Java学习笔记93——String类案例
案例1
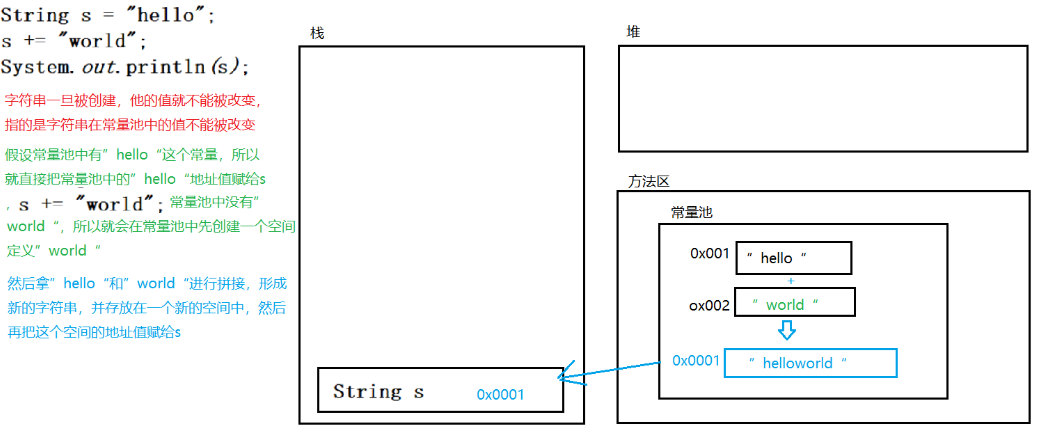
字符串是常量,它的值在创建之后不能更改 String s = “hello”; s += “world”; 问s的结果是多少?
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += "world";
System.out.println(s);//helloworld
}
}常量值的拼接图解
案例2
String s = new String(“hello”)和String s = “hello”;的区别? 字符串比较之看程序写结果 字符串拼接之看程序写结果
1、==比较引用数据类型的时候,比较的是地址值
2、String s1 = new String("hello");会在堆内存中创建对象
3、String类中重写了Object的equals方法
4、equals方法默认比较的是地址值,但是由于重写了,所以比较的是字符串内容
public class StringDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1==s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
}
}案例3
看程序写结果
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1==s2); //flase(==比较的是地址值,new的同时就会产生地址值)
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true(equals先比较地址值和内容,有一个相同即为true)
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3==s4);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "hello";
System.out.println(s5==s6);//true
System.out.println(s5==s4);//true
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));//true
}
}案例4
1、字符串如果是变量相加,是先开辟空间,然后再拼接
2、字符串如果是常量相加,是先相加,然后去常量池中找,如果找到了,就返回。如果找不到就创建。
public class StringDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "helloworld";
String s4 = "hello"+"world";
System.out.println(s3==s4); //true(s4中两字符先相加并存在于常量池中,s3找到相同常量并返回)
String s5 = s1+s2;
System.out.println(s3==s1+s2); //false(两变量相加先开辟空间,然后拼接,地址值不同)
System.out.println(s3.equals(s1+s2)); //true(内容相同)
//System下
//public static int identityHashCode(Object x)
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s3));//1163157884
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s4));//1163157884(常量相加与整体常量在常量池中对应同样的地址值)
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s5));//1956725890
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号