java3——多线程,定时器
------------恢复内容开始------------
cpu-高速缓存-主内存
cpu和高速缓存的速度非常的快,普通没运行的数据一般放在主内存,在运行的时候上高速缓存
java的线程内存模型
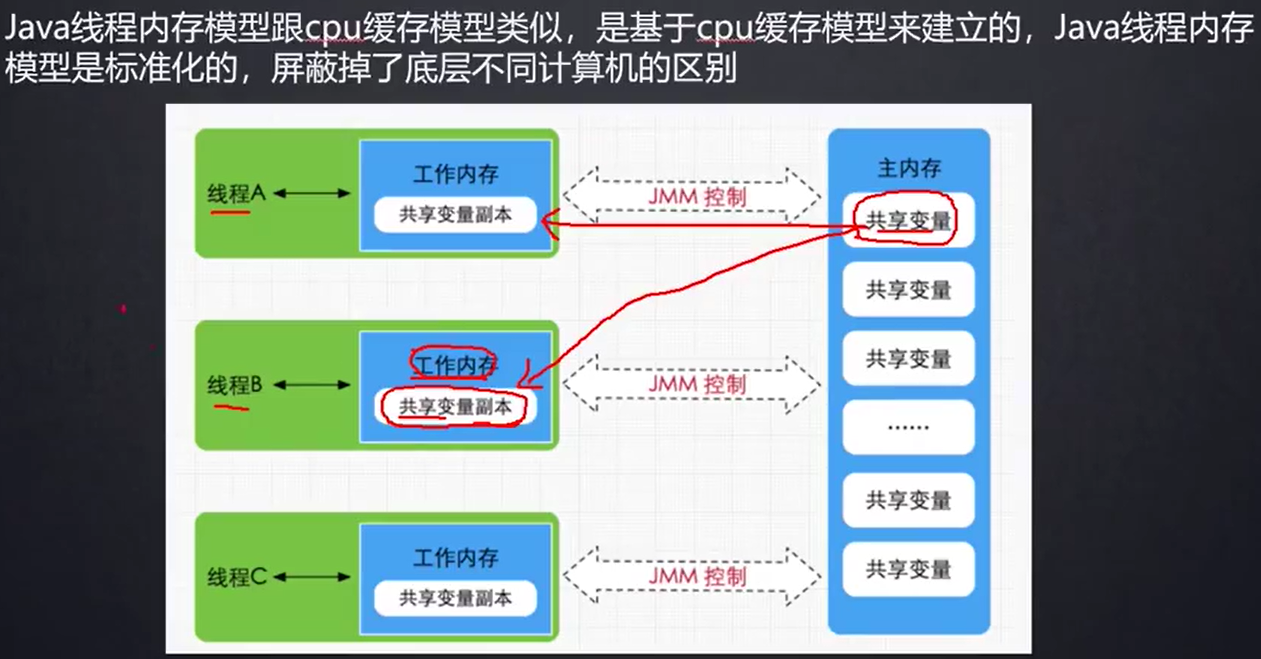
线程里用volatile为了保证程序运行时不同线程对此变量的可见性和共享性。不加这个一个线程改了这个变量另一个线程会感受不到改动
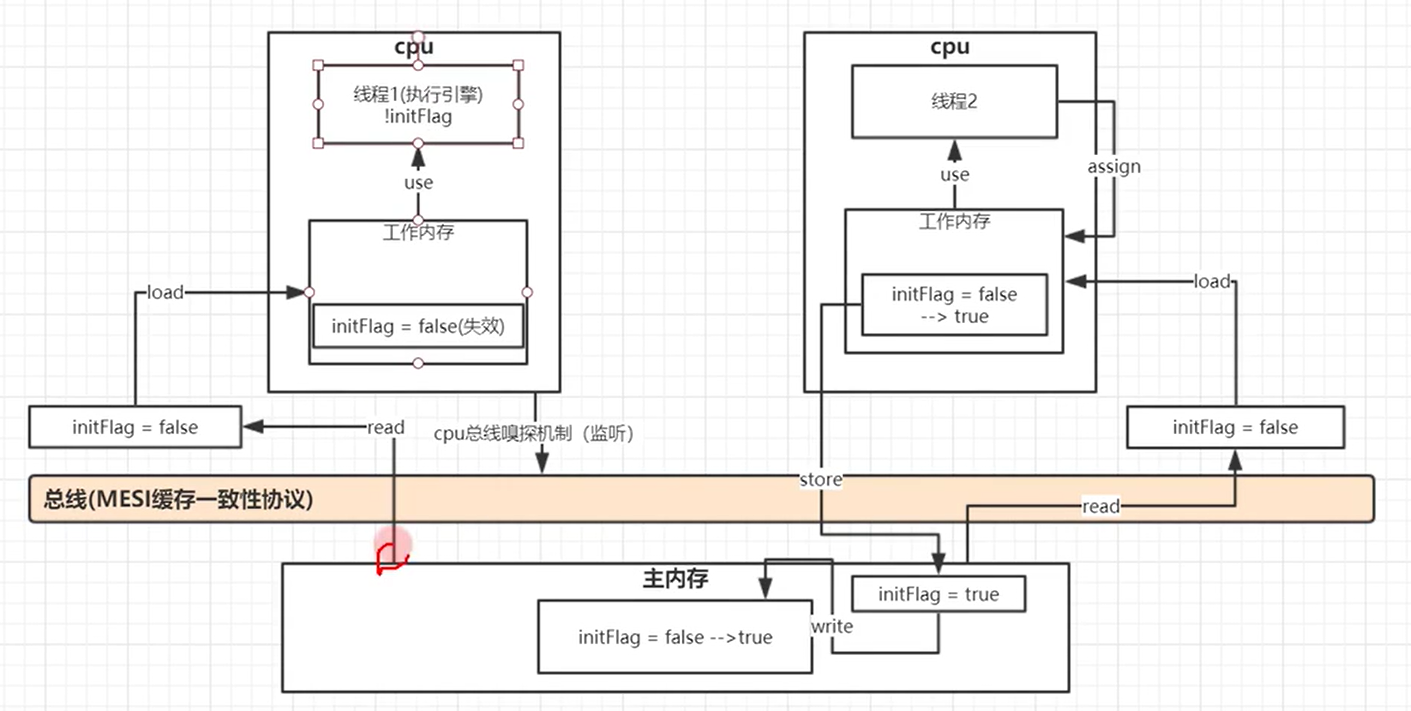
模型解释:首先线程1从主内存把数据提出来放到工作内存,然后线程对数据进行运算操作,假设线程1的运算是死循环那就会卡住在那里。这是线程2提取主内存的数据进行运算完然后放回主内存覆盖掉原来的那个数据,这个操作是需要经过总线的,volatile打开时即将覆盖在经过总线的时候就会被cpu的监听到,所有线程都会知道这个数据被更新了,旧的要失效,然后重新回主内存读取数据。
------------恢复内容结束------------
线程
第一种使用方法
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { thread1 th=new thread1(); th.start(); //启动线程 for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("主线程"); } } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("步数"); } } }
第二种使用方法
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Runnable r1=new runable_obj() ; //实例化可运行类 Thread th=new Thread(r1); //实例化线程的类并且传入可运行类 th.start(); //启动线程 for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("主线程"); } } } class runable_obj implements Runnable{ //编写一个可运行的类 public void run(){ //重写run for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("步数"); } } }
第三种使用方法
匿名内部类
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread th=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int i=1;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("fenzhi"); } } }); th.start(); for (int i=1;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("main"); } } }
线程的生命周期
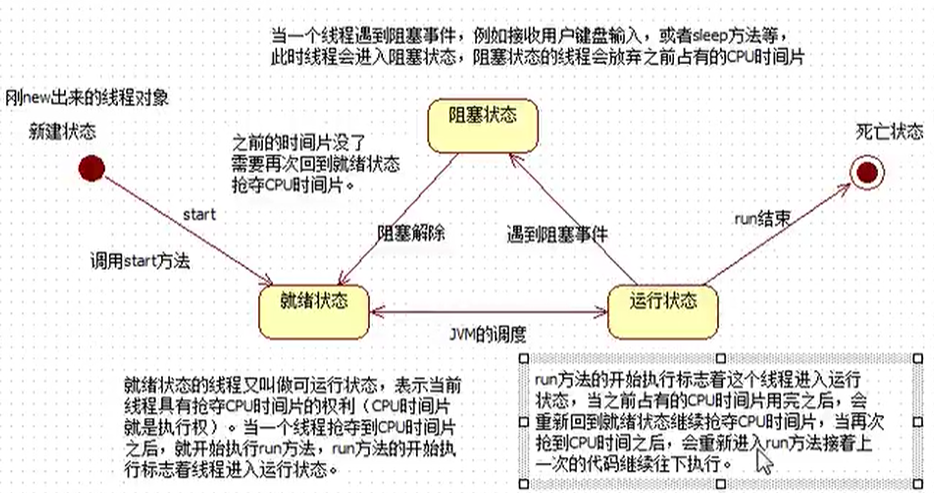
设置和获取线程的名字
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { thread1 th=new thread1(); //定义线程 th.setName("abc"); //设置线程的名字 String thname=th.getName(); //获取线程的名字 System.out.println(thname); th.start(); //启动线程 } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for (int i=1;i<=3;i++){ System.out.println("步数"); } } }
获取当前线程对象,这样可以控制不同的实例化线程
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread current_t=Thread.currentThread(); //静态方法,不用加new,获取当前的线程current_t,类似于this System.out.println("当前线程的名字"+current_t.getName()); thread1 th=new thread1(); //定义线程 th.setName("th1"); thread1 th2=new thread1(); //定义线程 th2.setName("th2"); th.start(); //启动线程 th2.start(); } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ Thread current_t=Thread.currentThread(); //静态方法,不用加new,获取当前的线程current_t,类似于this System.out.println("当前线程的名字"+current_t.getName()); } }
线程sleep
使当前线程放弃cpu时间片,陷入休眠状态。阻塞状态
thread.sleep 只会使得它出现在的线程里进行休眠,无法控制其他线程
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("计时开始"); Thread.sleep(5000); //5s System.out.println("计时完毕"); } }
终止线程的睡眠
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { zqhthread th1 =new zqhthread(); th1.start(); System.out.println("计时开始"); Thread.sleep(3000); //3s System.out.println("计时完毕"); th1.interrupt(); //在3s之后把th1线程打醒让它直接报错然后跳出 } } class zqhthread extends Thread{ public void run(){ try { Thread.sleep(5000*1000); //本来是要睡5000s的 }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("系统出错"); } System.out.println("停止睡眠,跑到这里了"); } }
正常的通过改变标志位停止线程
与停止睡眠不同,这个是正常终止,不会抛出异常
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { zqhthread th1 =new zqhthread(); th1.start(); System.out.println("计时开始"); Thread.sleep(3000); //3s System.out.println("计时完毕"); th1.run_status=false; } } class zqhthread extends Thread{ boolean run_status=true; public void run(){ try { for(int i=0;i<=14;i++){ Thread.sleep(1000); //本来是要睡5000s的 System.out.println(i); if (this.run_status==false){return;} //标志位改变return直接停掉线程 } }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("系统出错"); } System.out.println("停止睡眠,跑到这里了"); } }
如需要强制杀死线程,直接使用线程的实例化.stop
设置线程的优先级,优先级越高,线程越容易抢到cpu时间片
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Thread current_t=Thread.currentThread(); //静态方法,不用加new,获取当前的线程current_t,类似于this System.out.println("当前线程的名字"+current_t.getName()); System.out.println("当前线程的优先级"+current_t.getPriority()); System.out.println(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //常量-最高优先级 System.out.println(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);//常量-最低优先级 System.out.println(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);//常量-默认优先级 current_t.setPriority(2); //设主线程优先级是2 thread1 th=new thread1(); //定义线程 th.setName("th1"); th.start(); //启动线程 for (int i=0;i<=20;i++){ System.out.println("主线程"+i); } } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ Thread current_t=Thread.currentThread(); //静态方法,不用加new,获取当前的线程current_t,类似于this System.out.println("当前线程的名字"+current_t.getName()); System.out.println("当前线程的优先级"+current_t.getPriority()); current_t.setPriority(10); //设支线线程优先级是10 for (int i=0;i<=20;i++){ System.out.println("支线程"+i); } } }
线程让位
放弃当前抢到的时间片,回到就绪状态,重新抢cpu时间片
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { thread1 th=new thread1(); //定义线程 th.setName("th1"); th.start(); //启动线程 for (int i=0;i<=1000;i++){ System.out.println("主线程"+i); } } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for (int i=0;i<=1000;i++){ if (100<i && i<300){ Thread.yield(); //i在100-300的区间内进行让位 } System.out.println("支线程"+i); } } }
线程合并
import java.lang.Thread; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { thread1 th=new thread1(); //定义线程 th.setName("th1"); System.out.println("即将开始"); th.start(); //启动线程 th.join(); //阻塞,合并线程 System.out.println("结束"); } } class thread1 extends Thread{ public void run(){ for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){ System.out.println("支线程"+i); } } }
多线程由于网络延迟带来的危险问题
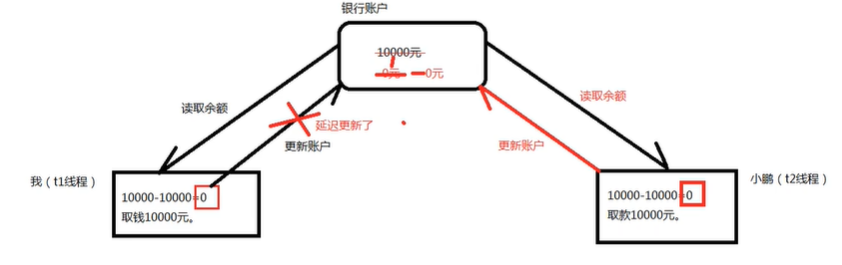

解决方法
!!!!!synchronized最好不要嵌套,否则死锁就完蛋
synchronized (共享的对象) { 修改共享对象内的参数的操作 }
守护线程
常用于定时器定时备份数据,该线程会一直执行,!!!!!!当整个程序终止,守护线程会自动关闭!!!!!!!
比如有线程t,想将其设置为守护线程只需要
t1.setDaemon(true);
定时器
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class Zqh_match { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Timer timer=new Timer(); //定义定时器 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //指定日期类格式 Date fisttime=simpleDateFormat.parse("2021-3-11 21:54:00"); //将输入的字符串转化成日期类 timer.schedule(new Task1(),fisttime,1000); //第一个是定时执行的任务,第二个参数是程序开始的时间,第三个是间隔时间, } } class Task1 extends TimerTask{ @Override public void run() { SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); //指定日期类格式 String strtime=simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); //获取当前的时间 System.out.println(strtime+"触发"); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号