力扣104题、559题、111题(二叉树的最大深度,n叉树的最大深度,二叉树的最小深度)
104、二叉树的最大深度
基本思想:
后序遍历
具体实现:
1.确定递归的参数和返回值:
参数:根节点
返回值:int类型,因为返回的是树的深度
2.确定终止条件
节点为空时,返回0,说明这个树的高度为0
3.单层递归的逻辑
先求左子树的深度,
再求右子树的深度,
最后求左右深度的最大的数值,然后+1(要算上当前的中间节点)
得到当前节点为根节点的树的深度
代码:
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left); int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right); return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1; } }
基本思想:
前序遍历,回溯算法
代码:
class Solution { int result; public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { result = 0; if (root == null) return result; result = getDepth(root, 1); return result; } public int getDepth(TreeNode node, int depth){ result = depth > result ? depth:result;//前序遍历 if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return result; if (node.left != null){//左子树 depth++;//深度+1 getDepth(node.left, depth); depth--;//回溯,深度-1 } if (node.right != null){ depth++; getDepth(node.right, depth); depth--; } return result; } }
基本思想:
迭代法,层序遍历
具体实现:
一层一层遍历二叉树,记录遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度
代码:
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.offer(root); int depth = 0; while(!deque.isEmpty()) { int size = deque.size(); depth++; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ TreeNode poll = deque.poll(); if (poll.left != null){ deque.offer(poll.left); } if (poll.right != null){ deque.offer(poll.right); } } } return depth; } }
559、n叉树的最大深度
递归法
class Solution { public int maxDepth(Node root) { if (root == null) {//二叉树不存在,返回高度0 return 0; } else if (root.children.isEmpty()) {//根节点没有孩子节点,返回高度1 return 1; } else { List<Integer> heights = new LinkedList<>(); for (Node item : root.children) {//根节点有孩子节点 heights.add(maxDepth(item)); //遍历每个孩子节点,求出以孩子节点为根的树的高度 } return Collections.max(heights) + 1; } } }
迭代法:
class Solution { public int maxDepth(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Deque<Node> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.offer(root); int depth = 0; while(!deque.isEmpty()) { int size = deque.size(); depth++; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ Node node = deque.poll(); for (int j = 0; j < node.children.size();j++){ if (node.children.get(j) != null){ deque.offer(node.children.get(j)); } } } } return depth; } }
class Solution { public int maxDepth(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; int depth = 0; Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<>(); que.offer(root); while (!que.isEmpty()) { depth ++; int len = que.size(); while (len > 0) { Node node = que.poll(); if (node.children != null){ for (Node child : node.children){ que.offer(child); } } len--; } } return depth; } }
111、二叉树的最小深度
具体实现:
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
所以不能用104题后序遍历的套路
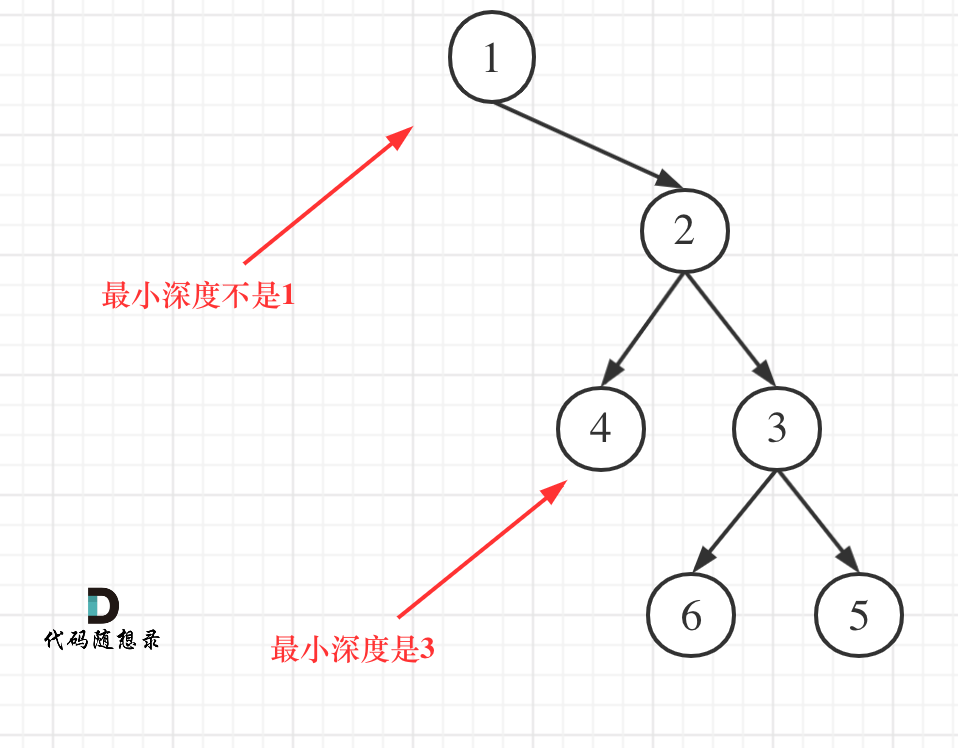
左子树为空,右子树不为空,最小深度是1+左子树的深度
右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是1+右子树的深度
左右子树都不为空,最小深度是左右子树深度最小值+1
代码:
class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left); int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null && root.right != null) { return rightDepth + 1; } if (root.right == null && root.left != null) { return leftDepth + 1; } // 左右结点都不为null return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1; } }
迭代法(层序遍历)
class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.offer(root); int depth = 0; while (!deque.isEmpty()){ int size = deque.size(); depth++; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ TreeNode poll = deque.poll(); if (poll.left == null && poll.right == null){ return depth; // 是叶子结点,直接返回depth,因为从上往下遍历,所以该值就是最小值 } if (poll.left != null){ deque.offer(poll.left); } if (poll.right != null){ deque.offer(poll.right); } } } return depth; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号