SpringBoot整合Redis和SpringBoot(SpringCache)整合Redis
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/lingerlan510/article/details/121906813
https://blog.csdn.net/user2025/article/details/106595257
https://blog.csdn.net/Confused_/article/details/124417403
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_56395837/article/details/121484260
SpringBoot整合Redis
源码码云地址:https://gitee.com/zhang-zhixi/springboot-redis
一、所需依赖
这里需要注意的一点是,从在SpringBoot 2.0+后,默认的redis client是lettuce而不是一直使用的jedis,在导入依赖的时候需要再单独导入commons-pool2
关于lettuc与Jedis有什么区别?
- lettuce: Lettuce 是 一种可伸缩,线程安全,完全非阻塞的Redis客户端,多个线程可以共享一个RedisConnection,它利用Netty NIO 框架来高效地管理多个连接,从而提供了异步和同步数据访问方式,用于构建非阻塞的反应性应用程序。
- Jedis: Jedis 在实现上是直连 redis server,多线程环境下非线程安全,除非使用连接池,为每个 redis实例增加 物理连接。 这种方式更加类似于我们 BIO 一条线程连一个客户端,并且是阻塞式的,会一直连接着客户端等待客户端的命令
<!--整合Redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--阿里巴巴JSON格式化转换-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.79</version>
</dependency>
<!--springboot2.x以后用得是lettuce:lettuce默认连接池使用 common-pool2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--WEB开发依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--MybatisPlus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL依赖。注意一下,不指定默认是MySQL8的连接器。-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
二、Redis原理
Redis的自动配置
在SpringBoot中导入Redis的Start,我们知道会有一个xxxAutoConfiguration,这样一个类来存放我们的一些自动配置。
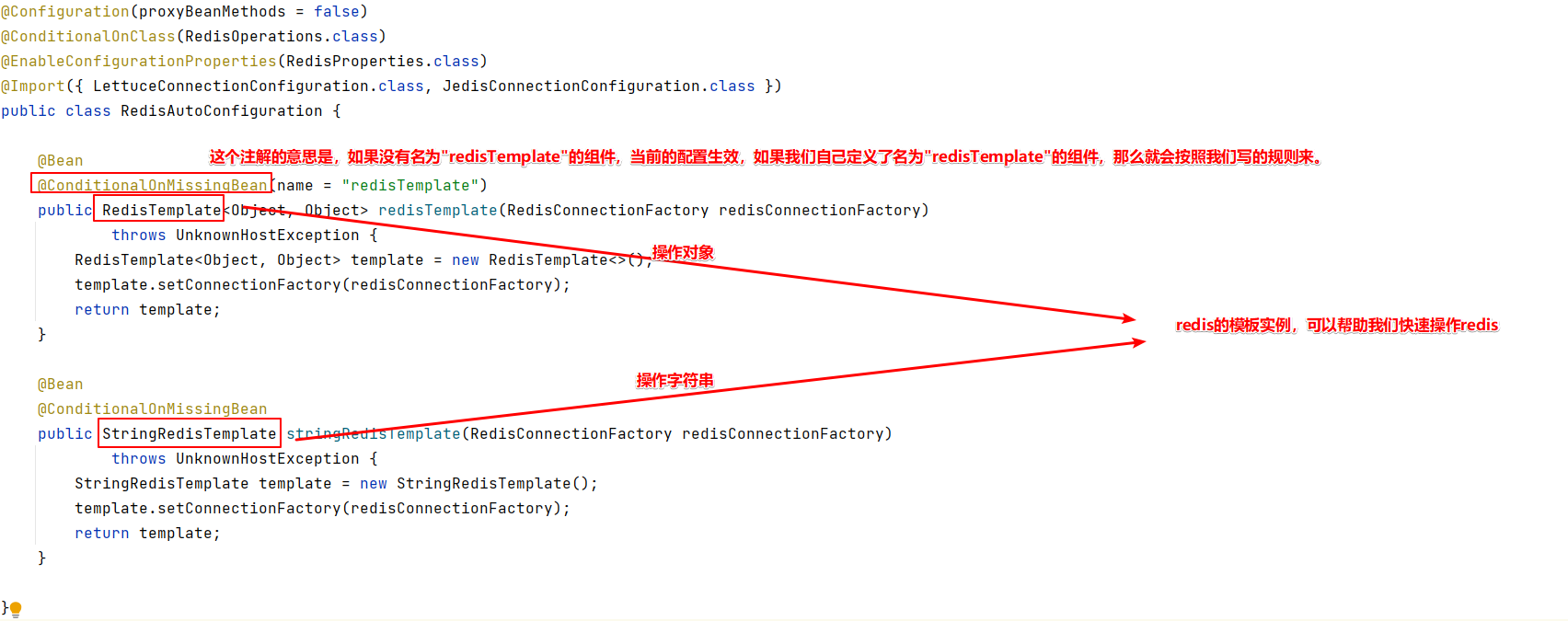
Redis的配置文件
点进去这个 @EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class) ,可以看到在SringBoot下我们可以对Redis进行的一些配置:
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis") 2 public class RedisProperties { 3 4 /** 5 * 可以配置使用的db下标 6 */ 7 private int database = 0; 8 9 /** 10 * 这个配置可以让我们连接到远程的redis中。例如: 11 * redis://user:password@example.com:6379 12 */ 13 private String url; 14 15 /** 16 * Redis服务端的主机名 17 */ 18 private String host = "localhost"; 19 20 /** 21 * Login username of the redis server. 22 */ 23 private String username; 24 25 /** 26 * Login password of the redis server. 27 */ 28 private String password; 29 30 /** 31 * Redis的端口号 32 */ 33 private int port = 6379; 34 35 /** 36 * 是否开启安全认证 37 */ 38 private boolean ssl; 39 40 /** 41 * Read timeout. 42 */ 43 private Duration timeout; 44 45 /** 46 * Connection timeout. 47 */ 48 private Duration connectTimeout; 49 50 /** 51 * Client name to be set on connections with CLIENT SETNAME. 52 */ 53 private String clientName; 54 55 /** 56 * Type of client to use. By default, auto-detected according to the classpath. 57 */ 58 private ClientType clientType; 59 60 private Sentinel sentinel; 61 62 private Cluster cluster; 63 }
其中主机名和端口号都有默认值,如果我们连自己的电脑,那么这两个配置都可以不用修改!我们这里不用修改配置文件,就使用默认的即可!
关于Redis的配置,仅供参考:
##########################Redis配置################################### # 连接的那个数据库(默认为0) spring.redis.database=0 # redis服务的ip地址(默认是本机-127.0.0.1) spring.redis.host=182.92.209.212 # redis端口号(默认) spring.redis.port=6379 # redis的密码,没设置过密码,可为空 spring.redis.password=123456 # 连接超时时间 spring.redis.timeout=10s # 连接池中的最小空闲连接 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0 # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8 # 连接池中的最大连接数 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8 # 连接池中的最大等待时间(-1表示没有限制) spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1ms
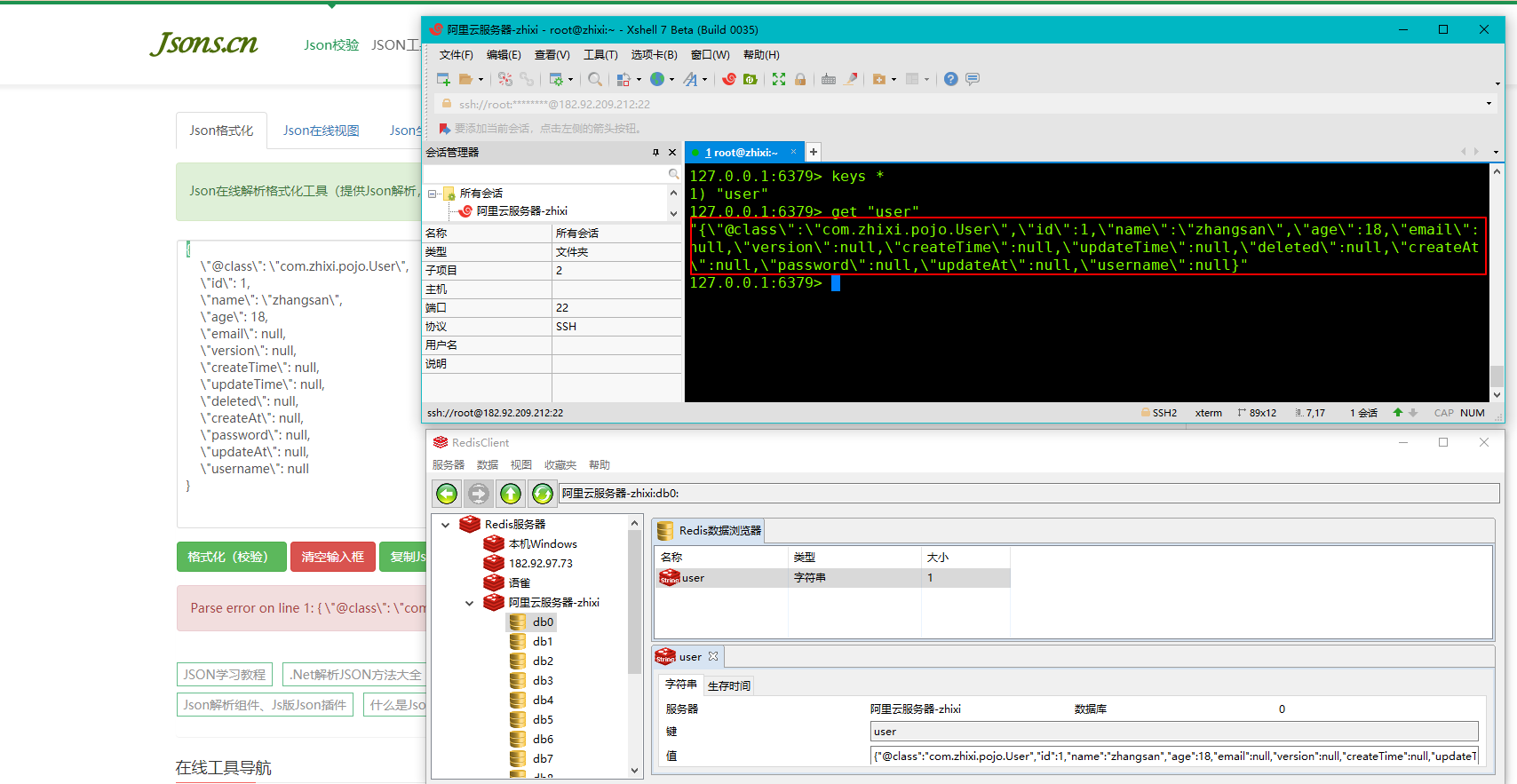
Redis简单存取数据测试
实体类:User.java

/** * @TableName user */ @TableName(value = "user") @Data public class User implements Serializable { /** * 主键ID */ @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private Long id; /** * 姓名 */ @TableField(value = "name") private String name; /** * 年龄 */ @TableField(value = "age") private Integer age; /** * 邮箱 */ @TableField(value = "email") private String email; /** * */ @TableField(value = "version") private Integer version; /** * */ @TableField(value = "create_time") private LocalDateTime createTime; /** * */ @TableField(value = "update_time") private LocalDateTime updateTime; /** * */ @TableField(value = "deleted") private Integer deleted; /** * */ @TableField(value = "create_at") private String createAt; /** * */ @TableField(value = "password") private String password; /** * */ @TableField(value = "update_at") private String updateAt; /** * */ @TableField(value = "username") private String username; @TableField(exist = false) private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override public boolean equals(Object that) { if (this == that) { return true; } if (that == null) { return false; } if (getClass() != that.getClass()) { return false; } User other = (User) that; return (this.getId() == null ? other.getId() == null : this.getId().equals(other.getId())) && (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() == null : this.getName().equals(other.getName())) && (this.getAge() == null ? other.getAge() == null : this.getAge().equals(other.getAge())) && (this.getEmail() == null ? other.getEmail() == null : this.getEmail().equals(other.getEmail())) && (this.getVersion() == null ? other.getVersion() == null : this.getVersion().equals(other.getVersion())) && (this.getCreateTime() == null ? other.getCreateTime() == null : this.getCreateTime().equals(other.getCreateTime())) && (this.getUpdateTime() == null ? other.getUpdateTime() == null : this.getUpdateTime().equals(other.getUpdateTime())) && (this.getDeleted() == null ? other.getDeleted() == null : this.getDeleted().equals(other.getDeleted())) && (this.getCreateAt() == null ? other.getCreateAt() == null : this.getCreateAt().equals(other.getCreateAt())) && (this.getPassword() == null ? other.getPassword() == null : this.getPassword().equals(other.getPassword())) && (this.getUpdateAt() == null ? other.getUpdateAt() == null : this.getUpdateAt().equals(other.getUpdateAt())) && (this.getUsername() == null ? other.getUsername() == null : this.getUsername().equals(other.getUsername())); } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((getId() == null) ? 0 : getId().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getName() == null) ? 0 : getName().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getAge() == null) ? 0 : getAge().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getEmail() == null) ? 0 : getEmail().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getVersion() == null) ? 0 : getVersion().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getCreateTime() == null) ? 0 : getCreateTime().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getUpdateTime() == null) ? 0 : getUpdateTime().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getDeleted() == null) ? 0 : getDeleted().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getCreateAt() == null) ? 0 : getCreateAt().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getPassword() == null) ? 0 : getPassword().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getUpdateAt() == null) ? 0 : getUpdateAt().hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((getUsername() == null) ? 0 : getUsername().hashCode()); return result; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(getClass().getSimpleName()); sb.append(" ["); sb.append("Hash = ").append(hashCode()); sb.append(", id=").append(id); sb.append(", name=").append(name); sb.append(", age=").append(age); sb.append(", email=").append(email); sb.append(", version=").append(version); sb.append(", createTime=").append(createTime); sb.append(", updateTime=").append(updateTime); sb.append(", deleted=").append(deleted); sb.append(", createAt=").append(createAt); sb.append(", password=").append(password); sb.append(", updateAt=").append(updateAt); sb.append(", username=").append(username); sb.append(", serialVersionUID=").append(serialVersionUID); sb.append("]"); return sb.toString(); } }
测试类:SpringbootRedisApplicationTests
@SpringBootTest class SpringbootRedisApplicationTests { /*操作Redis*/ @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Test public void redisTest() { ValueOperations<String, Object> redisTemplate = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue(); User user = new User(); user.setId(1L); user.setName("zhangsan"); user.setAge(18); System.out.println("存入redis"); redisTemplate.set("user", user); System.out.println("取出redis"); System.out.println(redisTemplate.get("user")); } }
我们来看下控制台打印的数据

看着很正常,但是如果我们去Redis客户端中去查看数据的话,明显看到的是一些乱码的数据,虽然这些数据不影响数据的传输,但是在我们看来,这些数据确实是比较难看得懂。
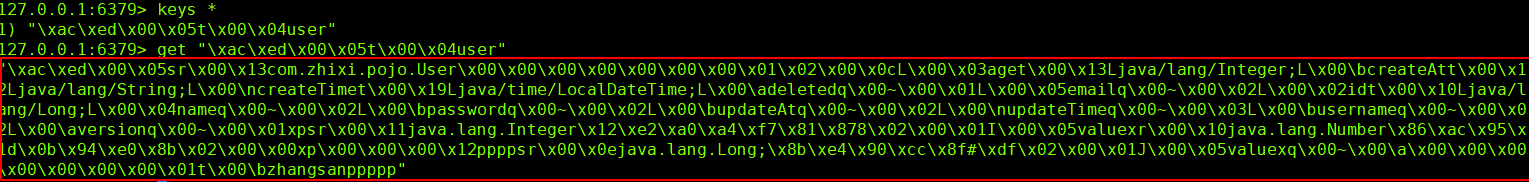
通过可视化工具来查看数据,也会发现是乱码的存在:
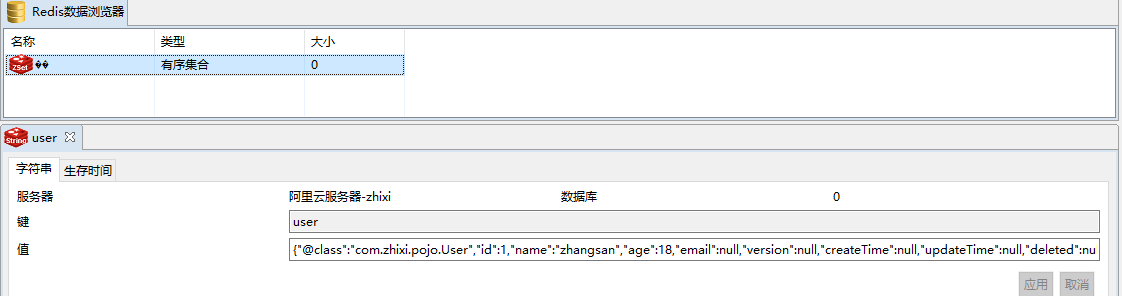
三、Redis的序列化
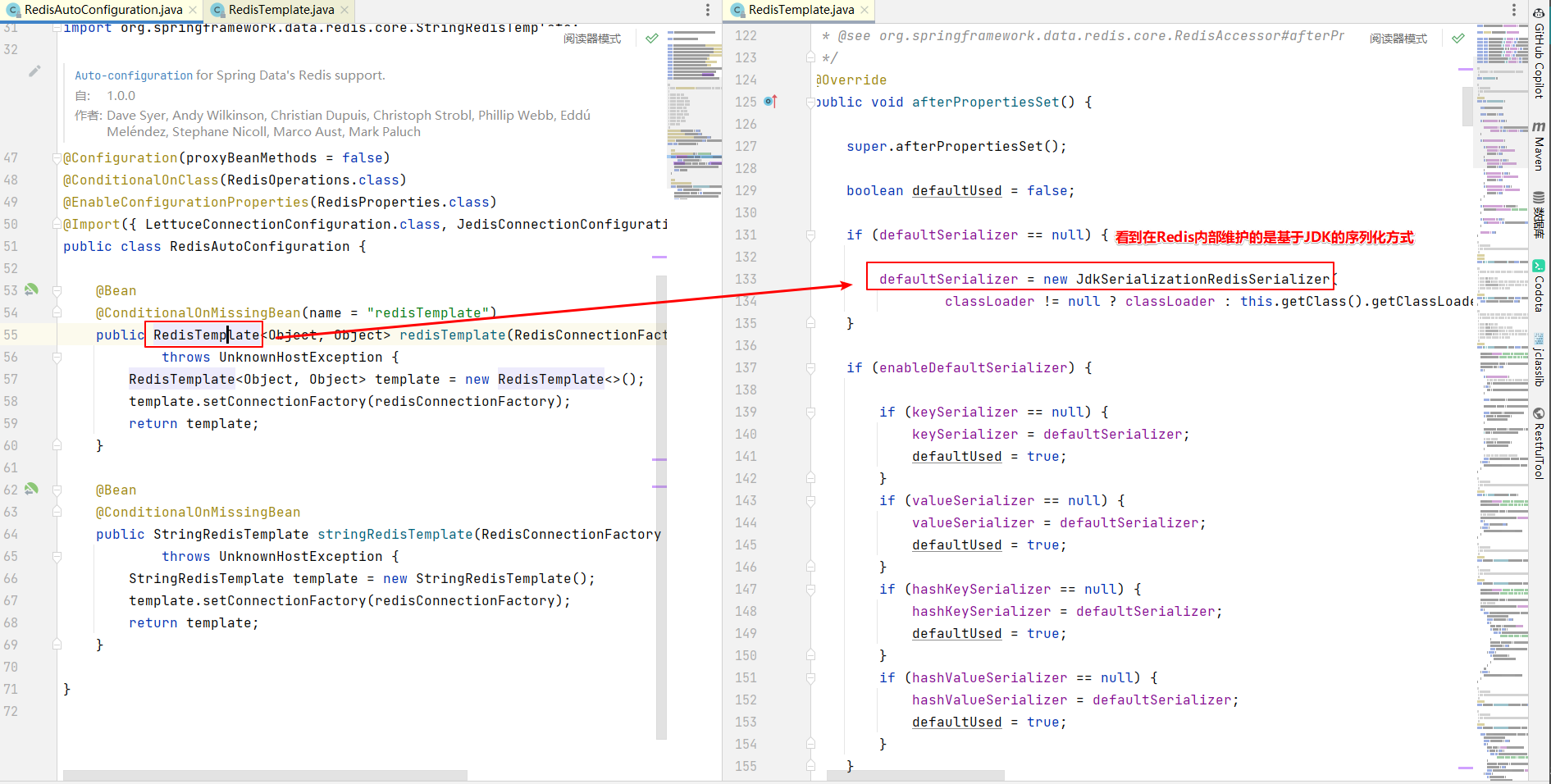
我们通常在传输数据的时候,肯定是比较想要统一格式,比如通过JSON字符串进行传输数据。
通过上面的RedisAutoConfiguration中,我们发现可以通过重写一个名为redisTemplate的Bean,就可以重新对Redis进行定制化,写个配置类,来进行重写Redis的序列化方式:
package com.zhixi.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; /** * @ClassName RedisConfig * @Author zhangzhixi * @Description Redis配置类 * @Date 2022-4-29 10:23 * @Version 1.0 */ @Configuration public class RedisConfig { /** * @param redisConnectionFactory:配置不同的客户端,这里注入的redis连接工厂不同: JedisConnectionFactory、LettuceConnectionFactory * @功能描述 :配置Redis序列化,原因如下: * (1) StringRedisTemplate的序列化方式为字符串序列化, * RedisTemplate的序列化方式默为jdk序列化(实现Serializable接口) * (2) RedisTemplate的jdk序列化方式在Redis的客户端中为乱码,不方便查看, * 因此一般修改RedisTemplate的序列化为方式为JSON方式【建议使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer】 */ @Bean(name = "redisTemplate") public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = serializer(); RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); // key采用String的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8); // value序列化方式采用jackson redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer); // hash的key也采用String的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8); //hash的value序列化方式采用jackson redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return redisTemplate; } /** * 此方法不能用@Ben注解,避免替换Spring容器中的同类型对象 */ public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer() { return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); } }
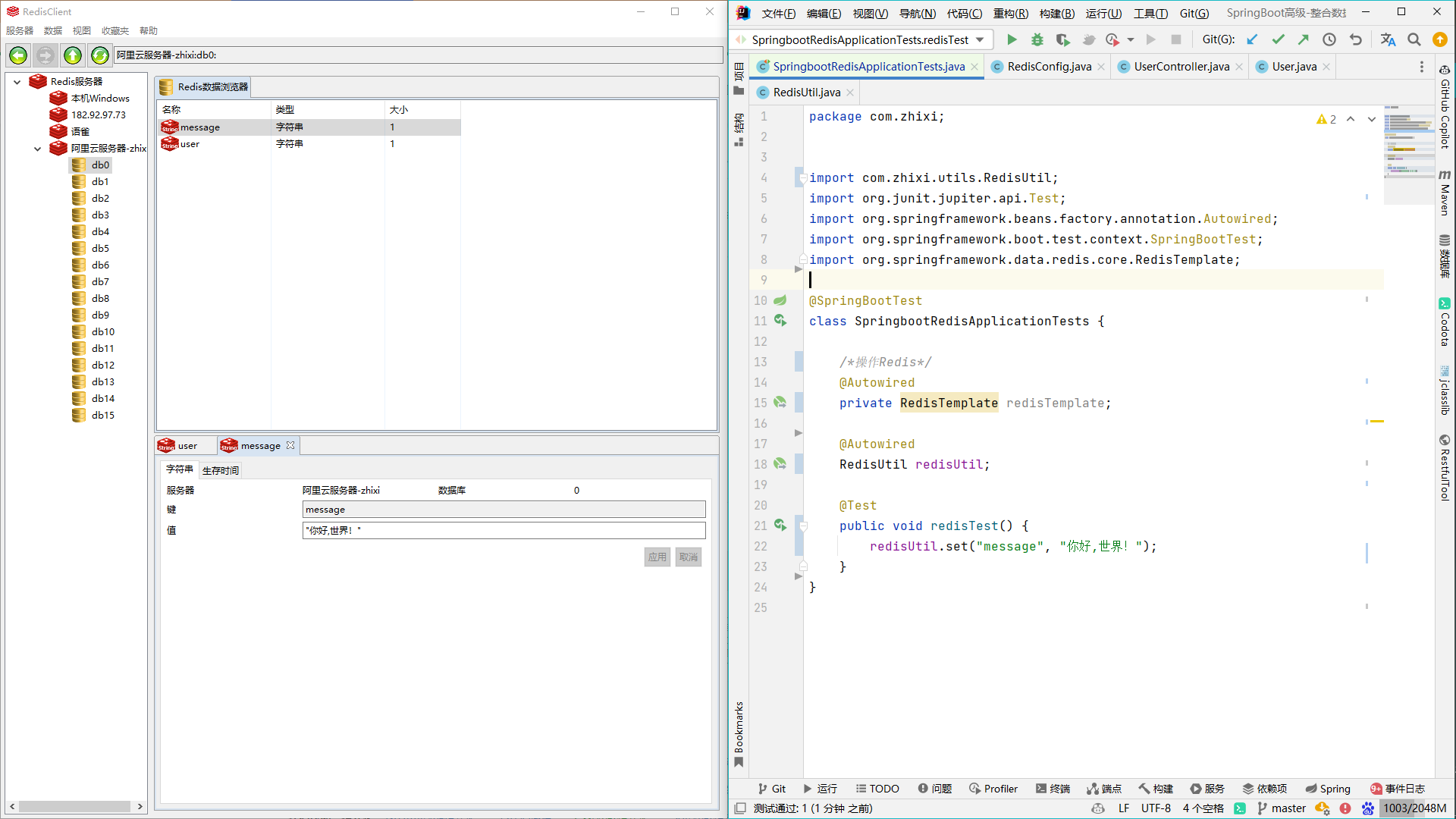
现在我们再继续测试一下上面的代码,看下这次存入的数据格式是否是我们想要的:发现这次存入的是JSON数据
四、Redis工具类
我们在SpringBoot中去操作Redis总是要写这么几个方法:

那么当我们频繁操作Redis的时候,这就会显得代码很冗余,加大了维护成本!
所以我们要编写自己的工具类去封装Redis中的方法!
这里只截取一部分,只要注入我们的redisTemplate,封装里面常用的的方法即可:
utils.RedisUtil.java

import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * @ClassName RedisUtil * @Author zhangzhixi * @Description redis工具类 * @Date 2022-4-29 10:29 * @Version 1.0 */ @Service public class RedisUtil { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; private static final double SIZE = Math.pow(2, 32); /** * 写入缓存 * * @param key 键 * @param offset 位 8Bit=1Byte * @return true成功 false失败 */ public boolean setBit(String key, long offset, boolean isShow) { boolean result = false; try { ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); operations.setBit(key, offset, isShow); result = true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } /** * 获取缓存 * * @param key 键 * @param offset 位 8Bit=1Byte * @return true成功 false失败 */ public boolean getBit(String key, long offset) { boolean result = false; try { ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); result = operations.getBit(key, offset); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } /** * 写入缓存-字符串 * * @param key 键 * @param value 值 * @return true成功 false失败 */ public boolean set(final String key, Object value) { boolean result = false; try { ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); operations.set(key, value); result = true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } /** * 写入缓存设置时效时间 * @param key 键 * @param value 值 * @param expireTime 时间(秒) * @return true成功 false失败 */ public boolean set(final String key, Object value, Long expireTime) { boolean result = false; try { ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); operations.set(key, value); redisTemplate.expire(key, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS); result = true; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return result; } /** * 批量删除对应的value * * @param keys 多个key */ public void remove(final String... keys) { for (String key : keys) { remove(key); } } /** * 删除对应的value * * @param key 键 */ public void remove(final String key) { if (exists(key)) { redisTemplate.delete(key); } } /** * 判断缓存中是否有对应的value * * @param key 键 * @return true存在 false不存在 */ public boolean exists(final String key) { return redisTemplate.hasKey(key); } /** * 读取缓存 * * @param key 键 * @return 值 */ public Object get(final String key) { Object result = null; ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); result = operations.get(key); return result; } /** * 哈希 添加 * * @param key 键 * @param hashKey 项 * @param value 值 */ public void hmSet(String key, Object hashKey, Object value) { HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = redisTemplate.opsForHash(); hash.put(key, hashKey, value); } /** * 哈希获取数据 * * @param key 键 * @param hashKey 项 * @return 值 */ public Object hmGet(String key, Object hashKey) { HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = redisTemplate.opsForHash(); return hash.get(key, hashKey); } /** * 列表添加 * * @param k 键 * @param v 值 */ public void lPush(String k, Object v) { ListOperations<String, Object> list = redisTemplate.opsForList(); list.rightPush(k, v); } /** * 列表获取 * * @param k 键 * @param l 起始位置 * @param l1 结束位置 * @return 值 */ public List<Object> lRange(String k, long l, long l1) { ListOperations<String, Object> list = redisTemplate.opsForList(); return list.range(k, l, l1); } /** * 集合添加 * * @param key 键 * @param value 值 */ public void add(String key, Object value) { SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet(); set.add(key, value); } /** * 集合获取 * * @param key 键 * @return 集合 */ public Set<Object> setMembers(String key) { SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet(); return set.members(key); } /** * 有序集合添加 * * @param key 键 * @param value 值 * @param scoure */ public void zAdd(String key, Object value, double scoure) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); zset.add(key, value, scoure); } /** * 有序集合获取 * * @param key 键 * @param scoure * @param scoure1 * @return */ public Set<Object> rangeByScore(String key, double scoure, double scoure1) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); redisTemplate.opsForValue(); return zset.rangeByScore(key, scoure, scoure1); } //第一次加载的时候将数据加载到redis中 public void saveDataToRedis(String name) { double index = Math.abs(name.hashCode() % SIZE); long indexLong = new Double(index).longValue(); boolean availableUsers = setBit("availableUsers", indexLong, true); } //第一次加载的时候将数据加载到redis中 public boolean getDataToRedis(String name) { double index = Math.abs(name.hashCode() % SIZE); long indexLong = new Double(index).longValue(); return getBit("availableUsers", indexLong); } /** * 有序集合获取排名 * * @param key 集合名称 * @param value 值 */ public Long zRank(String key, Object value) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); return zset.rank(key, value); } /** * 有序集合获取排名 * * @param key 集合名称 */ public Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> zRankWithScore(String key, long start, long end) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> ret = zset.rangeWithScores(key, start, end); return ret; } /** * 有序集合添加 * * @param key 键 * @param value 值 */ public Double zSetScore(String key, Object value) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); return zset.score(key, value); } /** * 有序集合添加分数 * * @param key * @param value * @param scoure */ public void incrementScore(String key, Object value, double scoure) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); zset.incrementScore(key, value, scoure); } /** * 有序集合获取排名 * * @param key 键 */ public Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> reverseZRankWithScore(String key, long start, long end) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> ret = zset.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores(key, start, end); return ret; } /** * 有序集合获取排名 * * @param key 集合名称 */ public Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> reverseZRankWithRank(String key, long start, long end) { ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> ret = zset.reverseRangeWithScores(key, start, end); return ret; } }
SpringBoot(SpringCache)整合Redis
基于SpringBoot(SpringCache)整合Redis+MybatisPlus
项目码云地址:https://gitee.com/zhang-zhixi/springboot-springcache-redis.git
参考链接:
SpringBoot实现Redis缓存(SpringCache+Redis的整合)
SpringBoot2.x—SpringCache(2)使用
Spring boot 之 spring-boot-starter-cache (整合redis)
一、前言知识说明
Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache ,ConcurrentMapCache等;
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
- 1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
缓存注解
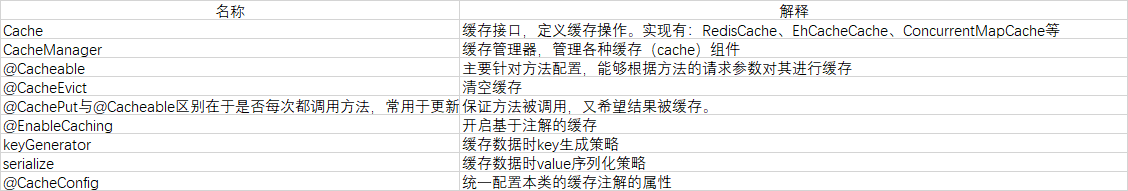
@Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数
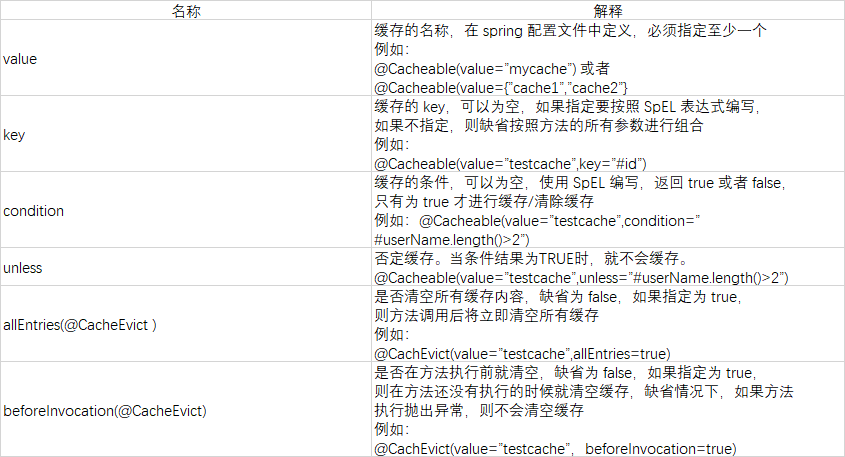
SpEL上下文数据
Spring Cache提供了一些供我们使用的SpEL上下文数据,下表直接摘自Spring官方文档:
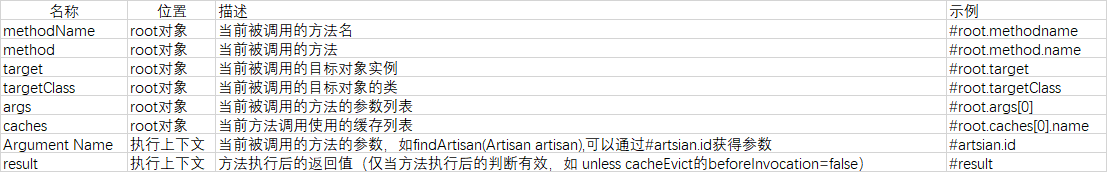
注意:
- 1.当我们要使用root对象的属性作为key时我们也可以将“#root”省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性。 如
- @Cacheable(key = "targetClass + methodName +#p0")
- 2.使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。 如:
- @Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
- @Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
SpEL提供了多种运算符:
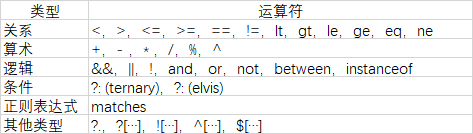
二、开始使用
pom文件
<!--阿里JSON格式化转换-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.79</version>
</dependency>
<!--整合Redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springboot2.x以后用得是lettuce:lettuce默认连接池使用 common-pool2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Spring缓存组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot-Web依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL数据库-默认是MYSQL8+-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--生成setter/getter方法-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
实体类
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonDeserialize; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer; import lombok.Data; import java.io.Serializable; import java.time.LocalDateTime; /** * @TableName user */ @TableName(value = "user") @Data public class User implements Serializable { /** * 主键ID */ @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private Long id; /** * 姓名 */ @TableField(value = "name") private String name; /** * 年龄 */ @TableField(value = "age") private Integer age; /** * 邮箱 */ @TableField(value = "email") private String email; /** * */ @TableField(value = "version") private Integer version; /** * 创建时间 */ @TableField(value = "create_time") @JsonDeserialize(using = LocalDateTimeDeserializer.class) @JsonSerialize(using = LocalDateTimeSerializer.class) private LocalDateTime createTime; /** * 更新时间 */ @TableField(value = "update_time") @JsonDeserialize(using = LocalDateTimeDeserializer.class) @JsonSerialize(using = LocalDateTimeSerializer.class) private LocalDateTime updateTime; /** * */ @TableField(value = "deleted") private Integer deleted; /** * */ @TableField(value = "create_at") private String createAt; /** * */ @TableField(value = "password") private String password; /** * */ @TableField(value = "update_at") private String updateAt; /** * */ @TableField(value = "username") private String username; @TableField(exist = false) private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; }
Redis配置类
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager; import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator; import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleKeyGenerator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @ClassName RedisConfiguration * @Author zhangzhixi * @Description Redis配置类 * @Date 2022-5-2 17:40 * @Version 1.0 */ @Configuration public class RedisConfiguration { /** * @param redisConnectionFactory redis连接工厂 * @功能描述 redis作为缓存时配置缓存管理器CacheManager,主要配置序列化方式、自定义 * <p> * 注意:配置缓存管理器CacheManager有两种方式: * 方式1:通过RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()获取到默认的RedisCacheConfiguration对象, * 修改RedisCacheConfiguration对象的序列化方式等参数【这里就采用的这种方式】 * 方式2:通过继承CachingConfigurerSupport类自定义缓存管理器,覆写各方法,参考: * https://blog.csdn.net/echizao1839/article/details/102660649 * <p> * 切记:在缓存配置类中配置以后,yaml配置文件中关于缓存的redis配置就不会生效,如果需要相关配置需要通过@value去读取 */ @Bean public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); redisCacheConfiguration = redisCacheConfiguration // 设置key采用String的序列化方式 .serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8)) //设置value序列化方式采用jackson方式序列化 .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(serializer())) //当value为null时不进行缓存 .disableCachingNullValues() // 配置缓存空间名称的前缀 .prefixCacheNameWith("spring-cache:") //全局配置缓存过期时间【可以不配置】 .entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30L)); //专门指定某些缓存空间的配置,如果过期时间【主要这里的key为缓存空间名称】 Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> map = new HashMap<>(); return RedisCacheManager .builder(redisConnectionFactory) .cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration) //默认配置 .withInitialCacheConfigurations(map) //某些缓存空间的特定配置 .build(); } /** * 自定义缓存的redis的KeyGenerator【key生成策略】 * 注意: 该方法只是声明了key的生成策略,需在@Cacheable注解中通过keyGenerator属性指定具体的key生成策略 * 可以根据业务情况,配置多个生成策略 * 如: @Cacheable(value = "key", keyGenerator = "keyGenerator") */ @Bean public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() { /* target: 类 method: 方法 params: 方法参数 */ return (target, method, params) -> { //获取代理对象的最终目标对象 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(target.getClass().getSimpleName()).append(":"); sb.append(method.getName()).append(":"); //调用SimpleKey的key生成器 Object key = SimpleKeyGenerator.generateKey(params); return sb.append(key); }; } /** * @param redisConnectionFactory:配置不同的客户端,这里注入的redis连接工厂不同: JedisConnectionFactory、LettuceConnectionFactory * @功能描述 :配置Redis序列化,原因如下: * (1) StringRedisTemplate的序列化方式为字符串序列化, * RedisTemplate的序列化方式默为jdk序列化(实现Serializable接口) * (2) RedisTemplate的jdk序列化方式在Redis的客户端中为乱码,不方便查看, * 因此一般修改RedisTemplate的序列化为方式为JSON方式【建议使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer】 */ @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer = serializer(); RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); // key采用String的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8); // value序列化方式采用jackson redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer); // hash的key也采用String的序列化方式 redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8); //hash的value序列化方式采用jackson redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(genericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return redisTemplate; } /** * 此方法不能用@Ben注解,避免替换Spring容器中的同类型对象 */ public GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer() { return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); } }
Service层
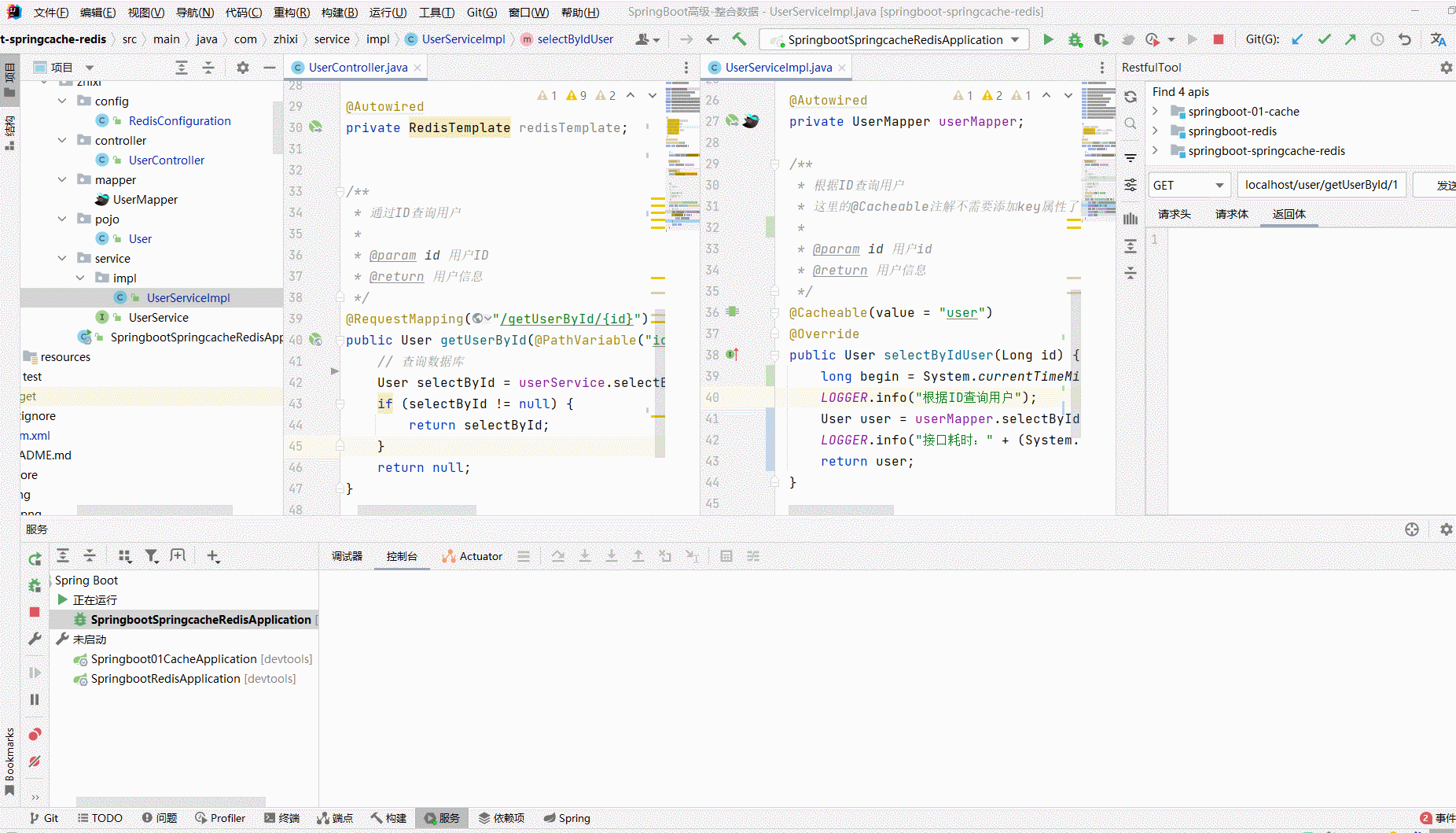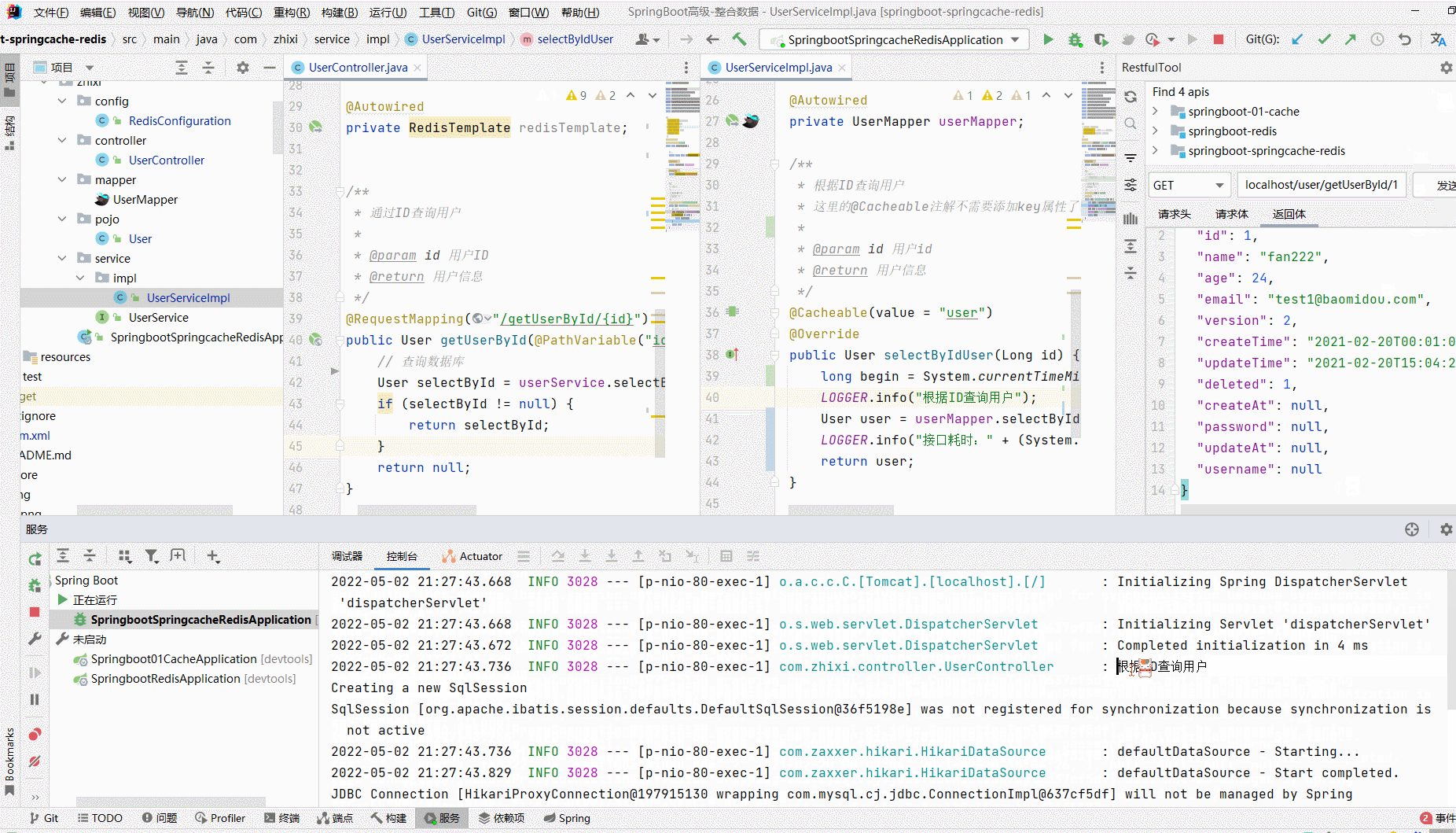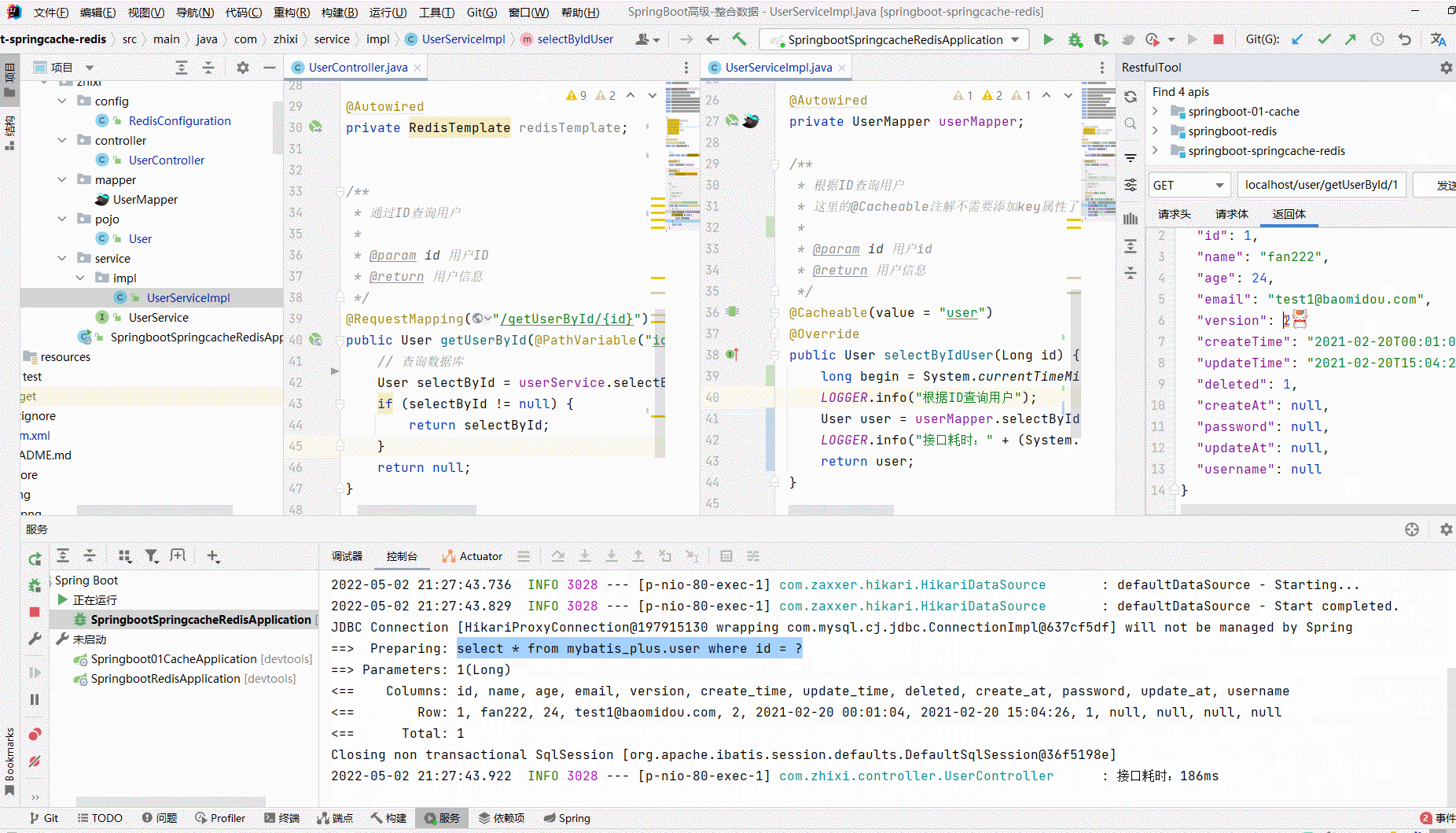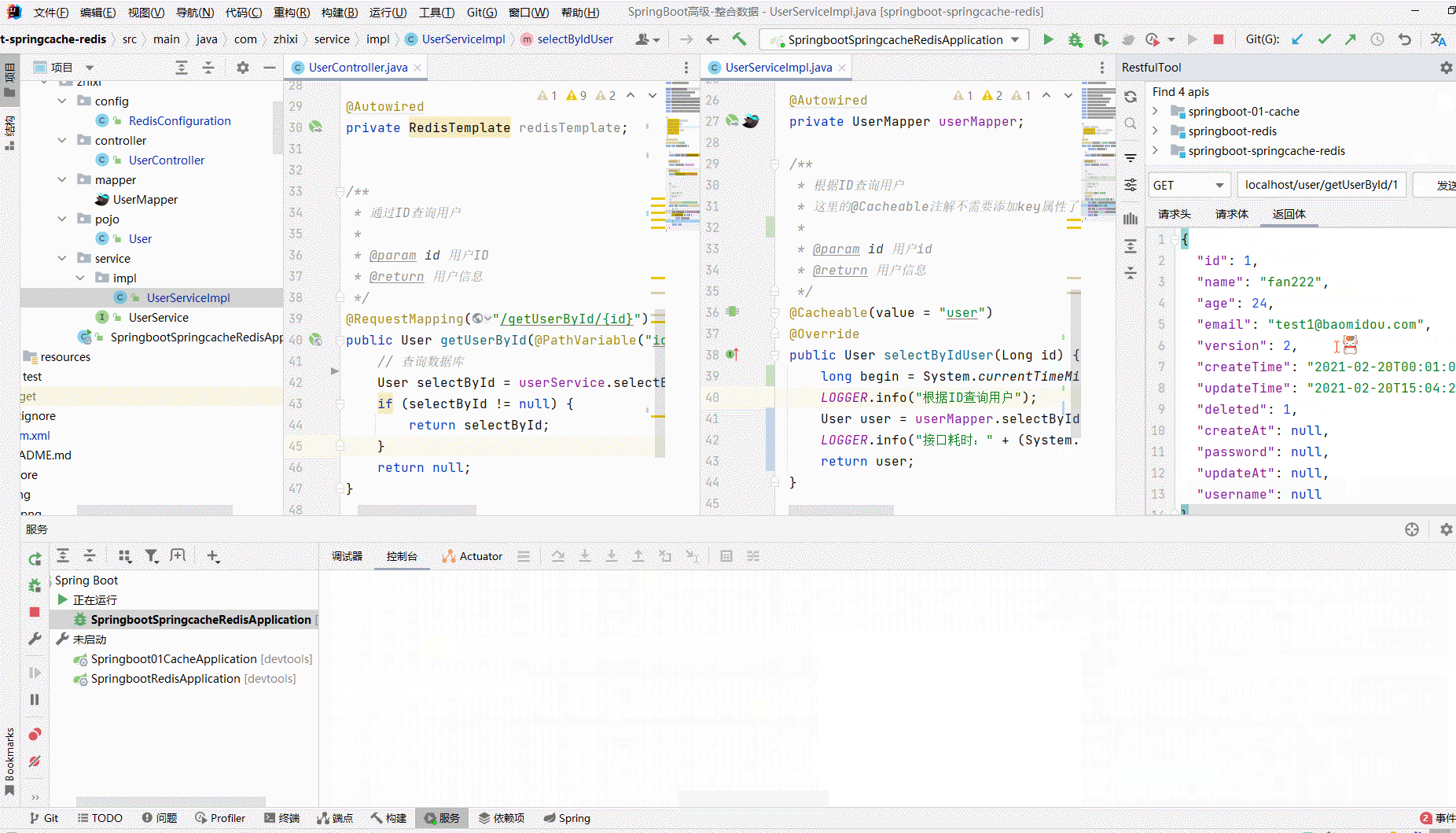
/** * @author zhangzhixi * @description 针对表【user】的数据库操作Service实现 * @createDate 2022-05-01 12:15:07 */ @Service @CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user", keyGenerator = "keyGenerator") public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService { // 日志 private static final org.slf4j.Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class); @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; /** * 根据ID查询用户 * 这里的@Cacheable注解不需要添加key属性了,因为已经在全局制定过了key的生成策略 * @param id 用户id * @return 用户信息 */ @Cacheable(value = "user") @Override public User selectByIdUser(Long id) { LOGGER.info("根据ID查询用户"); return userMapper.selectByIdUser(id); } }
Controller层
import com.zhixi.pojo.User; import com.zhixi.service.UserService; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @ClassName UserController * @Author zhangzhixi * @Description 用户访问 * @Date 2022-5-1 12:15 * @Version 1.0 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { // 日志 private static final org.slf4j.Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class); @Autowired private UserService userService; @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /** * 通过ID查询用户 * * @param id 用户ID * @return 用户信息 */ @RequestMapping("/getUserById/{id}") public User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { // 查询数据库 LOGGER.info("查询数据库"); User selectById = userService.selectByIdUser(id); if (selectById != null) { return selectById; } return null; } }
启动类
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; @EnableCaching //开启缓存 @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.zhixi.mapper") public class SpringbootSpringcacheRedisApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSpringcacheRedisApplication.class, args); } }
测试
三、小结
我觉得使用Springcache与直接使用SpringBoot整合Redis的区别,在于多了几个注解,去替代写一些重复的代码
- 查寻缓存中是否存在数据,如果存在则直接返回结果
- 如果不存在则查询数据库,查询出结果后将结果存入缓存并返回结果
- 数据更新时,先更新数据库
- 然后更新缓存,或者直接删除缓存
/** * 通过ID查询用户 * * @param id 用户ID * @return 用户信息 */ @RequestMapping("/getUserById/{id}") public User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { // 查询缓存 String user = JSONObject.toJSONString(redisUtil.get("user_" + id)); if ("null".equals(user)) { // 查询数据库 LOGGER.info("查询数据库"); User selectById = userMapper.selectById(id); if (selectById != null) { // 添加缓存 redisUtil.set("user_" + id, JSONObject.toJSON(selectById)); return selectById; } } LOGGER.info("从缓存中获取数据"); return JSONObject.parseObject(user, User.class); }
上面代码所示,就是我们上面描述的使用Redis作为缓存中间件来进行缓存的实列,我们不难发现,我们的查询和存储时都是使用到了SpringBoot整合Redis后的相关API的,并且项目中所有的使用缓存的地方都会如此使用,这样子提升了代码的复杂度,我们程序员更应该关注的是业务代码,因此我们需要将查询缓存和存入缓存这类似的代码封装起来用框架来替我们实现,让我们更好的去处理业务逻辑。
那么我们如何让框架去帮我们自动处理呢,这不就是典型的AOP思想吗?
是的,Spring Cache就是一个这样的框架。它利用了AOP,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,并且进行了合理的抽象,业务代码不用关心底层是使用了什么缓存框架,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能了。而且Spring Cache也提供了很多默认的配置,用户可以3秒钟就使用上一个很不错的缓存功能。















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号