首先我们创建一个名为GetAllCustomers()的方法,代码如下:
 [SqlProcedure]
[SqlProcedure]
 public static void GetAllCustomers()
public static void GetAllCustomers()
 {
{
 SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
 ("context connection=true");
("context connection=true");
 cnn.Open();
cnn.Open();
 SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
 cmd.Connection = cnn;
cmd.Connection = cnn;
 cmd.CommandText = "select * from customers";
cmd.CommandText = "select * from customers";
 SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
 SqlContext.Pipe.Send(reader);
SqlContext.Pipe.Send(reader);
 reader.Close();
reader.Close();
 cnn.Close();
cnn.Close();
 }
}
这个GetAllCustomers()方法用了一个[SqlProcedure]属性来修饰。 在方法内创建一个SqlConnection和一个SqlCommand对象。 然后使用ExecuteReader()方法来执行SELECT语句。 接下来用Send()方法将取得的SqlDataReader数据发送到客户端。 最后就是关闭SqlDataReader和SqlConnection。 在这种方法中,是我们自己创建的SqlDataReader。 其实,我们也可以把这个任务交给SqlContext类去完成,代码如下:
 [SqlProcedure]
[SqlProcedure]
 public static void GetCustomerByID
public static void GetCustomerByID
 (SqlString CustomerID)
(SqlString CustomerID)
 {
{
 SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
 ("context connection=true");
("context connection=true");
 cnn.Open();
cnn.Open();
 SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
 cmd.Connection = cnn;
cmd.Connection = cnn;
 cmd.CommandText = "select * from customers
cmd.CommandText = "select * from customers
 where customerid=@p1";
where customerid=@p1";
 SqlParameter p1 = new SqlParameter("@p1", CustomerID);
SqlParameter p1 = new SqlParameter("@p1", CustomerID);
 cmd.Parameters.Add(p1);
cmd.Parameters.Add(p1);
 SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd);
SqlContext.Pipe.ExecuteAndSend(cmd);
 cnn.Close();
cnn.Close();
 }
}
GetCustomerByID()方法需要一个参数 – CustomerID,它将从Customers表中返回某个customer的记录。 这个方法内的代码,除了ExecuteAndSend()方法外,你应该都已经比较熟悉了。 ExecuteAndSend()方法接收一个SqlCommand对象作为参数,执行它就会返回数据集给客户端。
有输出参数的存储过程
我们在使用存储过程时,经常会通过输出参数返回一个经过计算的值。 所以,现在让我们来看一看如何创建具有一个或多个输出参数的存储过程。
 [SqlProcedure]
[SqlProcedure]
 public static void GetCompanyName
public static void GetCompanyName
 (SqlString CustomerID,out SqlString CompanyName)
(SqlString CustomerID,out SqlString CompanyName)
 {
{
 SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
SqlConnection cnn = new SqlConnection
 ("context connection=true");
("context connection=true");
 cnn.Open();
cnn.Open();
 SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
 cmd.Connection = cnn;
cmd.Connection = cnn;
 cmd.CommandText = "select companyname from
cmd.CommandText = "select companyname from
 customers where customerid=@p1";
customers where customerid=@p1";
 SqlParameter p1 = new SqlParameter
SqlParameter p1 = new SqlParameter
 ("@p1", CustomerID);
("@p1", CustomerID);
 cmd.Parameters.Add(p1);
cmd.Parameters.Add(p1);
 object obj = cmd.ExecuteScalar();
object obj = cmd.ExecuteScalar();
 cnn.Close();
cnn.Close();
 CompanyName = obj.ToString();
CompanyName = obj.ToString();
 }
}
这是一个名为GetCompanyName()的方法,它需要两个参数。 第一个参数是CustomerID,它是一个输入参数;第二个参数是CompanyName,它是一个输出参数(用关键字out来指明)。 这两个参数都是SqlString类型的。 GetCompanyName()方法会接收一个CustomerID参数,然后返回CompanyName(作为输出参数)。
该方法内的代码首先设置了SqlConnection和SqlCommand对象。 然后,使用ExecuteScalar()方法来执行SELECT语句。 ExecuteScalar()方法返回的值是一个object类型,它其实就是公司名称。 最后将输出参数CompanyName设置为这个值。
返回一行或多行自定义数据的存储过程
我们在使用存储过程时,更多的还是从某些表中读取数据。 但是,某些情况下我们需要的数据可能不在任何表里。 例如,你可能会基于某些计算来生成一个数据表格。 因为它的数据不是从表中获得的,所以上面的方法就不在适用了。 幸运的是,SQL Server的CLR集成特性给我们提供了一个解决这个问题的方法。 请看如下代码:
 [SqlProcedure]
[SqlProcedure]
 public static void GetCustomRow()
public static void GetCustomRow()
 {
{
 SqlMetaData[] metadata = new SqlMetaData[2];
SqlMetaData[] metadata = new SqlMetaData[2];
 metadata[0= new SqlMetaData
metadata[0= new SqlMetaData
 ("CustomerID", SqlDbType.NVarChar,50);
("CustomerID", SqlDbType.NVarChar,50);
 metadata[1= new SqlMetaData
metadata[1= new SqlMetaData
 ("CompanyName", SqlDbType.NVarChar,50);
("CompanyName", SqlDbType.NVarChar,50);
 SqlDataRecord record = new SqlDataRecord(metadata);
SqlDataRecord record = new SqlDataRecord(metadata);
 record.SetString(0, "ALFKI");
record.SetString(0, "ALFKI");
 record.SetString(1, "Alfreds Futterkiste");
record.SetString(1, "Alfreds Futterkiste");
 SqlContext.Pipe.Send(record);
SqlContext.Pipe.Send(record);
 }
}
GetCustomRow()方法会返回一条记录并发送给客户端。 这个方法首先声明了一个SqlMetaData对象。 当你要用到自定义列的时候,就可以使用这个SqlMetaData类。 在我们的示例中,创建了两个类型为NVarChar,长度为50的列。然后创建了一个SqlDataRecord对象。 SqlDataRecord类可以用来表示一个自定义行。 它的构造函数需要一个SqlMetaData数组作为参数。 SqlDataRecord对象的SetString()方法用来设置列的值。 另外,还有许多不同的类似SetString()这样的方法,可以用来处理不同的数据类型。 最后,调用Send()方法将SqlDataRecord对象发送到客户端。
在上面的示例中,我们只返回了一行数据给调用者。 那么,如果要返回多行呢? 请看下面的代码:
 [SqlProcedure]
[SqlProcedure]
 public static void GetMultipleCustomRows()
public static void GetMultipleCustomRows()
 {
{
 SqlMetaData[] metadata = new SqlMetaData[2];
SqlMetaData[] metadata = new SqlMetaData[2];
 metadata[0= new SqlMetaData
metadata[0= new SqlMetaData
 ("CustomerID", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 50);
("CustomerID", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 50);
 metadata[1= new SqlMetaData
metadata[1= new SqlMetaData
 ("CompanyName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 50);
("CompanyName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 50);
 SqlDataRecord record = new SqlDataRecord(metadata);
SqlDataRecord record = new SqlDataRecord(metadata);
 SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsStart(record);
SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsStart(record);
 record.SetString(0, "ALFKI");
record.SetString(0, "ALFKI");
 record.SetString(1, "Alfreds Futterkiste");
record.SetString(1, "Alfreds Futterkiste");
 SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsRow(record);
SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsRow(record);
 record.SetString(0, "ANATR");
record.SetString(0, "ANATR");
 record.SetString(1, "Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados");
record.SetString(1, "Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados");
 SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsRow(record);
SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsRow(record);
 SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsEnd();
SqlContext.Pipe.SendResultsEnd();
 }
}
GetMultipleCustomRows()方法将会返回多个SqlDataRecord对象到客户端。 接下来创建自定义列和设置列的值都和之前的例子一样。 但是,我们使用的是SendResutlsStart()方法来传输数据。 SendResultsRow()方法也是发送一个SqlDataRecord对象到客户端,但是我们可以多次调用它,从而做到发送多条记录。 最后,调用SendResultsEnd()方法用来标记已经完成数据传输操作。
我们已经开发完了存储过程。 现在就可以将这个项目编译为一个程序集(.DLL)。 但是我们的工作并没有到此结束。 我们还需要部署这个程序集和存储过程到SQL Server数据库。 有两种方法可以完成这个工作 – 手动和自动。 手动方法是使用T-SQL语句注册你的程序集,并将存储过程部署到SQL Server数据库中。 在本例中,我将使用自动的方法来部署存储过程到SQL Server数据库。
右键单击你的项目,然后在菜单中选择“部署”选项。
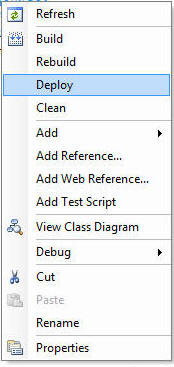
如此就会自动地完成注册程序集和部署存储过程的工作。 注意,只有在你创建项目时添加了数据库引用的时候,才会出现“部署”选项。 如果因为某些原因你没能添加数据库引用,那么你可以通过项目属性对话框来设置它。
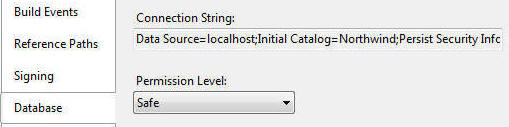
如果你在SQL Server Management Studio查看Northwind数据库的话,那么就应该可以看到和下图相似的结果。
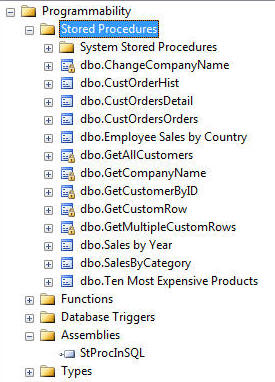
注意,在存储过程节点下出现了我们创建的所有方法(有“锁”图标的),并且在程序集节点下出现了我们的程序集。
就是这些东西,很简单吧。 现在你就可以在你的程序中调用这些存储过程了。 你也可以在SQL Server Management Studio中来测试它们。 










 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号