shell编程3-循环控制
脚本实战
nginx管理脚本
源码安装 NGINX
预先安装编译安装依赖的库
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake make yum -y install zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel pcre pcre-devel 或者 LANG=C yum -y groupinstall "Development tools"
去官网找包(稳定版)下载
[root@localhost ~]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.28.0.tar.gz
1、解压缩
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.28.0.tar.gz
2、进到解压目录进行编译安装
[root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.28.0
#定制安装信息,指定安装目录 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx_1.28.0
#或者 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-stream --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_sub_module
#1、--prefix 指定安装的目录,/usr/local/nginx 是安装目录
#2、带ssl stub_status模块 添加stream模块 –with-stream,这样就能传输tcp协议了
#3、http_stub_status_module 状态监控
#4、http_ssl_module 配置https
#5、stream 配置tcp得转发
#6、http_gzip_static_module 压缩
#7、http_sub_module 替换请求
3、编译
make -j 2 #并发2个任务去编译
4、安装
make install
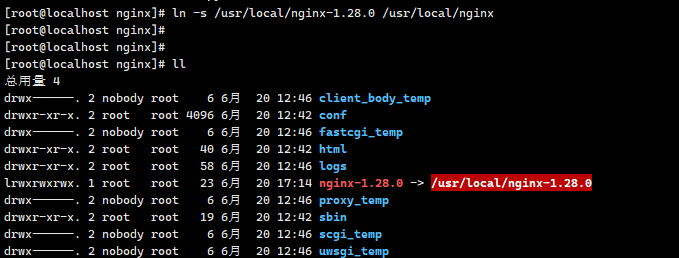
# 将程序设定一个软连接,便于后续的升级
[root@localhost nginx]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.28.0 /usr/local/nginx
注意:现在百分之90,能用上的软件,都提供了rpm包. --->使用户可以使用yum直接安装使用.
补充:连接多个命令组成一条大命令
分号:左边命令运行完毕,无论成功与否,都会执行左边的命令。
make j 2;make install
&&:左边命令运行成功之后才能执行右边的命令
make j 2 && make install
常用命令:
yum install net-tools -y
netstat -an |grep 80
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ps aux |grep nginx
pkill -9 nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
ll /usr/local/nginx/conf/
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
[root@localhost scripts]# netstat -an |grep ":80\b"
nginx_manager.sh脚本要实现哪些功能:start|stop|reload|restart|status

#!/bin/bash - #如果给脚本指定的命令行参数的数目小于1 ,则显示脚本的使用方法信 if [ $# -ne 1 ]; then echo "Usage: $0 start|stop|reload|restart|status" exit 1 fi args=$1 function f1() { if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "nginx $args 成功" else echo "nginx $args 失败" fi } #if [ "$1" = "start" ]; then # pass #elif [ "$1" = "stop" ]; then # pass #elif [ "$1" = "restart" ]; then # pass #elif [ "$1" = "staus" ]; then # pass # #fi case $1 in start) #判断如果已经是启动状态,只打印提示信息,nginx已经启动了,否则运行启动命令,并判断启动命令是否>运行成功。 netstat -an |grep ":80\b" &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "nginx原本已经启动了" else /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx &>/dev/null #if [ $? -eq 0 ];then # echo "nginx 启动成功" #else # echo "nginx 启动失败" #fi f1 fi ;; stop) #判断如果已经是关系状态,只打印提示信息,nginx已经关闭了,否则运行关闭命令,并判断关闭命令是否>运行成功。 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop &>/dev/null #if [ $? -eq 0 ];then # echo "nginx 关闭成功" #else # echo "nginx 关闭失败" #fi f1 ;; reload) /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx &>/dev/null f1 ;; restart) #先关闭 再启动 并判断是否重启成功 先判断如果是已经启动就直接关闭再启动 netstat -an |grep ":80\b" &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop &>/dev/null fi sleep 3 #再启动 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx &>/dev/null #判断是否重启成功 f1 ;; status) /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx &>/dev/null ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 start|stop|reload|restart|status" ;; esac
两种条件循环
循环就是重复做一件事情
while循环和until循环
while循环语法:
while 条件为真 do 代码块 done
until循环语法:
until 条件为假 do 代码块 done
区别是while的条件为真的时候,才会运行一次代码块,运行完一次之后会回过头来再判断一次条件是否为真,如果为真再执行一次代码块,再回头进行判断条件是否为真,直到条件为假也就停了。
而until是条件为假的时候它才执行代码块。
while循环脚本:
#!/bin/bash - i=0 #while true while [ $i -lt 6 ] do echo $i let i++ done
#!/bin/bash - i=0 until [ $i -eq 5 ] do echo $i let i++ done

#!/bin/bash - i=0 #while true #while (( i < 6 )) #do # echo $i # let i++ #done until (( i > 5 )) do echo $i let i++ done
break和continue
循环体内会用到的两个关键字
break:终止本层循环,意味着本层循环整体结束。
continue:继续的意思,终止本次循环,直接进入下一次。
continue与continue同一级别的代码永远运行不到。
循环体的最后一步代码也不能是continue。

#!/bin/bash - i=1 while [ $i -lt 6 ] do if [ $i -eq 3 ]; then let i++ continue fi echo $i let i++ done

#!/bin/bash - i=1 while [ $i -lt 6 ] do if [ $i -eq 3 ]; then let i++ break fi echo $i let i++ done
写一个跳板机程序:具体要求:
1、执行脚本就输出主机信息
1、backup 1.1.1.11
2、web01 1.1.1.12
3、db01 192.168.1.32
4、web02 1.1.1.34
2、用户输入编号则自动ssh连接到目标主机

#!/bin/bash - #执行脚本就输出主机信息 #cat << EOF #1、backup 1.1.1.11 #2、web01 1.1.1.12 #3、db01 192.168.1.32 #4、web02 1.1.1.34 #EOF #声明一个整型变量 declare -i num #显示提示输入一个数值的信息,然后将用户的输入促驽变量count中 read -p "Enter an num: " num while true do cat << EOF 1、backup 1.1.1.11 2、web01 1.1.1.12 3、db01 192.168.1.32 4、web02 1.1.1.34 EOF case $num in 1) echo "backup 1.1.1.11" ;; 2) echo "web01 1.1.1.12" ;; 3) ssh root@ "192.168.1.32" ;; 4) echo "web02 1.1.1.34" ;; quit) break ;; *) echo "输入编码错误" ;; esac done echo "跳板机结束"
优化思路:
定制化配置---->写一个配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /work
[root@localhost work]# cp /scripts/3.sh /work/
自己建一个配置文件目录
[root@localhost work]# mkdir conf [root@localhost work]# vim conf/jump.conf

0、backup 1.1.1.11 1、web01 1.1.1.12 2、db01 192.168.1.32 3、web02 1.1.1.34
jump脚本内容:
#!/bin/bash - ip_array=(`cat ./conf/jump.conf |awk '{print $NF}'`) while true do cat ./conf/jump.conf read -p "Enter an num: " num case $num in 1) echo $(ip_array[$num]) ;; 1) echo $(ip_array[$num]) ;; 2) ssh root@$(ip_array[$num]) ;; 3) echo $(ip_array[$num]) ;; quit) break ;; *) echo "输入编码错误" ;; esac done echo "跳板机结束"
登录认证脚本:

#!/bin/bash - username="zrg" psaaword="123" failed=0 while true do read -p "Enter a username: " inp_user read -p "Enter a password: " inp_pwd if [[ "$inp_user" = "$username" && "$inp_pwd" = "$psaaword" ]];then echo -e "\nLogin successful." #认证成功之后可以做后续的事 break else echo -e "\n用户名或密码错误。" let failed++ if [ $failed -eq 3 ]; then echo "输出的次数太多了,退出" break fi fi echo ""输出的次数:$failed done
[root@localhost scripts]# curl -I https://www.dongchedi.com/

[root@localhost scripts]# curl -I https://www.dongchedi.com/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: Tengine Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: 188250 Connection: keep-alive Date: Sat, 21 Jun 2025 14:20:37 GMT Vary: Accept-Encoding X-Tt-Logid: 202506212220372CE4E3C7AC3544EAF60B x-cache: HIT Cache-Control: private, max-age=180 Server-Timing: inner; dur=37,tt_agw; dur=22 Set-Cookie: ttwid=1%7Ca8LljL9MCxiIgF5T7uMDe7FrTpFSOBNTkSkqs2WLjZA%7C1750515637%7Ced42b760aef87eec9b5237acb41a9aeb9a0044a8681d8a18d888609b15061775; Domain=.dongchedi.com; Path=/; Expires=Sun, 21 Jun 2026 14:20:37 GMT; HttpOnly Set-Cookie: tt_webid=7518407331690382910; path=/; expires=Sun, 21 Jun 2026 14:20:37 GMT Set-Cookie: tt_web_version=new; path=/; expires=Thu, 18 Dec 2025 14:20:37 GMT Set-Cookie: is_dev=false; path=/ Set-Cookie: is_boe=false; path=/ x-tt-trace-host: 015683e821c8935e16e5ea9e507caf685b15919fcf8cb768b20560ddc58b2cf1feaccf1862c62490c8567214018dcb885e1cd9a77bedf40dd27569aad2a2e5628e9cbb6f046041ebe8c848e7f40018ab637a9c8af85de51d67ad4296f53164ec38a8ea751cb05900f15caa7b93f52e4392cf5b2ff536148f0b45450e2b3bdbb8c1b90f2c17b1a270ccc9a636ff2a076989 x-tt-trace-tag: id=03;cdn-cache=miss;type=dyn x-tt-trace-id: 00-2506212220372CE4E3C7AC3544EAF60B-391828254BCE957D-00 server-timing: cdn-cache;desc=MISS,edge;dur=0,origin;dur=101 Via: dynamic16.cn820[101,0] Timing-Allow-Origin: * EagleId: df6ff52417505156376173512e
不带任何前缀实现脚本调用:
把脚本路径写到PATH。
[root@localhost scripts]# vi /etc/profile
PATH=$PATH:/work:/scripts
export PATH
立即生效:
[root@localhost scripts]# source /etc/profile
或者软连接到已经存在于环境变量PATH的目录
迭代循环
for循环
语法
for 变量名 in 取值列表 do 循环体 done
for ((初始值;条件;步长)) do 循环体 done
展示:
for x in 111 112 113 113 do echo $x done
命令的结果也可以当做
for x in `ls /scripts/` do echo $x done
c语言风格:
for ((i=0;i<=3;i++)) do echo $i done
等同于:
i=0 while ((i<=3)) do echo $i ((i++)) done
控制循环次数
for x in {1..3} do echo hello echo world echo ! done
shell风格的for常用in列表格式
for i in 1 2 3 for i in {1,2,3} for i in {1..9} for i in {9..1} for i in {a..z} for i in {A..Z} for i in {X..Z} for i in $(命令) # 例如:for i in $(head -10 /etc/passwd);do echo $i|cut -d: -f1,2;done for i in $(find ...)
注意:命令的结果得是空格隔开的或者是换行符隔开的都行。
for循环的continue和break
continue:默认退出本次循环。
break:默认退出本层循环。
for ((i=1;i<=;i++)) do if [ $i -eq 3 ]; then continue fi echo $i done
得到某个网段的所有IP地址
for i in {1..254} do
ip_addr=192.168.1.$i
echo $ip_addrdone
ping -c1 ip_addr &>/dev/null
select
自动生成编号和read。
语法:
#!/bin/bash - #PS3='请输入选择的编号:' select month in Jan Feb mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec quit do if [ "$month" == "quit" ]; then break else echo "$month" fi done ~
1) Jan 3) mar 5) May 7) Jul 9) Sept 11) Nov 13) quit 2) Feb 4) Apr 6) Jun 8) Aug 10) Oct 12) Dec #? f #? 5 May #? 1) Jan 3) mar 5) May 7) Jul 9) Sept 11) Nov 13) quit 2) Feb 4) Apr 6) Jun 8) Aug 10) Oct 12) Dec #? 8 Aug #? 13





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号