H5-29 定位
1、定义
position属性指定了元素的定位类型
| 值 | 描述 |
| relative | 相对定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位 |
其中,绝对定位和固定定位会脱离文档流
设置定位之后:可以使用四个方向进行调整位置:left、top、right、bottom
2、相对定位
<div> </div>
div{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}

3、绝对定位
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a2"></div>
<div class="a3"></div>
.a1{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}

4、固定定位
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a2"></div>
<div class="a3"></div>
.a1{
width:100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: fixed;
right: 100px;
bottom: 100px;
}
.a2{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color:blueviolet;
}
.a3{
width:150px;
height: 150px;
background-color:blue;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
h3{
height: 150px;
}
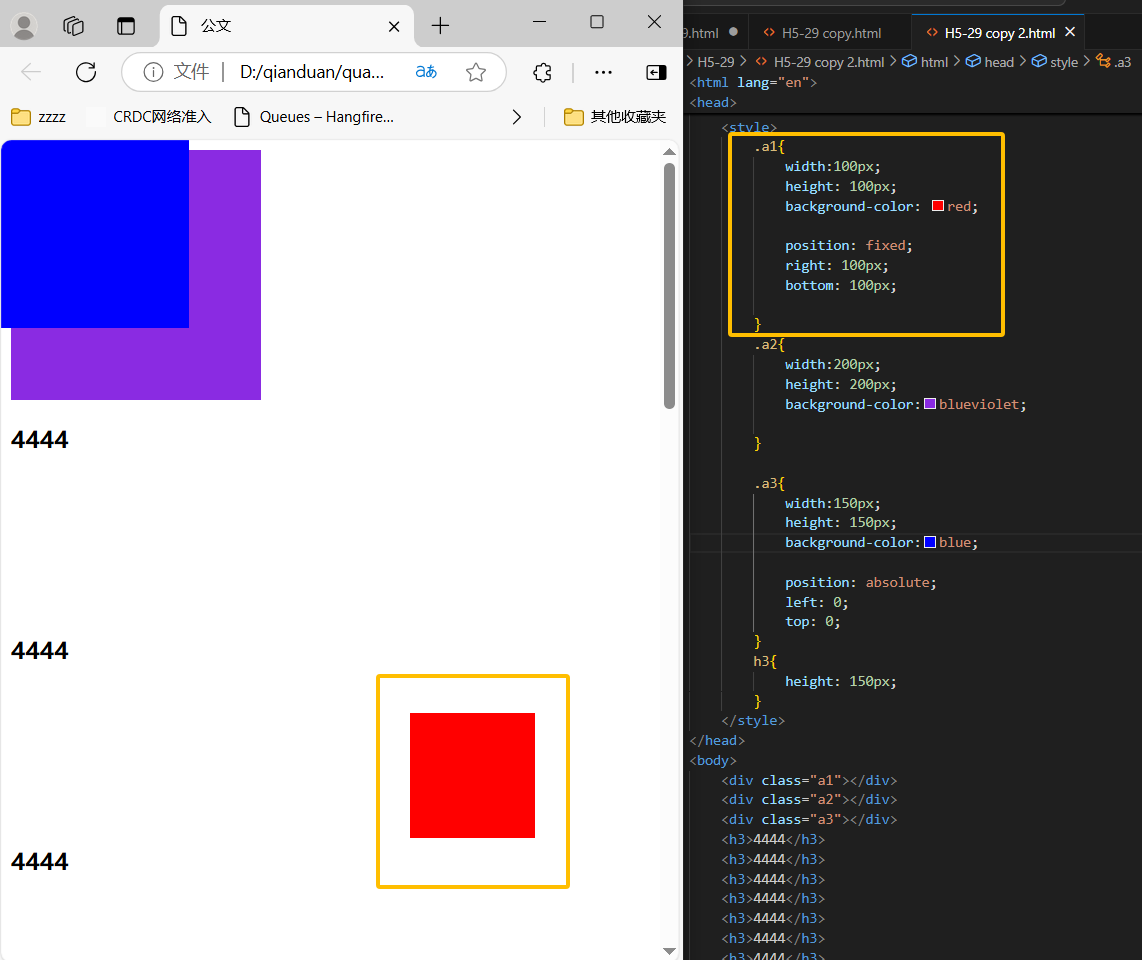
温馨提示:设定位置之后,相对定位和绝对定位他是相对于具有定位的父级元素进行位置调整,如果父级元素不存在定位,则继续向上逐级寻找,直到顶层文档
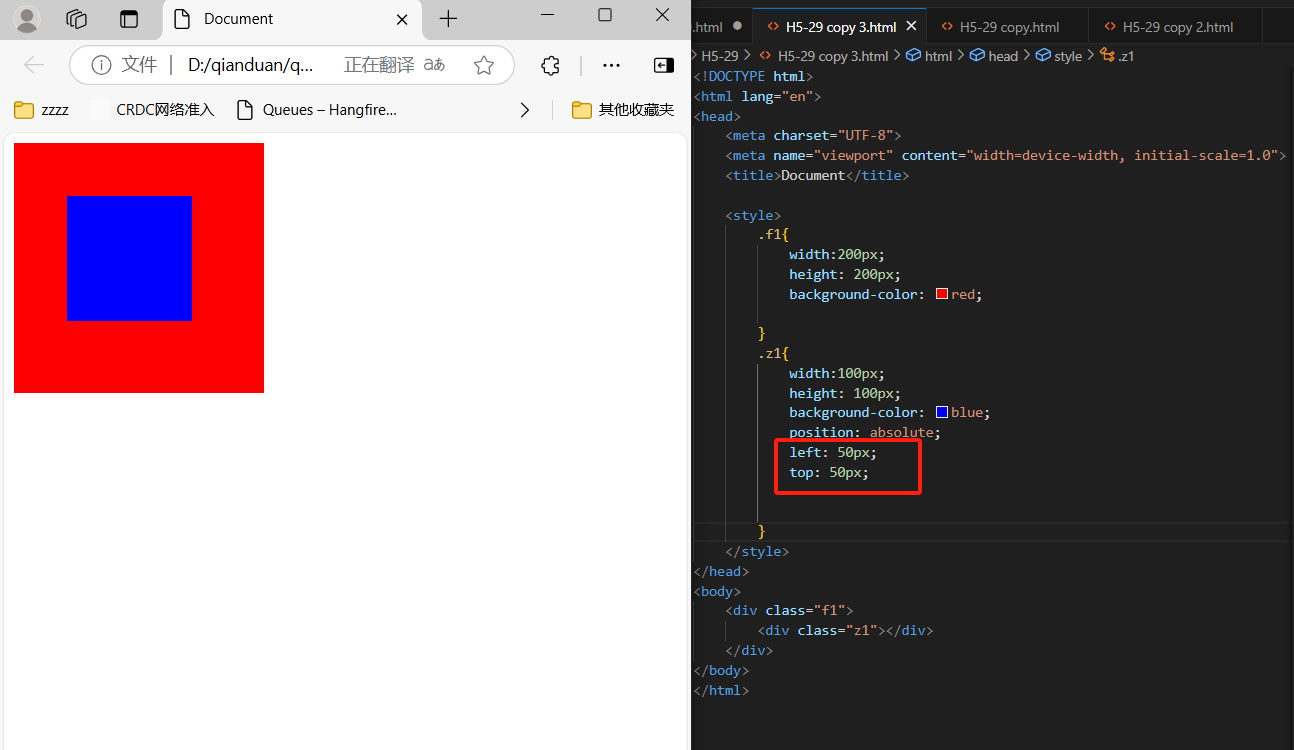
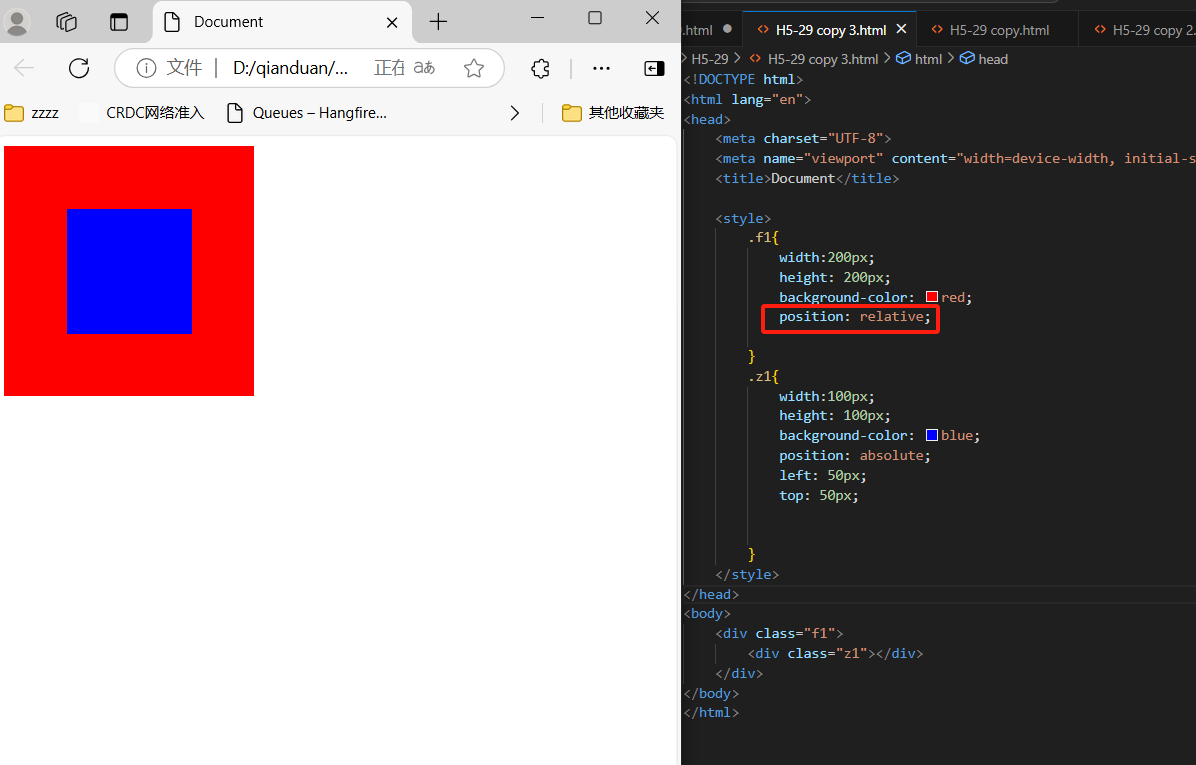
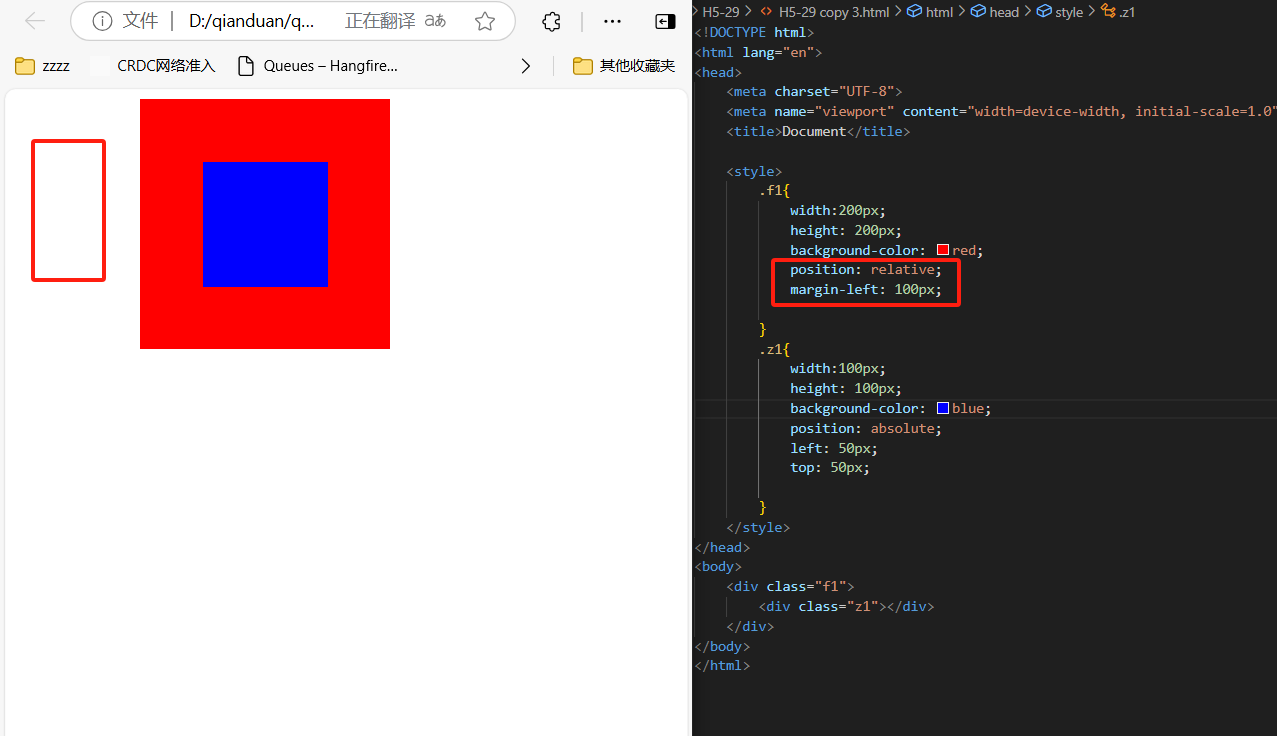
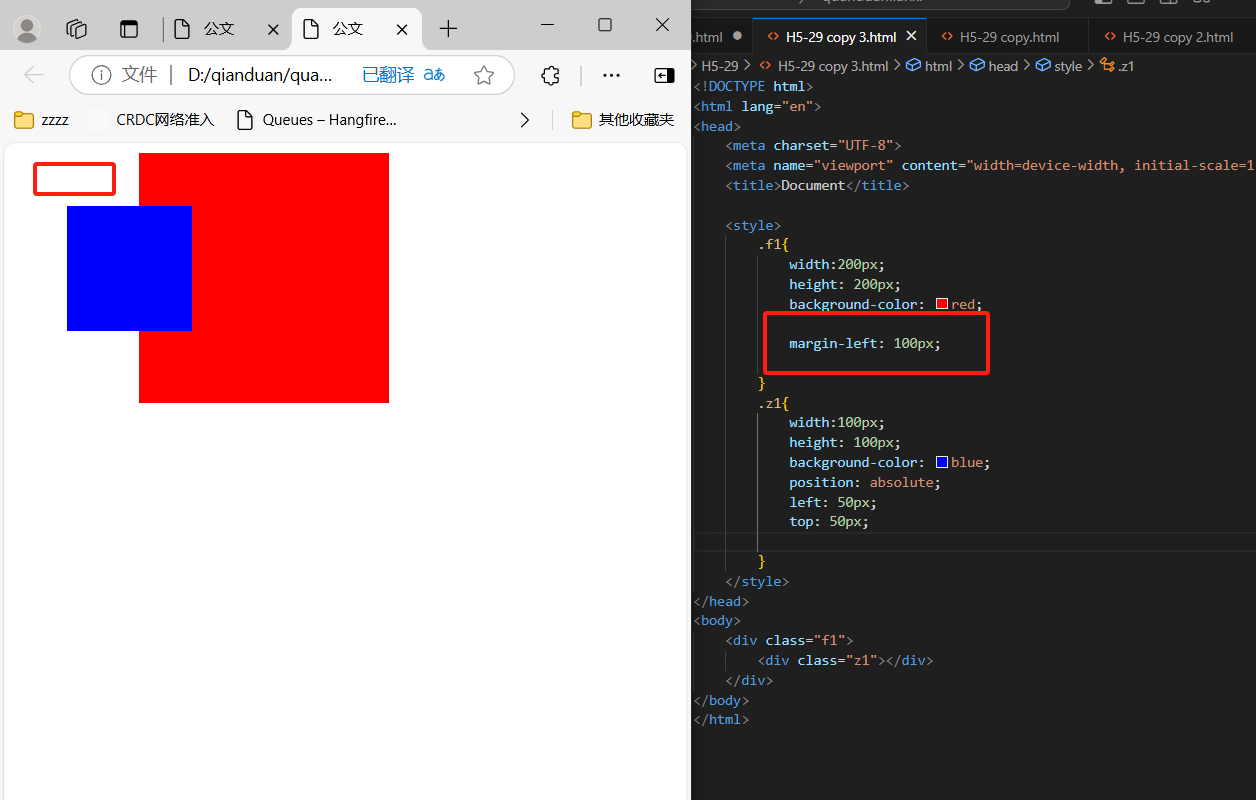
5、
<div class="f1">
<div class="z1"></div>
</div>
.f1{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.z1{
width:100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}

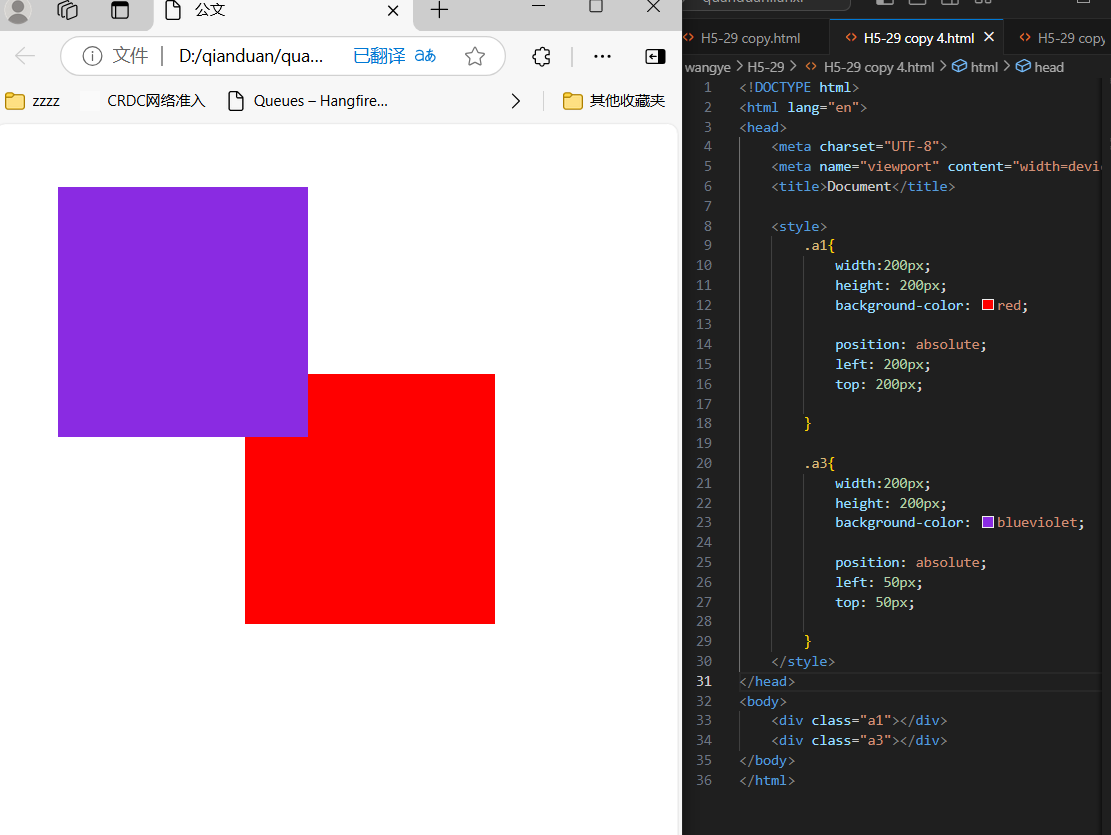
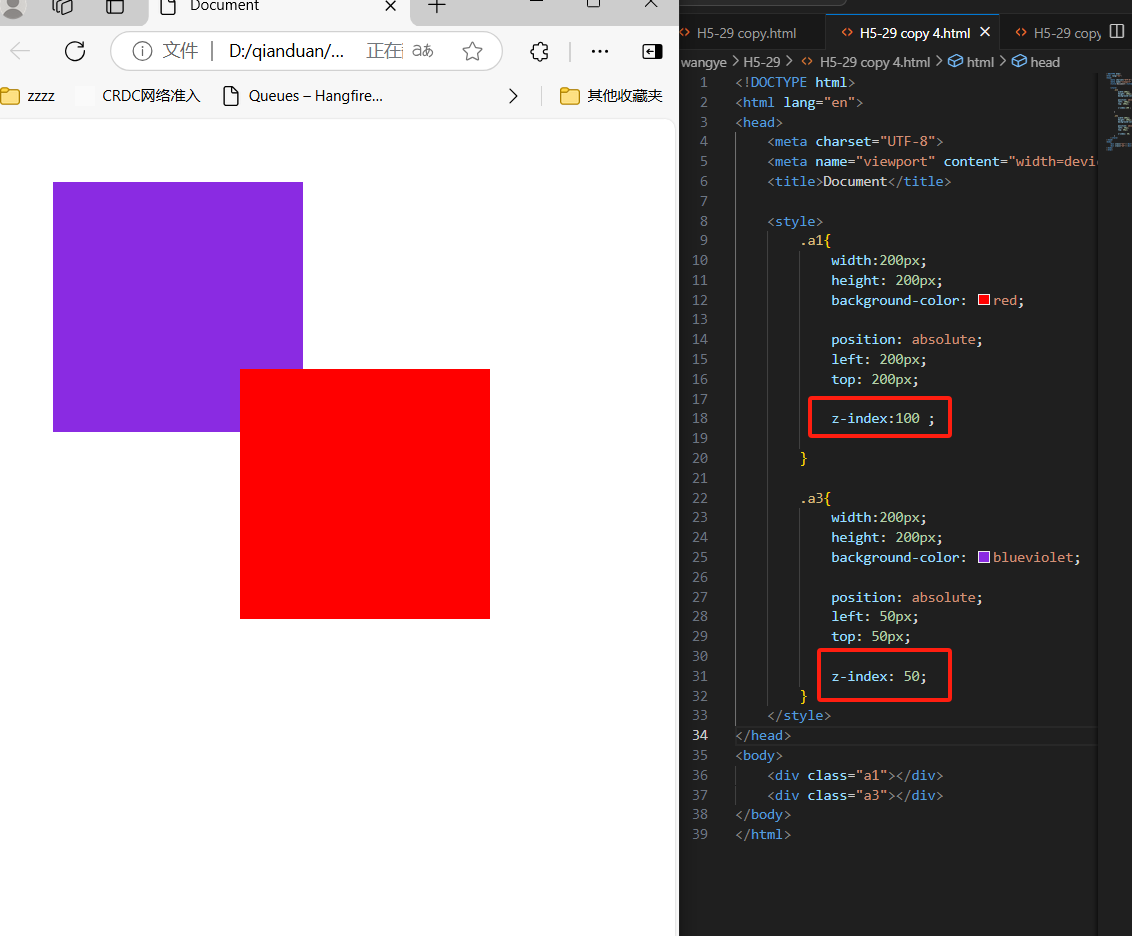
6、Z-index
z-index属性设置元素的堆叠顺序。拥有更高堆叠顺序的总是会处于堆叠顺序较低的元素的前面
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a3"></div>
.a1{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
z-index:100 ;
}
.a3{
width:200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blueviolet;
position: absolute;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
z-index: 50;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号