C++对象动态内存
对象的动态内存分配
Spread{
int ** arr = new int*[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
arr[i] = new int[10];
}
// 析构
for(auto i=0;i<10;i++)
{
delete[] arr[i];
}
delete[] arr;
}
Spread s1(1,2), s2(3,4);
内存空间:
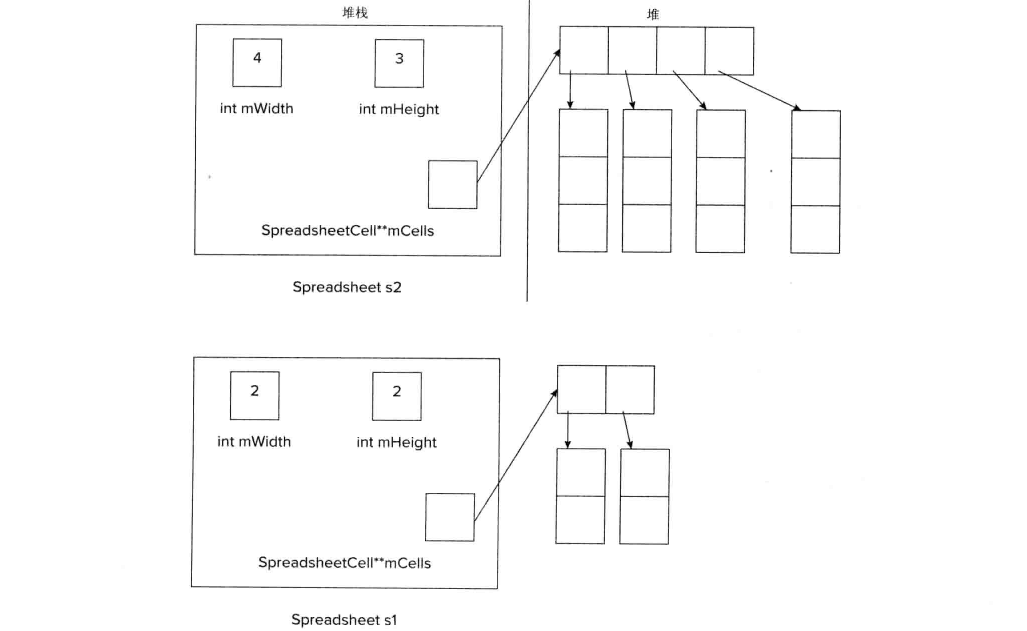
复制操作:-> 调用拷贝构造函数 (默认都是浅拷贝)
s2 = s1;
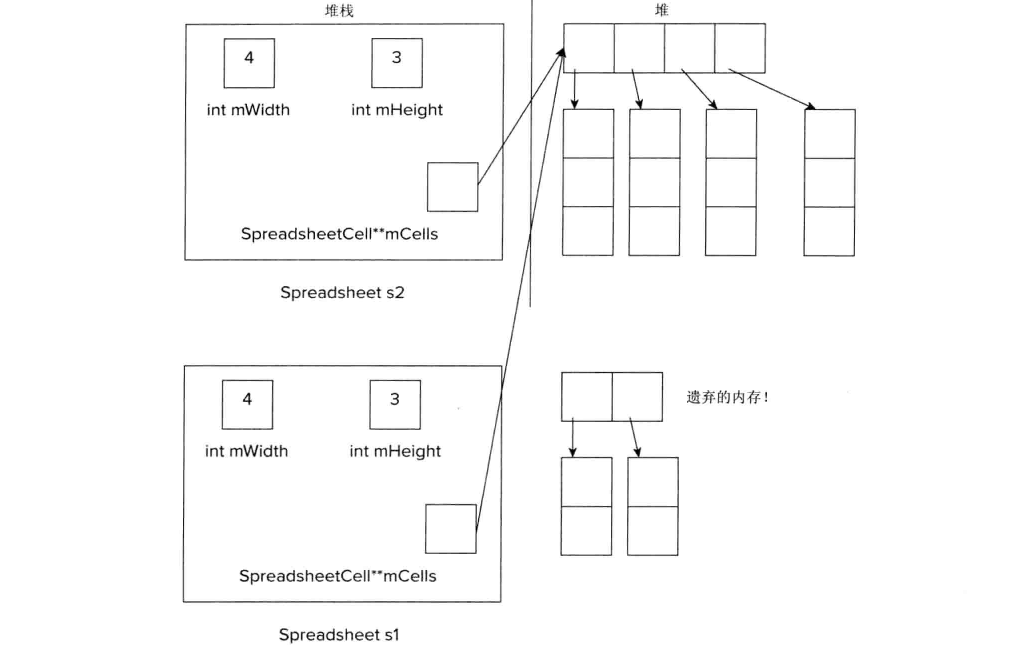
废弃的内存称为内存泄漏。
复制对象时,调用拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数
class Spread
{
public:
Spread(const Spread& s)
{
this->cells = new int* [10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cells[i] = new int* [0];
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<10;j++)
{
this->cells[i][j] = s.cells[i][j];
}
}
}
}
重写赋值运算符
class Spread
{
public:
Spread& operator=(const Spread& s)
{
if(this == &s)
{
return *this;
}
// other operate
}
}
只要动态分配了类内存,就必须重写拷贝构造、析构函数和复制运算符
禁止赋值和按值传递
当类中定义了动态内存,如果要禁止他人复制对象或者给对象复制,只需要显示的将operator=函数和拷贝构造方法定义为delete即可:
class Spread
{
public:
Spread& operator=(const Spread& s) = delete;
Spread(const Spread& s) = delete;
}
Records::Employee emp = Records::Employee(); // 报错
Records::Employee emp2; // ok
emp2.display();
不同的数据类型成员
静态成员|类成员
- 在成员函数中必须通过类名+
::访问
class Spread
{
static int port;
public int getPort()
{
return Spread::port;
}
}
const方法
const方法不可以修改数据成员。
class Spread
{
static int port;
public int getPort() const;
public int getPort() const
{
return Spread::port;
}
}
mutable数据成员
将数据成员定义为mutable,可以在const方法中修改
mutable int num;
内联方法
编译器将函数体直接插入到方法调用的位置,称为内联函数
inline Spread::getValue() const
{
return value;
}
对于将实现放在类中,实际上就是内联函数


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号