Tornado WebSocket
原文地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/560182e256f2
WebSocket协议
WebSocket是基于HTML5规范的网络协议,它实现了浏览器与服务器之间全双工full-duplex通信,即允许服务器主动发送消息给客户端。
WebSocket通信协议于2011年被IETF定为标准RFC 6455,并被RFC 7936所补充规范。在WebSocket的API中,浏览器和服务器只需要做一个握手动作。然后,浏览器和服务器之间就形成了一条快速通道,两者之间就直接可以用传输数据了。
WebSocket是HTML5规范中新提出的客户端与服务器之间的通信协议,协议本身使用新的ws://URL的格式。
WebSocket是独立的创建在TCP之上的协议,和HTTP唯一的关系是使用HTTP的101状态码进行协议转换,默认使用TCP端口是80,因此可以绕过大多数防火墙的限制。
WebSocket使客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,它允许服务器直接向客户端推送数据而无需客户端进行请求,两者之间可以创建持久化的连接,并允许数据进行双向传递。
WebSocket是一种网络通信协议,与HTTP协议不同的是,WebSocket连接允许客户端和服务器之间进行全双工通信,以便任意一方都可以通过建立的连接将数据推送到另一端。WebSocket仅需要建立一次连接就可以一直保持连接状态。
Tornado的WebSocket模块
浏览器通过JavaScript向服务器发出建立WebSocket连接的请求,连接建立以后,客户端和服务器就可以通过TCP连接直接交换数据。当你获取WebSocket连接后,可以通过send()方法向服务器发送数据,并通过onmessage事件来接收服务器返回的数据。
Tornado提供支持WebSocket的模块是tornado.websocket,并提供了WebSocketHandler类用于处理通信。
WebSocketHandler类提供的方法包括
# 当一个WebSocket连接建立后被调用
WebSocketHandler.open()
# 当客户端发送消息过来时被调用,此方法必须被重写。
WebSocketHandler.on_message(message)
# 当WebSocket连接关闭后调用
WebSocketHandler.on_close()
# 向客户端发送消息,消息可以是字符串或字典(字典会被转换为JSON字符串),若binary为False则消息会以utf8编码发送,否则以二进制格式发送。
WebSocketHandler.write_message(message, binary=False)
# 关闭WebSocket连接
WebSocketHandler.close()
# 判断请求源,对于符合条件的请求源允许其连接,否则返回403。可重写此方法来解决WebSocket的跨域请求。
WebSocketHandler.check_origin(origin)
# vim server.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from tornado.options import define, options from tornado.web import Application, RequestHandler from tornado.httpserver import HTTPServer from tornado.ioloop import IOLoop from tornado.websocket import WebSocketHandler import os, datetime define("port", type=int, default=8000) class IndexHandler(RequestHandler): def get(self): self.render("index.html") class MessageHandler(WebSocketHandler): connections = set() def open(self): print("message open") self.connections.add(self) def on_message(self, message): print("message send: %s" % message) ip = self.request.remote_ip dt = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%s") print(ip) for conn in self.connections: conn.write_message("[%s] %s : %s " % (dt, ip, message)) def on_close(self): print("message close") if conn in self.connections: self.connections.remove(conn) class App(Application): def __init__(self): handlers = [ (r"/index", IndexHandler), (r"/message", MessageHandler) ] settings = dict( debug = True, cookie_secret = "m2ho0d9", static_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "static"), template_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "template") ) Application.__init__(self, handlers, **settings) def main(): options.parse_command_line() app = App() server = HTTPServer(app) server.listen(options.port) IOLoop.current().start() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
异步websocket
class CommandHandler(WebSocketHandler): def check_origin(self, origin): # 返回True,支持跨域 return True async def open(self): pass async def on_message(self, message): pass def on_close(self): # 不能带async print("message close", id(self))
$ vim template/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>websocket</title> <link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/twitter-bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" /> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="form-group"> <label>消息</label> <textarea class="form-control" rows="3" id="message"></textarea> </div> <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="send">发送</button> <div id="result"></div> </div> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script>"" <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/twitter-bootstrap/4.3.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script> <script> if("WebSocket" in window){ var ws = new WebSocket("ws://192.168.56.103:8000/message"); ws.onopen = function(){ console.log("websocket open"); }; ws.onmessage = function(evt){ var data = evt.data; console.log(data); }; ws.onclose = function(){ console.log("websocket close"); }; $("#send").on("click", function(){ var message = $("#message").val(); console.log(message); if(message !== ""){ ws.send(message); } }); }else{ console.log("browser not support WebSocket"); } </script> </body> </html>
Vue+WebSocket 实现页面实时刷新长连接
<script> export default { name: "xxx", data() { return { websock: null, }; }, methods: { initWebSocket() { //初始化weosocket const wsuri = "ws://127.0.0.1/api/xxx"; //ws地址 this.websock = new WebSocket(wsuri); this.websock.onopen = this.webSocketOpen; this.websock.onerror = this.webSocketError; this.websock.onmessage = this.webSocketMessage; this.websock.onclose = this.webSocketClose; }, webSocketOpen() { console.log("WebSocket连接成功"); }, webSocketError(e) { //错误 console.log("WebSocket连接发生错误"); }, webSocketMessage(e) { //数据接收 const redata = JSON.parse(e.data); console.log(redata.value); }, webSocketSend(agentData) { //数据发送 this.websock.send(agentData); }, webSocketClose(e) { //关闭 console.log("connection closed (" + e.code + ")"); } }, mounted() {}, created() { //页面刚进入时开启长连接 // this.initWebSocket(); }, destroyed: function() { //页面销毁时关闭长连接 this.webSocketClose(); } }; </script>
CentOS防火墙开启指定端口供外部访问
# 查看状态 $ firewall-cmd --state $ firewall-cmd --get-services $ firewall-cmd --reload $ firewall-cmd --version $ firewall-cmd --help # 防火墙添加端口 $ firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8000/tcp --permanent # 重新载入 $ firewall-cmd --reload # 查看 $ firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-port=8000/tcp $ firewall-cmd --list-services $ firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports # 删除 $ firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8000/tcp --permanent
nginx反向代理webSocket配置
因为webSocket协议是基于http协议升级的(见下图),所以可以使用nginx反向代理webSocket.
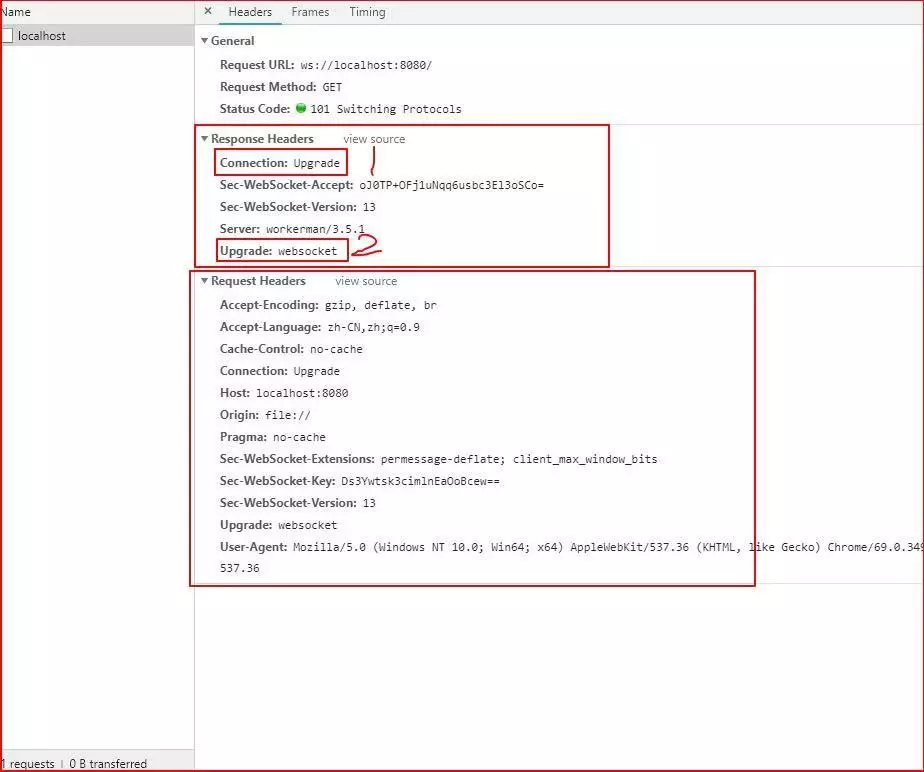
从这张图片上可以看出,webSocket连接的建立是在http协议的基础上。
GET /chat HTTP/1.1 Host: server.example.com Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw== Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat, superchat Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 Origin: http://example.com
熟悉HTTP的童鞋可能发现了,这段类似HTTP协议的握手请求中,只是多了几个东西。
Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade 这个就是Websocket的核心了,告诉Apache、Nginx等服务器:我发起的是Websocket协议。 Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw== Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat, superchat Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
首先,Sec-WebSocket-Key 是一个Base64 encode的值,这个是浏览器随机生成的,告诉服务器:泥煤,不要忽悠窝,我要验证尼是不是真的是Websocket助理。
最后,Sec-WebSocket-Version 是告诉服务器所使用的Websocket Draft(协议版本)
然后服务器会返回下列东西,表示已经接受到请求, 成功建立Websocket啦!
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Accept: HSmrc0sMlYUkAGmm5OPpG2HaGWk= Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
这里开始就是HTTP最后负责的区域了,告诉客户,我已经成功切换协议啦~
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
依然是固定的,告诉客户端即将升级的是Websocket协议。至此,HTTP已经完成它所有工作了,接下来就是完全按照Websocket协议进行了。
在nginx配置文件的service节点中添加如下配置
location /wss { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade"; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; }
我的配置已测试通过

location ~ ^/api/v2 { proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade"; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # 把请求方向代理传给tornado服务器,负载均衡 proxy_pass http://tornadoTCPServer; }
解释一下参数/wss这个是随便起的,告诉Nginx要代理的url,现在我的设置为wss,当我访问的我的服务器https://abc.com/wss时,Nginx会把我的请求映射到本机的8888端口。
proxy_pass要代理到的url,我的代理到本机的8888端口。proxy_http_version代理时使用的 http版本。
重点来了,代理webSocket的关键参数
proxy_set_header Upgrade把代理时http请求头的Upgrade设置为原来http请求的请求头,wss协议的请求头为websocketproxy_set_header Connection因为代理的wss协议,所以http请求头的Connection设置为Upgradeproxy_set_header X-Real-IP给代理设置原http请求的ip,填写$remote_addr即可
至于websocket协议的response的参数,在反向代理的时候不用管。
到这里,Nginx反向代理webSocket的配置就完成了,重启Nginx,用websocket连接试试,在原来wss地址的地方填写wss://abc.com/wss。如果websocket成功连接,说明Nginx反向代理websocket已经成功了。
现在的配置只是反向代理到本机时的配置,如果要反向代理到别的主机,在代理时可能会跨域问题,需要在Nginx的反向代理中做跨域的配置。
问题汇总
tornado websocket调用时出现403错误
原文地址:「harleylau」原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/harleylau/article/details/78390334
这个是tornado 4.0增加的特性,如果想允许所有的访问,
针对websocket处理类重写同源检查的方法:
class WebSocketHandler(tornado.websocket.WebSocketHandler): def check_origin(self, origin): return True
但是文档推荐自己根据cookie来针对性的开放,或者自己实现类似XSRF的保护
Override to enable support for allowing alternate origins.
The origin argument is the value of the Origin HTTP header, the url responsible for initiating this request. This method is not called for clients that do not send this header; such requests are always allowed (because all browsers that implement WebSockets support this header, and non-browser clients do not have the same cross-site security concerns).
Should return True to accept the request or False to reject it. By default, rejects all requests with an origin on a host other than this one.
This is a security protection against cross site scripting attacks on browsers, since WebSockets are allowed to bypass the usual same-origin policies and don’t use CORS headers.
Warning
This is an important security measure; don’t disable it without understanding the security implications. In particular, if your authentication is cookie-based, you must either restrict the origins allowed by check_origin() or implement your own XSRF-like protection for websocket connections. See these articles for more.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号