/*
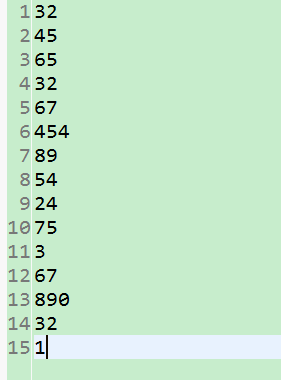
编写一个程序读取a.txt文件,将文件内容数字从小到大排序,并将排序结果写入b.txt。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
//插入排序
void InertionSort(int * arr,int len)
{
if(arr==NULL)
{
printf("传入参数不可以为空!\n");
return;
}
int i=0,j=0,k=0,temp=0;
for(i=1;i<len;i++)
{
k=i;
temp=arr[k];
for(j=i-1;j>=0&&temp<arr[j];j--)
{
arr[j+1]=arr[j];
k=j;
}
//k的作用是因为当temp>=arr[j]时,将不会进入循环,此时j是有序数组的最后一个元素
//arr[j]=temp;会将最后一个有序元素覆盖了
//arr[j]=temp; 错误
arr[k]=temp;
}
}
int main(int arg, char * args[])
{
if(arg<3)
{
printf("本程序需要两个参数!\n");
return 0;
}
//define file stream
FILE *pfr=NULL;
//open the file in read mode
pfr=fopen(args[1],"r");
//judge
if(pfr==NULL)
{
printf("read the file failed ! error msg:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
//create arr
int index=0;
//这里index是作为数组长度使用的,index的初始值是0,所以循环之后index会多1,正好此时index就是数组的长度
int arr[100]={0};
char buf[10]={0};
while(fscanf(pfr,"%s",buf)!=EOF)
{
arr[index++]=atoi(buf);
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
}
//close the file stream
if(pfr)
{
fclose(pfr);
pfr=NULL;
}
InertionSort(arr,index);
//define new file stream
FILE * pfw=NULL;
//open new file in append mode
pfw=fopen(args[2],"a");
if(pfw==NULL)
{
printf("write the file failed ! error msg:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
//write the file
int num=0;
while(num<index)
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
sprintf(buf,"%d\n",arr[num++]);
fputs(buf,pfw);
}
//close the file stream
if(pfw)
{
fclose(pfw);
pfw=NULL;
}
return 0;
}
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号