03.02 unidal之dal-jdbc
dal-jdbc 产生的必然条件有以下几个环境因素
- 公司范围级别的,属于自主研发的,灵活、机动
- 定制化需求的程度很高
- 需要链路的检测,其实就是与
Cat的整合,因为Cat是代码入侵型的,开源的如Hibernate、Ibatis|myBatis需要在很多地方修改或者适配源代码,维护成本相对高。 - 更重要的一个因数,团队有充足的人力和工程控制能力
总的来说,不论是 自主研发的 还是 开源的 ORM 框架,主要解决的问题,应用层的实体对象 到 JDBC 层的 SQL 和 事务的处理工作。如果 把 应用层和DB比作 一条数据河流的两岸,中间桥梁就是ORM框架,就是所有ORM需要解决的数据 交换和转化的 工作,或者 能力。
下面就开始剖析 unidal团队如何构建的 dal-jdbc.
0.准备&HelloWorld
0.1 解析版本
dal-jdbc:4.0.0
0.2 Maven的依赖如下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.unidal.framework</groupId>
<artifactId>foundation-service</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.unidal.framework</groupId>
<artifactId>dal-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
0.3 数据库配置信息
配置文件 datasources.xml 路径是 /data/appdatas/cat/datasources.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<data-sources>
<data-source id="cat">
<maximum-pool-size>3</maximum-pool-size>
<connection-timeout>1s</connection-timeout>
<idle-timeout>10m</idle-timeout>
<statement-cache-size>1000</statement-cache-size>
<properties>
<driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver>
<url><![CDATA[jdbc:mysql://10.1.1.1:3306/cat_local]]></url>
<user>root</user>
<password>123456</password>
<connectionProperties><![CDATA[useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&socketTimeout=120000]]></connectionProperties>
</properties>
</data-source>
<data-source id="app">
<maximum-pool-size>3</maximum-pool-size>
<connection-timeout>1s</connection-timeout>
<idle-timeout>10m</idle-timeout>
<statement-cache-size>1000</statement-cache-size>
<properties>
<driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver>
<url><![CDATA[jdbc:mysql://10.1.1.1:3306/cat_local]]></url>
<user>root</user>
<password>123456</password>
<connectionProperties><![CDATA[useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&socketTimeout=120000]]></connectionProperties>
</properties>
</data-source>
</data-sources>
0.4 配置 数据源信息
工程代码采用的 unidal 框架,使用的是 foundiation-service 和 dal-jdbc 基础服务 jar 依赖
配置 components-dao.xml, 路径 src/main/resources/META-INF/plexus/components-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<plexus>
<components>
<!--这个就是后面要提到HelloWorld的service服务组件-->
<component>
<role>org.dal.cat.service.ProjectService</role>
<implementation>org.dal.cat.service.ProjectService</implementation>
<requirements>
<!--依赖的服务组件-->
<requirement>
<role>org.dal.cat.core.dal.ProjectDao</role>
</requirement>
</requirements>
</component>
<!--- DAO的服务组件注册 -->
<component>
<role>org.dal.cat.core.dal.ProjectDao</role>
<implementation>org.dal.cat.core.dal.ProjectDao</implementation>
<requirements>
<requirement>
<role>org.unidal.dal.jdbc.QueryEngine</role>
</requirement>
</requirements>
</component>
<!-- dal-jdbc 框架需要需要注册的 DataSourceProvider,必须的-->
<component>
<role>org.unidal.dal.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceProvider</role>
<implementation>org.unidal.dal.jdbc.datasource.DefaultDataSourceProvider</implementation>
<configuration>
<datasourceFile>/data/appdatas/cat/datasources.xml</datasourceFile>
</configuration>
</component>
<!---TableProvider对应的数据库的表注册信息-->
<component>
<role>org.unidal.dal.jdbc.mapping.TableProvider</role>
<role-hint>project</role-hint>
<implementation>org.unidal.dal.jdbc.mapping.SimpleTableProvider</implementation>
<configuration>
<physical-table-name>project</physical-table-name>
<data-source-name>cat</data-source-name>
</configuration>
</component>
<!-- LoggerManager 的注册-->
<component>
<role>org.unidal.lookup.logging.LoggerManager</role>
<implementation>org.unidal.lookup.logging.TimedConsoleLoggerManager</implementation>
<configuration>
<dateFormat>yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS</dateFormat>
<showClass>true</showClass>
<logFilePattern>dat_{0,date,yyyyMMdd}.log</logFilePattern>
<baseDirRef>CAT_HOME</baseDirRef>
<defaultBaseDir>/data/applogs/cat</defaultBaseDir>
</configuration>
</component>
</components>
</plexus>
0.5 DAO|Service|Entity 层的数据对象
DAO
代码 采集 CAT 的 Project 的示例
import java.util.List;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.DalException;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.AbstractDao;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.Readset;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.Updateset;
public class ProjectDao extends AbstractDao {
public Project createLocal() {
Project proto = new Project();
return proto;
}
public int deleteByPK(Project proto) throws DalException {
return getQueryEngine().deleteSingle(
ProjectEntity.DELETE_BY_PK,
proto);
}
public List<Project> findAll(Readset<Project> readset) throws DalException {
Project proto = new Project();
List<Project> result = getQueryEngine().queryMultiple(
ProjectEntity.FIND_ALL,
proto,
readset);
return result;
}
public Project findByPK(int keyId, Readset<Project> readset) throws DalException {
Project proto = new Project();
proto.setKeyId(keyId);
Project result = getQueryEngine().querySingle(
ProjectEntity.FIND_BY_PK,
proto,
readset);
return result;
}
public Project findByDomain(String domain, Readset<Project> readset) throws DalException {
Project proto = new Project();
proto.setDomain(domain);
Project result = getQueryEngine().querySingle(
ProjectEntity.FIND_BY_DOMAIN,
proto,
readset);
return result;
}
public Project findByCmdbDomain(String domain, Readset<Project> readset) throws DalException {
Project proto = new Project();
proto.setDomain(domain);
Project result = getQueryEngine().querySingle(
ProjectEntity.FIND_BY_CMDB_DOMAIN,
proto,
readset);
return result;
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getEntityClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] { ProjectEntity.class };
}
public int insert(Project proto) throws DalException {
return getQueryEngine().insertSingle(
ProjectEntity.INSERT,
proto);
}
public int updateByPK(Project proto, Updateset<Project> updateset) throws DalException {
return getQueryEngine().updateSingle(
ProjectEntity.UPDATE_BY_PK,
proto,
updateset);
}
}
DAO中需要十分注意点有
- 继承
extends AbstractDao - 实现抽象方法
protected Class<?>[] getEntityClasses()
Service
import com.dianping.cat.Cat;
import org.dal.cat.core.dal.Project;
import org.dal.cat.core.dal.ProjectDao;
import org.dal.cat.core.dal.ProjectEntity;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.DalException;
import org.unidal.lookup.annotation.Inject;
import org.unidal.lookup.extension.Initializable;
import org.unidal.lookup.extension.InitializationException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class ProjectService implements Initializable {
@Inject
private ProjectDao m_projectDao;
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> m_domains = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project> m_domainToProjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project>();
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project> m_cmdbToProjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project>();
public static final String DEFAULT = "Default";
public boolean contains(String domain) {
return m_domains.containsKey(domain);
}
public Project create() {
return m_projectDao.createLocal();
}
public boolean delete(Project project) {
int id = project.getId();
String domainName = null;
for (Entry<String, Project> entry : m_domainToProjects.entrySet()) {
Project pro = entry.getValue();
if (pro.getId() == id) {
domainName = pro.getDomain();
break;
}
}
try {
m_projectDao.deleteByPK(project);
m_domainToProjects.remove(domainName);
m_cmdbToProjects.remove(project.getCmdbDomain());
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
Cat.logError("delete project error ", e);
return false;
}
}
public List<Project> findAll() throws DalException {
return new ArrayList<Project>(m_domainToProjects.values());
}
public Project findByDomain(String domainName) {
Project project = m_domainToProjects.get(domainName);
if (project != null) {
return project;
} else {
try {
Project pro = m_projectDao.findByDomain(domainName, ProjectEntity.READSET_FULL);
m_domainToProjects.put(pro.getDomain(), pro);
return project;
} catch (DalException e) {
} catch (Exception e) {
Cat.logError(e);
}
return null;
}
}
public Map<String, Department> findDepartments(Collection<String> domains) {
Map<String, Department> departments = new TreeMap<String, Department>();
for (String domain : domains) {
Project project = findProject(domain);
String department = DEFAULT;
String projectLine = DEFAULT;
if (project != null) {
String bu = project.getBu();
String productline = project.getCmdbProductline();
department = bu == null ? DEFAULT : bu;
projectLine = productline == null ? DEFAULT : productline;
}
Department temp = departments.get(department);
if (temp == null) {
temp = new Department();
departments.put(department, temp);
}
temp.findOrCreatProjectLine(projectLine).addDomain(domain);
}
return departments;
}
public Project findProject(String domain) {
Project project = m_domainToProjects.get(domain);
if (project == null) {
project = m_cmdbToProjects.get(domain);
}
return project;
}
@Override
public void initialize() throws InitializationException {
// if (!m_manager.isLocalMode()) {
refresh();
// }
}
public boolean insert(Project project) throws DalException {
m_domainToProjects.put(project.getDomain(), project);
int result = m_projectDao.insert(project);
if (result == 1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean insert(String domain) {
Project project = create();
project.setDomain(domain);
project.setCmdbProductline(DEFAULT);
project.setBu(DEFAULT);
try {
insert(project);
m_domains.put(domain, domain);
return true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
Cat.logError(ex);
}
return false;
}
protected void refresh() {
try {
List<Project> projects = m_projectDao.findAll(ProjectEntity.READSET_FULL);
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project> tmpDomainProjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project>();
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project> tmpCmdbProjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Project>();
ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> tmpDomains = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();
for (Project project : projects) {
String domain = project.getDomain();
tmpDomains.put(domain, domain);
tmpDomainProjects.put(domain, project);
String cmdb = project.getCmdbDomain();
if (cmdb != null) {
tmpCmdbProjects.put(cmdb, project);
}
}
m_domains = tmpDomains;
m_domainToProjects = tmpDomainProjects;
m_cmdbToProjects = tmpCmdbProjects;
} catch (DalException e) {
Cat.logError("initialize ProjectService error", e);
}
}
public boolean update(Project project) {
m_domainToProjects.put(project.getDomain(), project);
try {
m_projectDao.updateByPK(project, ProjectEntity.UPDATESET_FULL);
return true;
} catch (DalException e) {
Cat.logError(e);
return false;
}
}
public static class Department {
private Map<String, ProjectLine> m_projectLines = new TreeMap<String, ProjectLine>();
public ProjectLine findOrCreatProjectLine(String projectLine) {
ProjectLine line = m_projectLines.get(String.valueOf(projectLine));
if (line == null) {
line = new ProjectLine();
m_projectLines.put(projectLine, line);
}
return line;
}
public Map<String, ProjectLine> getProjectLines() {
return m_projectLines;
}
}
public static class ProjectLine {
private List<String> m_lineDomains = new ArrayList<String>();
public void addDomain(String name) {
m_lineDomains.add(name);
}
public List<String> getLineDomains() {
return m_lineDomains;
}
}
}
这个类的代码很多,主要为了保持阅读是代码的完整性,其实最需要关注的点是 ProjectDao 服务组件的注入。
@Inject
private ProjectDao m_projectDao
ProjectEntity的描述
@Entity(logicalName = "project", physicalName = "project", alias = "p")
public class ProjectEntity {
@Attribute(field = "id", nullable = false, primaryKey = true, autoIncrement = true)
public static final DataField ID = new DataField("id");
@Attribute(field = "domain", nullable = false)
public static final DataField DOMAIN = new DataField("domain");
@Attribute(field = "cmdb_domain")
public static final DataField CMDB_DOMAIN = new DataField("cmdb-domain");
@Attribute(field = "level")
public static final DataField LEVEL = new DataField("level");
@Attribute(field = "bu")
public static final DataField BU = new DataField("bu");
@Attribute(field = "cmdb_productline")
public static final DataField CMDB_PRODUCTLINE = new DataField("cmdb-productline");
@Attribute(field = "owner")
public static final DataField OWNER = new DataField("owner");
@Attribute(field = "email")
public static final DataField EMAIL = new DataField("email");
@Attribute(field = "phone")
public static final DataField PHONE = new DataField("phone");
@Attribute(field = "creation_date", insertExpr = "NOW()")
public static final DataField CREATION_DATE = new DataField("creation-date");
@Attribute(field = "modify_date", insertExpr = "NOW()", updateExpr = "NOW()")
public static final DataField MODIFY_DATE = new DataField("modify-date");
@Variable
public static final DataField KEY_ID = new DataField("key-id");
public static final Readset<Project> READSET_FULL = new Readset<Project>(ID, DOMAIN, CMDB_DOMAIN, LEVEL, BU, CMDB_PRODUCTLINE, OWNER, EMAIL, PHONE, CREATION_DATE, MODIFY_DATE);
public static final Updateset<Project> UPDATESET_FULL = new Updateset<Project>(ID, DOMAIN, CMDB_DOMAIN, LEVEL, BU, CMDB_PRODUCTLINE, OWNER, EMAIL, PHONE, MODIFY_DATE);
public static final QueryDef FIND_BY_PK = new QueryDef("findByPK", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.SELECT,
"SELECT <FIELDS/> FROM <TABLE/> WHERE <FIELD name='id'/> = ${key-id}");
public static final QueryDef INSERT = new QueryDef("insert", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.INSERT,
"INSERT INTO <TABLE/> (<FIELDS/>) VALUES(<VALUES/>) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE <FIELD name='domain'/> = ${domain}, <FIELD name='modify-date'/> = NOW()");
public static final QueryDef UPDATE_BY_PK = new QueryDef("updateByPK", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.UPDATE,
"UPDATE <TABLE/> SET <FIELDS/> WHERE <FIELD name='id'/> = ${key-id}");
public static final QueryDef DELETE_BY_PK = new QueryDef("deleteByPK", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.DELETE,
"DELETE FROM <TABLE/> WHERE <FIELD name='id'/> = ${key-id}");
public static final QueryDef FIND_ALL = new QueryDef("findAll", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.SELECT,
"SELECT <FIELDS/> FROM <TABLE/>");
public static final QueryDef FIND_BY_DOMAIN = new QueryDef("findByDomain", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.SELECT,
"SELECT <FIELDS/> FROM <TABLE/> WHERE binary(<FIELD name='domain'/>) = binary(${domain})");
public static final QueryDef FIND_BY_CMDB_DOMAIN = new QueryDef("findByCmdbDomain", ProjectEntity.class, QueryType.SELECT,
"SELECT <FIELDS/> FROM <TABLE/> WHERE binary(<FIELD name='cmdb-domain'/>) = binary(${domain})");
}
注意几个对象
DataField的定义Readset读取 列的顺序性和非重复性Updateset更新列的非重复性QueryDef各种查询的定义
Project实体Bean|Model
public class Project extends DataObject {
private int m_id;
private String m_domain;
private String m_cmdbDomain;
private int m_level;
private String m_bu;
private String m_cmdbProductline;
private String m_owner;
private String m_email;
private String m_phone;
private java.util.Date m_creationDate;
private java.util.Date m_modifyDate;
private int m_keyId;
@Override
public void afterLoad() {
m_keyId = m_id;
super.clearUsage();
}
public String getBu() {
return m_bu;
}
public String getCmdbDomain() {
return m_cmdbDomain;
}
public String getCmdbProductline() {
return m_cmdbProductline;
}
public java.util.Date getCreationDate() {
return m_creationDate;
}
public String getDomain() {
return m_domain;
}
public String getEmail() {
return m_email;
}
public int getId() {
return m_id;
}
public int getKeyId() {
return m_keyId;
}
public int getLevel() {
return m_level;
}
public java.util.Date getModifyDate() {
return m_modifyDate;
}
public String getOwner() {
return m_owner;
}
public String getPhone() {
return m_phone;
}
public Project setBu(String bu) {
setFieldUsed(BU, true);
m_bu = bu;
return this;
}
public Project setCmdbDomain(String cmdbDomain) {
setFieldUsed(CMDB_DOMAIN, true);
m_cmdbDomain = cmdbDomain;
return this;
}
public Project setCmdbProductline(String cmdbProductline) {
setFieldUsed(CMDB_PRODUCTLINE, true);
m_cmdbProductline = cmdbProductline;
return this;
}
public Project setCreationDate(java.util.Date creationDate) {
setFieldUsed(CREATION_DATE, true);
m_creationDate = creationDate;
return this;
}
public Project setDomain(String domain) {
setFieldUsed(DOMAIN, true);
m_domain = domain;
return this;
}
public Project setEmail(String email) {
setFieldUsed(EMAIL, true);
m_email = email;
return this;
}
public Project setId(int id) {
setFieldUsed(ID, true);
m_id = id;
setFieldUsed(KEY_ID, true);
m_keyId = id;
return this;
}
public Project setKeyId(int keyId) {
setFieldUsed(KEY_ID, true);
m_keyId = keyId;
return this;
}
public Project setLevel(int level) {
setFieldUsed(LEVEL, true);
m_level = level;
return this;
}
public Project setModifyDate(java.util.Date modifyDate) {
setFieldUsed(MODIFY_DATE, true);
m_modifyDate = modifyDate;
return this;
}
public Project setOwner(String owner) {
setFieldUsed(OWNER, true);
m_owner = owner;
return this;
}
public Project setPhone(String phone) {
setFieldUsed(PHONE, true);
m_phone = phone;
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(1024);
sb.append("Project[");
sb.append("bu: ").append(m_bu);
sb.append(", cmdb-domain: ").append(m_cmdbDomain);
sb.append(", cmdb-productline: ").append(m_cmdbProductline);
sb.append(", creation-date: ").append(m_creationDate);
sb.append(", domain: ").append(m_domain);
sb.append(", email: ").append(m_email);
sb.append(", id: ").append(m_id);
sb.append(", key-id: ").append(m_keyId);
sb.append(", level: ").append(m_level);
sb.append(", modify-date: ").append(m_modifyDate);
sb.append(", owner: ").append(m_owner);
sb.append(", phone: ").append(m_phone);
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
这个对象必须继承 基类 DataObject
表面上看,这些配置(除pom.xml)和类代码,书写工作很大,其实不然,这些代码的配置的都是固定,不需要人工参与,unida团队同样为了这些代码的编写相应的代码生成工具,后续介绍。
0.6 HelloWorld的测试类
import org.dal.cat.core.dal.Project;
import org.dal.cat.service.ProjectService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
public class TestProjectDao extends ComponentTestCase {
@Test
public void findAllProject() {
log.info("测试日志");
try {
ProjectService service = lookup(ProjectService.class);
List<Project> list = service.findAll();
if (null == list || 0 == list.size()) {
log.warn("没有项目");
} else {
for (Project proj : list) {
log.info(proj.toString());
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("发生异常", ex);
}
}
@Test
public void insert() {
log.info("insert test case");
try {
ProjectService service = lookup(ProjectService.class);
Project project = new Project();
project.setBu("bu===").setCmdbDomain("1===")
.setCmdbProductline("111==")
.setLevel(1222)
.setDomain("22222")
.setEmail("aaa@a.com")
.setCreationDate(new Date());
boolean bool = service.insert(project);
Assert.assertEquals(true, bool);
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("插入失败", ex);
}
}
}
0.7 测试效果输出
[2021-02-04 15:20:10.807] [INFO] [TestProjectDao] Project[bu: bu===, cmdb-domain: 1===, cmdb-productline: 111==, creation-date: 2021-02-04 15:20:10.0, domain: 22222, email: aaa@a.com, id: 10, key-id: 10, level: 1222, modify-date: 2021-02-04 15:20:12.0, owner: null, phone: null]
有了上面的 HelloWorld 的感性认识,下面我们将切入正题,进行 dal-jdbc 的实现原理的剖析
1.面向应用开发人员的顶级接口
1.1 org.unidal.dal.jdbc.AbstractDao
```java
package org.unidal.dal.jdbc;
import org.unidal.dal.jdbc.entity.EntityInfoManager;
import org.unidal.lookup.ContainerHolder;
import org.unidal.lookup.extension.Initializable;
import org.unidal.lookup.extension.InitializationException;
public abstract class AbstractDao extends ContainerHolder implements Initializable {
private QueryEngine m_queryEngine;
protected QueryEngine getQueryEngine() {
return m_queryEngine;
}
protected abstract Class<?>[] getEntityClasses();
public void initialize() throws InitializationException {
m_queryEngine = lookup(QueryEngine.class);
// register relevant entity class
EntityInfoManager entityInfoManager = lookup(EntityInfoManager.class);
for (Class<?> entityClass : getEntityClasses()) {
entityInfoManager.register(entityClass);
}
}
}
```
解说
protected abstract Class<?>[] getEntityClasses()获取的DAO操作对象实体的描述、定义,这个信息为initialize方法所用,进行EntityInfoManager信息的注册使用。private QueryEngine m_queryEngine对象的初始化,从IOC容器的获取的。
1.2 org.unidal.dal.jdbc.entity.EntityInfoManager
// Entity info manager
public interface EntityInfoManager {
public EntityInfo getEntityInfo(Class<?> entityClass);
public EntityInfo getEntityInfo(String logicalName);
public void register(Class<?> entityClass);
}
package org.unidal.dal.jdbc.entity;
....
@Named(type = EntityInfoManager.class)
public class DefaultEntityInfoManager implements EntityInfoManager, LogEnabled, Initializable {
@Inject
private QueryNaming m_reservedKeyword;
private Map<String, Class<?>> m_logicalNameToEntityClass = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
private Map<Class<?>, EntityInfo> m_entityClassToEntityInfo = new HashMap<Class<?>, EntityInfo>();
....
public synchronized void register(Class<?> entityClass) {
if (m_entityClassToEntityInfo.containsKey(entityClass)) {
m_logger.debug(entityClass + " is already initialized yet");
return;
}
Entity entity = (Entity) entityClass.getAnnotation(Entity.class);
if (entity == null) {
throw new DalRuntimeException(entityClass + " should be annotated by Entity");
}
Map<DataField, Relation> relations = new HashMap<DataField, Relation>();
Map<DataField, Attribute> attributes = new LinkedHashMap<DataField, Attribute>();
Map<DataField, Variable> variables = new HashMap<DataField, Variable>();
Map<Readset<?>, SubObjects> subobjects = new HashMap<Readset<?>, SubObjects>();
Field[] fields = entityClass.getFields();
int index = 0;
for (Field field : fields) {
Class<?> type = field.getType();
if (type == DataField.class) {
if (!Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new DalRuntimeException("Field " + field.getName() + " of " + entityClass
+ " should be modified as static");
}
Relation relation = field.getAnnotation(Relation.class);
Attribute attribute = field.getAnnotation(Attribute.class);
Variable variable = field.getAnnotation(Variable.class);
DataField dataField;
try {
dataField = (DataField) field.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new DalRuntimeException("Can't get value of Field " + field.getName() + " of " + entityClass);
}
if (attribute != null) {
attributes.put(dataField, attribute);
} else if (variable != null) {
variables.put(dataField, variable);
} else if (relation != null) {
relations.put(dataField, relation);
} else {
m_logger.warn("Field " + field.getName() + " of " + entityClass + " should be annotated by "
+ "Attribute or Relation");
}
if (dataField != null) {
dataField.setEntityClass(entityClass);
dataField.setIndex(index++);
}
} else if (type == Readset.class) {
if (!Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new DalRuntimeException("Readset " + field.getName() + " of " + entityClass
+ " should be modified as static");
}
SubObjects subobject = field.getAnnotation(SubObjects.class);
Readset<?> readset;
try {
readset = (Readset<?>) field.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new DalRuntimeException("Can't get value of Field " + field.getName() + " of " + entityClass);
}
if (subobject != null) {
subobjects.put(readset, subobject);
}
}
}
if (attributes.size() == 0 && entityClass != RawEntity.class) {
m_logger.warn("No fields defined with type DataField in " + entityClass);
}
Class<?> otherClass = m_logicalNameToEntityClass.get(entity.logicalName());
if (otherClass != null) {
throw new DalRuntimeException("Logical name(" + entity.logicalName() + ") has been used by " + otherClass
+ ", can't use it in " + entityClass);
} else {
m_logicalNameToEntityClass.put(entity.logicalName(), entityClass);
}
EntityInfo info = new EntityInfo(entity, relations, attributes, variables, subobjects);
m_entityClassToEntityInfo.put(entityClass, info);
}
@Override
public void initialize() throws InitializationException {
register(RawEntity.class);
}
}
解说
- 方法
initialize默认register(RawEntity.class) 方法
register处理逻辑通过 注解[
Entity.class]的解析,获取表的信息[逻辑表、物理表和表别名],详见下面Entity的描述@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Entity {
String logicalName();
String physicalName() default "";
String alias();
}通过 注解[
Relation,Attribute,Variable,SubObjects],分别去描述 表的 其他的表的关联关系、属性、变量、嵌套表。其中注解说明
Relation@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Relation {
String logicalName();
String alias();
String join();
boolean multiple() default false;
}Attribute@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Attribute {
String field();
boolean primaryKey() default false;
boolean nullable() default true;
boolean autoIncrement() default false;
String selectExpr() default "";
String insertExpr() default "";
String updateExpr() default "";
}Variable@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Variable {
int sqlType() default Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int scale() default 0;
}SubObjects@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface SubObjects {
String[] value();
}
Readset、Subobject的 等注解的解析,目的构建EntityInfo的缓存,这样避免每次进行表操作时,都要进行表信息解析,一般表的描述信息解析都是放在项目启动处理,这样后面数据操作直接享用 启动 时的缓存,提升处理性能。
2.核心API org.unidal.dal.jdbc.QueryEngine
2.1 接口定义
public interface QueryEngine {
public String HINT_QUERY = "QUERY";
public String HINT_DATA_OBJECT = "DATA_OBJECT";
public <T extends DataObject> int[] deleteBatch(QueryDef query, T[] protos) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int deleteSingle(QueryDef query, T proto) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int[] insertBatch(QueryDef query, T[] protos) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int insertSingle(QueryDef query, T proto) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> List<T> queryMultiple(QueryDef query, T proto, Readset<?> readset) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> T querySingle(QueryDef query, T proto, Readset<?> readset) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int[] updateBatch(QueryDef query, T[] protos, Updateset<?> updateset) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int updateSingle(QueryDef query, T proto, Updateset<?> updateset) throws DalException;
}
目视 方法 的签名 ,与一般的ORM的框架的定义没有什么区别,都是 insert,update,delete 和 query 操作。
关注焦点
DataObject所有的Entity必须实现的 基类。package org.unidal.dal.jdbc; import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public abstract class DataObject {
/* Indicates whether a field contains data or not */
private BitSet m_usages;
private Map<String, Object> m_queryHints;
public DataObject() {
m_usages = new BitSet();
}
/**
* Called after the object is loaded with values from the database.
*/
public void afterLoad() {
m_usages.clear();
// OVERRIDE IT IN SUB-CLASS
}
/**
* Called before the object will be saved to the database.
*/
public void beforeSave() {
// OVERRIDE IT IN SUB-CLASS
}
protected void clearUsage() {
m_usages.clear();
}
public Map<String, Object> getQueryHints() {
return m_queryHints;
}
public boolean isFieldUsed(DataField field) {
return m_usages.get(field.getIndex());
}
protected void setFieldUsed(DataField field, boolean used) {
if (used) {
m_usages.set(field.getIndex());
} else {
m_usages.clear(field.getIndex());
}
}
public void setQueryHint(String hint, Object value) {
if (value == null) {
if (m_queryHints != null) {
m_queryHints.remove(hint);
}
} else {
if (m_queryHints == null) {
m_queryHints = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
m_queryHints.put(hint, value);
}
}
}需要提示的,变量
BitSet m_usages,它的目的更加有效快速的判断是否存在,这是 位运算 , 效率很高的;最终的是通过 这个 位运算 进行 查询条件列的判断,是否需要查询。QueryDef的定义。见ProjectEntity中的定义。public class QueryDef { private String m_name;
private Class<?> m_entityClass;
private String m_pattern;
private QueryType m_type;
private List<Token> m_tokens;
private boolean m_storeProcedure;
private boolean m_raw;需要提示和说明
m_name标记QueryDef唯一的标记值。m_entityClass查询对象的实体m_patternSQL中的正则表达式或者函数m_type是个枚举详细见下代码public enum QueryType { SELECT,
INSERT,
UPDATE,
DELETE;
}m_tokensSQL 标记语句 的特定 字段 解析,小的SQL内容替换,解析模块public interface Token { public TokenType getType();
}public enum TokenType { TABLES,
TABLE,
FIELDS,
FIELD,
VALUES,
JOINS,
IN,
IF("type", "field", "value"),
STRING,
PARAM,
VALUE,
;
private List<String> m_supportAttributes;
private TokenType(String... supportAttributes) {
m_supportAttributes = Arrays.asList(supportAttributes);
}
public List<String> getSupportAttributes() {
return m_supportAttributes;
}
}m_storeProcedure是否是存储过程m_raw是否是原生SQL语句
2.2 org.unidal.dal.jdbc.engine.DefaultQueryEngine
在 2.1 节中对 QueryEngine 接口进行功能定义,不然而喻,默认实现肯定需要实现的
@Named(type = QueryEngine.class)
public class DefaultQueryEngine extends ContainerHolder implements QueryEngine {
@Inject
private EntityInfoManager m_entityManager;
@Inject
private QueryExecutor m_queryExecutor;
@Inject
private TransactionManager m_transactionManager;
@Inject
private QueryResolver m_queryResolver;
protected <T extends DataObject> QueryContext createContext(QueryDef query, T proto) {
QueryContext ctx = new DefaultQueryContext();
EntityInfo enityInfo = m_entityManager.getEntityInfo(query.getEntityClass());
Map<String, Object> queryHints = getQueryHints(query, proto);
ctx.setQuery(query);
ctx.setProto(proto);
ctx.setEntityInfo(enityInfo);
ctx.setQueryHints(queryHints);
return ctx;
}
m_entityManager对entityManager的缓存 提取EntityInfo信息m_queryExecutor核心组件 , 查询(insert、update和delete,都是一种特殊的查询)执行器。m_transactionManager事务管理器 ,后面详细说明,这里先带过。m_queryResolver解析器 ,对 标记的SQL进行解析,还原至 JDBC 可用的SQL|可识别的语句;其中可识别的,如insert中 常常 使用 ?,?,? 替代值,目的是防止SQL注入。方法
QueryContext构建查询面板,可以简单直视为DTO@Named(type = QueryContext.class, instantiationStrategy = Named.PER_LOOKUP) public class DefaultQueryContext implements QueryContext {
private QueryDef m_query;
private DataObject m_proto;
private Readset<?> m_readset;
private Updateset<?> m_updateset;
private EntityInfo m_entityInfo;
private String m_sqlStatement;
private List<Parameter> m_parameters = new ArrayList<Parameter>();
private List<DataField> m_outFields = new ArrayList<DataField>();
private List<String> m_outSubObjectNames = new ArrayList<String>();
private int m_fetchSize;
private boolean m_withinInToken;
private boolean m_withinIfToken;
private boolean m_tableResolved;
private boolean m_sqlResolveEnabled;
private boolean m_rawSql;
private Map<String, Object> m_queryHints;
private String m_dataSourceName;
private Object[] m_parameterValues;值得说的一点,不需要容器管理,每次的操作内容面板的对象都是不一样的。
![]()
2.2.1 org.unidal.dal.jdbc.query.token.TokenParser
这是一个语句解析器
2.2.2 org.unidal.dal.jdbc.query.token.resolver.TokenResolver
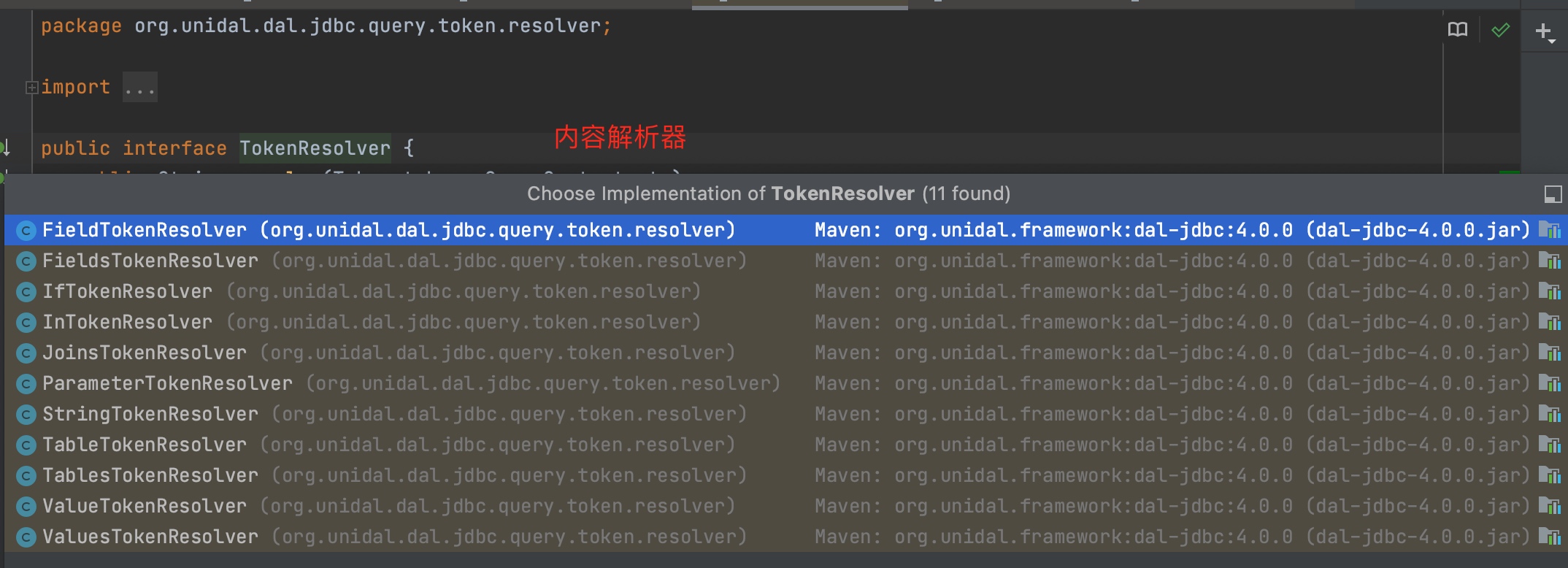
不同的标记 需要不同的解析器进行解析处理
3. org.unidal.dal.jdbc.query.QueryExecutor
public interface QueryExecutor {
public <T extends DataObject> List<T> executeQuery(QueryContext ctx) throws DalException;
public int executeUpdate(QueryContext ctx) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int[] executeUpdateBatch(QueryContext ctx, T[] protos) throws DalException;
}
从 操作需要不要事务的焦点,进行 执行 签名方法的划分 ,这是从一般的角度,但是也有读操作含有事务的,很少很少。
@Named(type = QueryExecutor.class)
public class DefaultQueryExecutor implements QueryExecutor {
@Inject("mysql")
private ReadHandler m_readHandler;
@Inject("mysql")
private WriteHandler m_writeHandler;
支持 热点话题 读写分离
3.1 读接口 ReadHandler
public interface ReadHandler {
public <T extends DataObject> List<T> executeQuery(QueryContext ctx) throws DalException;
}
默认实现
@Named(type = ReadHandler.class, value = "mysql")
public class MysqlReadHandler extends MysqlBaseHandler implements ReadHandler {
@Inject
private TransactionManager m_transactionManager;
@Inject
private DataObjectAssembly m_assembly;
@Named(type = ReadHandler.class, value = "mysql")
public class MysqlReadHandler extends MysqlBaseHandler implements ReadHandler {
@Inject
private TransactionManager m_transactionManager;
@Inject
private DataObjectAssembly m_assembly;
......
m_transactionManager提供数据连接connectionm_assembly负责将数据库中提取的数据 转换 Java的应用对象
3.2 写接口 WriteHandler
public interface WriteHandler {
public int executeUpdate(QueryContext ctx) throws DalException;
public <T extends DataObject> int[] executeUpdateBatch(QueryContext ctx, T[] protos) throws DalException;
}
默认实现 MysqlWriteHandler
@Named(type = WriteHandler.class, value = "mysql")
public class MysqlWriteHandler extends MysqlBaseHandler implements WriteHandler {
@Inject
private TransactionManager m_transactionManager;
@Override
public int executeUpdate(QueryContext ctx) throws DalException {
....
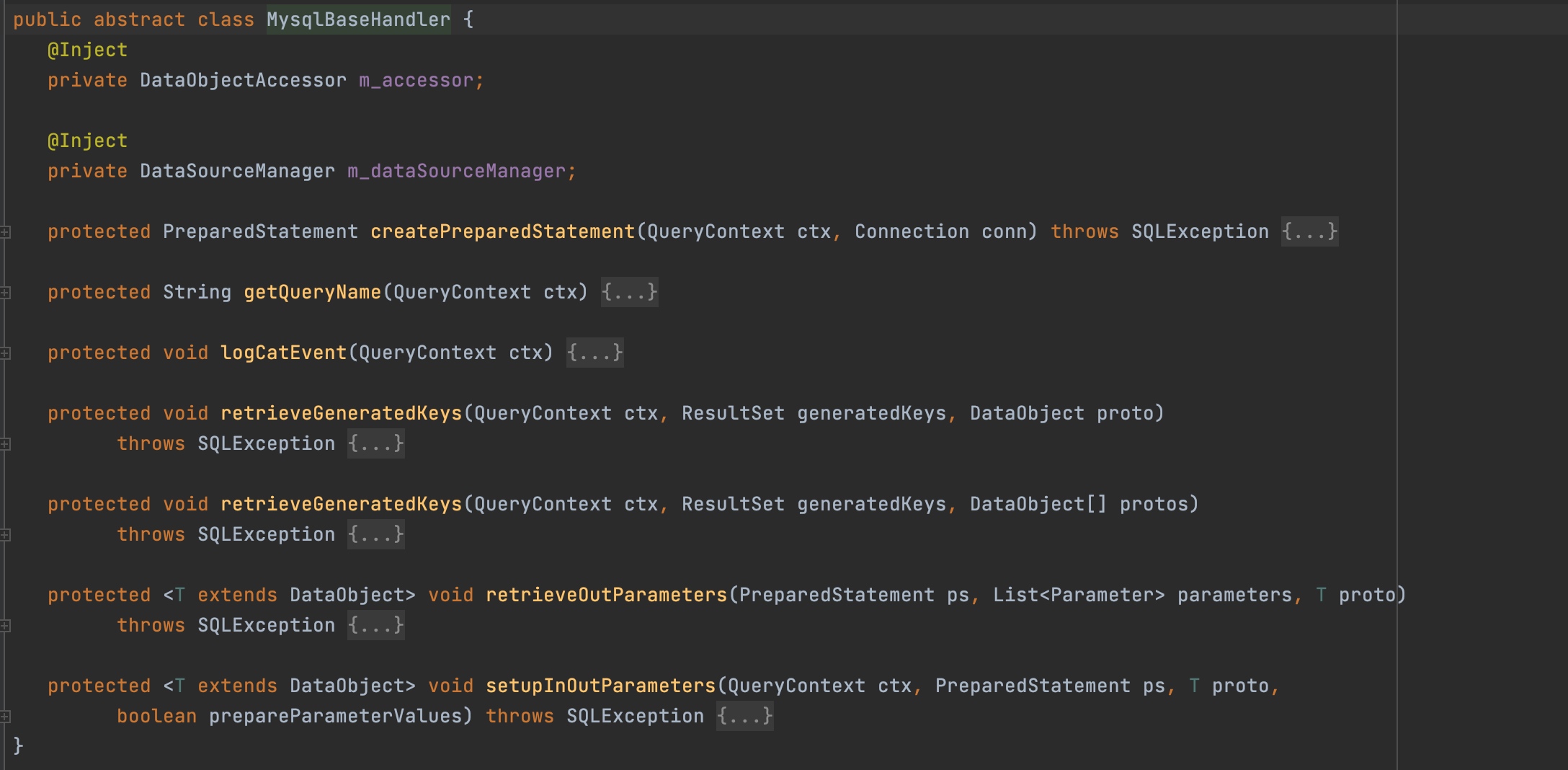
3.3 MysqlBaseHandler
4.org.unidal.dal.jdbc.transaction.TransactionManager
4.1 接口定义
public interface TransactionManager {
public void closeConnection();
public void commitTransaction();
public Connection getConnection(QueryContext ctx);
public boolean isInTransaction();
public void rollbackTransaction();
public void startTransaction(String datasource);
}
4.2 默认实现
@Named(type = TransactionManager.class)
public class DefaultTransactionManager implements TransactionManager, LogEnabled {
private static ThreadLocalTransactionInfo m_threadLocalData = new ThreadLocalTransactionInfo();
@Inject
private TableProviderManager m_tableProviderManager;
@Inject
private DataSourceManager m_dataSourceManager;
- 数据源
m_dataSourceManager的管理 - 具体表服务
m_tableProviderManager管理, 等同于mybatis的mapper
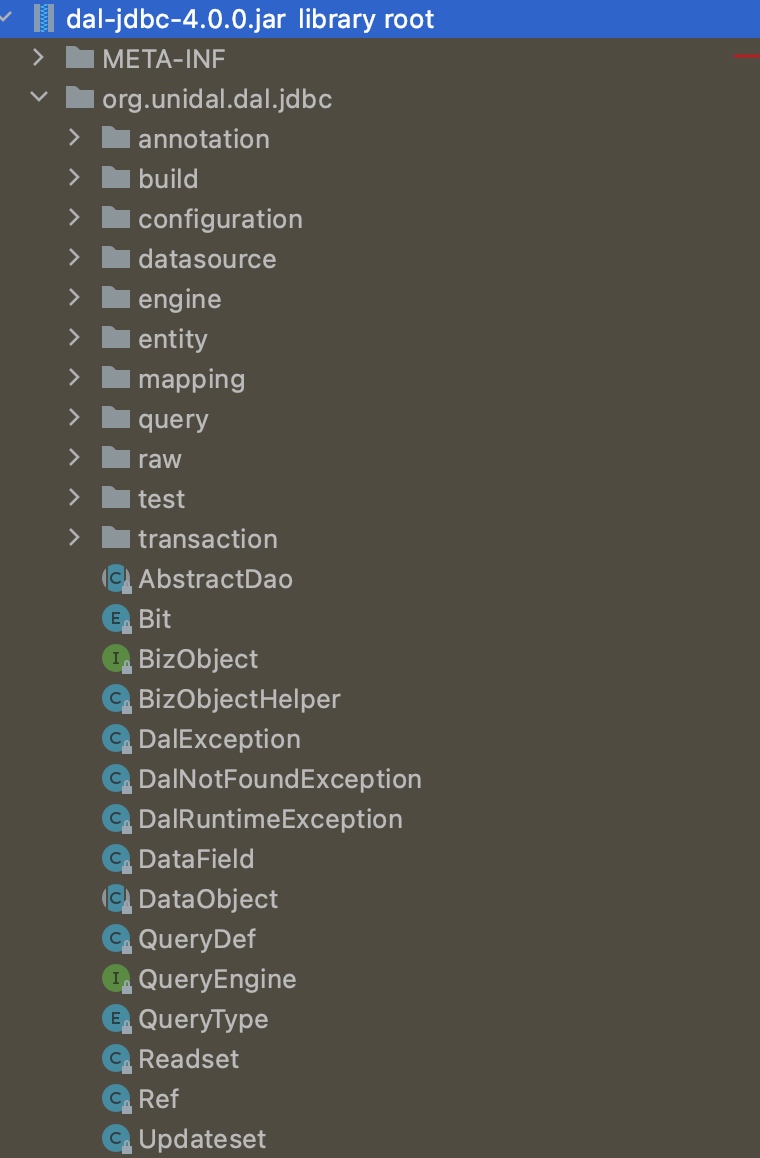
5.工程结构
小结
- 简单
- 定制需求化
- 开发一个ORM框架,如何做?




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号