Django-http协议
Http协议:超文本传输协议(应用层程序)。它是客户端和服务端请求和应答的标准。
Http的请求响应模型:
1.客户端连接到web服务器
一个http客户端,与web服务器的http端口(默认是80)建立了一个tcp的套接字连接。
2.发送http请求
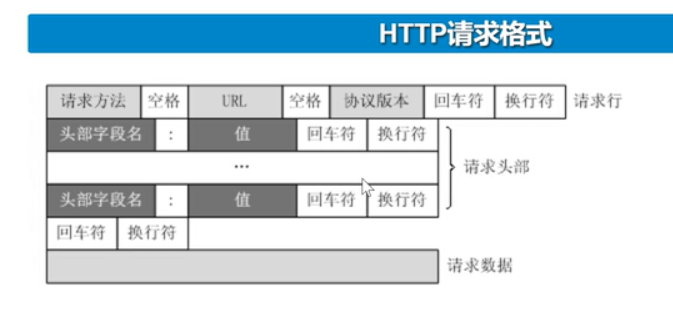
通过tcp套接字,客户端向web服务器发送了一个文本的请求报文,报文由请求行,
请求头,空行和请求数据4部分组成
3.服务器接受并且返回http相应
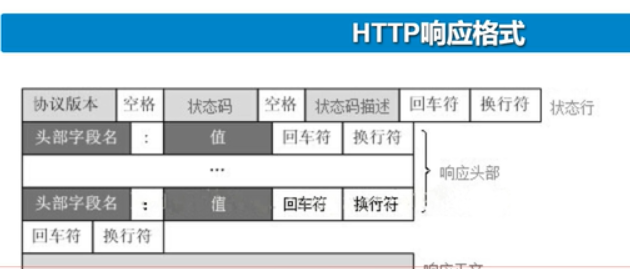
web解析请求,定位请求资源再以报文的形式重新发回去给客户端。报文由请求行,
请求头,空行和请求数据4部分组成
4.释放连接tcp链接
如果链接关闭,服务器将会主动关闭tcp链接。如果链接模式保持存活,则连接会保持
一段时间,这段时间里面可以持续接收请求
5.客户端解析html的内容
6.域名的背后是ip和端口号。
http的请求方法
1.GET方法
向指定的资源发出显示的请求,要去获取,拿到具体的一个资源
2.POST方法
向指定资源提交数据,请求服务器进行处理,例如提交表单或者上传文件。
3.HEAD方法
http状态码
1xx——请求已经为服务器接收,还需要继续处理
2xx——请求已经为服务器接收,理解并接受(表示是成功的)
3xx——重定向,需要后续操作才能完成这一请求
4xx——请求错误,请求含有语法错误或者无法被执行
5xx——服务器正在处理某个正确的请求时出错
URL
唯一的标识上互联网中的某一个资源
http端口默认80,https端口默认443
URL有一串复杂的查询模块(GET方法窗体),以?开头,&为分隔符,=分开参数名称和数据
最简单的框架:浏览器发出请求,服务器回应些字母显示在浏览器上
from socket import * ip_port=('127.0.0.1',35038) devicenum=5 buffer_size=1024 tcp_serve=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)#第一个参数代表基于网络通信,第二个参数代表基于tcp协议 tcp_serve.bind(ip_port) tcp_serve.listen(devicenum) while 1: conn,addr=tcp_serve.accept() print('双向链接时:',conn) print('客户端地址:',addr) msg=conn.recv(buffer_size) print('客户端发来的消息是',msg) conn.send(b'''HTTP/1.1 200 Ok\r\n\r\n masha ok ''') #中间的是响应正文
根据浏览器输入不同的路径来返回不同的结果
from socket import * ip_port=('127.0.0.1',35038) devicenum=5 buffer_size=2048 tcp_serve=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)#第一个参数代表基于网络通信,第二个参数代表基于tcp协议 tcp_serve.bind(ip_port) tcp_serve.listen(devicenum) while 1: conn,addr=tcp_serve.accept() msg=conn.recv(buffer_size) print(msg) print('将接收到的按空格进行分割',msg.split()) path=msg.split()[1].decode('utf-8') print('提取出路径',path) conn.send(b'''HTTP/1.1 200 OK \r\ncontent-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 \r\n\r\n''') #第二行charset=utf-8 用于指定编码格式 if path == '/lashi': #如果浏览器输入127.0.0.1:35038/lashi 会显示你去厕所吃饭 conn.send('你去厕所吃饭'.encode('utf-8')) elif path == '/chifan': #如果浏览器输入127.0.0.1:35038/chifan 会显示你吃屎 conn.send('你吃屎'.encode('utf-8')) else: #如果浏览器输入127.0.0.1:35038/其他 会显示无操作 conn.send('无操作'.encode('utf-8')) conn.close()
根据浏览器输入不同的路径来返回不同的结果(升级版)
from socket import * ip_port=('127.0.0.1',35038) devicenum=5 buffer_size=2048 tcp_serve=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)#第一个参数代表基于网络通信,第二个参数代表基于tcp协议 tcp_serve.bind(ip_port) tcp_serve.listen(devicenum) def lashi(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) def chifan(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) list1=[ ('/lashi',lashi), ('/chifan',chifan), ] while 1: conn,addr=tcp_serve.accept() msg=conn.recv(buffer_size) print(msg) print('将接收到的按空格进行分割',msg.split()) path=msg.split()[1].decode('utf-8') print('提取出路径',path) conn.send(b'''HTTP/1.1 200 OK \r\ncontent-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 \r\n\r\n''') #第二行charset=utf-8 用于指定编码格式 func=None for i in list1: if path == i[0]: func=i[1] break if func: #如果func不等于none jieguo=func(path) else: jieguo='无操作' conn.send(jieguo.encode('utf8')) print(jieguo) conn.close()
根据地址来返回html
里面的html
<html lang="'en"> <head> <meta charset='utf-8'> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>欢迎回家</h1> </body> </html>
主程序
from socket import * ip_port=('127.0.0.1',35038) devicenum=5 buffer_size=2048 tcp_serve=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)#第一个参数代表基于网络通信,第二个参数代表基于tcp协议 tcp_serve.bind(ip_port) tcp_serve.listen(devicenum) def lashi(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) def chifan(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) def home(path): with open('home.html','r',encoding='utf8') as f: ret=f.read() return ret list1=[ ('/lashi',lashi), ('/chifan',chifan), ('/home', home), ] while 1: conn,addr=tcp_serve.accept() msg=conn.recv(buffer_size) print(msg) print('将接收到的按空格进行分割',msg.split()) path=msg.split()[1].decode('utf-8') print('提取出路径',path) conn.send(b'''HTTP/1.1 200 OK \r\ncontent-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 \r\n\r\n''') #第二行charset=utf-8 用于指定编码格式 func=None for i in list1: if path == i[0]: func=i[1] break if func: #如果func不等于none jieguo=func(path) else: jieguo='无操作' conn.send(jieguo.encode('utf8')) print(jieguo) conn.close()
动态页面和静态界面:
静态界面指的是写死的,不变的。动态页面指的是向图片啊文本之类的都是放在数据库里,生成网页时时调用数据库资源,可以更换的。
动态页面
dthome里面的
<html lang="'en"> <head> <meta charset='utf-8'> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>当前时间是:@@time@@</h1> </body> </html>
主程序
from socket import * import time ip_port=('127.0.0.1',35038) devicenum=5 buffer_size=2048 tcp_serve=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)#第一个参数代表基于网络通信,第二个参数代表基于tcp协议 tcp_serve.bind(ip_port) tcp_serve.listen(devicenum) def lashi(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) def chifan(path): return '欢迎进入{}模块'.format(path) def home(path): with open('home.html','r',encoding='utf8') as f: ret=f.read() return ret def dthome(path): now=time.asctime() #获取当前时间 with open('time.html','r',encoding='utf8') as f: ret=f.read() #读取文件放到ret里面 return ret.replace('@@time@@',now) #将文件里面的@@time@@替换成now list1=[ ('/lashi',lashi), ('/chifan',chifan), ('/home', home), ('/dthome',dthome) ] while 1: conn,addr=tcp_serve.accept() msg=conn.recv(buffer_size) print(msg) print('将接收到的按空格进行分割',msg.split()) path=msg.split()[1].decode('utf-8') print('提取出路径',path) conn.send(b'''HTTP/1.1 200 OK \r\ncontent-type: text/html; charset=utf-8 \r\n\r\n''') #第二行charset=utf-8 用于指定编码格式 func=None for i in list1: if path == i[0]: func=i[1] break if func: #如果func不等于none jieguo=func(path) else: jieguo='无操作' conn.send(jieguo.encode('utf8')) print(jieguo) conn.close()
Django的安装:
可以输入命令行,先找到python解释器下面的scripts目录
然后输入django-admin startproject 项目名称
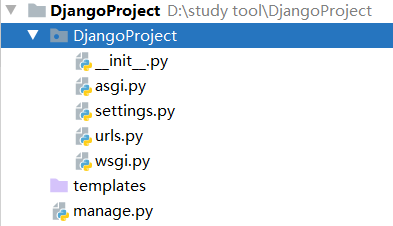
Django的启动:
找到django项目里面的manage.py
使用命令行输入python manage.py runserver ip:端口号
setting.py里面的参数行
1.BASE_DIR 是工程文件的根目录
2.DEBUG 是否开启开发模式,一般选择True
3.TEMPLATES 模板,所有html文件应该存放于的位置,如果没有我们要自己建一个
而且setting.py里面的
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')]
一定要弄好templates的路径
4.STATIC_URL:
这个是用来存放css,js等文件的,如果没有static文件夹要自己建
5.STATICFILES_DIRS需要自己加的地方
STATIC_URL = '/static/' #加在stattic_url后 STATICFILES_DIRS=[os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static')]
URL.PY里面的写法
sb.html的内容
<!DOCTYPE html> <head> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="txt/html; charset=utf-8" /> <style> .city { float: left; margin: 5px; padding: 15px; width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>克莱比的小木屋</h1> <h2>Resize this responsive page!</h2> <br> <div class="city"> <h2>London</h2> <p>London is the capital city of England.</p> <p>It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.</p> </div> <div class="city"> <h2>Paris</h2> <p>Paris is the capital and most populous city of France.</p> </div> <div class="city"> <h2>Tokyo</h2> <p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.</p> </div> </body> </html>
主程序:
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse,render def index(request): #业务 res=HttpResponse('进来的页面时index') #返回自己想要的字符串 return res def sb(request): return render(request,'sb.html') #返回自己想展示的网页 urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), #这一条是自带的 path('index/',index), #这一条是自己写的,如果输入index的界面那么跳转到index函数 path('sb',sb) #这一条是自己写的,如果输入sb的界面那么跳转到sb函数 ]
html的模板可以看https://v3.bootcss.com/,找到合适的模板,直接对着浏览器右键然后检查
接着将想要的部分缩好然后复制粘贴就行



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号