torch.nn.KLDivLoss
KL散度
KL散度,又叫相对熵,用于衡量两个分布之间的距离。设$p(x),q(x)$是关于随机变量$x$的两个分布,则$p$相对于$q$的KL散度为:

- 信息论中,熵$H(P)$表示对来自$P$的随机变量进行编码所需的最小字节数,
- 而交叉熵$H(P,Q)$则表示使用基于$Q$的编码对来自$P$的变量进行编码所需的字节数,它也可以作为损失函数,即交叉熵损失函数,

- 因此,KL散度可以认为是使用基于$Q$的编码对来自$P$的变量进行编码所需的“额外”字节数;显然,额外字节数必然非负,当且仅当$P=Q$时,额外字节数为0,
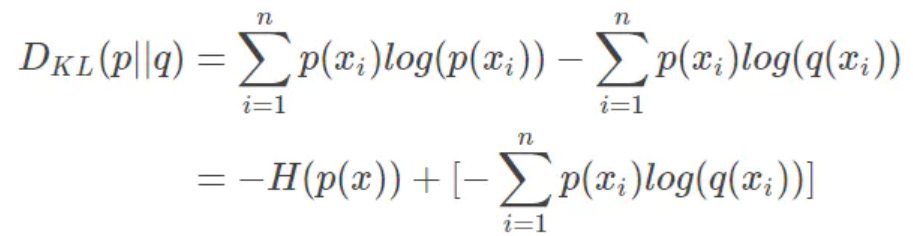 等式的前一部分恰巧就是$P$的熵,等式的后一部分,就是交叉熵,
等式的前一部分恰巧就是$P$的熵,等式的后一部分,就是交叉熵,
CLASS torch.nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', log_target=False)
The Kullback-Leibler divergence loss.
For tensors of the same shape $y_{\text{pred}},\ y_{\text{true}}$,where $y_{\text{pred}}$ is the input and $y_{\text{true}}$ is the target,we define the pointwise KL-divergence as
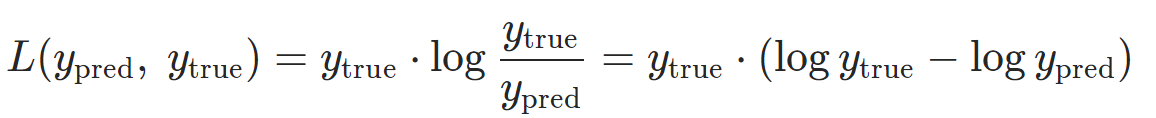
To avoid underflow(下溢) issues when computing this quantity, this loss expects the argument input in the log-space. The argument target may also be provided in the log-space if log_target= True.
To summarise, this function is roughly equivalent to computing
if not log_target: # default
loss_pointwise = target * (target.log() - input)
else:
loss_pointwise = target.exp() * (target - input)
and then reducing this result depending on the argument reduction as
if reduction == "mean": # default
loss = loss_pointwise.mean()
elif reduction == "batchmean": # mathematically correct
loss = loss_pointwise.sum() / input.size(0)
elif reduction == "sum":
loss = loss_pointwise.sum()
else: # reduction == "none"
loss = loss_pointwise
reduction= “mean” doesn’t return the true KL divergence value, please use reduction= “batchmean” which aligns with the mathematical definition. In a future release, “mean” will be changed to be the same as “batchmean”.
参数:
- size_average,reduce Deprecated (see
reduction) -
reduction (string, optional) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output. Default: “mean”
-
log_target (bool, optional) – Specifies whether target is the log space. Default: False
Shape:
- Input: (*), where * means any number of dimensions.
- Target: (*), same shape as the input.
- Output:
- scalar by default.
- If reduction is ‘none’, then (*), same shape as the input.
kl_loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean") # input should be a distribution in the log space input = F.log_softmax(torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)) # Sample a batch of distributions. Usually this would come from the dataset target = F.softmax(torch.rand(3, 5)) output = kl_loss(input, target) kl_loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean", log_target=True) log_target = F.log_softmax(torch.rand(3, 5)) output = kl_loss(input, log_target)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号