8.4 8.5 8.7 8.8 8.9
8.4
点击查看代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
def system(t, state):
x, y = state
dxdt = -x*3 - y
dydt = x - y*3
return [dxdt, dydt]
t_span = (0, 30)
y0 = [1, 0.5]
sol = solve_ivp(system, t_span, y0, t_eval=np.linspace(t_span[0], t_span[1], 1000))
x = sol.y[0]
y = sol.y[1]
t = sol.t
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(t, x, label='x(t)')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('x(t)')
plt.title('x(t) vs t')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(t, y, label='y(t)')
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('y(t)')
plt.title('y(t) vs t')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.plot(x, y, label='Phase Trajectory')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Phase Plane (x, y)')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("3010")
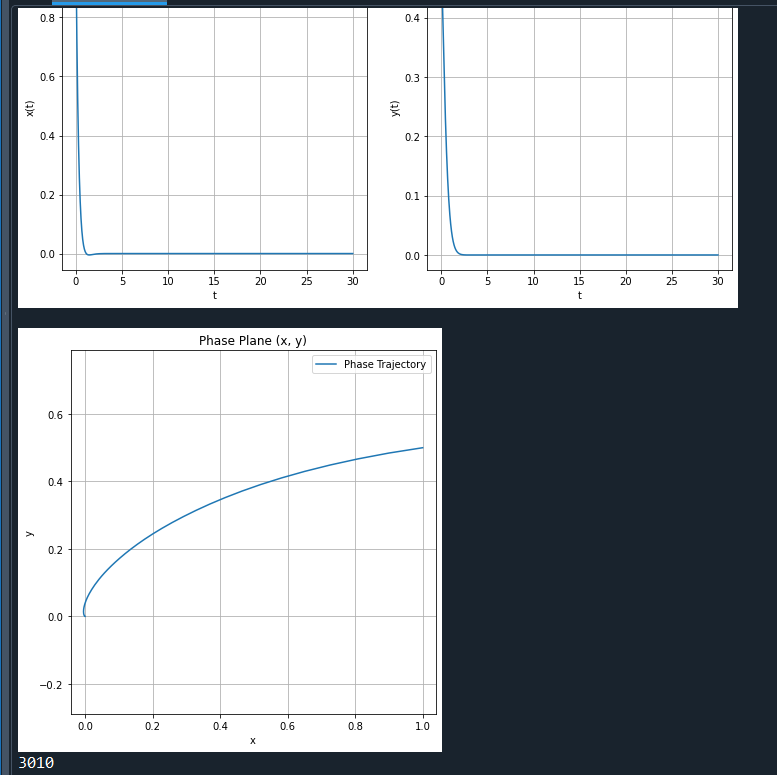
7.5
点击查看代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
def model(t, y):
f, df_dm, d2f_dm2, T, dT_dm = y
d3f_dm3 = -3*f*d2f_dm2 + 2*(df_dm)**2 - T
d2T_dm2 = -2.1*f*dT_dm
return [df_dm, d2f_dm2, d3f_dm3, dT_dm, d2T_dm2]
y0 = [0, 0, 0.68, 1, -0.5]
t_span = (0, 10)
t_eval = np.linspace(t_span[0], t_span[1], 1000)
sol = solve_ivp(model, t_span, y0, t_eval=t_eval, method='RK45')
f = sol.y[0]
T = sol.y[3]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(sol.t, f, label='f(m)')
plt.xlabel('m')
plt.ylabel('f(m)')
plt.title('Solution for f(m)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(sol.t, T, label='T(m)', color='orange')
plt.xlabel('m')
plt.ylabel('T(m)')
plt.title('Solution for T(m)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("3010")
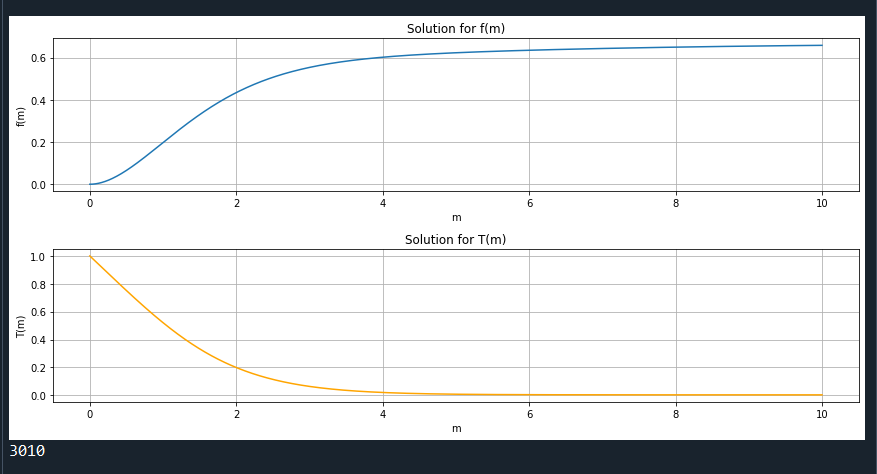
8.7
点击查看代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.integrate import odeint
def pendulum_ode_1(y, t, g, l):
theta, omega = y
dydt = [omega, -g / l * np.sin(theta)]
return dydt
l = 1
g = 9.8
theta_0 = 15 / 180 * np.pi
y0 = [theta_0, 0]
t = np.linspace(0, 30, 1000)
sol_1 = odeint(pendulum_ode_1, y0, t, args=(g, l))
plt.plot(t, sol_1[:, 0])
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('theta(t)')
plt.title('Pendulum without viscous medium')
plt.show()
def pendulum_ode_2(y, t, g, l, lambda_):
theta, omega = y
dydt = [omega, -g / l * np.sin(theta) - lambda_ / l * omega]
return dydt
lambda_ = 0.1
y0 = [theta_0, 0]
sol_2 = odeint(pendulum_ode_2, y0, t, args=(g, l, lambda_))
plt.plot(t, sol_2[:, 0])
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('theta(t)')
plt.title('Pendulum with viscous medium')
plt.show()
print("3010")
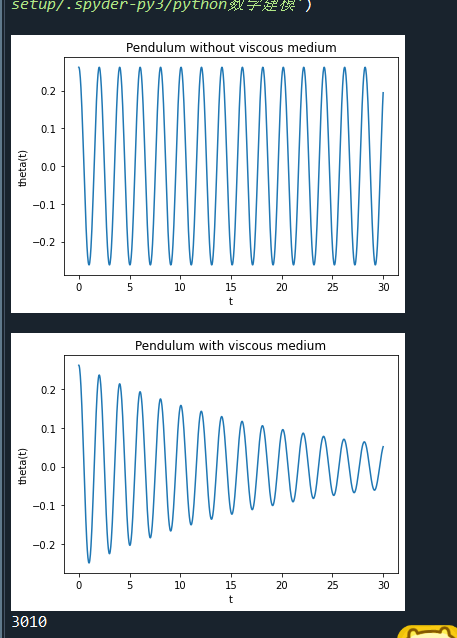
8.8
点击查看代码
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import odeint
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义参数
b3 = 0.5 * 1.109 * 10**5
b4 = 1.109 * 10**5
s = lambda n: 1.22 * 10**11 / (1.22 * 10**11 + n)
d = 0.8
w3 = 17.86
w4 = 22.99
q3 = 0.42
q4 = 1
E = 1 # 初始捕捞努力量,后面会进行优化
def fish_model(x, t):
x1, x2, x3, x4 = x
n = b3 * x3 + b4 * x4
dx1dt = (b3 * x3 + b4 * x4) * s(n) - d * x1
dx2dt = x1 * (1 - d) - d * x2
dx3dt = x2 * (1 - d) - d * x3 - q3 * E * x3
dx4dt = x3 * (1 - d) - d * x4 - q4 * E * x4
return [dx1dt, dx2dt, dx3dt, dx4dt]
# 初始鱼群数量
x0 = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
t = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)
sol = odeint(fish_model, x0, t)
# 计算捕捞量
def calculate_yield(x, E):
x3, x4 = x[2], x[3]
return (w3 * q3 * E * x3 + w4 * q4 * E * x4)
# 寻找最优捕捞努力量(简单示例,实际可能需要更复杂的优化算法)
Es = np.linspace(0, 5, 100)
yields = []
for e in Es:
E = e
sol = odeint(fish_model, x0, t)
x_end = sol[-1]
yield_value = calculate_yield(x_end, E)
yields.append(yield_value)
optimal_E_index = np.argmax(yields)
optimal_E = Es[optimal_E_index]
# 绘制结果
plt.plot(Es, yields)
plt.xlabel('Fishing Effort (E)')
plt.ylabel('Yield')
plt.title('Optimal Fishing Strategy')
plt.show()
print("3010")
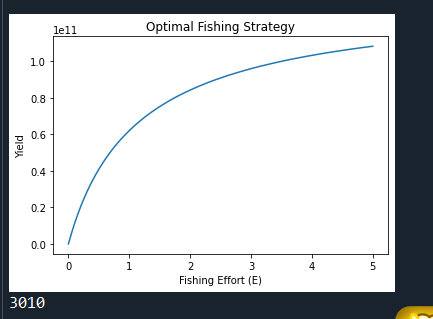
8.9
点击查看代码
r=0.0036
N=360
Q=400000
x=round((1+r)**N*Q*r/((1+r)**N-1),2)
xt=x*N
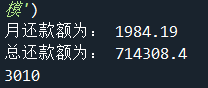
print('月还款额为:',x);print('总还款额为:',xt)
print("3010")



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号