python中os模块
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39541558/article/details/79971971
1、os.name————输出当前执行平台, windows返回 'nt’,linux返回'posix'。
2、os.getcwd()————当前py文件所在的目录路径。get current working dir。
3、os.listdir(path)————列出指定path下的所有文件和文件夹,以list形式返回。
4、os.makedirs(path)————创建指定path的目录路径,可以增加多层目录。
5、os.mkdir(path)————创建指定path的目录路径,单层。
6、os.rmdir(path)————删除指定path的目录。
7、os.remove(path)————删除指定文件。
8、os.chdir(path)————改变当前执行目录
9、os.path.exists(path)————检查指定path是否存在,存在返回True,失败返回False
10、os.path.join(path,*paths)————拼接2个或者更多的目录
11、os.path.split(path)————以最后一个'/'分割path成为两部分,以元祖形式返回。path:D:\test\test1\test2 =>('D:\\test\\test1', test2)
12、os.path.abspath(path)————获得绝对路径
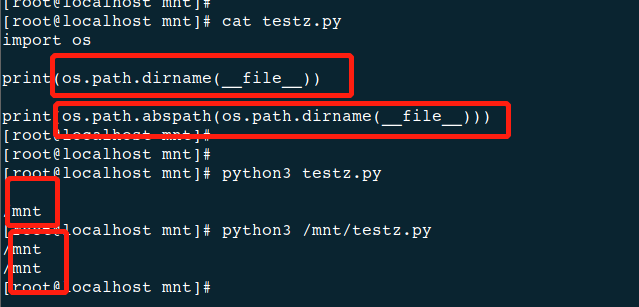
13、os.path.basename(path)————返回tail
14、os.path.dirname(path)————返回文件路径相对路径,head
15、os.path.getmtine(filename)————last modification time,最后修改时间
16、os.path.getctime(filename)————the metadata change time,元数据(访问权限等等)更改时间
17、os.path.getatime(filename)————the last access time ,最后访问时间
18、os.path.isfile(path)————判断path是不是文件,是True, 否则False
19、os.path.isdir(path)————判断path是不是目录,是True, 否则False
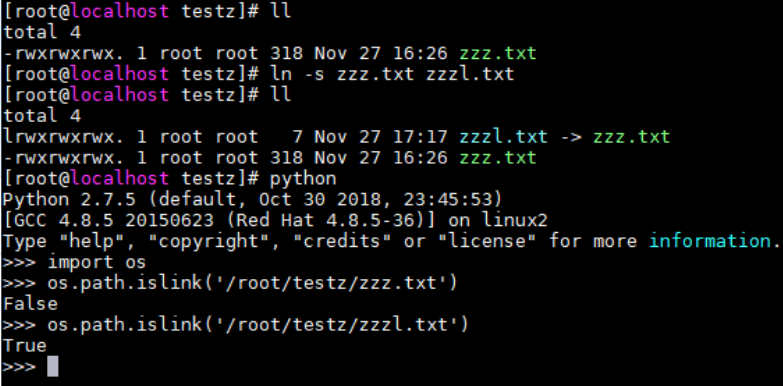
20、os.path.islink(path)————判断path是不是link的,是True, 否则False
21、os.path.ismount(path)—————判断是否是mount点,,是True, 否则False
22、os.path.getsize(filename)————文件大小(bytes)。不准确:数字占一个字节,英文占一个字节,标点占一个字节,一个汉字占三个字节。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号