
G[y].push_back({x, w});
}
dis[1] = INF;
dfs1(1, 0);
init();
int qq = read();
while (qq--) {
solve();
}
Usd();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号