揭开面纱-ThreadGroup
开门见山
ThreadGroup在实际开发中很少用到,不过由于它跟Thread的关系比较密切,所以还是了解下为妙,揭开ThreadGroup的面纱是基于JDK1.8。通过阅读注释及相关文章,可以知道ThreadGroup的结构如下:
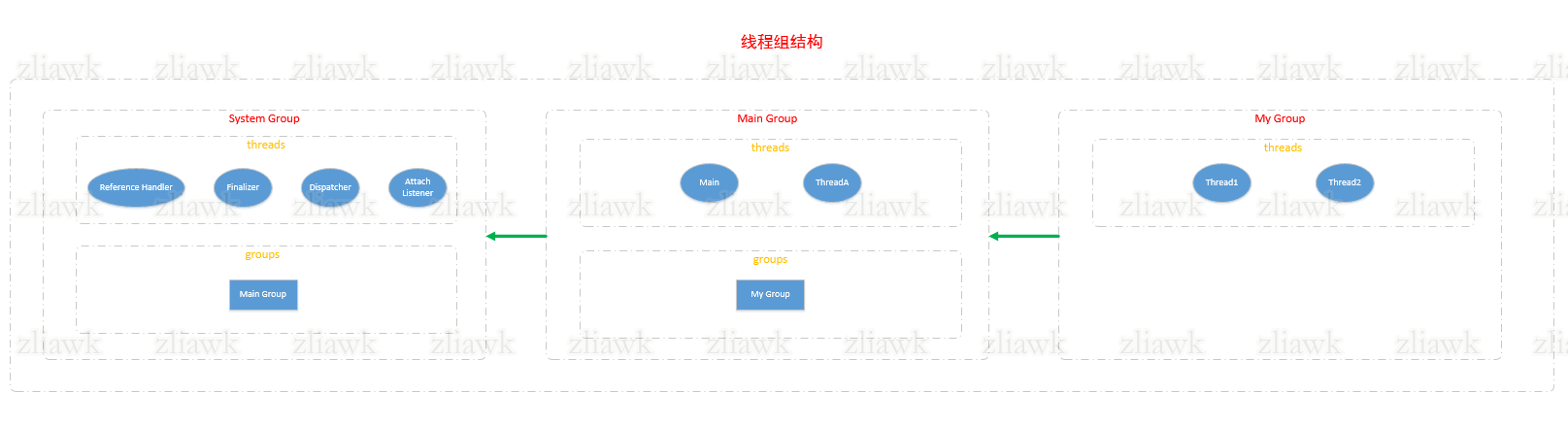
除了初始线程组(JVM所属)以外,每个线程组都有一个父线程组及子线程组,父线程组中有个成员变量(groups)来记录它所有的子线程组,所以线程组之间的关系被看作是一棵树。线程组下有多个线程,我们可以将线程组理解成是对一组线程进行操作。
数据结构
public class ThreadGroup implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
//父线程组
private final ThreadGroup parent;
//线程组的名称
String name;
//线程组的最大优先级,该优先级不能大于父线程组的优先级
int maxPriority;
//线程组是否已经销毁(清除)
boolean destroyed;
//线程组是否是守护线程组
boolean daemon;
//未启动的线程个数,即未调用start方法的线程个数
int nUnstartedThreads = 0;
//已启动的线程个数,即已调用start方法的线程个数
int nthreads;
//已启动的线程个数,该数组会通过创建新数组拷贝源数组的方式进行扩容,新数组的容量是源数据的2倍
Thread threads[];
//子线程组的个数
int ngroups;
//存储所有子线程组
ThreadGroup groups[];
}
构造函数
/**
* 构造线程组,该构造方式通常是创建系统级别的线程组,如由底层C代码来构造初始线程组
*/
private ThreadGroup() {
this.name = "system";
this.maxPriority = Thread.MAX_PRIORITY;
this.parent = null;
}
/**
* 构造线程组
* @param name 线程组的名称
*/
public ThreadGroup(String name) {
this(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), name);
}
/**
* 构造线程组并指定父线程组
* @param parant 父线程组
* @param name 线程组的名称
*/
public ThreadGroup(ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this(checkParentAccess(parent), parent, name);
}
/**
* 构造线程组并指定父线程组
* @param unused 未使用
* @param parant 父线程组
* @param name 线程组的名称
*/
private ThreadGroup(Void unused, ThreadGroup parent, String name) {
this.name = name;
this.maxPriority = parent.maxPriority;
this.daemon = parent.daemon;
this.vmAllowSuspension = parent.vmAllowSuspension;
this.parent = parent;
parent.add(this); //指定父线程组后,要将其添加到父线程组所属的子线程组数组中,维护其关系
}
简单方法
/**
* 获取线程组的名称
* @return 线程组的名称
*/
public final String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 获取线程组的父线程组
*/
public final ThreadGroup getParent() {
if (parent != null)
parent.checkAccess();
return parent;
}
/**
* 获取线程组的最大优先级
* @return 线程组的最大优先级
*/
public final int getMaxPriority() {
return maxPriority;
}
/**
* 线程组是否是守护线程组
* 若当前线程组是守护线程组,则当线程组中的线程都终止了或其子线程组都终止了则会自动调用destroy方法
* 实际上在线程终止底层后调用Thread#exit方法,通过该方法来终止守护线程组
* @return 是否是守护线程组
*/
public final boolean isDaemon() {
return daemon;
}
/**
* 线程组是否已销毁
* @return 是否已销毁
*/
public synchronized boolean isDestroyed() {
return destroyed;
}
/**
* 设置线程组是否是守护线程组
* true-属于守护线程组
* @param daemon 标志
*/
public final void setDaemon(boolean daemon) {
checkAccess();
this.daemon = daemon;
}
/**
* 设置线程组的最大优先级
* 线程的优先级与线程组的最大优先级互不影响,也就是说即使线程的优先级比线程组的最大优先级还高也不影响
* 当前线程组的最大优先级不能超过父线程组的最大优先级
* @param pri 最大优先级
*/
public final void setMaxPriority(int pri) {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
checkAccess();
if (pri < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || pri > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
return;
}
maxPriority = (parent != null) ? Math.min(pri, parent.maxPriority) : pri; //当前线程组的最大优先级不能超过父线程组的最大优先级
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
groupsSnapshot[i].setMaxPriority(pri); //递归更改其子线程组的最大优先级
}
}
/**
* 当前线程组是否与指定线程组是同一个对象或是指定线程组的父线程组
* @param g 指定线程组
* @return 结果值
*/
public final boolean parentOf(ThreadGroup g) {
for (; g != null ; g = g.parent) {
if (g == this) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 获取当前线程组的活跃线程个数
* 注意:线程组中还有子线程组,所以计算时也会包含子线程组
* 该结果只是一个估算值,因为线程数一直在动态变化着,同时JVM也会有一些线程,所以可能会影响该计数结果
* 该方法主要用来调试与监控
* @return 线程组的活跃线程个数
*/
public int activeCount() {
int result;
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return 0;
}
result = nthreads;
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
result += groupsSnapshot[i].activeCount();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 将当前线程组及其子线程组的活跃线程拷贝到指定数组中
* 要严格确保指定数组的大小大于活跃线程的个数
* @param tarray 指定数组
* @return 线程组的活跃线程个数
*/
public int enumerate(Thread list[]) {
checkAccess();
return enumerate(list, 0, true);
}
/**
* 将当前线程组的活跃线程拷贝到指定数组中
* 通过recurse参数来决定是否拷贝子线程组
* 要严格确保指定数组的大小大于活跃线程的个数
* @param tarray 指定数组
* @param recurse 决定是否拷贝子线程组
* @return 线程组的活跃线程个数
*/
public int enumerate(Thread list[], boolean recurse) {
checkAccess();
return enumerate(list, 0, recurse);
}
/**
* 将当前线程组的活跃线程拷贝到指定数组中
* 通过recurse参数来决定是否拷贝子线程组
* 要严格确保指定数组的大小大于活跃线程的个数
* @param tarray 指定数组
* @param n 从指定数组的指定起始索引开始添加
* @param recurse 决定是否拷贝子线程组
* @return 线程组的活跃线程个数
*/
private int enumerate(Thread list[], int n, boolean recurse) {
int ngroupsSnapshot = 0;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot = null;
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return 0;
}
int nt = nthreads;
if (nt > list.length - n) { //若指定数组的长度小于活跃线程的个数,则超过的活跃线程将被忽略
nt = list.length - n;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nt; i++) { //
if (threads[i].isAlive()) {
list[n++] = threads[i];
}
}
if (recurse) { // 是否加入子线程组的活跃线程
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
}
if (recurse) {
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
n = groupsSnapshot[i].enumerate(list, n, true);
}
}
return n;
}
/**
* 获取当前线程组的子线程组个数
* 注意:当前线程组中还有子线程组,所以计算时也会包含子线程组
* 该结果只是一个估算值,因为线程数一直在动态变化着
* 该方法主要用来调试与监控
* @return 线程组的活跃线程个数
*/
public int activeGroupCount() {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return 0;
}
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
int n = ngroupsSnapshot;
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
n += groupsSnapshot[i].activeGroupCount();
}
return n;
}
/**
* 将当前线程组及其子线程组的子线程组拷贝到指定数组中
* 要严格确保指定数组的大小大于子线程组的个数
* @param tarray 指定数组
* @return 线程组的子线程组个数
*/
public int enumerate(ThreadGroup list[]) {
checkAccess();
return enumerate(list, 0, true);
}
////////////////其他enumerate方法就不做展示了,都是类似的/////////////////////
/**
* 终止当前线程组的所有线程,包括其子线程下的所有线程
* 由于Thread#stop方法已废弃,故而该方法也是没啥用的
*/
@Deprecated
public final void stop() {
if (stopOrSuspend(false))
Thread.currentThread().stop();
}
/**
* 递归挂起或终止当前线程组的所有线程,除了当前线程之外(会在调用方挂起或终止当前线程)
* 同时也会挂起或终止其子线程组的所有线程
* 该方法通过返回值来判断当前线程是否存在于当前线程组或子线程组中,若存在则在该方法返回后也会对当前线程进行挂机或终止,若不存在则不会进行任何操作
* @param suspend true表示挂起 false表示终止
* @return 当前线程是否存在于当前线程组或子线程组中
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private boolean stopOrSuspend(boolean suspend) {
boolean suicide = false;
Thread us = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot = null;
synchronized (this) {
checkAccess();
for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
if (threads[i]==us)
suicide = true;
else if (suspend)
threads[i].suspend();
else
threads[i].stop();
}
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++)
suicide = groupsSnapshot[i].stopOrSuspend(suspend) || suicide;
return suicide;
}
/**
* 中断当前线程组的所有线程,包括子线程组的所有线程
*/
public final void interrupt() {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
checkAccess();
for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
threads[i].interrupt();
}
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
groupsSnapshot[i].interrupt();
}
}
/**
* 销毁当前线程组及其子线程组
*/
public final void destroy() {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
checkAccess();
if (destroyed || (nthreads > 0)) { //如果还有运行中的线程则不允许销毁
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
if (parent != null) { //除了初始线程以外,线程组在销毁后需要清理资源
destroyed = true;
ngroups = 0;
groups = null;
nthreads = 0;
threads = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i += 1) { //销毁子线程组
groupsSnapshot[i].destroy();
}
if (parent != null) { //从父线程组中移除当前线程组,解除关系
parent.remove(this);
}
}
/**
* 从当前线程组的子线程组中移除指定线程组
* 若当前线程组是守护线程组,且不存在运行中及未启动的线程,且不不存在子线程组,相当于要移除的线程组是最后一个线程组,则销毁自身
* @param g 指定线程组
*/
private void remove(ThreadGroup g) {
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroups ; i++) {
if (groups[i] == g) {
ngroups -= 1;
System.arraycopy(groups, i + 1, groups, i, ngroups - i); //在子线程组中移除指定线程组
groups[ngroups] = null; //手动置为null以便垃圾回收器能回收它
break;
}
}
if (nthreads == 0) { //这里我唯一想到的是可能有其他线程使用了当前对象锁
notifyAll();
}
if (daemon && (nthreads == 0) && (nUnstartedThreads == 0) && (ngroups == 0)) //当前线程组是守护线程组,且不存在运行中及未启动的线程,且不存在子线程组
{
destroy();
}
}
}
/**
* 对未启动的线程进行计数
* 未启动的线程不会添加到线程组中,这样即使从未启动过的线程也会被收集,但是必须对它们进行计数,以便不会破坏守护线程组.
*/
void addUnstarted() {
synchronized(this) {
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
nUnstartedThreads++;
}
}
/**
* 添加已启动的线程到线程组中
* 该方法可能会被JVM调用,因为有初始线程组要添加已启动的系统线程
*/
void add(Thread t) {
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
if (threads == null) {
threads = new Thread[4];
} else if (nthreads == threads.length) {
threads = Arrays.copyOf(threads, nthreads * 2);
}
threads[nthreads] = t; //添加已启动的线程
nthreads++; //计数已启动的线程个数
//因为只有在线程启动后才会调用该方法,故而未启动的线程个数应该减去1
nUnstartedThreads--;
}
}
/**
* 指定线程启动失败后会调用此方法
* 线程启动失败后,应该对未启动的线程个数进行计数
* @param t 指定线程
*/
void threadStartFailed(Thread t) {
synchronized(this) {
remove(t);
nUnstartedThreads++;
}
}
/**
* 从当前线程组中移除指定线程
* @param t 指定线程
*/
private void remove(Thread t) {
synchronized (this) {
if (destroyed) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
if (threads[i] == t) {
System.arraycopy(threads, i + 1, threads, i, --nthreads - i);
threads[nthreads] = null;
break;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 指定线程终止后调用此方法
* @param t 指定线程
*/
void threadTerminated(Thread t) {
synchronized (this) {
remove(t);
if (nthreads == 0) { //这里我唯一想到的是可能有其他线程使用了当前对象锁
notifyAll();
}
if (daemon && (nthreads == 0) && (nUnstartedThreads == 0) && (ngroups == 0)) //当前线程组是守护线程组,且不存在运行中及未启动的线程,且不存在子线程组
{
destroy();
}
}
}
/**
* 打印线程组的信息到标准输出,包括活跃的线程及其子线程组的信息
*/
public void list() {
list(System.out, 0);
}
/**
* 打印线程组的信息到标准输出,包括活跃的线程及其子线程组的信息
*/
void list(PrintStream out, int indent) {
int ngroupsSnapshot;
ThreadGroup[] groupsSnapshot;
synchronized (this) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < indent ; j++) {
out.print(" ");
}
out.println(this);
indent += 4;
for (int i = 0 ; i < nthreads ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < indent ; j++) {
out.print(" ");
}
out.println(threads[i]);
}
ngroupsSnapshot = ngroups;
if (groups != null) {
groupsSnapshot = Arrays.copyOf(groups, ngroupsSnapshot);
} else {
groupsSnapshot = null;
}
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < ngroupsSnapshot ; i++) {
groupsSnapshot[i].list(out, indent);
}
}
/**
* 当线程未设置自定义异常处理器,则当线程发生异常时,会调用该方法
* @param t 当前发生异常的线程
* @param e 异常信息
*/
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
if (parent != null) {
parent.uncaughtException(t, e); //若线程未设置自定义异常处理器,则使用父线程组的异常
} else {
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh = Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler();
if (ueh != null) { //线程是否设置了默认的异常处理器
ueh.uncaughtException(t, e);
} else if (!(e instanceof ThreadDeath)) {
System.err.print("Exception in thread \"" + t.getName() + "\" ");
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
}
}
/**
* 打印信息
* @return 信息
*/
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + getName() + ",maxpri=" + maxPriority + "]";
}
总结
-
除了初始线程组以外,每个线程组都有一个父线程组及子线程组,这样子的关系被看作是一棵树。
-
若线程组是守护线程组,则在满足一定的条件下会自动调用销毁方法。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号