pytest 参数化用例和数据驱动
pytest 数据参数化
字典:{'name:Joker'}
列表:['Joker','Joe','Jack]数据可变
元组:names = ('Joker','Joe','Jack')数据不可改变
参数化使用
@pytest.mark.parametrize(argnames,argvalues)
argnames:要参数化的变量,string(逗号分割),list,tuple
argvalues:参数化的值,list,list[tuple]
使用string(字符串)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b"[(10,20),(10,30)])
def test_param(self,a,b): T
print(a+b)
使用list(列表)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(["a","b"],[(10,20),(10,30)])
def test_param(self,a,b):
print(a+b)
使用tuple(元组)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(("a","b"),[(10,20),(1030)])
def test_param(self,a,b):
print(a+b)
yaml的用法(- 后面需要空格)
记一个问题:https://blog.csdn.net/saberpan/article/details/111243233
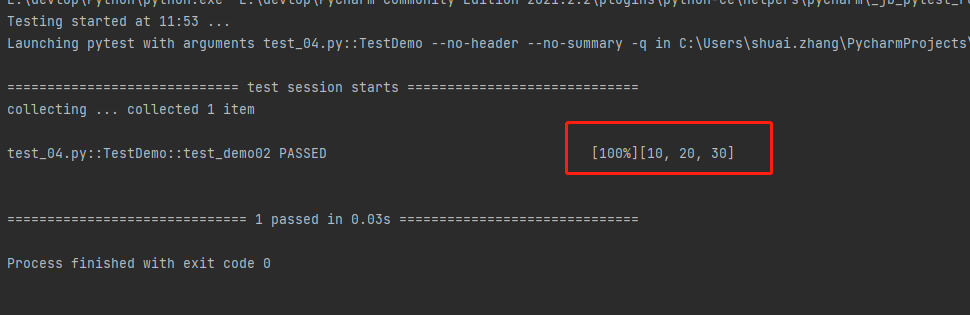
list
- 10
- 20
- 30
输出
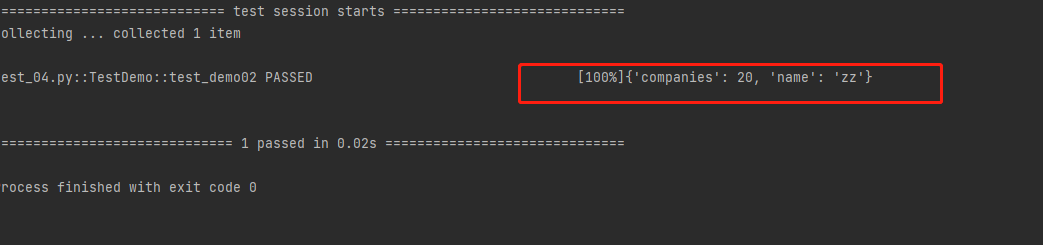
字典(dict)
companies:
20
name:
zz
输出
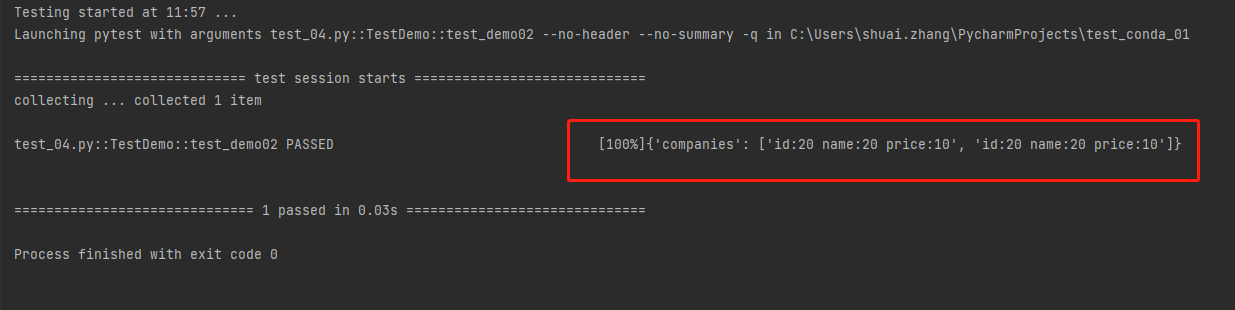
嵌套
companies:
-
id:20
name:20
price:10
-
id:20
name:20
price:10
输出
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/bendouyao/p/9153553.html
数据驱动
数据驱动就是数据的改变从而驱动自动化测试的执行,最终引起测试结果的改变。
简单来说,就是参数化的应用。数据量小的测试用例可以使用代码的参数化来实现数据驱动,
数据量大的情况下建议大家使用一种结构化的文件(例如 yaml,json等)来对数据进行存储,
然后在测试用例中读取这些数据。
import pytest
import yaml
## 需求:对一个列表的三组值进行求值
##{(10,20),(10,10),(10,30)}
class TestDemo:
# @pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b",[(10,20),(10,30),(10,40)])
@pytest.mark.parametrize(["a", "b"], yaml.safe_load(open("./data.yaml")))
def test_demo01(self, a, b):
print('----')
print(a)
print(b)
print('----')
print(a+b)
print('----')
def test_demo02(self):
print(yaml.safe_load(open("data.yaml")))
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main("-v -x TestDemo")
data.yaml如下:
输出: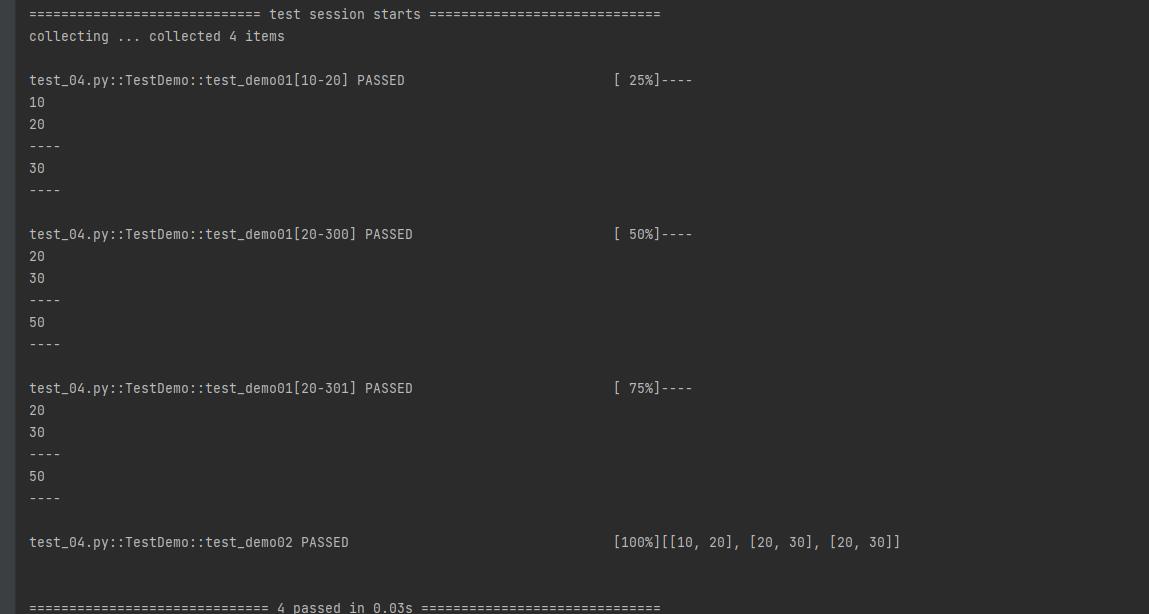


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号