MySQL root密码正确,却无法从本地登录MySQL
本文有许多废话,可以直接跳到分割线
补上周的博客,这个是最近遇到的坑,mac brew安装的mysql5.6 刚开始是正常的 但是 某天 我mysql root突然登录不上了 我觉得密码应该是正确的
报错图忘记截了(以后要记得遇到问题截图 写博客用) 报错内容如下(注意报错信息 )
1 ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES);
好的,登录不上 咋办 改root密码呗,首先要跳过密码认证skip-grant-tables 那么要找到mysql的配置文件,然后我发现mac安装mysql 在etc下根本没有my.cnf 后来发现在下列目录中有个默认配置文件,进去看了里面的内容,感觉配置项有点少 我就自建了my.cnf文件,网上找了配置复制下来(这个默认的也能用,不过我没试过,如果要用就拷到etc下改为my.cnf 然后配置一下就好了)
/usr/local/opt/mysql\@5.6/support-files/my-default.cnf
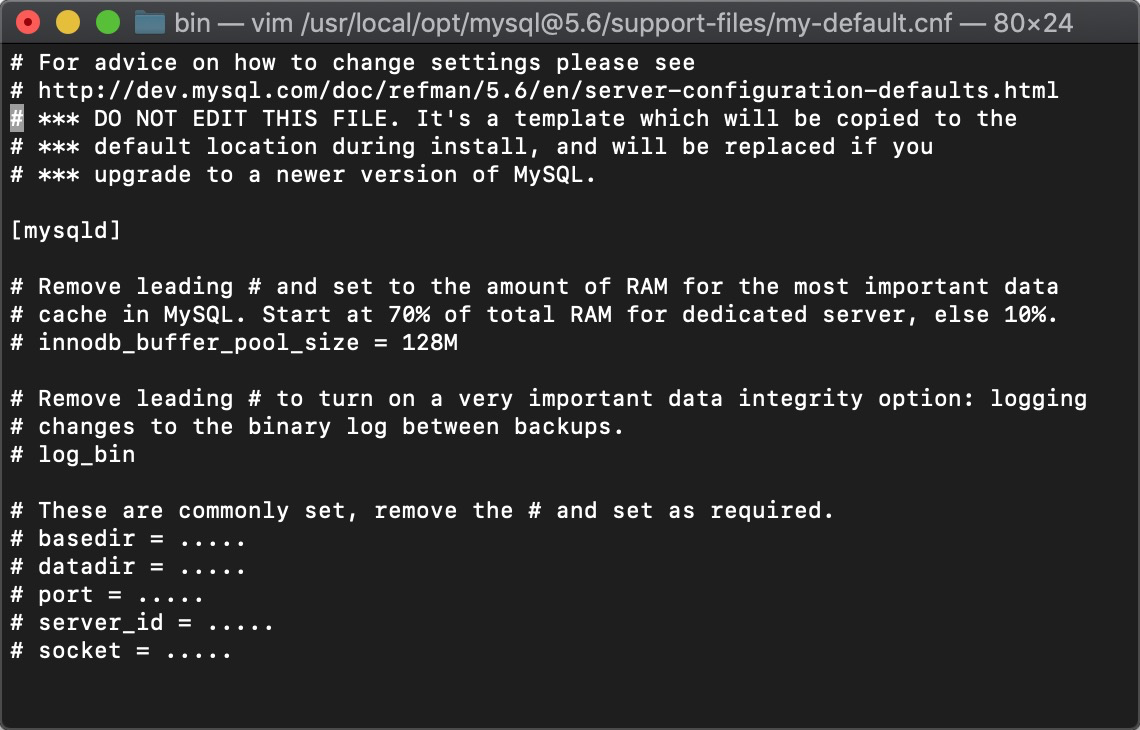
网上找的 my.cnf的配置 在etc下新建my.cnf然后复制进去就行了
# Example MySQL config file for medium systems. # # This is for a system with little memory (32M - 64M) where MySQL plays # an important part, or systems up to 128M where MySQL is used together with # other programs (such as a web server) # # MySQL programs look for option files in a set of # locations which depend on the deployment platform. # You can copy this option file to one of those # locations. For information about these locations, see: # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/option-files.html # # In this file, you can use all long options that a program supports. # If you want to know which options a program supports, run the program # with the "--help" option. # The following options will be passed to all MySQL clients [client] default-character-set=utf8 #password = your_password port = 3306 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock # Here follows entries for some specific programs # The MySQL server [mysqld]
# skip character-set-server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8 port = 3306 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock skip-external-locking key_buffer_size = 16M max_allowed_packet = 1M table_open_cache = 64 sort_buffer_size = 512K net_buffer_length = 8K read_buffer_size = 256K read_rnd_buffer_size = 512K myisam_sort_buffer_size = 8M character-set-server=utf8 init_connect='SET NAMES utf8' # Don't listen on a TCP/IP port at all. This can be a security enhancement, # if all processes that need to connect to mysqld run on the same host. # All interaction with mysqld must be made via Unix sockets or named pipes. # Note that using this option without enabling named pipes on Windows # (via the "enable-named-pipe" option) will render mysqld useless! # #skip-networking # Replication Master Server (default) # binary logging is required for replication l og-bin=mysql-bin # binary logging format - mixed recommended binlog_format=mixed # required unique id between 1 and 2^32 - 1 # defaults to 1 if master-host is not set # but will not function as a master if omitted server-id = 1 # Replication Slave (comment out master section to use this) # # To configure this host as a replication slave, you can choose between # two methods : # # 1) Use the CHANGE MASTER TO command (fully described in our manual) - # the syntax is: # # CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST=<host>, MASTER_PORT=<port>, # MASTER_USER=<user>, MASTER_PASSWORD=<password> ; # # where you replace <host>, <user>, <password> by quoted strings and # <port> by the master's port number (3306 by default). # # Example: # # CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='125.564.12.1', MASTER_PORT=3306, # MASTER_USER='joe', MASTER_PASSWORD='secret'; # #OR # # 2) Set the variables below. However, in case you choose this method, then # start replication for the first time (even unsuccessfully, for example # if you mistyped the password in master-password and the slave fails to # connect), the slave will create a master.info file, and any later # change in this file to the variables' values below will be ignored and # overridden by the content of the master.info file, unless you shutdown # the slave server, delete master.info and restart the slaver server. # For that reason, you may want to leave the lines below untouched # (commented) and instead use CHANGE MASTER TO (see above) # # required unique id between 2 and 2^32 - 1 # (and different from the master) # defaults to 2 if master-host is set # but will not function as a slave if omitted # server-id = 2 # # The replication master for this slave - required #master-host = <hostname> # # The username the slave will use for authentication when connecting # to the master - required #master-user = <username> # # The password the slave will authenticate with when connecting to # the master - required #master-password = <password> # # The port the master is listening on. # optional - defaults to 3306 #master-port = <port> # # binary logging - not required for slaves, but recommended #log-bin=mysql-bin # Uncomment the following if you are using InnoDB tables #innodb_data_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/data #innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:10M:autoextend #innodb_log_group_home_dir = /usr/local/mysql/data # You can set .._buffer_pool_size up to 50 - 80 % # of RAM but beware of setting memory usage too high #innodb_buffer_pool_size = 16M #innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 2M # Set .._log_file_size to 25 % of buffer pool size #innodb_log_file_size = 5M #innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M #innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1 #innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 50 [mysqldump] quick max_allowed_packet = 16M [mysql] no-auto-rehash # Remove the next comment character if you are not familiar with SQL #safe-updates default-character-set=utf8 [myisamchk] key_buffer_size = 20M sort_buffer_size = 20M read_buffer = 2M write_buffer = 2M [mysqlhotcopy] interactive-timeout
然后在[mysqld]下 加入划红线的 (不用了就#号注释掉)
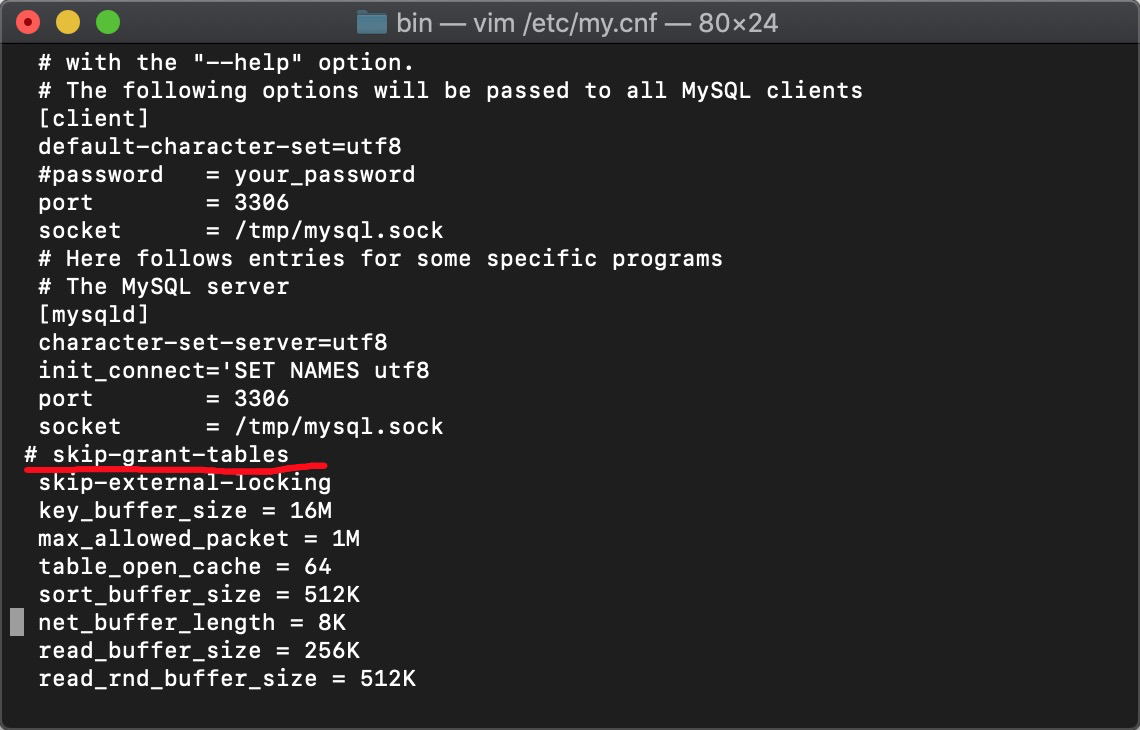
OK 然后mysql -uroot -p 登录数据库 不需要密码直接回车
mysql> use mysql; # 改密码 新版本数据库需要把左边的password改成authentication_string mysql> update user set password=password('123') where user='root' and host='localhost'; # 刷新权限 mysql> flush privileges;
# 退出
mysql> exit
之后进my.cnf 将跳过密码的skip-grant-tables 注释掉 退出,mysql -uroot -p 输入密码 还是报错,,, 好吧 那咋办呢,继续查呗
手动分割线
然后看到几个博客里说不能本地登录可能是localhost没有和host对应,那么看看呗,重复上面步骤,跳过密码登录(否则无密码游客登录是看不到mysql库的)
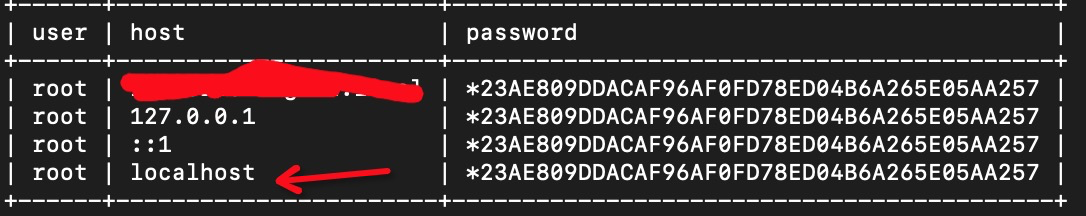
mysql> use mysql Database changed mysql> select user,host,password from user where user='root';
(无图,干说借助下图脑补)
我发现 host 这一栏没有对应 localhost 而是变成了我虚拟机的NAT映射的那个ip (这个真是坑)而host中 有127.0.0.1 那也就是说 通过mysql -uroot -p123 -h127.0.0.1 是可以登录的
那么解决问题也就很简单了
update user set host='localhost' where user='root' and host='我之前NAT映射的ip';
或者
insert into user(user,host) values('root',localhost);
再看
select user,host,password from user where user='root';
记得刷新权限
flush privileges;
然后退出 回配置文件 注释掉skip-grant-tables
mysql -uroot -p
password:
oK!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号