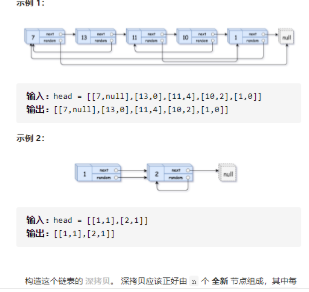
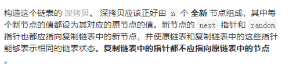
A
遍历简洁正确完整思路
dfs,形参head,得到拷贝的head链表,headClone哈希表存放head链表对应拷贝head链表,if head空边界返回,if headClone有拷贝的head链表提前返回,否则,new head的拷贝节点放进headClone,再dfs求head->next和head->random的拷贝链表,求出来后就得到了拷贝的head链表返回
精确定义
dfs,形参head,得到拷贝的head链表
headClone哈希表存放head链表对应拷贝的head链表
class Solution { public: unordered_map<Node*,Node*>headClone; Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { return dfs(head); } Node*dfs(Node*head){ if(!head)return nullptr; if(headClone[head])return headClone[head]; Node*clone=new Node(head->val); headClone[head]=clone; clone->next=dfs(head->next); clone->random=dfs(head->random); return headClone[head]; } };
踩过的坑
Node*clone=new Node(head);
不需要另外两个参数,因为next和random我需要dfs才能得到他们
拷贝的链表,而不是仅仅借用原来的
如果dfs递归构建的时候,
clone=new Node(head->val,head->next->val,head->random->val
则不是深拷贝
拷贝的head链表生成方法也就是dfs返回值,先new head->val,再dfs(next)dfs(random)
生成拷贝的next链表和拷贝的random链表


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号