#代码7-6 清洗空值与异常值
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
datafile = "./data/air_data.csv"
cleanedfile = "./data/data_cleaned.csv"
#读取数据
airline_data = pd.read_csv(datafile,encoding = 'utf-8')
print('原始数据的形状为:',airline_data.shape)
#去除票价为空的记录
airline_notnull = airline_data.loc[airline_data['SUM_YR_1'].notnull() &
airline_data['SUM_YR_2'].notnull(),:]
print('删除缺失记录后数据的形状为:',airline_notnull.shape)
# 只保留票价非零的,或者平均折扣率不为0且总飞行公里数大于0的记录
index1 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_1'] != 0
index2 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_2'] != 0
index3 = (airline_notnull['SEG_KM_SUM']>0) & (airline_notnull['avg_discount'] != 0)
index4 = airline_notnull['AGE'] >100 # 去除年龄大于100的记录
airline = airline_notnull[(index1 | index2) & index3 & ~index4]
print('数据清洗后数据的形状为:', airline.shape)
airline.to_csv(cleanedfile) # 保存清洗后的数据
原始数据的形状为: (62988, 44)
删除缺失记录后数据的形状为: (62299, 44)
数据清洗后数据的形状为: (62043, 44)
# 7-7 属性选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 读取数据清洗后的数据
cleanedfile = "./data/data_cleaned.csv" # 数据清洗后保存的文件路径
airline = pd.read_csv(cleanedfile, encoding='utf-8')
# 选取需求属性
airline_selection = airline[['FFP_DATE', 'LOAD_TIME', 'LAST_TO_END', 'FLIGHT_COUNT', 'SEG_KM_SUM', 'avg_discount']]
print('筛选的属性前5行为:\n', airline_selection.head())
筛选的属性前5行为:
FFP_DATE LOAD_TIME LAST_TO_END FLIGHT_COUNT SEG_KM_SUM avg_discount
0 2006/11/2 2014/3/31 1 210 580717 0.961639
1 2007/2/19 2014/3/31 7 140 293678 1.252314
2 2007/2/1 2014/3/31 11 135 283712 1.254676
3 2008/8/22 2014/3/31 97 23 281336 1.090870
4 2009/4/10 2014/3/31 5 152 309928 0.970658
# 7-8 属性构造与数据标准化
# 构造属性L
L = pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['LOAD_TIME']) - pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['FFP_DATE'])
L = L.astype('str').str.split().str[0]
L = L.astype('int')/30
# 合并属性
airline_features = pd.concat([L,airline_selection.iloc[:,2:]],axis=1)
print('构建的LRFMC属性前5行为:\n', airline_features.head())
# 数据标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
data = StandardScaler().fit_transform(airline_features)
np.savez('./data/airline_scale.npz', data)
print('标准化后LRFMC 5个属性为:\n', data[:5,:])
构建的LRFMC属性前5行为:
0 LAST_TO_END FLIGHT_COUNT SEG_KM_SUM avg_discount
0 90.200000 1 210 580717 0.961639
1 86.566667 7 140 293678 1.252314
2 87.166667 11 135 283712 1.254676
3 68.233333 97 23 281336 1.090870
4 60.533333 5 152 309928 0.970658
标准化后LRFMC 5个属性为:
[[ 1.43579256 -0.94493902 14.03402401 26.76115699 1.29554188]
[ 1.30723219 -0.91188564 9.07321595 13.12686436 2.86817777]
[ 1.32846234 -0.88985006 8.71887252 12.65348144 2.88095186]
[ 0.65853304 -0.41608504 0.78157962 12.54062193 1.99471546]
[ 0.3860794 -0.92290343 9.92364019 13.89873597 1.34433641]]
#代码7-9 K-Meas聚类标准化后的数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans #导入K-Mmeans算法
#读取标准化后的数据
airline_scale = np.load('./data/airline_scale.npz')['arr_0']
k = 5 #确定聚类中心数
#构建模型,随机种子设为123
kmeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=k,random_state=123)
fit_kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(airline_scale) #模型训练
#查看聚类结果
kmeans_cc = kmeans_model.cluster_centers_ #聚类中心
print('各聚类中心为:\n',kmeans_cc)
kmeans_labels = kmeans_model.labels_ #样本的类别标签
print('各样本的类别标签为:\n',kmeans_labels)
r1 = pd.Series(kmeans_model.labels_).value_counts() #统计不同类别样本的数目
print('最终每个类别的数目为:\n',r1)
#输出聚类分群的结果
cluster_center = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.cluster_centers_,\
columns = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC']) #将聚类中心放在数据中
cluster_center.index = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.labels_).\
drop_duplicates().iloc[:,0] #将样本类别作为数据框索引
print(cluster_center)
各聚类中心为:
[[-0.70030628 -0.41502288 -0.16081841 -0.16053724 -0.25728596]
[ 0.0444681 -0.00249102 -0.23046649 -0.23492871 2.17528742]
[ 0.48370858 -0.79939042 2.48317171 2.42445742 0.30923962]
[ 1.1608298 -0.37751261 -0.08668008 -0.09460809 -0.15678402]
[-0.31319365 1.68685465 -0.57392007 -0.5367502 -0.17484815]]
各样本的类别标签为:
[2 2 2 ... 0 4 4]
最终每个类别的数目为:
0 24630
3 15733
4 12117
2 5337
1 4226
dtype: int64
ZL ZR ZF ZM ZC
0
2 -0.700306 -0.415023 -0.160818 -0.160537 -0.257286
1 0.044468 -0.002491 -0.230466 -0.234929 2.175287
3 0.483709 -0.799390 2.483172 2.424457 0.309240
0 1.160830 -0.377513 -0.086680 -0.094608 -0.156784
4 -0.313194 1.686855 -0.573920 -0.536750 -0.174848
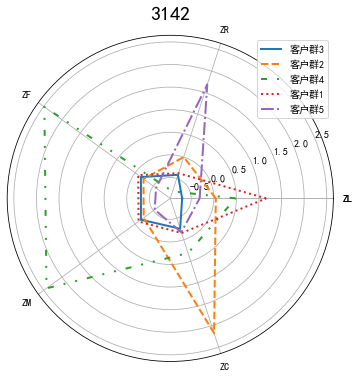
# 7-10 绘制客户分群雷达图
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
airline_scale = np.load('./data/airline_scale.npz')['arr_0']
k = 5
kmeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=k, random_state=123)
fit_kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(airline_scale)
kmeans_cc = kmeans_model.cluster_centers_
kmeans_labels = kmeans_model.labels_
r1 = pd.Series(kmeans_model.labels_).value_counts()
cluster_center = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.cluster_centers_,columns=['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC'])
cluster_center.index = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.labels_).drop_duplicates().iloc[:,0]
print(cluster_center)
labels = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC']
# labels = labels.append('ZL')
legen = ['客户群' + str(i + 1) for i in cluster_center.index]
lstype = ['-','--',(0,(3,5,1,5,1,5)),':','-.']
kinds = list(cluster_center.iloc[:,0])
cluster_center = pd.concat([cluster_center,cluster_center[['ZL']]], axis=1)
centers = np.array(cluster_center.iloc[:,0:])
n = len(labels)
angle = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n, endpoint=False)
# print([angle[0]])
angle = np.concatenate((angle, [angle[0]]))
labels = np.concatenate((labels, [labels[0]]))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,polar=True)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# print(cluster_center)
# print(centers)
# print(angle)
for i in range(len(kinds)):
ax.plot(angle, centers[i], linestyle=lstype[i], linewidth=2, label=kinds[i])
# ax.plot(angle, centers, linestyle=lstype[i], linewidth=2, label=kinds[i])
ax.set_thetagrids(angle*180/np.pi,labels)
plt.title('3142',fontsize=20)
plt.legend(legen)
plt.show()
plt.close
![]()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.ticker as mtick
data = pd.read_csv('./data/WA_Fn-UseC_-Telco-Customer-Churn.csv')
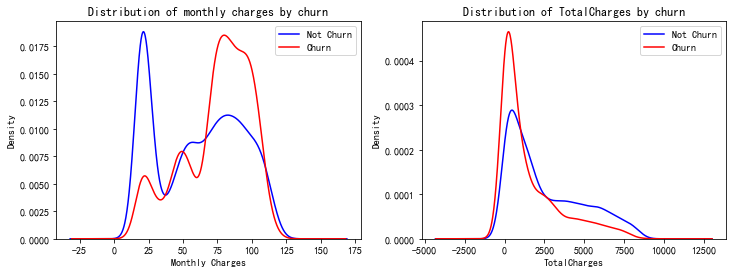
# #用密度图展现月消费、总消费与流失的关系
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(12,4))
data.MonthlyCharges[data['Churn'] == 'No'].plot(kind = 'kde',color ='blue',ax=ax[0])
data.MonthlyCharges[data['Churn'] == 'Yes'].plot(kind = 'kde',color ='red',ax=ax[0])
ax[0].legend(["Not Churn","Churn"],loc='upper right')
ax[0].set_ylabel('Density')
ax[0].set_xlabel('Monthly Charges')
ax[0].set_title('Distribution of monthly charges by churn')
ax[0].set_ylim(0)
#总消费需要转化数据类型,并把空值填充为0
data['TotalCharges'] = data['TotalCharges'].replace(" ", 0).astype('float')
data.TotalCharges[data['Churn'] == 'No'].plot(kind = 'kde',color ='blue',ax=ax[1])
data.TotalCharges[data['Churn'] == 'Yes'].plot(kind = 'kde',color ='red',ax=ax[1])
ax[1].legend(["Not Churn","Churn"],loc='upper right')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Density')
ax[1].set_xlabel('TotalCharges')
ax[1].set_title('Distribution of TotalCharges by churn')
ax[1].set_ylim(0)
![]()
# 对数据进行虚拟变量处理,也叫哑变量和离散特征编码,可用来表示分类变量、非数量因素可能产生的影响。
data_xy = data.drop(['customerID','gender','PhoneService','MultipleLines'],axis=1)
data_xy['Churn'].replace(to_replace='Yes', value=1, inplace=True)
data_xy['Churn'].replace(to_replace='No', value=0, inplace=True)
data_dummies = pd.get_dummies(data_xy)
# 归一化数据
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standard = StandardScaler()
standard.fit(data_dummies[['tenure','MonthlyCharges','TotalCharges']])
data_dummies[['tenure','MonthlyCharges','TotalCharges']] = standard.transform(data_dummies[['tenure','MonthlyCharges','TotalCharges']])
#划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = data_dummies.drop('Churn', axis=1)
y = data_dummies['Churn']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=101)
from sklearn.svm import SVC #支持向量机
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression #逻辑回归
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB#朴素贝叶斯
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier#决策树分类器
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score,f1_score,precision_score, accuracy_score
Classifiers = [['SVM',SVC()],
['LogisticRegression',LogisticRegression()],
['GaussianNB',GaussianNB()],
['DecisionTreeClassifier',DecisionTreeClassifier()]]
Classify_results = []
names = []
prediction = []
for name ,classifier in Classifiers:
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)#训练这4个模型
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)#预测这4个模型
recall = recall_score(y_test,y_pred)#评估这四个模型的召回率
precision = precision_score(y_test,y_pred)#评估这四个模型的精确率
f1 = f1_score(y_test,y_pred)#评估这四个模型的f1分数
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
class_eva = pd.DataFrame([recall,precision,f1,acc])#将召回率、精确率和f1分数放在df中,方便接下来对比
Classify_results.append(class_eva)
name = pd.Series(name)
names.append(name)
y_pred = pd.DataFrame(y_pred)
prediction.append(y_pred)
pred = y_pred.values
test = y_test.values
i = 0
sum = 0
lost = 0
norm = 0
wlost = 0
wnorm = 0
for j in test:
if(j == pred[i]):
sum += 1
# 正确预测保留
if( j == 0 ):
norm += 1
# 正确预测流失
elif( j == 1):
lost += 1
else:
# 错误预测保留
if( j == 0 ):
wnorm += 1
# 错误预测流失
elif( j == 1):
wlost += 1
i = i + 1
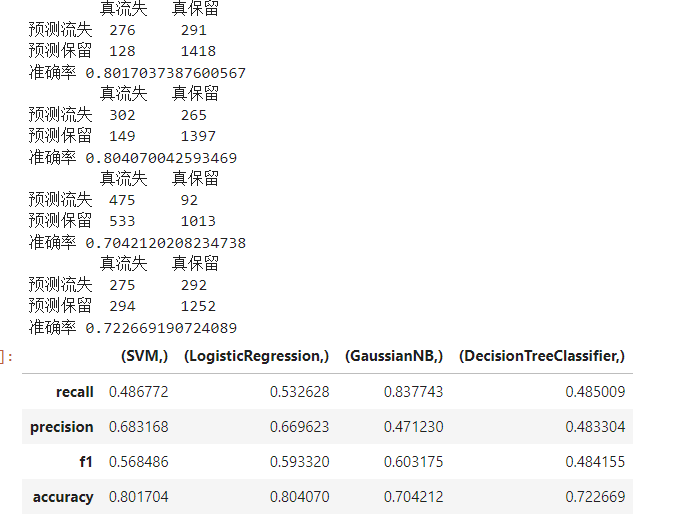
print('\t真流失\t真保留')
print('预测流失\t',lost,'\t',wlost)
print('预测保留\t',wnorm,'\t',norm)
print('准确率',sum/len(pred))
names = pd.DataFrame(names)
result = pd.concat(Classify_results,axis=1)
result.columns = names
result.index=[['recall','precision','f1','accuracy']]
result
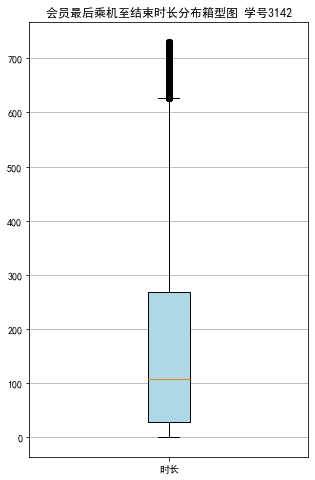
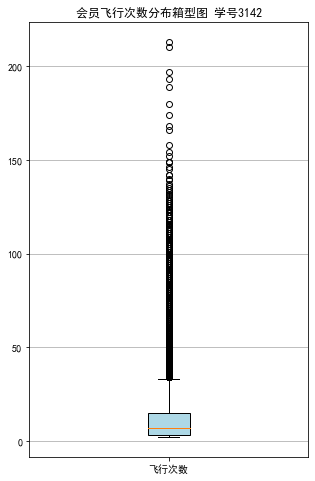
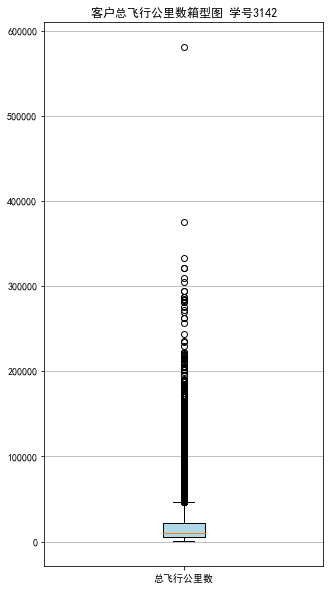


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号