算法笔记--排序算法
1、选择排序
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法,无论什么数据进去都是 O(n²) 的时间复杂度。所以用到它的时候,数据规模越小越好。唯一的好处可能就是不占用额外的内存空间。
步骤:
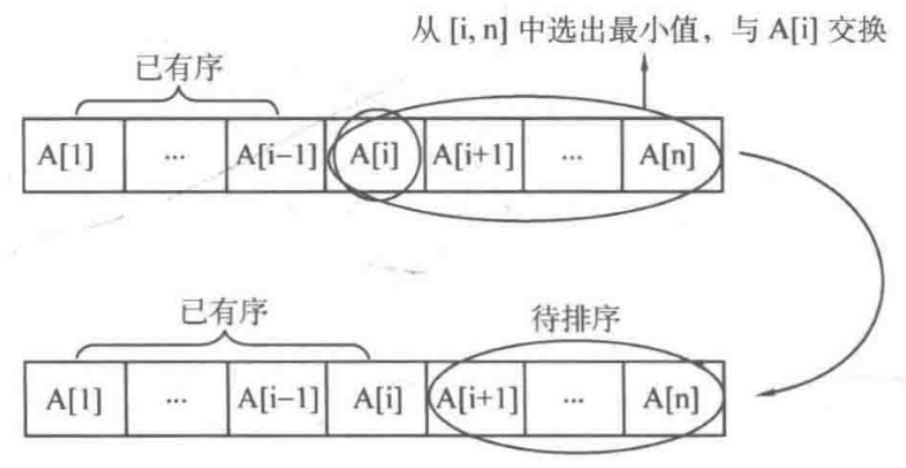
- 首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置。
- 再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。
- 重复第二步,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
总共需要进行n趟操作(1≤ i ≤ n),每趟操作选出待排序部分[i, n] 中最小的元素,令其与A[i] 交换,所以总复杂度为O(n2)
代码:(注意 i j k 之间的关系)
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
const int n = 6;
int a[n];
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("排序前:");
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){ // 进行n趟排序
int k = i;
for(int j=i; j < n; j++){ // 从[i,n-1]中寻找最大值
if(a[j] > a[k]){
k = j;
}
}
int temp = a[k]; // 交换
a[k] = a[i];
a[i] = temp;
}
printf("排序后:");
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
2、插入排序
插入排序是一种最简单直观的排序算法,它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。
插入排序和冒泡排序一样,也有一种优化算法,叫做拆半插入。
步骤:
- 将第一待排序序列第一个元素看做一个有序序列,把第二个元素到最后一个元素当成是未排序序列。
- 从头到尾依次扫描未排序序列,将扫描到的每个元素插入有序序列的适当位置。(如果待插入的元素与有序序列中的某个元素相等,则将待插入元素插入到相等元素的后面。)
- 注意元素后移

代码:(先移后放)
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
const int n = 6;
int a[n];
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("排序前:");
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(int i=1; i < n; i ++){ // 进行n-1趟排序
int temp = a[i], j = i; // temp临时存放a[i],j从i开始从前枚举
while(j > 0 && temp > a[j-1]){ // 只要temp小于前一个元素a[j-1]
a[j] = a[j-1]; // 把a[j-1]后移一位a[j]
j --;
}
a[j] = temp; // 插入位置为j
}
printf("排序后:");
for(int i=0; i < n; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
3、STL 之 sort()
#include<algorithm> using namespace std; sort(首元素地址(必填),尾元素地址的下一个地址(必填),比较函数(选填));
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a, int b){
return a > b;
}
int main(){
int a[7] = {12, 3, 0, 23, 99, 199, 20};
int len = sizeof(a) / 4;
sort(a, a + 7);
printf("没有使用cmp函数的sort排序:");
for(int i=0; i < len; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
sort(a, a + 7, cmp);
printf("\n使用自定义cmp函数的sort排序:");
for(int i=0; i < len; i ++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
结果:
没有使用cmp函数的sort排序: 0 3 12 20 23 99 199
用自定义cmp函数的sort排序:199 99 23 20 12 3 0
【PAT A1025】PAT Ranking
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Student{
char id[15]; // 学号
int score; // 成绩
int location_number; // 考场号
int location_rank; // 考场排名
}stu[1000];
bool cmp(Student a, Student b){
if(a.score != b.score)return a.score > b.score; // 成绩按照从大到小排序
else return strcmp(a.id, b.id) < 0; // 成绩相同,学号从小到大排序
}
int main(){
int n;//考场数
scanf("%d", &n);
int num = 0; // 记录考试总数量
for(int i=1; i <= n; i++){
int k; // 考场学生数
scanf("%d", &k);
for(int j=0; j < k; j++){
scanf("%s %d", stu[num].id, &stu[num].score); // 输入学号、成绩信息
stu[num].location_number = i; // 设置考场号
num ++;
}
sort(stu + num -k, stu + num, cmp); // 对考场内进行排序
stu[num-k].location_rank = 1; // 设置该考场第一名
for(int j=1; j < k; j++){
if(stu[num-k+j].score == stu[num-k+j-1].score){
stu[num-k+j].location_rank = stu[num-k+j-1].location_rank; // 输出后序排名,如 1 2 2 2 5(并列占位)
}else{
stu[num-k+j].location_rank = num - k + j - (num - k) + 1;
}
}
}
printf("\n%d\n", num); // 总考生数
sort(stu, stu + num, cmp); // 对所有考生排序
int r = 1;
for(int j=0; j < num; j++){
if(stu[j].score != stu[j-1].score){
r = j + 1;
}
printf("%s %d %d %d\n", stu[j].id, r, stu[j].location_number, stu[j].location_rank);
}
return 0;
}
result:
输入: 2 5 1234567890001 95 1234567890005 100 1234567890003 95 1234567890002 77 1234567890004 85 4 1234567890013 65 1234567890011 25 1234567890014 100 1234567890012 85 输出: 9 1234567890005 1 1 1 1234567890014 1 2 1 1234567890001 3 1 2 1234567890003 3 1 2 1234567890004 5 1 4 1234567890012 5 2 2 1234567890002 7 1 5 1234567890013 8 2 3 1234567890011 9 2 4


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号