01Fuzzing学习之Fuzzer性能提升
Fuzzer性能提升
前面已经实现了一个简单的Fuzzer,这里我们将关注如何提高Fuzzer的性能。
具体来说,我们将该进前面实现的Fuzzer,让它能够更快的执行模糊测试。
耗时分析及优化
前面我们实用python编写的Fuzzer,所以可以使用python的cProfile模块来测试来查看程序中耗时的地方。
对前面的代码进行了一些小的改动,其他代码参考前面的内容。
def exif(counter,data):
command = "exif mutated.jpg -verbose"
out, returncode = run("sh -c " + quote(command), withexitstatus=1)
if b"Segmentation" in out:
with open("crashes/crash.{}.jpg".format(str(counter)), "ab+") as w:
w.write(data)
print("Segmentation")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: JPEGfuzz.py <valid_jpg>")
else:
filename = sys.argv[1]
data = get_bytes(filename)
for i in range(1000):
select_mutation = random.randint(0, 1) # 随机选择变异方法
select_mutation = 0
if select_mutation == 0:
mutated_data = bit_flip(data)
else:
mutated_data = magic(data)
create_new(mutated_data)
exif(i+1, mutated_data)
具体命令:python -m cProfile -s cumtime fuzzer.py Canon_40D.jpg
注:添加这个cProfile工具可能会降低性能,但是对于本文中使用的迭代次数,其影响不大。
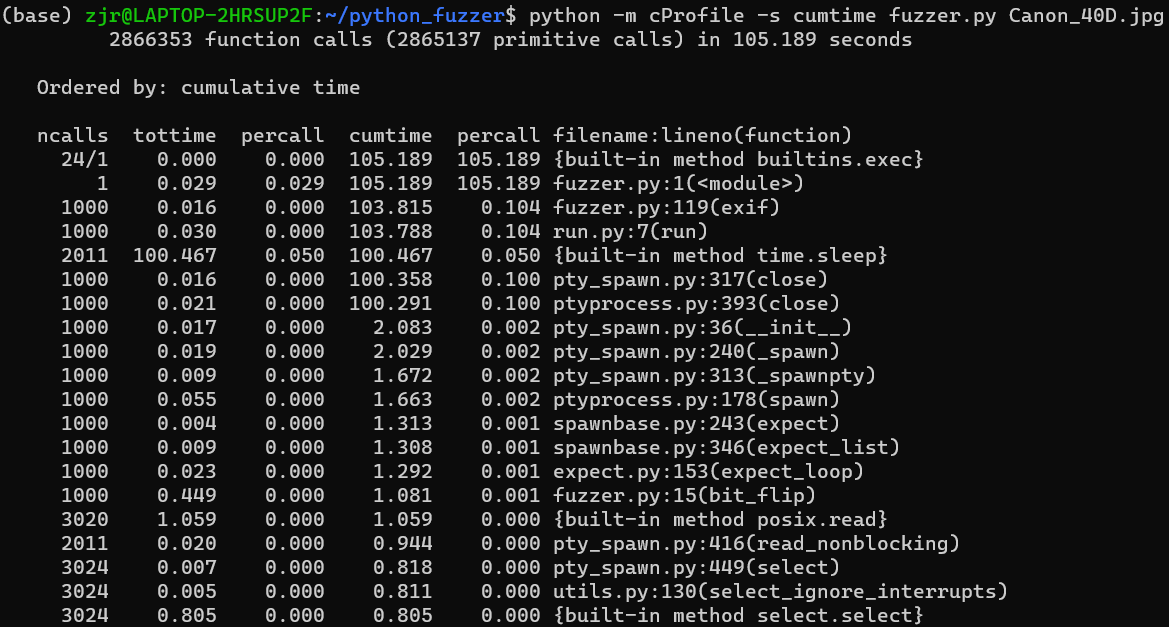
可以看到我们写的代码中最耗时的是fuzzer.py:119(exif)部分。
优化
接下来的时间花费也都与该函数直接相关,而其中大量的时间又是因为pexpect模块中的基本库pty的使用。所以接下来我们用subprocess模块中的Popen对exit()函数进行重写,看看性能能提升多少。
from subprocess import Popen, PIPE
def exif(counter,data):
p = Popen(["exif", "mutated.jpg", "-verbose"], stdout=PIPE, stderr=PIPE)
(out,err) = p.communicate()
if p.returncode == -11:
with open(f"crashes2/crash.{str(counter)}.jpg", "ab+") as f:
f.write(data)
print("Segfault!")
需要导入subprocess模块才能使用,上面给出了改进部分代码。查看运行耗时情况:
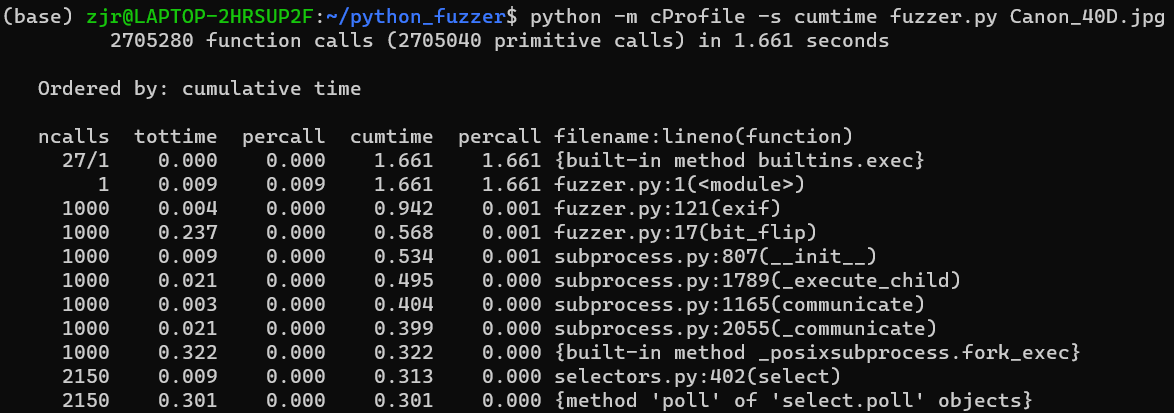
性能有了显著的提升。重写 exit()函数的Fuzzer用1.6秒钟就完成了同样的工作!而旧的Fuzzer需要105秒。
进一步优化
接下来将Fuzzing的次数调整为50000,查看优化后的Fuzzer耗时情况。
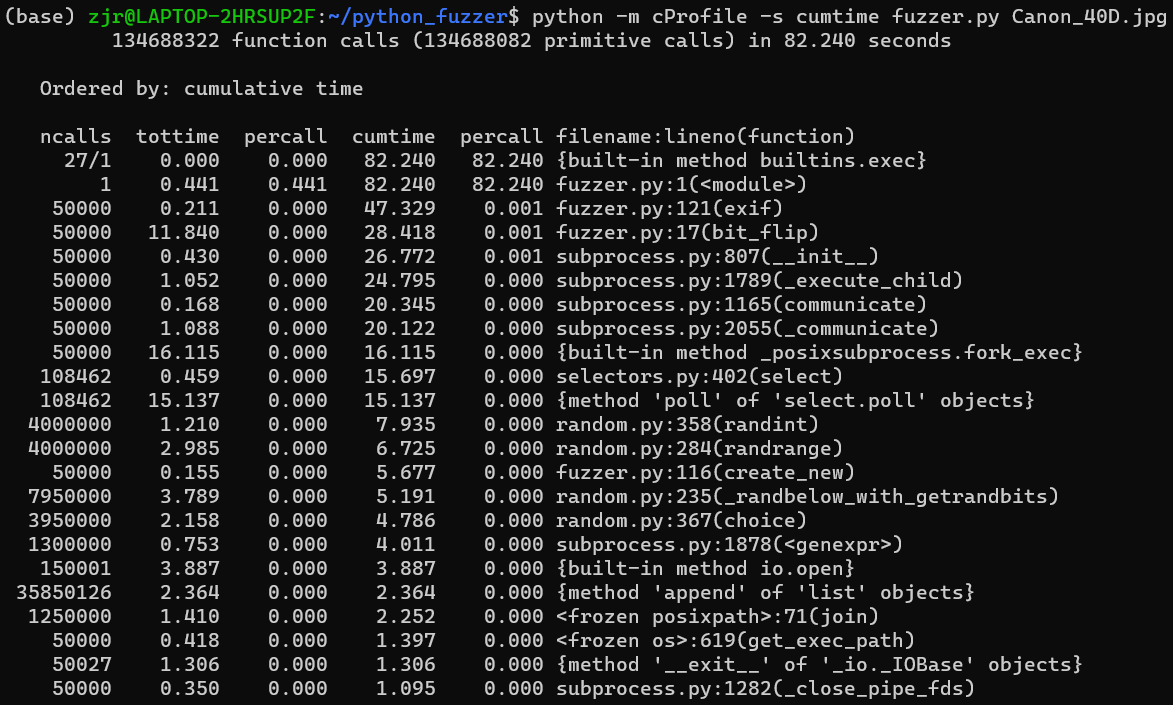
大部分时间仍然是消耗在 exif()函数上。紧接着 bit_flip()函数也比较耗时,这是比特位翻转函数用于生成变异数据。
对这个函数进行重写:
def bit_flip(data):
length = len(data) - 4
num_of_flips = int(length * .01)
picked_indexes = []
flip_array = [1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128]
counter = 0
while counter < num_of_flips:
picked_index = random.choice(range(0,length))
if picked_index not in picked_indexes: # 防止翻转位置相同
picked_indexes.append(picked_index)
counter += 1
for x in picked_indexes:
mask = random.choice(flip_array)
data[x] = data[x] ^ mask # 通过异或运算进行位翻转,效率提升最快的改动
return data
再次测试:
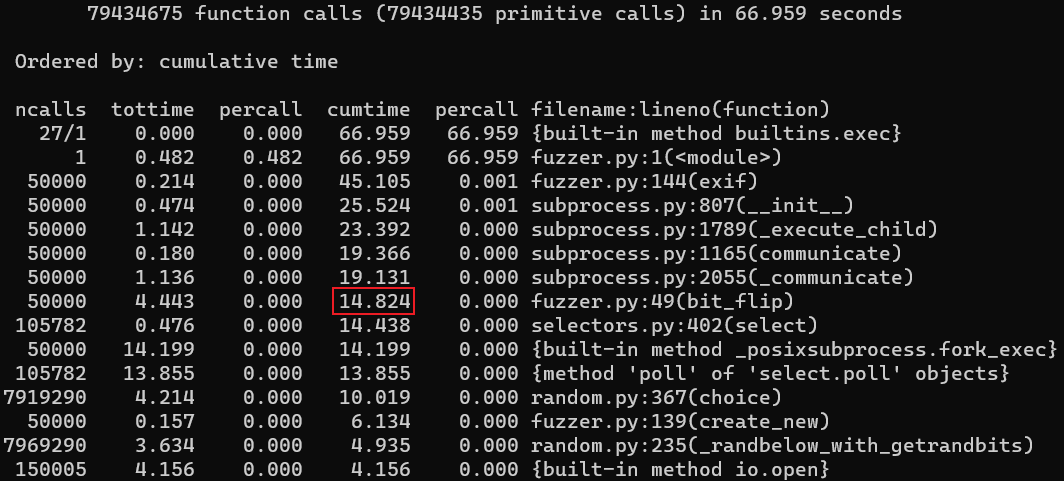
可以看到,效率得到进一步提高。
目前暂时还没有用到多线程或多进程,现在有了使用python写的Fuzzer作为基准,接下来使用C++编写以进一步提高Fuzzer的性能。
C++实现
具体代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <chrono>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 以二进制的方式读取文件,并用“字符串”存储
std::string get_bytes(std::string filename)
{
std::ifstream fin(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (fin.is_open())
{
fin.seekg(0, std::ios::end);
std::string data;
data.resize(fin.tellg());
fin.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
fin.read(&data[0], data.size());
return data;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to open " << filename << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
// 位翻转
std::string bit_flip(std::string data)
{
int size = (data.length() - 4);
int num_of_flips = (int)(size * 0.01);
// 随机选取1%的字节翻转位置
std::vector<int> picked_indexes;
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_flips; i++)
{
int picked_index = rand() % size;
picked_indexes.push_back(picked_index);
}
for (int i = 0; i < picked_indexes.size(); ++i)
{
int index = picked_indexes[i];
char current = data.at(index);
int decimal = ((int)current & 0xff); // 将字符转换为整数类型,并使用位与操作符&与0xff进行按位与运算,目的是确保只留下低8位的值,将高位清零。这是为了确保操作的是无符号字节值。
int bit_to_flip = rand() % 8; // 生成一个范围在0到7之间的随机数,表示要翻转的位的位置。
decimal ^= 1 << bit_to_flip; // 通过将1左移bit_to_flip位,然后与decimal进行异或运算,可以将对应位的值取反。
decimal &= 0xff; // 再次使用位与操作符&与0xff进行按位与运算,确保结果仍然是一个有效的无符号字节值。
data[index] = (char)decimal;
}
return data;
}
// 创建变异文件
void create_new(std::string mutated)
{
std::ofstream fout("mutated.jpg", std::ios::binary);
if (fout.is_open())
{
fout.seekp(0, std::ios::beg);
fout.write(&mutated[0], mutated.size());
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to create mutated.jpg" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
// 通过使用popen函数执行给定的命令,并逐行读取命令的输出结果,并最终返回命令的输出结果。
std::string get_output(std::string cmd)
{
std::string output;
FILE *stream;
char buffer[256];
stream = popen(cmd.c_str(), "r");
if (stream)
{
while (!feof(stream))
if (fgets(buffer, 256, stream) != NULL)
output.append(buffer);
pclose(stream);
}
return output;
}
// 处理exif输出结果,出现crash的时候保存变异文件
void exif(std::string mutated, int counter)
{
std::string command = "exif mutated.jpg -verbose 2>&1";
std::string output = get_output(command);
std::string segfault = "Segmentation";
std::string floating_point = "Floating";
std::size_t pos1 = output.find(segfault);
std::size_t pos2 = output.find(floating_point);
if (pos1 != -1)
{
// std::cout << "Segfault!" << endl;
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "/home/zjr/c++_Fuzzer/crashs/crash." << counter << ".jpg";
std::string filename = oss.str();
std::ofstream fout(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (fout.is_open())
{
fout.seekp(0, std::ios::beg);
fout.write(&mutated[0], mutated.size());
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to create " << filename << ".jpg" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
else if (pos2 != -1)
{
// std::cout << "Floating Point!" << endl;
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "/home/zjr/c++_Fuzzer/crashs/crash." << counter << ".jpg";
std::string filename = oss.str();
std::ofstream fout(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (fout.is_open())
{
fout.seekp(0, std::ios::beg);
fout.write(&mutated[0], mutated.size());
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to create " << filename << ".jpg" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
}
// 使用vector存储magic值
std::vector<std::string> vector_gen()
{
std::vector<std::string> magic;
using namespace std::string_literals;
magic.push_back("xff");
magic.push_back("x7f");
magic.push_back("x00"s);
magic.push_back("xffxff");
magic.push_back("x7fxff");
magic.push_back("x00x00"s);
magic.push_back("xffxffxffxff");
magic.push_back("x80x00x00x00"s);
magic.push_back("x40x00x00x00"s);
magic.push_back("x7fxffxffxff");
return magic;
}
// 随机选取magic值进行替换
std::string magic(std::string data, std::vector<std::string> magic)
{
int vector_size = magic.size();
int picked_magic_index = rand() % vector_size;
std::string picked_magic = magic[picked_magic_index];
int size = (data.length() - 4);
int picked_data_index = rand() % size;
data.replace(picked_data_index, magic[picked_magic_index].length(), magic[picked_magic_index]);
return data;
}
// 用于选取变异方法
int func_pick()
{
int result = rand() % 2;
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if (argc < 3)
{
std::cout << "Usage: ./fuzzer <valid jpeg> <number_of_fuzzing_iterations>n" << endl;
std::cout << "Usage: ./fuzzer Canon_40D.jpg 10000n" << endl;
return 1;
}
// 开始时间
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
// 初始化随机种子
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
// 生成magic值
std::vector<std::string> magic_vector = vector_gen();
std::string filename = argv[1];
int iterations = atoi(argv[2]);
int counter = 0;
while (counter < iterations)
{
std::string data = get_bytes(filename);
int function = func_pick();
function = 1;
if (function == 0)
{
std::string mutated = magic(data, magic_vector);
create_new(mutated);
exif(mutated, counter);
counter++;
}
else
{
std::string mutated = bit_flip(data);
create_new(mutated);
exif(mutated, counter);
counter++;
}
}
// 停止时间
auto stop = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(stop - start);
std::cout << "Execution Time: " << duration.count() << "msn" << endl;
return 0;
}
进行50000次测试,总耗时70秒左右与之前改进的python版本fuzzer差不多,但是C++能够发现更多的crash,具体原因未知。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号