C 语言 之 面向对象(一)和 mmap的使用
C 语言 之 面向对象(一)
了解C语言面向对象之前首先需要对C语言的指针、结构体有基本了解。
指针
正常使用数组:
void hello(){
#define count 10
// sh
int a[count] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
printf("================================\n");
int *b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
free(b);
b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
b[1] = 44;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
free(b);
}
数组默认是个指针常量,无法修改指针指向,但可以修改内容
指针常量
void hello(){
#define count 10
// sh
int a[count] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
printf("================================\n");
int * const b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10); // 定义指针常量
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
// free(b);
// b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
b[1] = 44;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
free(b);
}
指针常量const在指针名称之前,意味着指针指向不可修改
常量指针
// 【关键补充】4. Person_SetAge函数的实现(之前缺失的部分)
void Person_SetAge(Person* self, int new_age) {
if (self == NULL) return; // 避免空指针访问
// 可选:添加参数校验(如年龄不能为负数)
if (new_age >= 0) {
self->age = new_age; // 修改结构体的age成员
} else {
printf("Invalid age: %d (must be non-negative)\n", new_age);
}
}
void hello(){
#define count 10
// sh
int a[count] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, a[i]);
}
printf("================================\n");
// const int * b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10); // 定义常量指针 or
int const * b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10); // 定义常量指针
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
free(b);
b = malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
// b[1] = 44;
for(int i = 0; i < count; i ++ ){
printf("i: %d, value: %d\n", i, b[i]);
}
free(b);
}
常量指针意味着值是无法被修改的,但是你可以直接换新值。
结构体
定义结构体
// 定义结构体类型:struct Student
struct Student {
char name[20]; // 姓名(字符数组)
int age; // 年龄(整数)
float score; // 成绩(浮点数)
};
使用结构体1
void hello(){
struct Student stu1, stu2;
struct Student stu3 = {
"zsh",
18,
95.5F
};
struct Student stu4 = {
.age = 19,
.name = "zsh1",
.score = 96.5F
};
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu1.name, stu1.age, stu1.score);
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu2.name, stu2.age, stu2.score);
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu3.name, stu3.age, stu3.score);
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu4.name, stu4.age, stu4.score);
}
使用结构体2
void hello(){
struct Student *stu1 = malloc(sizeof(struct Student));
stu1->name = "zsh";
stu1->age = 17;
stu1->score = 95.5F;
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu1 -> name, stu1 -> age, stu1 -> score);
free(stu1);
stu1 = NULL;
}
结构体2
使用别名
// 定义结构体类型:struct Student
typedef struct Student {
char *name; // 姓名(字符数组)
int age; // 年龄(整数)
float score; // 成绩(浮点数)
} Student;
// or
typedef struct Student Student;
// 定义结构体类型:struct Student
struct Student {
char *name; // 姓名(字符数组)
int age; // 年龄(整数)
float score; // 成绩(浮点数)
};
简化调用
void hello(){
Student *stu1 = malloc(sizeof(Student));
stu1->name = "zsh";
stu1->age = 17;
stu1->score = 95.5F;
free(stu1);
printf("name: %s, age: %d, score: %f\n", stu1 -> name, stu1 -> age, stu1 -> score);
}
给结构体定义方法
定义结构体
#ifndef LEARNC01_H
#define LEARNC01_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 定义类型别名
typedef struct Student Student;
// 定义方法别名
/**
* 方法别名类型toStringFunc,参数void,返回值void
*/
typedef void (*ToStringFunc)(Student*);
// 定义结构体类型:struct Student
struct Student {
char *name; // 姓名(字符数组)
int age; // 年龄(整数)
float score; // 成绩(浮点数)
ToStringFunc toString;
};
// 定义方法
/**
* 创建对象
*/
Student* StudentCreate(const char *name, const int age, const float score);
void StudentPrint(Student* self);
void StudentDestroy(Student* self);
void hello();
#endif // LEARNC01_H
源文件
// ==================
Student* StudentCreate(const char* name, const int age, const float score){
Student* self = malloc(sizeof(Student));
if (self == NULL){
printf("内存不足\n");
return NULL;
}
const int nameLength = strlen(name);
self->name = malloc(nameLength);
strcpy(self -> name, name);
printf("name: %s, nameLength: %d, self->name: %s, self->nameLength: %d\n", name, nameLength, self->name, strlen(self->name));
self->age = age;
self -> score = score;
self->toString = StudentPrint; // 引用头文件方法别名,链接时指向实现方法
return self;
}
void StudentDestroy(Student *self){
if (self == NULL) return;
free(self->name); // 先释放姓名的堆内存
free(self);
}
void StudentPrint(Student* self) {
printf("Student(name=%s, age=%d, score=%f)", self->name, self->age, self->score);
}
void hello(){
Student *student = StudentCreate("zsh", 18, 95.5F);
if(student == NULL){
printf("student == NULL\n");
return;
}
student->toString(student);
StudentDestroy(student);
}
多态TODO
头文件
#ifndef LEARNC01_H
#define LEARNC01_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 1. 基类
typedef struct Person Person;
// 基类方法
typedef void (*ToStringFunc)(Person*);
typedef void (*DestroyFunc)(Person*);
// 基类结构体
struct Person {
char *name;
int age;
ToStringFunc toString;
DestroyFunc destroy;
};
// 2. 定义派生类类型别名
typedef struct Student Student;
// 定义结构体类型:struct Student
struct Student {
Person parent;
float score; // 成绩(浮点数)
char *school;
};
// 3. 定义派生类类型别名
typedef struct Teacher Teacher;
struct Teacher {
Person parent;
char *education;
char *school;
};
// 定义方法
/**
* 创建 Student 对象方法
*/
Student* StudentCreate(const char *name, const int age, const float score, const char *school);
static void StudentToString(Person *person);
static void StudentDestroy(Person *person);
/**
* 创建 Teacher 对象方法
*/
Teacher* TeacherCreate(const char *name, const int age, const char *education, const char *school);
static void TeacherDestroy(Person *person);
static void TeacherToString(Person *person);
/**
* 多态方法
*/
void printPersonInfo(Person *person);
void hello();
#endif // LEARNC01_H
源文件
#include "learnc01.h"
// ========= Student =========
Student* StudentCreate(const char* name, const int age, const float score, const char *school){
Student* self = malloc(sizeof(Student));
if (self == NULL){
printf("内存不足\n");
return NULL;
}
self->parent.toString = StudentToString;
self->parent.destroy = StudentDestroy;
const int nameLength = strlen(name);
self->parent.name = malloc(nameLength);
strcpy(self->parent.name, name);
self->parent.age = age;
self->score = score;
const int schoolLength = strlen(school);
self->school = malloc(schoolLength);
strcpy(self->school, school);
printf("构造函数 -> Student(name=%s, age=%d, score=%f, school=%s)\n", self->parent.name, self->parent.age, self->score, self->school);
return self;
}
static void StudentToString(Person *person){
Student *student = (Student*) person;
// student.
printf("Student(name=%s, age=%d, score=%f, school=%s)\n", student->parent.name, student->parent.age, student->score, student->school);
}
static void StudentDestroy(Person *person){
Student *student = (Student*) person;
free(student->parent.name);
free(student->school);
free(student);
}
// ========= Teacher =========
Teacher* TeacherCreate(const char *name, const int age, const char *education, const char *school){
Teacher *self = malloc(sizeof(Teacher));
if(self == NULL){
printf("Teacher 内存不足\n");
return NULL;
}
self->parent.toString = TeacherToString;
self->parent.destroy = TeacherDestroy;
const int nameLength = strlen(name) + 1;
self->parent.name = malloc(nameLength);
strcpy(self->parent.name, name);
self->parent.age = age;
const int educationLength = strlen(education) + 1; // 带上 \0 空字符
self->education = malloc(educationLength);
strcpy(self->education, education);
const int schoolLength = strlen(school) + 1;
self->school = malloc(schoolLength);
strcpy(self->school, school);
printf("构造函数 Teacher(name=%s, age=%d, education=%s, school=%s, nameLength=%d)\n", self->parent.name, self->parent.age, self->education, self->school, nameLength);
return self;
}
static void TeacherToString(Person *person){
Teacher *teacher = (Teacher*) person;
printf("Teacher(name=%s, age=%d, education=%s, school=%s)\n", teacher->parent.name, teacher->parent.age, teacher->education, teacher->school);
}
static void TeacherDestroy(Person *person){
Teacher *teacher = (Teacher*) person;
free(teacher->parent.name);
free(teacher->school);
free(teacher->education);
free(teacher);
}
/**
* 多态方法
*/
void printPersonInfo(Person *person){
if(person == NULL){
printf("person == NULL\n");
return;
}
person->toString(person);
}
void hello(){
Person *student = (Person*)StudentCreate("s_zsh", 18, 95.5, "tyut");
Person *teacher = (Person*)TeacherCreate("t_zsh", 18, "本科", "tyut");
printPersonInfo(teacher);
printPersonInfo(student);
student->destroy(student);
teacher->destroy(teacher);
}
MMAP 函数的使用
在需要了解mmap之前需要了解一下其他几个api
open函数
open函数在fcntl.h头文件
声明如下:
extern int open (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...) __nonnull ((1));
第一个参数为非空文件路径,第二个参数访问类型,第三个参数是文件创建时权限模式.
调用方式如下
/*
000 0
001 1
010 2
011 3
100 4
101 5
110 6 rw-
111 7
*/
const int fd = open("../hello.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0666); // 八进制
ftruncate函数
ftruncate手册
该函数在头文件unistd.h
声明如下:
extern int ftruncate (int __fd, __off_t __length) __THROW __wur;
__THROW: 在C啥也不是,在C++相当于throw(),相当于C++11的noexcept,相当于 __attribute__((nothrow))
__wur: 即warn unused result.
调用方式如下:
int result = ftruncate(fd, 1024);
指定文件大小为1024,执行成功返回0
fstat函数
fstat函数在头文件<sys/stat.h>
函数声明如下:
/* Get file attributes for the file, device, pipe, or socket
that file descriptor FD is open on and put them in BUF. */
extern int fstat (int __fd, struct stat *__buf) __THROW __nonnull ((2));
获取文件属性。
调用方式如下:
struct stat stat;
int result = fstat(fd, &stat);
const off_t fileSize = stat.st_size;
printf("file size: %ld\n", fileSize);
printf("laTime: %ld\n", stat.st_atime); // 最后修改时间
获取文件大小和修改时间.
mmap
mmap
mmap有两种使用方式一种是映射到文件,一种是映射到匿名虚拟内存.
映射到文件
修改内存即修改文件
void learn002(){
/*
000 0
001 1
010 2
011 3
100 4
101 5
110 6 rw-
111 7
*/
// 打开文件
const int fd = open("../hello.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0666); // 八进制
printf("fd: %d\n", fd); // 一般为3
if(fd < 0){
perror("文件打开异常\n");
return;
}
// 读取内容
const int N = 1024;
char buffer[N];
ssize_t length = 0;
while((length = read(fd, buffer, N - 1)) > 0){
buffer[length] = '\0';
printf("%s", buffer);
}
puts("");
// 设置文件大小为1024字节
int result = ftruncate(fd, 1024);
printf("ftruncate result: %d\n", result);
// 读取文件信息
struct stat stat;
result = fstat(fd, &stat);
const off_t fileSize = stat.st_size;
printf("file size: %ld\n", fileSize);
printf("laTime: %ld\n", stat.st_atime); // 最后修改时间
// 文件大小必须确认,多大的文件就映射多大的内存
char *data = mmap(NULL, fileSize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
printf("修改前: \n%s\n", data);
// 修改内存即修改文件
data[111] = 'a';
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
puts("修改后:");
while((length = read(fd, buffer, N - 1)) > 0){
buffer[length] = '\0';
printf("%s", buffer);
}
puts("");
// 解绑
result = munmap(data, fileSize);
printf("munmap -> result: %d\n", result);
result = close(fd);
printf("close -> result: %d\n", result);
}
参数NULL, 代表由系统返回虚拟内存地址。
参数fileSize, 代表映射和文件大小一样的内存。
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE代表可读可写。
MAP_SHARED: 映射区域的更新对其他映射同一区域的进程可见,对于文件 - backed 映射(基于文件的映射),更新内容会同步到底层文件;
fd: 为需要映射文件的文件描述符.
offset:一般为0.
映射到匿名共享对象
void learn003() {
printf("Hello World\n");
printf("page-aligned: %ld\n", sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE));
printf("page-aligned: %d\n", getpagesize());
#define MMAP_SIZE 4096
char* data = mmap(NULL, MMAP_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
printf("data: \n%s\n", data);
const int pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork error\n");
int result = munmap(data, MMAP_SIZE);
printf("munmap result: %d\n", result);
return;
}
if(pid == 0){
printf("子进程 pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
sleep(1u);
printf("子进程 读数据: \n%s\n", data);
strcpy(data, "i am sub proc");
return;
}
// 父进程
strcpy(data, "I am parent proc");
wait(NULL);
printf("父进程pid: %d, 读取到的子进程的内容为:\n%s\n", getpid(), data);
int result = munmap(data, MMAP_SIZE);
printf("父进程 munmap result: %d\n", result);
}
系统会在内核空间开辟4kb的共享内存,然后进程A和子进程B可以共享该内存,实现IPC通信.
如下图所示:
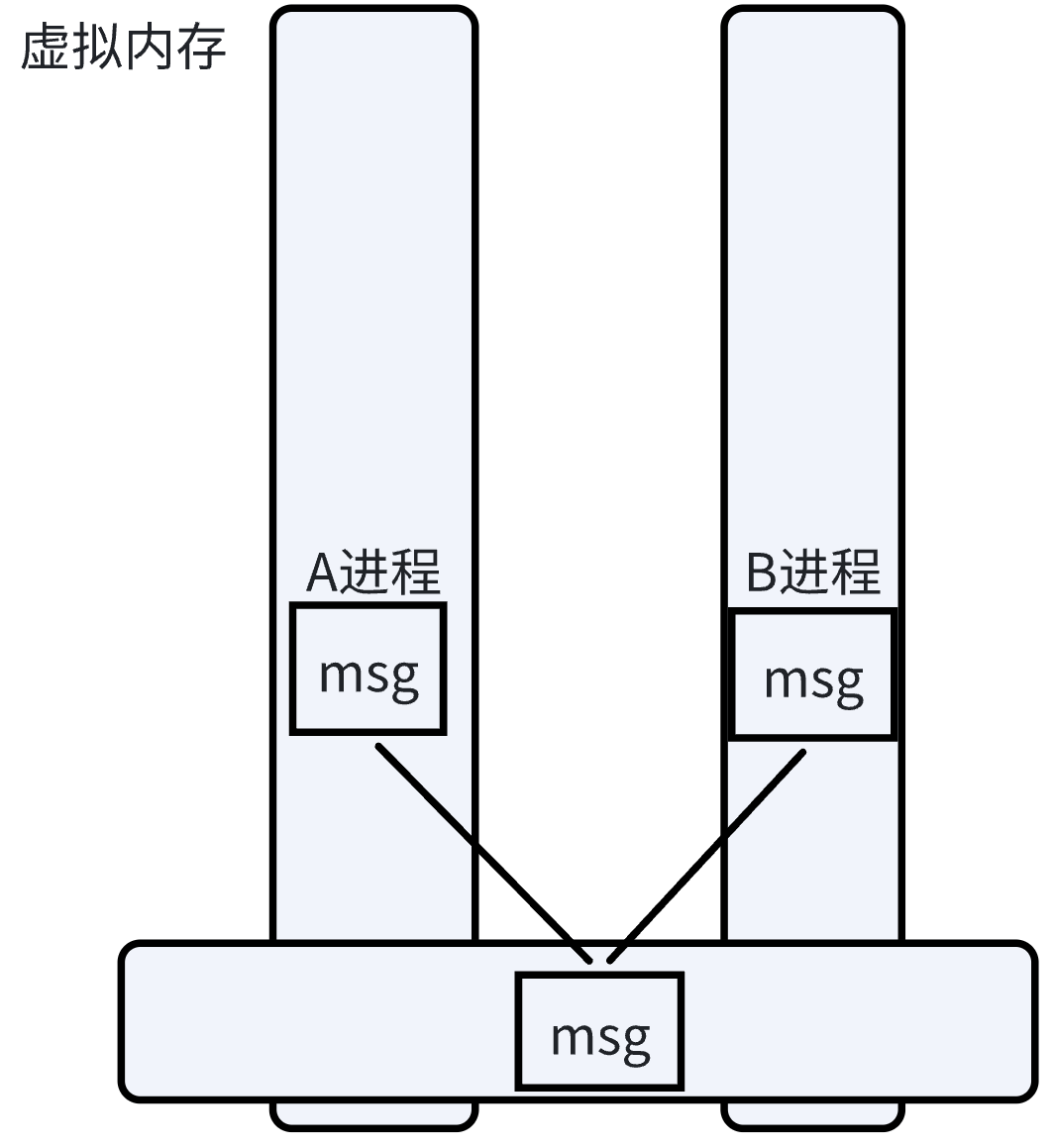
在子线程无需munmap.
学会使用mmap那看mmkv源码就是手拿把掐.
https://github.com/Tencent/MMKV/blob/master/Core/MemoryFile.cpp
wait含义是如何子进程退出获取状态变化则返回对应子进程pid,否则阻塞.
参数是个int指针,对应子进程的状态.
void learn003() {
printf("Hello World\n");
printf("page-aligned: %ld\n", sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE));
printf("page-aligned: %d\n", getpagesize());
#define MMAP_SIZE 4096
char* data = mmap(NULL, MMAP_SIZE, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
printf("data: \n%s\n", data);
int pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork error\n");
int result = munmap(data, MMAP_SIZE);
printf("munmap result: %d\n", result);
return;
}
if(pid == 0){
printf("子进程 pid: %d, ppid: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
sleep(1u);
printf("子进程 读数据: \n%s\n", data);
strcpy(data, "i am sub proc");
return;
}
// 父进程
strcpy(data, "I am parent proc");
int status;
pid = wait(&status);
if (WIFEXITED(status)) {
printf("child exited with code %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
printf("status: %d, pid: %d\n", status, pid);
printf("父进程pid: %d, 读取到的子进程的内容为:\n%s\n", getpid(), data);
int result = munmap(data, MMAP_SIZE);
printf("父进程 munmap result: %d\n", result);
}

 C 语言 之 面向对象(一)
C 语言 之 面向对象(一)

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号