力扣347,BM46,BM47(堆)
347、前k个高频元素
基本思想:
要统计元素出现频率
对频率排序
找出前K个高频元素
具体实现:
对频率进行排序,使用优先级队列
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35326718/article/details/72866180
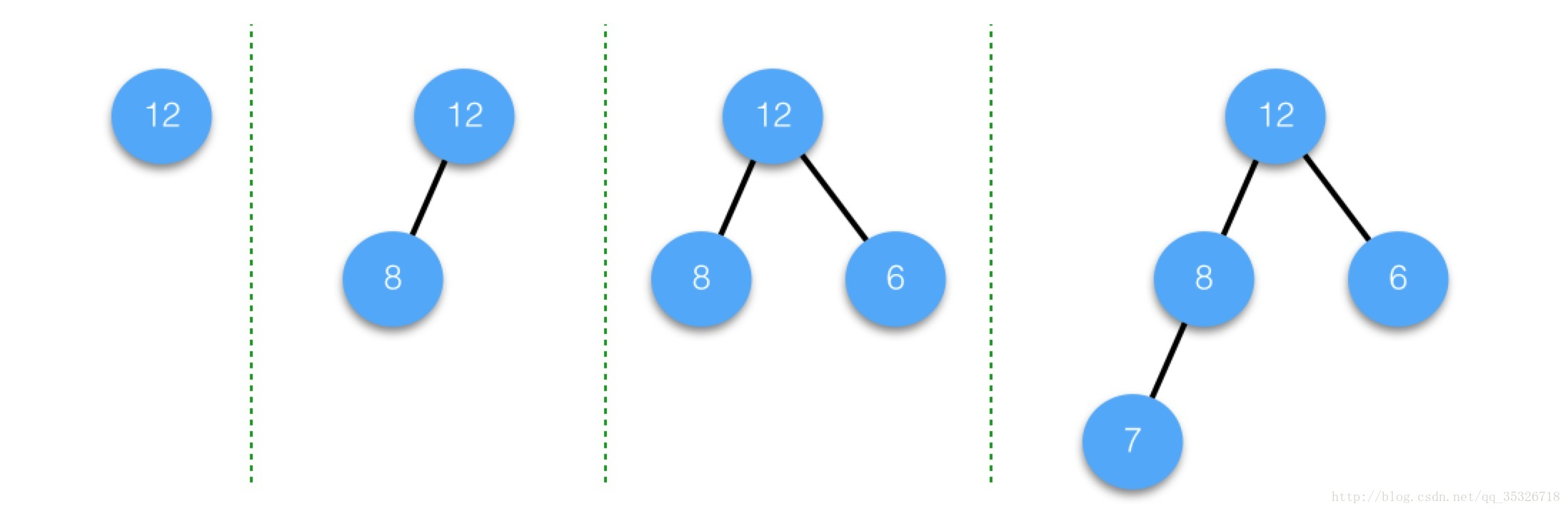
1.满二叉树除了叶子节点,其余所有节点都有左右孩子节点
完全二叉树的非叶子节点,孩子一定要按照从左到右的顺序
完全二叉树的同一层上,前面的节点没有孩子节点,后面的节点就不能有孩子节点
每个节点必须先有左节点才能有右节点
完全二叉树优点:从任意节点根据公式推算出该节点左右孩子,父节点位置
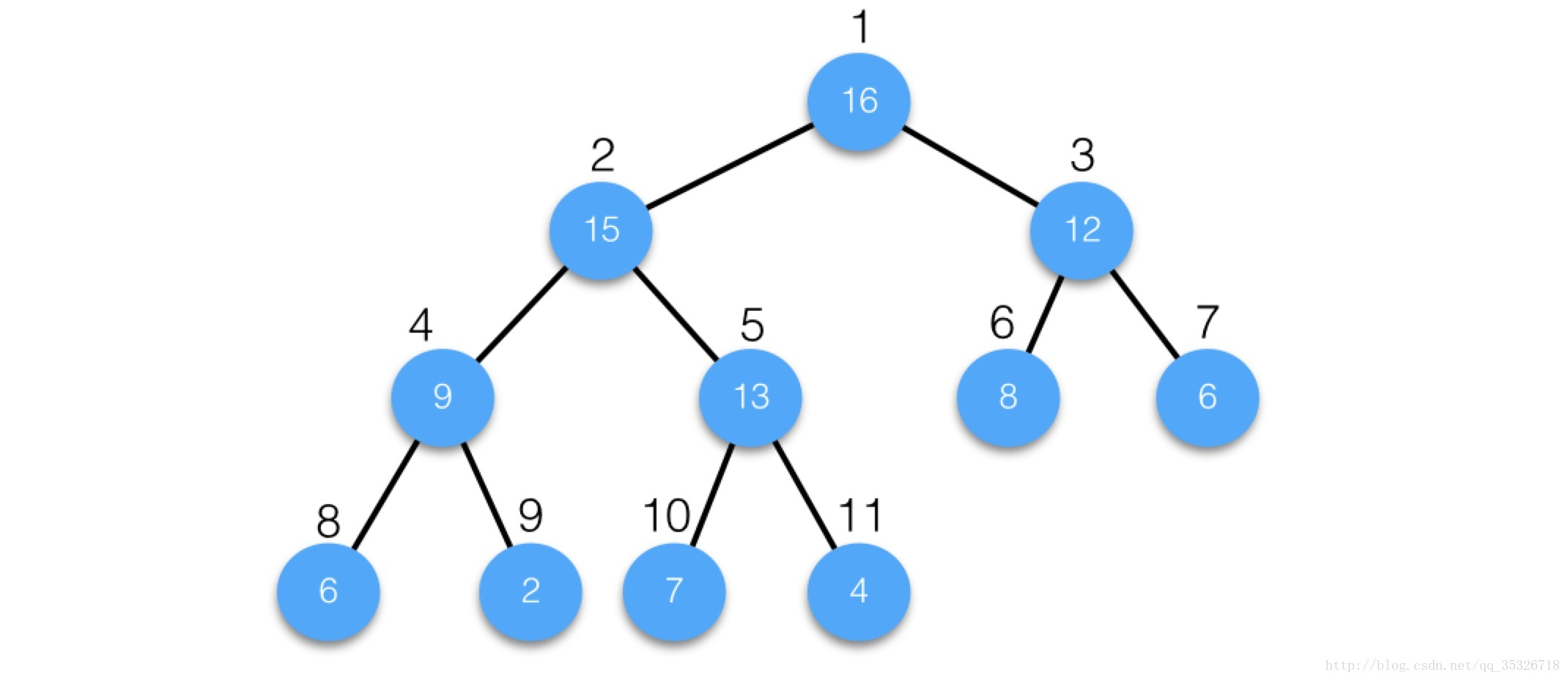
4号节点:
父节点为4/2=2 i/2
左孩子节点:2*4 = 8 2*i
右孩子节点:2*4 + 1 = 9 2*i +1
2.上述完全二叉树存储在数组中
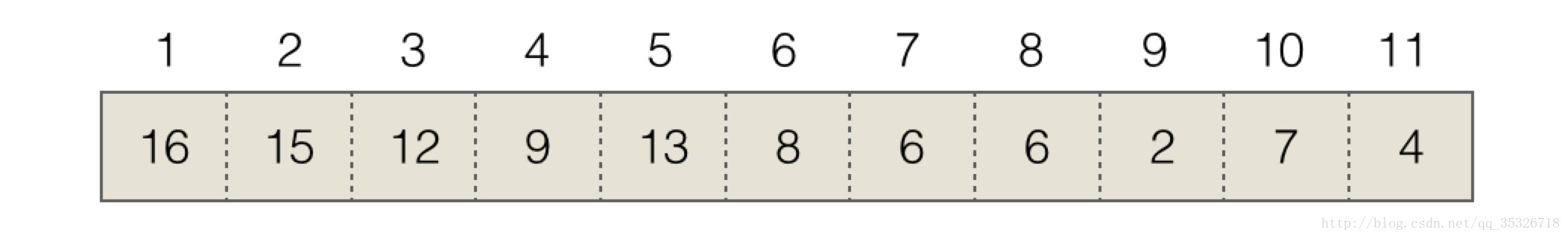
定义一个Entry类,分别一个parent引用,left引用,right引用,并使用它们维护当前节点和别的节点之间的关系。
堆:完全二叉树+数组
2.堆分大根堆和小根堆。
大根堆的要求是父节点比子节点的值大,
小根堆要求父节点的值比子节点的值小
什么是优先级队列呢?
1、是一个用队列存储的堆,对外接口从队头取元素,从队尾添加元素,再无其他取元素的方式
2、优先级队列内部元素是自动依照元素的权值排列。
PriorityQueue总是先输出根节点的值,然后调整树使之继续成为一棵完全二叉树 样每次输出的根节点总是整棵树优先级最高的,要么数值最小要么数值最大。
如何有序排列?
此题不能使用大顶堆,
定义一个大小为k的大顶堆,在每次移动更新大顶堆的时候,每次弹出都把最大的元素弹出去了,不能保留下来前K个高频元素。
此题用小顶堆,因为要统计最大前k个元素,只有小顶堆每次将最小的元素弹出,最后小顶堆里积累的才是前k个最大元素。
代码:
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { int[] result = new int[k]; HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int num : nums){ map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); // map.put,将指定key-value添加到(或修改)当前map对象中 //map.getOrDefault,当map集合中有这个num时,就使用这个num对应的值;如果没有就使用0。 } Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet(); //Set entrySet():返回所有key-value对构成的Set集合 PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue()); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : entries) { queue.offer(entry); if (queue.size() > k) { queue.poll(); } } // 找出前K个高频元素,因为小顶堆先弹出的是最小的,所以倒叙来输出到数组 // for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // result[i] = queue.poll().getKey(); // } // return result; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { result[i] = queue.poll().getKey(); } return result; } }
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { int[] res = new int[k]; HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> que = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.getValue(), o2.getValue())); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { que.offer(entry); if (que.size() > k) que.poll(); } for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) res[i] = que.poll().getKey(); return res; } }
BM47 寻找第k大
用小顶堆,顶是最小的,保持堆中k个元素,顶就是第k个大的元素
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) { ArrayList<Integer> r = new ArrayList<>(); PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2)); for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) q.offer(a[i]); for (int i = K; i < n; i++) { if (q.peek() < a[i]) { q.poll(); q.offer(a[i]); } }return q.poll(); } }
BM46 最小的k个数
用大顶堆,数字是从大到小,顶是最大的数,
只要保持堆中k个元素从大到小,每进来一个数比顶大的全不要,比顶小的全要并把顶踢出去。
顶已经是最大的了,最大的比新进元素还小,那剩下的数就更小了
import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (input.length == 0 || k == 0) return res; PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2.compareTo(o1)); for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { q.offer(input[i]); } for (int i = k; i < input.length; i++) { if (q.peek() > input[i]) { q.poll(); q.offer(input[i]); } } for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { res.add(q.poll()); } return res; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号