左神算法-基础05-二叉树
左神算法-基础05-二叉树
二叉树节点结构
class Node<V>{ V value; Node left; Node right; }用递归和非递归两种方式实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
图片引自添加链接描述
如何直观的打印一颗二叉树如何完成二叉树的宽度优先遍历(常见题目:求一棵二叉树的宽度)
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
/**
* 1
* 2 3
* 4 5 6 7
* 递归序: 1->2->4->4->4->2->5->5->5->2->1->3->6->6->6->3->7->7->7->3->1
* @param head
*/
public static void myPreOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + "\t");
myPreOrderRecur(head.left);
myPreOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void myInOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
myPreOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + "\t");
myPreOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void myPosOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
myPreOrderRecur(head.left);
myPreOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + "\t");
}
非递归方式实现前序遍历
具体过程:
首先申请一个新的栈,记为stack;
将头结点head压入stack中;
每次从stack中弹出栈顶节点,记为cur,然后打印cur值,如果cur右孩子不为空,则将右孩子压入栈中;如果cur的左孩子不为空,将其压入stack中;
重复步骤3,直到stack为空.
public static void myPreOrderUnRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); while(!stack.isEmpty()) { Node cur = stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.value); //先压右孩子,再压左孩子--->出的顺序就是 先左->后右 if (cur.right != null) { stack.push(cur.right); } if (cur.left != null) { stack.push(cur.left); } } System.out.println(); }
非递归方式实现中序遍历
具体过程:
申请一个新栈,记为stack,申请一个变量cur,初始时令cur为头节点;
先把cur节点压入栈中,对以cur节点为头的整棵子树来说,依次把整棵树的左子树压入栈中,即不断令cur=cur.left,然后重复步骤2;
不断重复步骤2,直到发现cur为空,此时从stack中弹出一个节点记为node,打印node的值,并让cur = node.right,然后继续重复步骤2;
当stack为空并且cur为空时结束。
public static void myInOrderUnRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); Node cur = head; while(!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) { while (cur != null) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } cur = stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.value + "\t"); cur = cur.right; } System.out.println(); }
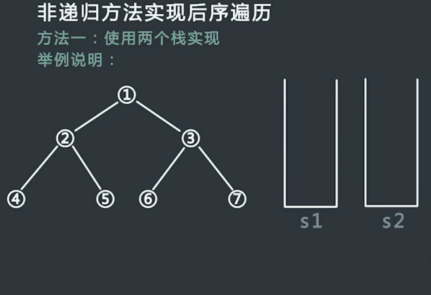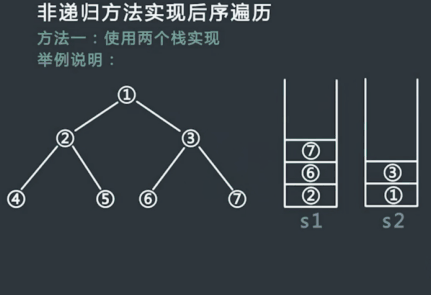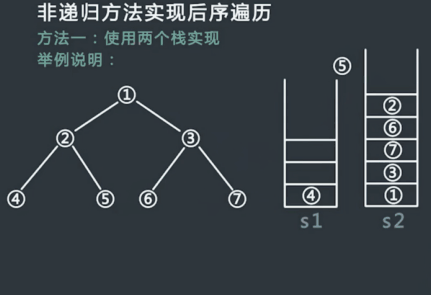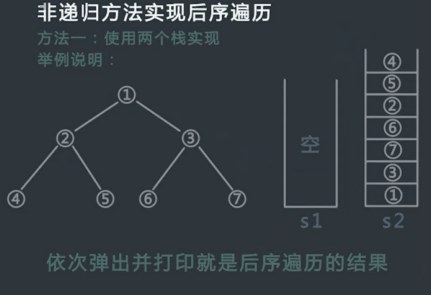
非递归方式实现后序遍历一
具体过程:
使用两个栈实现
申请两个栈stack1,stack2,然后将头结点压入stack1中;
从stack1中弹出的节点记为cur,然后先把cur的左孩子压入stack1中,再把cur的右孩子压入stack1中;
在整个过程中,每一个从stack1中弹出的节点都放在第二个栈stack2中;
不断重复步骤2和步骤3,直到stack1为空,过程停止;
从stack2中依次弹出节点并打印,打印的顺序就是后序遍历的顺序;
public static void myPosOrderUnRecurTwoStack(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } Stack<Node> stack1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<Node> stack2 = new Stack<>(); stack1.push(head); while(!stack1.isEmpty()) { Node cur = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(cur); if (cur.left != null) { stack1.push(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null) { stack1.push(cur.right); } } while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(stack2.pop().value + "\t"); } System.out.println(); }
非递归方式实现后序遍历二
具体过程:
使用一个栈实现
- 申请一个栈stack,将头节点压入stack,同时设置两个变量 h 和 c,在整个流程中,h代表最近一次弹出并打印的节点,c代表当前stack的栈顶节点,初始时令h为头节点,,c为null;
- 每次令c等于当前stack的栈顶节点,但是不从stack中弹出节点,此时分一下三种情况:
(1)如果c的左孩子不为空,并且h不等于c的左孩子,也不等于c的右孩子,则吧c的左孩子压入stack中
(2)如果情况1不成立,并且c的右孩子不为空,并且h不等于c的右孩子,则把c的右孩子压入stack中;
(3)如果情况1和2不成立,则从stack中弹出c并打印,然后令h等于c;
一直重复步骤2,直到stack为空.
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-F9q2X2RX-1637408224370)(https://files.cnblogs.com/files/songwenjie/后序遍历2.gif)]
public static void myPosOrderUnRecurOneStack(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node lastPop = head; //记录上次访问的节点 Node curTop = null; //记录当前的栈顶节点 while(!stack.isEmpty()) { curTop = stack.peek(); //只要左孩子没被访问的话,右孩子一定没被访问 if (curTop.left != null && lastPop != curTop.left && lastPop != curTop.right) { //curTop有左孩子,并且左孩子没被访问过,右孩子也没被访问过 stack.push(curTop.left); }else if (curTop.right != null && lastPop != curTop.right) { //curTop有右孩子,并且右孩子没被访问过 stack.push(curTop.right); }else { //curTop没有左右孩子,或者左右孩子都被访问过 lastPop = stack.pop(); System.out.print(lastPop.value + "\t"); } } System.out.println(); }
层序遍历
具体过程:
首先申请一个新的队列,记为queue;
将头结点head压入queue中;
每次从queue中出队,记为node,然后打印node值,如果node左孩子不为空,则将左孩子入队;如果node的右孩子不为空,则将右孩子入队;
重复步骤3,直到queue为空。
public static void LevelOrder(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.add(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { head = queue.poll(); System.out.print(head.value + "\t"); if (head.left != null) { queue.add(head.left); } if (head.right != null) { queue.add(head.right); } } System.out.println(); }统计一棵二叉树的最大宽度
//使用hashmap的方法 public static int getMaxWidthWithMap(Node head) { if (head == null) { return 0; } int curWidth = 0; int maxWidth = 0; int curLevel = 1; HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.add(head); levelMap.put(head, 1); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { head = queue.poll(); if (head.left != null) { queue.add(head.left); levelMap.put( head.left, levelMap.get(head) + 1); } if (head.right != null) { queue.add(head.right); levelMap.put( head.right, levelMap.get(head) + 1); } if (levelMap.get(head) > curLevel) { //结算上一层的宽度 maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, curWidth); curWidth = 1; curLevel = levelMap.get(head); }else { curWidth++; } } //最后要再结算一次,(最后一层) maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, curWidth); return maxWidth; } //使用指针的方法 public static int getMaxWidthWithoutMap(Node head) { if (head == null) { return 0; } int maxWidth = 0; int curWidth = 0; Node curEnd = head; //当前层最后一个节点 Node curNextEnd = null; //下一层最后一个节点 Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.add(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { head = queue.poll(); if (head.left != null) { queue.add(head.left); curNextEnd = head.left; } if (head.right != null) { queue.add(head.right); curNextEnd = head.right; } if (head == curEnd) { curWidth++; maxWidth = Math.max(curWidth, maxWidth); curWidth = 0; curEnd = curNextEnd; }else { curWidth++; } } return maxWidth; }
二叉树的相关概念及其实现判断
如何判断一颗二叉树是否是搜索二叉树?
如何判断一颗二叉树是完全二叉树?
如何判断一颗二叉树是否是满二叉树?
如何判断一颗二叉树是否是平衡二叉树?(二叉树题目套路)
//递归方式中序遍历实现
public static int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean myCheckBSTRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
if (!myCheckBSTRecur(head.left)) {
return false;
}
if (preValue >= head.value) {
return false;
}else {
preValue = head.value;
}
return myCheckBSTRecur(head.right);
}
//非递归中序遍历实现
public static boolean checkBSTUnRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
if (head.value <= preValue) {
return false;
}else {
preValue = head.value;
}
head = head.right;
}
}
return true;
}
//使用递归套路解决
public static class ReturnData{
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public ReturnData(boolean isBST, int max, int min) {
this.isBST = isBST;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
public static ReturnData process(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ReturnData leftData = process(head.left);
ReturnData rightData = process(head.right);
//先令min 和max 都等于自己
//==========这部分可以优化去掉============
int min = head.value;
int max = head.value;
if (leftData != null) {
min = Math.min(min, leftData.min);
max = Math.max(max, leftData.max);
}
if (rightData != null) {
min = Math.min(min, rightData.min);
max = Math.max(max, rightData.max);
}
//=====================================
boolean isBST = true; //初始默认它是搜索二叉树,出现不满足的情况就置为false
if (leftData != null && (!leftData.isBST || leftData.max > head.value) ) {
isBST = false;
}
if (rightData != null && (!rightData.isBST || rightData.min < head.value) ) {
isBST = false;
}
//另一种判断方式,初始为false
//只有当left.max < value < right.min 时,才置为 true
// boolean isBST = false;
// if (
// (leftData!=null ? (leftData.isBST && leftData.max < x.value) : true)
// &&
// (rightData!=null ? (rightData.isBST && rightData.min > x.value) : true)
// ) {
// isBST = true;
// }
//如果当前树是搜索二叉树的话,当前树的最大值就是右最大值,最小值就是左最小值
//如果不是的话,isBST就是false,最大最小值也就无所谓了
return new ReturnData(isBST,rightData.max,leftData.min);
}
//判断是否是完全二叉树
public static boolean myIsCBT(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
boolean beginLeaf = false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
if (head.right != null && head.left == null) { //有右孩子,无左孩子--->一定不是
return false;
}
if (beginLeaf && head.left != null) { //叶子节点已经开始,它的左孩子必须是空
return false;
}
if (head.left != null) {
queue.add(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
queue.add(head.right);
}else { //右孩子为空,说明叶子节点开始了
beginLeaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
//是否是满二叉树
public static boolean isFT(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
ReturnType data = process(head);
if (data.nodeNums == (1 << data.height ) - 1 )
return true;
return false;
//==========process2==========
// return process2(head) != null;
}
public static class ReturnType {
public int nodeNums;
public int height;
public ReturnType(int nodeNums, int height) {
this.nodeNums = nodeNums;
this.height = height;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return new ReturnType(0,0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(head.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(head.right);
return new ReturnType(leftData.nodeNums + rightData.nodeNums + 1,
Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1);
}
public static ReturnType process2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return new ReturnType(0,0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(head.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(head.right);
if (leftData == null || rightData == null) {
return null;
}
if (leftData.height != rightData.height || leftData.nodeNums != rightData.nodeNums){
return null;
}
return new ReturnType(leftData.nodeNums + rightData.nodeNums + 1,
Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1);
}
//判断是否是平衡二叉树
public static boolean isBalanced(Node head) {
return process(head).isBalanced;
}
public static class ReturnType {
public boolean isBalanced; //是否平衡
public int height; //高度
public ReturnType(boolean isB, int hei) {
isBalanced = isB;
height = hei;
}
}
public static ReturnType myProcess(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return new ReturnType(true, 0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(head.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(head.right);
boolean isBalanced = true;
int height = 0;
if (!leftData.isBalanced || !rightData.isBalanced || Math.abs(leftData.height - rightData.height) > 1) {
isBalanced = false;
}
height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height);
return new ReturnType(isBalanced,height);
}
public static ReturnType process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return new ReturnType(true, 0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(x.left);
ReturnType rightData = process(x.right);
int height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height);
boolean isBalanced = leftData.isBalanced && rightData.isBalanced
&& Math.abs(leftData.height - rightData.height) < 2;
return new ReturnType(isBalanced, height);
}
给定两个二叉树的节点node1和node2,找到他们的最低公共祖先节点
//递归方式找两个节点的最低公共祖先,
//利用左右子树返回的信息判断o1,o2是分散在两棵树上,还是在其中一棵树上
public static Node myLowestAncestor(Node head, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (head == null || head == o1 || head == o2) {
return head;
}
Node left = myLowestAncestor(head.left, o1, o2);
Node right = myLowestAncestor(head.right, o1, o2);
if (left != null && right != null) {
return head;
}
return left == null ? right : left;
}
//使用map记录所有节点的父节点,从o1,o2依次往上遍历,找到最低公共祖先
public static Node getLowestAncestor(Node head, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (head == null || head == o1 || head == o2) {
return head;
}
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
map.put(head, null);
LinkedList<Node> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
nodes.add(head);
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = nodes.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
map.put(cur.left, cur);
nodes.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
map.put(cur.right, cur);
nodes.add(cur.right);
}
}
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
while(map.containsKey(o1)) {
set.add(o1);
o1 = map.get(o1);
}
while(!set.contains(o2)) {
o2 = map.get(o2);
}
return o2;
}
// 创建一个内部类来解决最低公共祖先的问题,可以使用递归方式赋值map
public static class Record1 {
private HashMap<Node, Node> map;
public Record1(Node head) {
map = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); //记录 孩子--->父亲节点
if (head != null) {
map.put(head, null);
}
setMap(head);
}
private void setMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.left != null) {
map.put(head.left, head);
}
if (head.right != null) {
map.put(head.right, head);
}
setMap(head.left);
setMap(head.right);
}
public Node query(Node o1, Node o2) {
HashSet<Node> path = new HashSet<Node>();
while (map.containsKey(o1)) { //迭代找o1的父节点们,放到set中
path.add(o1);
o1 = map.get(o1);
}
while (!path.contains(o2)) {
o2 = map.get(o2);
}
return o2;
}
}
在二叉树中扩找到一个节点的后继节点
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node parent; public Node(int val) { value = val; } }该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。
假设有一棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,头节点的parent指向null。
只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点node,请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。
在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中, node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点。
public static Node myGetSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
//情况1:有右树,它的后继就是右树的最左节点
if (node.right != null) {
return getLeftMost(node.right);
} else {
//情况2:没有右树,他的后继就是自己作为左子树最右节点的头节点
while (node.parent != null && node != node.parent.left){
node = node.parent;
}
return node.parent;
// Node parent = node.parent;
// while (parent != null && node != parent.left) {
// node = parent;
// parent = node.parent;
// }
// return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
二叉树的序列化和反序列化
就是内存里的一棵树如何变成字符串形式,又如何从字符串形式变成内存里的树
如何判断一颗二叉树是不是另一棵二叉树的子树?
//前序序列化
public static String serialByPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = head.value + "!";
res += serialByPre(head.left);
res += serialByPre(head.right);
return res;
}
//前序反序列化
public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr) {
String[] values = preStr.split("!");
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i != values.length; i++) {
queue.offer(values[i]);
}
return reconPreOrder(queue);
}
public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue) {
String value = queue.poll();
if (value.equals("#")) {
return null;
}
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));
head.left = reconPreOrder(queue);
head.right = reconPreOrder(queue);
return head;
}
//中序序列化
public static String serialByIn(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = "";
res += serialByIn(head.left);
res += head.value + "!";
res += serialByIn(head.right);
return res;
}
//无法恢复,递归过程丢失根节点信息
public static Node reconInOrder(Queue<String> queue) {
return null;
}
//后序序列化
public static String serialByPos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = "";
res += serialByPos(head.left);
res += serialByPos(head.right);
res += head.value + "!";
return res;
}
//后序反序列化
public static Node reconByPosString(String preStr) {
String[] values = preStr.split("!");
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//逆序存到队列中,队首元素就是根节点的值
for (int i = values.length - 1; i != -1; i--) {
queue.offer(values[i]);
}
return reconPosOrder(queue);
}
public static Node reconPosOrder(Queue<String> queue) {
String value = queue.poll();
if (value.equals("#")) {
return null;
}
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));
head.right = reconPosOrder(queue);
head.left = reconPosOrder(queue);
return head;
}
//层序序列化
public static String mySerialByLevel(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = head.value + "!";
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
if (head.left != null) {
res += head.left.value + "!";
queue.add(head.left);
} else {
res += "#!";
}
if (head.right != null) {
res += head.right.value + "!";
queue.add(head.right);
} else {
res += "#!";
}
}
return res;
}
//层序反序列化
public static Node myReconByLevelString(String levelStr) {
String[] values = levelStr.split("!");
int index = 0;
if (values[index].equals("#")){
return null;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(values[index]));
queue.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
cur.left = values[++index].equals("#") ? null : new Node(Integer.valueOf(values[index]));
cur.right = values[++index].equals("#") ? null : new Node(Integer.valueOf(values[index]));
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
return head;
}
折纸问题
请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折1次,压出折痕后展开。
此时折痕是凹下去的,即折痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。
如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。
给定一个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次。
请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。
例如:N=1时,打印: down N=2时,打印: down down up
public static void printAllFolds(int N) {
printProcess(1, N, true);
}
public static void myPrintAllFolds(int N) {
myPrintProcess(1, N, true);
}
//i记录当前深度
//N记录对折次数,也就是二叉树的最大深度
//down用来记录当前节点的值,在递归过程就可以实现输出,无需先构建二叉树,再进行中序遍历
public static void myPrintProcess(int i, int N, boolean down) {
if (i > N){
return;
}
myPrintProcess(i + 1, N, true);
System.out.println(down ? "凹" : "凸");
myPrintProcess(i + 1, N, false);
}
public static void printProcess(int i, int N, boolean down) {
if (i > N) {
return;
}
printProcess(i + 1, N, true);
System.out.println(down ? "down " : "up ");
printProcess(i + 1, N, false);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号